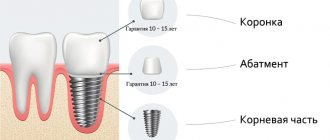
198
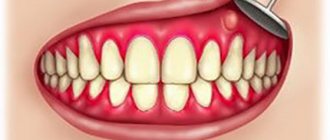
If we adhere to the exact wording, then a fistula or fistula (Latin “fistula” means “tube”, “channel”) is a passage in the tissues that has formed spontaneously to release the purulent masses accumulated in the source of inflammation.
However, often a fistula is called not only the canal itself, but also the source of inflammation, which, in essence, is incorrect.
Reasons for education
Complications of various kinds after implantation of an implant into the jawbone occur infrequently in dental practice. During the implantation process, the specialist uses all his knowledge and skills to avoid this trouble.
However, in exceptional cases, for the patient, an expensive procedure may result in rejection of the structure or the formation of a fistula on the gum.
An abscess appears due to infection of the implantation site and requires immediate medical attention.
Unlike ordinary purulent formation, a fistula is characterized by the presence of deep inflammation under the mucous membranes. Yellow-green or grayish effusion quickly accumulates in the tissues and finds its way out through the fistula canal.
At the point of the breakthrough, a large wound area is formed, which becomes an ideal environment for the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms. They can provoke secondary infection.
The problem is accompanied by the addition of streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus and other pathogenic pathogens.
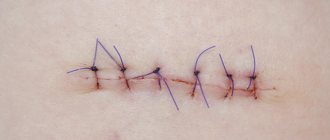
For free and low-traumatic screwing of the tooth root analogue into the bone structure of the jaw, the implantologist makes an incision in the gum. During this simple manipulation, it is important to have sterile instruments and consumables on hand and pay special attention to the treatment of sutures.
If these requirements are neglected, there is a risk of microbes and bacteria contained in saliva entering the tissue. Also, according to statistics, a fistula under the implant can form due to a number of other reasons:
- Lack of preparation before implantation. The procedure for replacing teeth with artificial analogues requires preliminary sanitation of the oral cavity.
Without fail, the doctor must treat existing carious lesions, eliminate pathological changes and functional disorders of the oral cavity, remove tartar and other bacterial deposits. - Consequences of periodontitis or periostitis. Inflammatory processes localized near the tooth root, without treatment, lead to dangerous diseases.
These include a fistula, which occurs as a natural drainage after the formation of an abscess or cellulitis. These pyogenic abscesses are a consequence of advanced periodontitis. - Complications of chronic periodontal disease or stomatitis. Dental diseases, characterized by deep lesions of the periodontal tissue of a chronic nature, tend to worsen.
During the period of intensification of destructive and inflammatory processes, exudate freely penetrates into the gum structure and onto the implant, causing oxidation. - Infection of the socket after tooth extraction. If bacteria enter the open tissue at the site of a missing tooth, then their further production inevitably leads to decay.
The process may begin in the soft structures of the gums, sinuses or jaw. - Sinus perforation. Nearby maxillary sinuses can become infected through direct contact with the implant.
- Violation of the protocol for preparing the alveolar bone for a titanium rod. In rare cases, the doctor may overheat the instrument used and burn healthy tissue. After a burn, bone necrosis or a serious inflammatory process of a different nature is possible.
When implanted in the upper jaw, a fistula on the gum can also form due to a cold (rhinitis, ARVI, influenza, etc.).
Predisposing factors for the formation of a post-implantation purulent canal may be:
- general weakening of the body's immune system;
- hypothermia, characterized by a decrease in body temperature and accompanied by inhibition of the normal functioning of many systems and organs;
- infectious diseases regardless of the area affected by them;
- weakening of body functions, exhaustion;
- neurasthenia, mental disorders;
- hyperthermia (increased body heat content).
Remember! Dental fistula is one of the most dangerous dental diseases that can provoke not only the loss of a tooth or implant, but also significantly affect the health of the body as a whole.
Many patients often blame implantologists for mistakes, but in vain. Indeed, in some cases, the cause of complications may be the poor quality of the implant and poor oral hygiene after installation.
Therefore, first of all, you should not skimp on the design and thorough sanitation of the oral cavity. A high-quality and reliable implant, combined with proper hygiene, is the main measure to prevent the formation of abscesses.
What is a fistula on the gum?
A fistula is a kind of channel between the source of infection and the surface. Fistulas are classified by etiology - congenital and acquired, as well as in relation to the environment - external and internal. They can occur in various organs. It is the gingival fistula (fistula gingivalis) that forms the fistula tract, through which an abscess in the periodontium or in the thickness of the jaw communicates with the oral cavity. The disease can be detected primarily using radiography. But the diagnosis of “odontogenic fistula” can also be made during a routine examination by a dentist.
A fistula on the gum has the following symptoms:
- toothache that gets worse when touched;
- tooth mobility;
- redness and swelling of the gums around the tooth;
- purulent discharge from the fistula tract.
Types of pathology
Dentists distinguish between internal and external dental fistula. The first ends on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, the second - removes purulent exudate deep into the tissues or internal cavities.
When the fistula is open, the pus is discharged outward, bypassing the bloodstream, so the degree of danger is lower than that of the closed form.
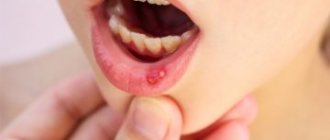
An “immature” fistula, which does not have a through hole in the gum, is a bulge in the center of which there is a white spot edged with redness. The tissues around the pathological area are inflamed.
The opened canal has a passage through which purulent masses and yellowish liquid (lymph) mixed with blood flow out.
Preventive measures
A neglected hole in the gum leads to various unattractive results; Among them, the worst consequence would be tooth extraction. Implantation will cost a pretty penny, and dental implantation may also fail, which will hit your wallet even harder. So, a small hole in the gum will create a giant hole in your pocket, and will even undermine your physical health.
Remember why holes appear in the tooth, which then lead to the appearance of inflammation on milk and permanent teeth. “Everything that happens to you is the result of one reason, and that reason is only you.” Based on this, several rules of prevention can be deduced:
- Brush and floss your teeth to remove plaque. It is recommended to do this in the morning after breakfast and in the evening. Mouth rinse mixtures, which are sold in pharmacies or made independently, can also help deal with plaque. Do the same with your gums - clean them and rinse them.
- Don't forget that crowns also need care. The crown will last you longer, will not smell and will not become a source of disease if you take care of its cleanliness.
- Do not forget about self-diagnosis - check the condition of your teeth. Be serious about symptoms. If symptoms of the disease are detected, it would not be superfluous to visit a doctor: it is easier to work with a fistula if it is at an early stage. The examination is inexpensive compared to the cost of dental treatment. Visit your dentist regularly, even without symptoms of the disease - check the condition of your teeth every six months.
Read also: Purulent bubble on the gum
After this prophylaxis, the possibility of a purulent tract or relapse will be lower than without it. If the disease does occur, it will be easier to resolve if the hole is treated not only at the dentist, but also at home with the help of herbal decoctions. Don’t leave the hole a chance to recur: follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Associated symptoms
To prevent post-implantation undesirable consequences, the patient must carefully monitor the condition of the oral cavity during the period of implantation. If unfavorable symptoms appear, it is important to immediately seek medical help.
The process of fistula formation is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Swelling and redness of the gums in the implant area. If you press on the inflamed area, ichor may be released.
- The appearance of a putrid taste in the mouth.
- A feeling of mild pain near the implanted rod, which intensifies when palpating the gums, sharply turning the head or while chewing food.
- Increased sensitivity of the gum mucosa to contact with hot and cold.
It is worth noting that mild pain, redness and swelling in the first 5-7 days after implantation are considered normal phenomena that go away without medical intervention as soon as the tissues begin to accept the foreign body and get used to it.
If the listed manifestations bother you for a long period (more than 10-15 days), this is a good reason to worry and visit a doctor.
The following signs indicate an already formed pathological canal:
- sharp, strong and acute painful sensations;
- foul odor from the mouth;
- release of purulent masses with impurities of blood from under the gums at the site of the installed implant;
- unsteadiness of the structure;
- the appearance on the gum of a tubercle with a pathological hole from which exudate flows;
- weakness, malaise, increased body temperature, signaling a disorder in the functioning of the body.
The listed symptoms are harbingers of serious danger. They talk about the development of inflammation of the gum and bone tissue around the implant and the risk of its rejection. A preventive measure in this case would be to immediately consult a doctor.
After opening the abscess on his own, the patient feels temporary relief: the pain subsides and overall well-being improves. However, the weakening of symptoms is a false retreat of the disease.
The pathological process in the implant area continues, and when the channel for the release of pus is closed, a relapse of painful and uncomfortable symptoms inevitably occurs.
What is the Lioplast membrane and the technique of its use in dentistry.
Come here to take a closer look at the design features of the screw implant.
At this address we will consider the unique properties of Gapsil sealant.
What symptoms does it manifest?
It is easy to guess about the development of the disease even before a hole forms in the mucosa. Although the affected soft tissue may not hurt, a number of the following symptoms may be a cause for concern :
An increase in temperature indicates the possible development of the disease
- the appearance of bad breath, even with regular brushing of teeth;
- hyperemia, redness or swelling of soft tissues;
- bleeding gums and the presence of “pockets”;
- sharp or aching pain when biting or eating cold/hot food;
- itching in the gum area, and painful sensations from touching;
- loosening of the implant;
- purulent taste in the mouth;
- the appearance of ulcers of different sizes on the gums;
- increased body temperature (more than 38°).
Dangers and possible complications
Self-medication and lack of professional medical care leads to negative consequences in the form of systemic and local reactions of the body.
The first include the following manifestations:
- inflammation of the jaw bone, during which an abscess appears (periostitis);
- odontogenic infection of soft and bone tissues in the area of the dental implant, accompanied by bone resorption (peri-implantitis);
- formation of cystogranulomas;
- destructive and inflammatory processes leading to loss of stability of the dental structure and its rejection.
Implant rejection is considered the most severe complication of fistula development. Accompanied by acute pain, pronounced pathological changes in the tissues of the peri-implant zone, mucositis, and infection of the whole body.
If the titanium analogue of the tooth root is not removed, over time it will be pushed out by purulent masses.
Rejection has dire consequences. The condition of the bone deteriorates, requiring long-term rehabilitation therapy aimed at stimulating the formation of new bone tissue . However, implantologists do not guarantee the possibility of re-implantation after treatment.
Systemic complications include:
- infection of the serous membrane of the heart;
- inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinuses;
- infectious damage to the respiratory system, excretory system of the body and others;
- blood poisoning.
Systemic complications develop against the background of prolonged entry of exudate into the structure of tissues and organs, when the effusion does not exit through the fistula canal to the outside.
The most dangerous consequence of this condition is sepsis, which leads to severe overload of the immune system, widespread inflammation, and in some cases, death.
Why did a fistula form after dental implantation?
Nobel implants were placed on the left lower jaw in the place of the sixth and seventh teeth.
Before this there was a removal of six. Seven was deleted a long time ago. After implantation there was severe pain for 14 days. The doctor calmed me down and told me to take painkillers. Then a second course of antibiotics was prescribed. But the swelling and minor pain lasted until the nineteenth day. Then the fistula came out. When contacting the clinic, an intervention was performed and drainage was installed. She did not take antibiotics after the intervention. There was no temperature. Today is the fourth day after the second operation. There is no pain, but swelling is observed again. The doctor said that this is quite normal. Why is there a fistula and does this mean that the implants do not take root?
Fistula is a consequence of the inflammatory process. Most likely, the implants will have to be removed. Perhaps the inflammation will go away for a while, but soon you will feel an exacerbation again. I recommend that you see another doctor.
Contact phone number
Comments and reviews 18
On January 5, I got implants, everything took root well and didn’t bother me, but after 4.5 months. They began to install the formers, for some reason swelling (at the top) and whiteness formed on one implant, the doctor prescribed a course of antibiotics and baths. After taking antibiotics, the pain subsided, but the swelling remained, later it turned into a fistula, there is no pain. The doctor said to continue salt baths and Metragil Denta. He looked at the picture and said that the implant was stable, perhaps some piece. I have a suspicion that the implant did not take root. Answer
This may be due to the development of an inflammatory process in the implant area. It is necessary to evaluate the situation on an x-ray. Answer
General dentist
Three implants were installed on the lower jaw on the left. One implant continued to hurt, the gums were similar, and pus and blood periodically came out. The attending physician put a gum former on him and said that the pus would drain out through it and everything would heal. At the same time, he removed a neighboring tooth (before that it was under a crown) - allegedly it was a breeding ground for dirt. Three weeks have passed, there is still a slight swelling, there is no toothache during the day, but at night I wake up from a toothache, drink Nemisil, and fall asleep until the morning. Pus and blood continue to come out from under the implant. Two weeks before the installation, three implants were installed on the left. Pah-pah, it seems like there are no problems with them. I read on the Internet that if a fistula occurs, then the implant must be removed. So then why doesn’t the doctor remove it? Or maybe it will really take root. Answer
The need to remove the implant can be assessed using an x-ray. If there is destruction in the area of the implant and the created outflow is insufficient, the implant must be removed. Answer
Please, help! A year ago I placed an implant on the last molar tooth on the lower right. There was pain from the very beginning, but the doctor calmed me down and asked me to be patient. In August I took a 3D photo and the surgeon said that it hurt because the implant was very close to the edge of the bone and besides, it was 50% exposed. He suggested monitoring the implant. And another surgeon said to remove it immediately. As a result, I removed 10 days of pain, throbbing and not giving rest, at night with pain relief. The ear, temple, and iron under the jaw hurt. When the implant was removed, they put some kind of bone tissue replacement mixed with my blood into the hollow (they took it from a vein). Please tell me what I should do, because I can’t take so many painkillers. Answer
Postoperative pain occurs within 10-14 days after surgery to remove the implant. But the pain should be relieved with painkillers. If after 10 days you do not observe a decrease in pain sensitivity, contact a dental surgeon. Answer
General dentist
I have the same situation - a fistula appeared in the side of the gum a few months after installing the implant on the seventh tooth. Do you think it’s still worth removing the implant, or cleaning (treating) the implant? I think it is necessary to remove the implant, because... fistula is difficult to treat. I have consulted the doctor several times, I no longer trust him, he is disingenuous to me. Can I insist on removal and return of the implant? Answer
This implant must be removed. With successful implantation, no fistula tract or purulent exudate is detected. It is usually not possible to “treat an implant” without removing it. Answer
General dentist
On January 23, 2017, surgery was performed on the lower jaw. We placed implants on 6 teeth on both sides, today on one side I discovered something like a growth in the gum above the implant, and pus and blood come out from under this growth, nothing hurts. What could this be and is there a risk of implant removal? After 4 visits, the doctor did not notice anything, another doctor who installed braces discovered. Answer
Most likely, this implant did not take root. It will need to be removed. Answer
General dentist
1.5 months ago I had the implantation of the lower seven. The picture showed that the implant had taken root, but a fistula had formed on top and pus was coming out, there was no pain. The doctor says to rinse with salt. It hasn't been 2 weeks already. What could it be? How to speed up the healing process? Answer
Read also: The root of the tooth is exposed, what to do?
The healing process does not occur, and the implant cannot take root after 1.5 months. Unfortunately, your doctor is lying; the implant must be removed. There are many reasons for infection, the main one being unsterile manipulation. See a doctor and don't delay. The fistula indicates the need to remove the screw and wait for the bone structure to recover, then repeat the operation. Answer
Contact phone number
God! I am terrified!. Something came out again, a pink bubble. I am terrified! Answer
Don't panic and consult your doctor. Answer
Contact phone number
With your permission, I am attaching pictures of the implants. Thirteen days after implantation. Answer
Due to the fact that the implants were placed too early, it was necessary to install them along the Bifurcation. And then there would be no problems. Answer
Contact phone number
Thanks for the answer. To be honest, I can guess it myself, but I really wanted to believe in the good. The fact is that after implantation I was able to meet with my implantologist only once, and that was at my insistence. Because of the pain, I called my Dental Way clinic and asked to comment on my condition. Still, she insisted and the implantologist invited me. This was on the seventh day. He never came to the clinic in Odintsovo again. All four of my other visits were performed by a regular surgeon. The repeated intervention was performed by a surgeon. No one took pictures before implantation. My clinic also did not take pictures after implantation, citing lack of information. I took pictures at another clinic, where the implantologist told me that the bone after the removal of the sixth tooth was not ready for implantation, and he would not have given me anything else. He also said that I was losing my implants. All this happened before the second year of digital studies. And after digitalization, on the third day, a fistula appeared. The implantologist comes only for operations, on Fridays. And I can’t see him for two weeks. My condition is like a powder keg. I worry. How should financial issues be resolved? The Nobel system provides guarantees. But it turns out that I am tied to this clinic with which I entered into an agreement. I still hope to see an implantologist this Friday. But I’m afraid he will hope in vain, I’m wasting time and walking around with inflammation in my gums. Is it possible to remove implants without pain? Because I just cried during surgery. The anesthesia didn't work. They were constantly hammering away. It's about fistula. I'm just asking for help. I'm desperate because no one at the clinic is being transparent. Answer
Without pictures before and after surgery, this is an extreme violation of surgical protocol. And I still recommend that you run away from such would-be surgeons. Insist on an incorrect operation leading to infection and contact the management for a refund rather than a redo. Implants have a warranty from the manufacturer, but only for the product itself. The implants are removed without pain, don’t worry. Answer
Stages of treatment
The inflammatory process develops very rapidly, so it is necessary to seek medical help when the first signs appear . The danger of a fistula lies in the fact that it is difficult to determine at the first stage of its development where it is localized.
The source of inflammation can form directly in the oral cavity on the gum or deep in the tissues. To accurately determine the location of the abscess, the doctor prescribes a CT scan (computed tomography) to the patient during the initial examination.
If the fistula has formed above or near the dental structure, there is no need to remove the implant. Purulent masses can be eliminated by cutting the swelling in the center.
To thoroughly clean the wound area and completely remove the exudate, a tape elastic drainage is installed. It prevents premature healing of the wound, prevents swelling and hematoma formation.
Drainage is stopped after 3-4 days. At the final stage of treatment, the fistula canal is filled with an antiseptic.
A fistula under an implant is more difficult to treat. The purulent sac is located close to the structure, in close contact with the metal surface of the product, which provokes the development of chemical reactions and oxidation.
To prevent rejection, dentists often decide to remove the structure. The hole in the gum structure is carefully processed, and it is cleaned of necrotic tissue and biological fluid. Finally, the wound is washed with Chlorhexine, Rotokan or Fukortsin.
Sutures are applied if, after treatment and removal of all pathological particles, the diameter of the canal has increased. In this case, the dentist prescribes antiseptic mouth baths for the patient at home.
For the first 2-3 days after the procedure, the patient should perform manipulation every 5-6 hours. To speed up regeneration and prevent the appearance of scars, the use of Solcoseryl or another healing stimulator is prescribed. Therapy is supplemented by mandatory antibiotics.
All the pros and cons of installing an implant immediately after tooth extraction.
In this publication, we will consider options for dental implantation in the lower jaw.
Here is all about the technique of dental implantation without bone tissue augmentation.
Possible complications
The most common complication is that bumps containing pus appear on the gums. A cyst containing pus forms at the root of the tooth. It is gradually growing. Over time, the pus tends to break out. This is how fistulas appear.
Please note: The patient should absolutely not open the lump on their own. This procedure should be performed by an experienced doctor using sterile instruments.
The patient should absolutely not open the lump on his own.
Another complication is growth in the gum area. This is a fairly dense formation, inside of which there is a reddish liquid. This neoplasm cannot be ignored. It can provoke the development of osteomyelitis. At the same time, the patient’s temperature rises, the lymph nodes swell, he complains of general weakness and deterioration in health. This symptomatology is especially pronounced in children.
Preventive measures
Prevention of fistula formation after implantation requires compliance with certain rules not only from the patient, but also from the doctor.
The dentist and implant surgeon must take the following preventive measures:
- Carry out thorough sanitation of the patient’s oral cavity before implantation.
- Strictly follow the protocol for implanting the structure into the jawbone and the rules of antiseptics.
- Carefully select an implant that fully corresponds to the specific clinical picture.
- Consider the volume of bone for installation, use water cooling when working with the bur.
For the patient, prevention implies strict adherence to medical recommendations in the post-implantation period:
- Special oral care - the use of an irrigator, brushes, low-abrasive toothpastes and soft bristle brushes.
- Compliance with a special diet - in the first week after implantation, solid and tough foods are prohibited. Hot foods should also be avoided. The daily menu must include vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements.
- Carrying out antiseptic rinses - after each meal, it is necessary to treat the wound area and the entire oral cavity with antibacterial agents, to prevent inflammatory processes by taking antibiotics and herbal decoctions.
- Scheduled visits to the attending physician - it is important to come to the dentist strictly according to the schedule, which will help to identify the fistula at the initial stage of its development.
In the video, a specialist will talk about the rules of recovery after implantation.
A fistula on the gum requires timely treatment
How to cure a fistula on the gum? Treatment of gingival fistula begins with treatment of the root cause – periodontitis. After eliminating caries and filling the tooth, treating a dental cyst, the necessary medications and means are prescribed for additional treatment of the oral cavity from microorganisms. During this period, it is also recommended to use antibacterial pastes and gels. At the same time, antibiotics and antihistamines are prescribed. As an addition to treatment, salt baths are recommended to relieve swelling and reduce inflammation.
It is clear that periodontitis with a complication in the form of a fistula cannot be cured in one visit to the dentist, but if you take into account timely access to a doctor, you can shorten the treatment process and avoid surgical removal of granulations. Often this removal is carried out using a laser. If you do not seek medical help in time, then treatment will consist of removing the tooth that caused the formation of a gingival fistula and curettage of the fistulous tract itself.
Reviews
Only a doctor can select an effective method for treating a fistula after a thorough visual examination and hardware diagnostics. In most cases, it is possible to save the implant, even if an abscess has formed near the structure.
The main thing is not to delay treatment and seek help from a highly qualified specialist.
Under the article, in the “comments” section, you can share your personal experience of treating a fistula. Tell your readers why you encountered such a problem, in which clinic the implantation was performed, and what opinion you have about the work of the specialists.
Perhaps your review will help many to avoid such a complication as a dental fistula.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: implantation, complications of implantation
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
More about the reasons
A hole appears on the gum as a consequence of one of two factors: the incompetence of the doctor or the carelessness of the patient. All other reasons follow from these two, and if a medical error cannot be predicted, it is always possible to overcome one’s own frivolity.
- Lack of treatment. The consequences of delayed or absent treatment of diseased teeth are numerous. If this is excusable for a child - after all, he depends on his parents, then for an adult such behavior is unforgivable. Some people put off treatment for caries: “they say, the tooth doesn’t hurt yet, you can be patient.” Caries turns into pulpitis, then into periodontitis. The consequence of neglect is purulent inflammation of the tooth root. A hole appears.
- No one is immune from mistakes, not even a doctor. After removing the pulp in severe forms of caries, the dentist must fill the canals. It is not always possible to seal them completely, often due to the doctor’s inattention, sometimes due to the tortuosity of the canal structure. An infection gets inside, and here it’s not far from pus.
- Some operations require perforation - i.e. drilling a hole in the root wall. Infections easily enter through these openings.
Treatment of gingival fistula
The treatment of fistulas on the gums is based on the principle of eliminating all factors that contribute to the formation of fistulas. Along with treatment of the underlying disease, the patient is prescribed a course of rehabilitation measures. In particular, the affected gum is treated with ultrasound or laser, cauterized with diathermic current, and antibacterial solutions, special gels, rinses and toothpastes are used to eliminate the inflammatory process. If necessary, the patient is prescribed antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil and others).
If complications develop, for example, if the pathological process spreads to the periosteal tissue, surgical removal of the fistula is performed. After completion of the operation, the patient is also prescribed a course of rehabilitation measures.
Types of gum fistulas
In modern dental practice, there are two types of gingival fistulas:
An external fistula is a flow channel ending with a hole on the surface of the gum, through which purulent and other pathological masses are discharged into the patient’s oral cavity. In turn, internal fistulas are called passages that do not have access to the gum surface, do not interact with the external environment and remove pus from the source of inflammation into free anatomical spaces in the thickness of the tissue.