Inflammation of the gums after tooth extraction: the most complete information on how to solve the problem
The process of tooth extraction (extraction) is not always easy and simple. Many people know that this small operation causes a lot of discomfort. Yes, thanks to effective techniques, modern equipment and medications, dentistry today can make this procedure less painful and safer. However, this is still a surgical intervention, which sometimes even requires suturing. Therefore, after such manipulations, the patient may feel pain for some time, and the gums may swell.
These symptoms do not always signal that something is wrong. But sometimes they can actually indicate the development of a complication - inflammation of the gums after tooth extraction (this is the main symptom of alveolitis). Below in the article you will find useful information on how to recognize the problem, what treatment for the pathology exists, and how to prevent the development of serious complications.
Possible complications
Alveolitis after tooth extraction.
After tooth extraction, the following complications are possible:
- increased temperature - if the reading exceeds 37.5° for more than 2 days, the doctor prescribes antibiotics;
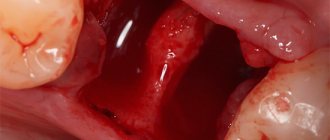
- alveolitis - the presence of temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, swelling around the wound and pain indicate inflammation;
- damage to the gums is a medical error; inept use of the instrument leads to dissection of the soft tissues or roots of adjacent teeth;
- perforation of the maxillary sinus - recognized by sinusitis, voice deformation, bleeding (the cause of the injury is explained by the close proximity of the roots and the maxillary sinus);
- nerve damage - injury occurs due to the proximity of the nerve to the tooth roots; the problem can be recognized by numbness and loss of sensitivity (more often manifested in the tongue and lower lip);
- dislocations and fractures of the jaw - the cause of the injury is the application of physical force by the doctor to extract a tooth or its fragments, the problem is recognized by severe pain in the lower part
- jaw, difficulties in opening/closing it.
Many complications can be prevented by timely seeking help from a doctor and choosing the right dental center, in particular a specialist.
Symptoms of the pathological process
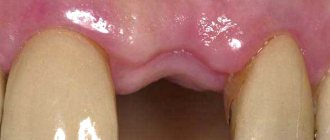
If you are concerned about slight bleeding of the gums and soreness of the wound immediately after tooth extraction, this is quite natural and is the result of intervention in the living tissues of the body. There is no need to be afraid, but it is important to observe your condition over time. Swelling, inflammation and swelling of the gums, and a slight increase in body temperature should normally subside 2-3 days after the procedure. But in cases where alarming symptoms increase, it’s time to think about visiting a dentist.
Signs that should alert you include other unpleasant phenomena: acute paroxysmal or constant aching pain radiating to the jaw, head, increased body temperature (it can reach 39 degrees or even higher), bad breath. It is also time to sound the alarm when there is no blood clot at the site of a recently extracted tooth, but the suppurating area is clearly visible. The gums around will be swollen, inflamed, covered with a gray-greenish coating. Do not be surprised that in such a situation your submandibular lymph nodes will be enlarged and painful.
Removing gums from a wisdom tooth: indications and removal process | All about gums
It has long been proven that wisdom teeth or “eights” are a kind of rudiment in the human body.
They received their original name due to eruption in a fairly “adult” period after 16 years. They are not involved in the process of chewing food or speech formation, but they cause a lot of problems for every second patient. Sometimes the process is so painful and unpleasant that the gums from the wisdom tooth have to be removed.
The minor operation is quick and eliminates the risk of infection and inflammation.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
Pericoronitis
Unlike other molars, the figure eight begins to emerge when the jaw and dentition are fully formed.
By this time, the gum tissue has become quite dense and elastic, and can partially cover the crown, creating a kind of hood. It easily accumulates food plaque and bacteria, causing inflammation and even dangerous suppuration.
This disease in dentistry is called “pericoronitis” and threatens a person with serious complications.
Such an area cannot be properly cleaned or rinsed, so the doctor often suggests cutting or removing the hood from the wisdom tooth. Sometimes this is simply necessary if the patient:
- there is a sharp and “rotten” smell from the mouth;
- the person complains that he cannot chew or bite the product, open his mouth wide or yawn;
- the cheek swells and looks swollen, the temperature has risen;
- swollen lymph nodes behind the ears or under the jaw;
- the gums above the figure eight are very red, a cloudy liquid or ichor is released;
- Gingivitis with acute pain is diagnosed.
These are clear symptoms of hood inflammation that cannot be ignored. When the infection is advanced, it goes deep inside the gums and can affect the muscles responsible for chewing and damage the salivary glands.
The accumulation of pus near the wisdom tooth often ends in dangerous phlegmon or a painful fistula. All this not only affects performance, but also ends in infection of internal organs.
Pericoronitis - hood over the tooth
How to prepare for surgery
Removing gum from a wisdom tooth is an actual dental procedure and requires little preparation. It is advisable for a person to undergo a series of tests to ensure that he is not allergic to anesthetics and antibiotics. An important diagnostic step is radiography or panoramic photography of the jaw from different angles and projections. This helps the doctor resolve issues:
- Is it possible to limit myself to cutting off the hood above the crown?
- Is there a purulent focus in the periodontium?
- Is it necessary to completely remove the “eights”?
When wisdom teeth grow correctly and evenly, the dentist tries to preserve them and only removes the mucous membrane to avoid infection. When the crown is positioned to the side, it is better to immediately pull out the molar without waiting for possible complications.
Preparation includes certain points:
- high-quality cleaning of enamel and oral cavity from plaque and tartar (by any method);
- short-term use of antibiotics to prevent infection of gum tissue (often replaced by rinsing with antiseptics for several days);
- complex treatment of periodontal disease or gingivitis, installation of temporary fillings on carious teeth.
Only after all “alarming” points have been eliminated, the dentist performs the operation. The entire procedure is performed under local anesthesia and takes little time.
Removing gum from a wisdom tooth: main stages
In dentistry, such operations are performed in two ways: traditionally with a scalpel or, more modernly, with a laser. The latter option is offered in large centers where the necessary equipment is available.
Among its positive aspects are instant sealing of sutures and absence of bleeding, quick rehabilitation. The only negative is the cost is unaffordable for most patients.
Therefore, standard excision remains the most popular procedure.
Removing the hood from a wisdom tooth is carried out in several stages:
- The required amount of anesthetic drug is injected into the gums, the dosage of which is calculated individually. Usually Ultracaine, Lidocaine or similar agents are used that “freeze” the nerve endings for a while.
- The oral cavity is dried from accumulated saliva and treated with special antiseptic solutions based on iodine or chlorhexidine.
- Using a scalpel, the overhanging hood is incised in several places and carefully removed. The dentist shapes the correct position of the gums to facilitate the eruption of wisdom teeth.
- At this stage, the doctor can remove the figure eight along with the root. In this case, it is necessary to put stitches on the hole to close the bleeding wound and reduce its size.
- After the operation is completed, a compress soaked in liquid with iodoform is applied to the stitched area. It is a hemostatic agent that improves clotting and helps blood clots form. It seals the hole from the root and prevents bacteria from entering.
For approximately 30 minutes after gum removal from a wisdom tooth, the patient remains under the supervision of a dentist. He gives recommendations for wound care and will help you choose an antibiotic.
Gum care after hood removal
After excision of the inflamed area of the mucosa, anesthesia usually wears off within a few hours. If a person experiences severe pain, it can be relieved with an analgesic. The most effective drugs after surgery: Nurofen, Nimesil, Tempalgin, Pentalgin. In case of severe unbearable attacks, it is recommended to give an injection of Ketanov or Ketarolac.
Home care consists of regular rinsing with antiseptics. Most often it is proposed to use solutions:
- Miramistin;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Betadine;
- Chlorhexidine.
Rinsing is carried out in a special way: a person takes a small sip of the product into his mouth and holds it without moving for about one minute. It is important not to wash the clot out of the sutured hole so that active bleeding does not begin. During lunch, it is better to cover it with a cotton swab, trying to chew on the other side.
Cholisal gel for gums
To ensure that the gums recover faster after removing the hood and do not tear, they can be treated with a special ointment. It should contain vitamins, collagen, anti-inflammatory and regenerating components:
- Holisal;
- Asepta;
- Dentamed;
- Kamistad.
The first week after excision of an overhanging area of mucous membrane, the patient should regularly visit the dentist, who monitors the condition of the hole or wound. To alleviate the condition, it is necessary to avoid hot drinks and dishes throughout this period, and switch to pureed food. In order not to injure the gums, it is better to eat semi-liquid soups and purees, and avoid eating foods that should be chewed thoroughly.
After removing the stitches, you can rinse your mouth with fresh decoctions of medicinal plants: sage, oak bark, St. John's wort or bay leaf.
To inhibit the growth of bacteria, you can apply a cotton swab soaked in propolis or calendula tincture. Antiseptic solutions are an excellent replacement for salt or soda baths with the addition of a few drops of iodine.
If all recommendations are followed, pain and discomfort completely disappear after 7–10 days.
Source: https://vdesnah.com/udalenie-desnyi-s-zuba-mudrost.html
Why inflammation develops
Common factors against which a pathological process can develop include quite a few situations that provoke inflammation. Among them are colds and acute respiratory viral infections that occur in the body, a general weakening of the immune system, and deep caries, which is a source of pathogenic microorganisms. As for the main reasons, experts identify the following:
- deep damage to the gums as a result of trauma: firstly, the dental surgeon who performed the procedure could have made a mistake (leaving root fragments in the wound, for example). Also, trouble could also occur against the background of complex tooth extraction, for example, eights (wisdom teeth), whose roots were intertwined, severely damaged or crooked, not fully erupted teeth.
- errors during the administration of anesthesia,
- infection due to poor handling of medical instruments,
- there is no blood clot in the hole: immediately after the removal procedure, the doctor compresses the edges of the wound so that it fills with blood. After some time, it turns into a clot, which is designed to protect the damaged area from the effects of harmful microorganisms. Now do you understand why experts strongly recommend eliminating sharp rinses on the first day after surgery? In order not to damage this very clot or wash it,
- infection of the wound due to the patient’s negligence: the lack of intensive rinsing is not a reason to completely exclude daily hygiene procedures. It is also important to remember the rule: after you have eaten, make mouth baths with decoctions of herbs or antiseptics (but not rinses!!!).
Important! Gum inflammation after extraction occurs in approximately 4% of cases. The same complication after the removal of a “wisdom tooth” occurs much more often - in 25-30%,1 because eights most often grow incorrectly or erupt with deviations from the norm. The most striking example of this is the joint manifestation of retention and dystopia.
Removal of gums over wisdom teeth
The eruption of the last molar in the row, which is called the wisdom tooth, very often brings a lot of difficulties to a person.
The appearance of this element in the jaw row often occurs later than all other teeth, and also entails various problems.
One of the most common complications is inflammation of the gum tissue over the molar and the formation of a so-called hood, in which infection can develop.
articles:
General idea of pathology
During the eruption of a wisdom tooth, it is often covered by a mucous membrane of gum tissue, which is not completely sealed, but maintains a gap between itself and the growing molar. Dentists call this tissue formation a hood.
The main danger of forming a hood over an erupting molar is the possibility of tiny food particles penetrating underneath it, which are almost impossible to remove through normal hygiene procedures.
These food particles become a site for the development and reproduction of pathogenic microflora, upon interaction with which rotting processes begin, causing the development of infection .
At the same time, the gum tissue loses its density and begins to bleed under any mechanical stress.
In dental practice, such inflammation of the gum mucosa is called pericoronitis .
The pathology requires immediate professional treatment , as over time it can lead to more serious consequences for the oral cavity.
Complications and symptoms
The first time after the formation of a hood over the erupting wisdom tooth, the person does not experience any unpleasant sensations. However, after food particles penetrate the mucous membrane, the process of decomposition and rotting begins, leading to the following symptoms:
- the appearance of an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth;
- soreness of the soft tissue in the area of the growing tooth;
- swelling of the gums.
In the absence of therapeutic measures at this stage, the inflammatory process develops very quickly.
A person experiences the following signs of the development of an inflammatory process:
- increased swelling of the gums, its redness, which can spread to the surrounding areas of soft tissue and the cheek;
- discharge of purulent contents from the hood upon pressure or spontaneously;
- increased pain, especially when eating or other jaw movements;
- limited mobility of the lower jaw.
In addition to specific signs of the inflammatory process, a person experiences general weakness, headache, and increased body temperature . When palpating the submandibular lymph nodes, severe pain occurs.
Learn more about inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth and the symptoms of the pathology from the video.
Indications for gum excision
When pericoronitis passes from the initial stage to an advanced form, the only method of getting rid of the pathology is surgical intervention.
Experts insist on the need for surgical treatment of pathology in the following cases:
- the presence of purulent exudate in the space between the erupting molar and the soft tissue , which leads to its periodic release and the formation of a persistent putrid odor from the oral cavity;
- persistent pain during communication, chewing and swallowing food;
- the development of gingivitis - an acute inflammatory process occurring in soft tissue, as a result of which a person experiences constant pain radiating to the ear and temples;
- spread of swelling to the buccal area , which leads to the impossibility of fully opening the oral cavity;
- increased body temperature and its retention at a high level , soreness and swelling of the lymph nodes.
The presence of one or more of the listed conditions indicates the need to take prompt surgical measures to eliminate inflammation, since its further development is fraught with serious consequences.
Reasons for performing flap surgery on the gums and contraindications to the procedure.
Read here about the reasons for the appearance of exostosis after tooth extraction and methods for eliminating the problem.
Preparation
Despite the fact that excision of the hood is a fairly simple operation, careful preparation is required for its successful implementation.
It consists of performing the following procedures:
- Visual examination of the patient’s oral cavity and identification of complaints. At the initial appointment, the dentist finds out the characteristics and duration of the inflammatory process in the patient.
This will help to establish the cause of the development of pericoronitis and draw up an optimal treatment plan. Instrumental examination of the oral cavity. The specialist refers the patient to X-ray and tomography.
These research methods make it possible to determine the direction of growth of the third molar, the number and location of its roots, and determine the condition of the jaw bone tissue.
Based on the data obtained, the specialist determines whether it is possible to preserve the wisdom tooth or whether extraction will be required. Determination of a person's health status.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo a general blood and urine test to identify the presence of hepatitis, HIV infection, and syphilis.
An important stage in preparing for surgery is determining the level of blood clotting and identifying the reaction to anesthetic drugs that can be used during surgery. Preparatory therapeutic measures. Often, the operation to excise the hood is preceded by measures aimed at relieving the acute inflammatory process.
Often it is necessary to remove mineralized deposits and eliminate carious lesions of adjacent molars. This allows you to reduce the risk of developing postoperative complications and speed up the further rehabilitation process.
The final date for the operation is set only after all of the above points have been completed and the person is fully ready to perform it.
Course of action
The operation to remove the hood over a wisdom tooth is performed as follows:
- Introduction of anesthesia. Based on the collected medical history, the dentist administers the selected painkiller to the patient. The procedure is often performed under local anesthesia, but if there are individual contraindications, it can be performed without it.
- Excision of gum tissue. After identifying the area of gum that overhangs the growing molar, using surgical scissors or a scalpel, the dentist excises the soft tissue. The purpose of this procedure is to completely expose the erupting tooth.
- Treatment of the wound surface. The excised soft tissue is treated with antiseptic drugs, cleaned of food residues, purulent contents and blood.
- Applying iodoform turunda or a compress with a healing preparation. This minimizes the risk of infection penetrating the treated surface and also promotes better healing of the gum tissue.
Upon completion of the procedure, the dentist sets a date for the patient’s next examination and prescribes medications that will need to be taken throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
Recovery period
The duration of healing of gum tissue depends on many factors - the anatomical features of the human body, the correctness of the operation, as well as the accuracy of the patient’s compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician.
To shorten the rehabilitation period, you should adhere to the following rules:
- do not eat for the first 2-3 hours after surgery;
- remove iodoform turunda when the specialist says, but no later than the next day after the operation;
- try not to chew food on the side of the jaw that was operated on;
- ensure that the food consumed is at a comfortable temperature for the oral cavity;
- During hygiene procedures, try not to touch the treated area of the gum with a toothbrush.
First aid at home
So, if your gums are inflamed and hurt, but you still can’t get to the doctor, what should you do to relieve gum inflammation at home? You can make baths from warm decoctions of plants that have an antiseptic effect - chamomile, sage. Just don’t forget that you can’t rinse your mouth with them! You just need to hold the decoction in your mouth for about 1-2 minutes. It is recommended to repeat this procedure several times an hour until the discomfort subsides.
Important! Do not use baths or rinses with baking soda and hydrogen peroxide. In this case, they will do more harm than good, because... will have an aggressive effect on damaged tissues, causing their irritation.
In the first days, cold can be applied to the cheek on the sore side, which eases the discomfort and inhibits the development of pathogens. In addition, cold compresses perfectly relieve swelling and reduce the risk of hematomas after surgery. For this purpose, a towel soaked in cold water, ice or other products from the freezer (they must be wrapped in a towel or other cloth), and a bottle of cold water are well suited. If the pain does not subside, you can take painkillers “Ketorol”, “Nise”, “Baralgin”, etc.
You should not get carried away with self-medication, because... The above measures will only help alleviate the symptoms, but not eliminate the root cause of the pathology.
How to relieve pain after tooth extraction
Immediately after surgery, applying a cold compress to the painful area reduces swelling and pain.
Before taking painkillers, you must read the instructions for use, even if the drugs were prescribed by a doctor. There may be contraindications. For example, for derivatives of aspirin and analgin, this means low blood clotting and a tendency to ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract.
The following are taken as painkillers:
- Xefocam or Xefokam Rapid 1 tablet. 1-2 times a day.
- Ketanov, Ketorol (prescription) - 1 tablet each. 2 times a day
- Nimesulide - 1 tablet. 2 times a day
- Baralgin - 1 tablet. 3–4 times a day.
- Spasmalgon - 1 tablet. 3 times a day
You should not rinse your mouth in the first 3–5 days, so as not to wash the clot out of the hole. You can make anesthetic applications, for example, with a tampon with Lidocaine or Novocaine.
Relieving swelling with antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetrin, Tavegil) also reduces pain.
Antibiotics, acting on infectious inflammation, also help eliminate pain.
Uncontrolled, self-administration of antibiotics leads to bacterial resistance and ineffective treatment.
How to rinse
Rinsing with antiseptics and means to accelerate healing is carried out 5–6 times a day and always after meals:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Romazulan;
- Stomatophyte;
- Baking soda or soda-salt solution - 1 tsp. soda and/or salt per 1 tbsp. water at room temperature;
- Propolis - 30 drops of official pharmaceutical solution diluted in 1 tbsp. water.
You can rinse with infusions and decoctions of herbs: oak bark, chamomile, sage.
What to do to speed up the gum healing process
Healing includes:
- Formation of a blood clot.
- On the 3rd day, the wound is covered with young epithelium, the clot begins to dissolve.
- After 7 days, the epithelium completely covers the socket.
- After 2 weeks, the hole is almost undetectable.
- After 1 month active bone formation is underway.
- After 4 months the bone is restored.
To speed up regeneration, take measures to prevent inflammation and prevent additional injury to the socket.
Professional dental and drug treatment
So, how to cure gum disease? Of course, by contacting a specialist. The doctor will evaluate the picture and select the most effective treatment. In some cases, you will have to carry out the following procedures:
- installation of drainage, which is a tube: through it, pus, ichor will flow out of the hole,
- high-quality cleansing of the wound from pieces of food, suppuration or remaining in it after removing root fragments, treatment with antiseptic solutions,
- suturing: the stitches will close the wound, which means the infection will not be able to penetrate there again.
The doctor will also prescribe medications for topical use, for example, antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine) and analgesics (Oralsept, Tenflex sprays, etc.). To relieve pain, the doctor will recommend taking painkillers for several days: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketanov. It is better to avoid Aspirin, as it thins the blood and can cause bleeding.
Antibiotics for gum inflammation are prescribed only when the pathology is actively developing or if the process has been sufficiently advanced. The course of such treatment is 5-7 and even 10 days. The drugs used are “Oletetrin”, “Lincomycin”, “Gramicidin”. Remember that you should never stop taking antibiotics halfway through - the body will get used to them, after which resuming treatment will not be as effective, plus you will get intestinal dysbiosis. We prescribed a course of 10 days - we take the drug for all ten days, even if already on the fifth you feel much better.
What can you do during pregnancy?
It all depends on how far along the pregnant woman is, as well as on the possible threat to the health of the expectant mother and baby. The risk should not exceed the benefit. Inflammation must be treated in any case - after all, the source of infection and infection is dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the baby himself. The only thing that concerns pregnant women is the advisability of prescribing certain medications and the absence of contraindications to them.
In any case, there is no need to listen to the advice of friends, recommendations on various forums on the Internet and try to independently choose a safe folk remedy. It is imperative to consult a doctor.
What definitely won’t do any harm are baths of saline solutions and herbal decoctions. However, you must strictly follow the dosage and adhere to the schedule of these activities. In the second trimester of pregnancy (relatively safe), you can take some non-steroidal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects and homeopathic remedies. But it’s worth repeating once again: only a specialist can decide how dangerous inflammation is for the pregnant woman and the fetus, and what measures are best to take.
Why is gum inflammation dangerous?
In addition to unpleasant sensations, alveolitis is fraught with a lot of dangers. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, the human body can be seriously damaged. So, alveolitis can cause gumboil, i.e. inflammation of the periosteum, which is expressed in swelling of the gums, swelling of the cheeks, increased temperature and unbearable pain.
“They once removed my lower wisdom tooth... The removal was difficult, not only did the tooth not fully erupt, but it also climbed crookedly, resting against the neighboring one. The doctor suffered a lot, but managed. Afterwards she gave me recommendations on how to care for the wound. And I’m terribly shy and suspicious, so I decided that nothing would happen if I rinsed my mouth that same day so that there would be no unpleasant odor. After a couple of days, the pain began to intensify, the whole jaw and head seemed to hurt, the temperature rose, and the lymph nodes became enlarged. Let's run to the doctor! The doctor said that because I washed the blood clot, an infection got into the wound and inflammation began. They performed a sanitation, prescribed antibiotics, and after a week everything got better. I will never disobey the doctor again.”
Elena M., from a review on the website Woman.ru
In addition, the growth of purulent inflammation of the gums threatens the development of osteomyelitis, and this disease will certainly lead to the formation of purulent abscesses or phlegmon, which will spread to the entire jaw, and not just to one tooth. In this case, the infection spreads with lightning speed and can penetrate the blood, causing infection (sepsis). The outcome of this complication is very sad - the person dies in a matter of days. Do not self-medicate, but at the first warning signs, consult a specialist.