Unilateral pain
Pain on the right or left side of the face is classified according to its origin as follows:
- headache;
- neurology;
- neuralgia;
- pathology of the skull bones;
- bruises;
- pathologies of the sinuses;
- eye pathology;
- toothaches;
- atypical pain.
The right side of the face and eyes hurt
Facial pain is a consequence of infection or mechanical damage to tissue on the right side.
As a result of tissue damage, inflammation occurs. Since all the bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerve nodes, and nerves that can be affected by the inflammatory process are located symmetrically on the face, a pain symptom occurs on either one side or the other.
Note! When the source of inflammation is located on the right, the pain spreads to the right side.
Pain in left eye and left side of face
When a focus of infection occurs on the left, pain occurs on the left side of the face. It is also possible that the cause of the pain depends on the inflammatory processes in the eye, with the pain spreading to the entire half of the face.
In rare cases, inflammation and pain can affect both sides of the face.
For some treatment methods, the location of the pain is an important factor.
Important! This is especially true for homeopathy treatment. Many homeopathic medicines are prescribed when pain is localized on one side or another; such symptoms dictate the choice of homeopathic remedy, which is why it is so important where exactly the pain is localized.
Causes of pain in the cheek or gum
Why does my cheek hurt? As a rule, pain appears due to swollen gums, which can be caused by many factors:
- Inflammatory process in the dental part of the root. It can occur after prolonged caries or pulpitis, usually when the nerve has long been removed. In this case, the inflammation spreads to the root of the tooth. The doctor can determine this cause by redness in the area of the diseased tooth and slight swelling of the gums.
- Pericoronitis. It occurs when a wisdom tooth erupts with certain difficulties. As a rule, this occurs between 17 and 30 years. An inflammatory process appears in the area of this tooth, the painful area swells, and a hematoma may even form.
- Tumor. It can be malignant or benign. In this case, the gums or cheek swell. Formed as a result of injury or prolonged inflammation.
- Abscess or cellulitis. It develops when the gum or cheek cavity fills with pus. With an abscess, there is a clear localization of pus formation with its own boundaries; with phlegmon, pus can spread to adjacent tissues.
- Gingivitis. This is the initial stage of periodontal disease, characterized by bleeding and swelling of the gums. Appears as a result of poor oral hygiene at the site of accumulation of food or plaque, as well as poor attachment of the crown.
- Thermal or chemical burn of the gums or cheeks.
- Mechanical injury.
Read also: Cheek is swollen after tooth extraction
All these reasons require medical intervention. An exception may be tumors of the gums and cheeks that arise as a result of tooth extraction or treatment of its root. This is all considered a natural process that will go away on its own over time.
In addition, the cheek can become sore and swollen due to an insect bite, due to an infectious disease such as mumps, bruise of soft tissue in the cheek area, herpes, etc. Pain in the cheek can be the result of neuralgia.
Causes of unilateral pain
Headache
The Latin name for this disease is hemicrania, which translates as “half the head.” This is a neurological pathology that affects the blood supply to the brain. Migraine is characterized by constant severe pain on one side of the head and face, often throbbing. The pain intensifies from a bright sound or light, with any movement of the head. Accompanied by nausea.
Cluster pain
This is severe paroxysmal pain that occurs without identified causes. Pain occurs in the area of the right or left eye at approximately the same time every day. Attacks are more common in men.
Neurology
Pain that occurs in the muscles of the face usually has neurological causes and is associated with increased tone.
In these conditions, the function of the nerve centers involved in the regulation of muscle function is often disrupted. As a result, pain occurs in a constantly tense muscle. Often this occurs only on the right or left side.
Osteochondrosis of the neck
Develops as a result of metabolic disorders and loss of strength of the intervertebral discs. Pain that occurs in the neck can spread to the face. In addition, the tone of several muscle groups increases: those supporting the spinal column, suboccipital, and facial, which also causes pain.
Neuralgia is a syndrome associated with inflammation or compression of a nerve. In this case, severe pain occurs on the face on one side, behind the ear, often accompanied by herpetic rashes.
- violation of facial expressions on one half, asymmetry during laughter and expression of other emotions;
- enlarged palpebral fissure, lagophthalmos (dry eye);
- taste disturbance.
Important! The nature of the pain and its localization depend on the location of the nerve affected by the pathology.
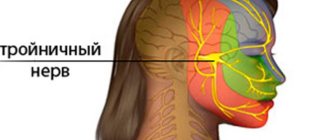
Trigeminal nerve
This is the main sensory nerve in the face. It is called trigeminal because it has three branches. Symptoms: severe, short-term shooting pain only on the right or left. The pain spreads to the ear, jaw, neck, index finger. An attack of pain is provoked by a weak touch and is accompanied by a tic (muscle contraction).
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Attacks of pain in the tonsils and root of the tongue. Attacks occur from cold, hot. The pain is accompanied by tachycardia, loss of consciousness, and a sharp decrease in pressure.
Superior laryngeal nerve
Pain in the larynx on one side, radiating to the shoulder. The attack is provoked by coughing or sudden movement.
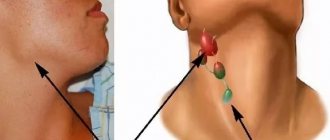
Pterygopalatine ganglion
When this node is inflamed, the patient suffers from profuse lacrimation, swelling, and nasal discharge. Pain occurs on one side in the cheekbone, jaw, eye, temple, ear.
Nasociliary ganglion
An extremely rare pathology. Paroxysmal unilateral pain at the base of the nose, runny nose.
Facial bone pathologies
Osteomyelitis
Purulent processes in the bone marrow. Most often it is a complication of purulent pulpitis or periodontitis. The pain is throbbing, accompanied by fever, general weakness, swelling of the face, and inflammation of the lymph nodes. The pain spreads along the same side on which the inflammation occurred.
Sharp pain, swelling, change in skin color in the damaged area, displacement or retraction of the bone. Location and symptoms of fracture:
- Orbit: dull pain that gets worse with eye movement, double vision, limited mobility or retraction of the eyeball.
Disorders of the temporomandibular joint
This pathology occurs due to:
- fracture;
- dislocation;
- inflammation due to infection.
The pain spreads to the entire side of the face and is felt in the ear. Pains of various types: aching or throbbing, paroxysmal or constant.
Facial pain also occurs due to soft tissue injury: sharp, accompanied by swelling and subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Pathologies of the sinuses
Inflammation that occurs in the sinuses. With sinusitis, pain in the cheekbone, eye, ear is accompanied by noise in the ear, deterioration of the general condition, and increased temperature.
Eye pathologies
Pain arising from eye disease is often transmitted to other parts of the corresponding half of the face.
Inflammation of the eye socket
Caused by hormonal imbalances and infection. Accompanied by swelling and aching pain.
Irreversible damage due to high pressure inside the eye. Accompanied by redness of the eyes, dilated pupils, pain that extends to the temporal part of the face.
Conjunctivitis
Develops due to infection of the conjunctiva or due to allergic reactions. Symptoms: redness, itching, purulent discharge from the lacrimal canal.
Toothaches
Dental diseases are the most common cause of asymmetrical pain on the face. Diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw often radiate to the eye and are localized only on one side:
- deep caries;
- pulpitis (inflammation inside the tooth - in soft tissues);
- periodontitis (inflammation near the root of the tooth);
- abscess (accumulation of pus in cavities);
- osteomyelitis (inflammation in the jaw with the formation of pus - described above).
Atypical facial pain
This term refers to facial pain, the causes of which have not been identified. The diagnosis is made if other pathologies are excluded as a result of a complete examination of the patient.
Features of atypical pain
- They affect only one side of the face or are asymmetrical on both sides.
- Permanent in nature, aggravated by heat and stress.
- Superficial, of various types (severe burning, aching; itching and other sensations).
- Sometimes they feel like toothaches or tongue pain.
- They may disappear for long periods and reappear.
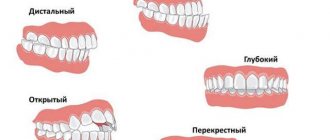
Classification of facial pain
Diagnosis of pain in the head, face, by foci of pain and classification of causes for diagnosis.
The photo is clickable. 1. Somatalgia is:
- – neuralgia is a disease that is accompanied by pain in the face and separately in areas affected by the disease; frequent attacks of burning pain occur, depending on the severity of the disease.
- – neuralgia of the laryngeal nerves, larynx - pain in the larynx, immediate or constant.
2. Sympathalgia - throbbing pain in the facial area in the arterial trunks, accompanied by autonomic reactions:
- – facial vascular pain (migraine) is a neurological disease accompanied by severe and frequent headaches or pain in different areas of the face; pain can last from several minutes to several days.
- - sympathalgia, damage to the innervation of the face (neuralgia of the ear ganglion, auriculo - temporal syndrome...).
3. Other pains, different parts of the face, long-term or instantaneous pains.
4. Hysteria, hypochondriacal - depressive state - a syndrome that is characterized by other symptoms and syndromes, such as inhibition of movement and brain activity, as well as bad mood.
5. Disease of internal organs, prosopalgia.
In this large video from Neurologist Marina Igorevna Koreshkina: About facial pain, causes and treatment.
What to do?
If you experience the following symptoms after a head injury, you should immediately call a doctor at home:
- loss of consciousness;
- sudden onset of nasal discharge;
- persistent nosebleeds;
- visual impairment (double image, blurriness, etc.);
- hearing impairment;
- facial asymmetry;
- malocclusion, inability to close the jaws or close the mouth;
- any pain or other unusual sensations;
- open wounds.
Important! For any pain on the face, self-medication is dangerous! To avoid complications of any of the above diseases, you need to consult a doctor: a neurologist, ENT specialist or dentist. After examination, the specialist prescribes a course of treatment depending on the nature of the pain and the diagnosis.
Swollen cheek: what to do
Pain in the cheek and absence of pain in the tooth appears, as it has been found, for many reasons. But a doctor must install them, as well as prescribe treatment. If the patient begins to treat himself, taking painkillers, he will finally blur the whole picture of the disease. Then it will be difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
If it is not possible to see a doctor at the moment, then temporary measures of assistance can be provided to yourself at home:
- If you have a cheek injury, an insect bite, or after a tooth extraction, apply a cold compress to the cheek. If the body temperature is elevated or there is a suspicion of an infectious process, then such actions are prohibited.
- Rinse your mouth with a solution containing equal amounts of baking soda and salt. Such measures are advisable for problems with teeth or oral cavity. Take 1/2 tsp per glass of warm boiled water. salt and soda.
- If an insect bite occurs, apply a soda compress to your cheek and drink an antihistamine.
- The pain from the eruption of wisdom teeth can be soothed with special freezing gels and ointments. They are usually sold for infants. Or you can take a painkiller.
All these measures can be carried out if a person knows the exact cause of the pain in the cheek and its swelling. If the pain and swelling does not go away after 1–2 days, you should consult a doctor. Urgent medical care is also required by the rapid growth of the tumor, an increase in body temperature and a sharp deterioration in the person’s condition.
For example, after an insect bite, a person’s tumor may begin to rapidly increase, he may have difficulty breathing, and he may feel dizzy. All this indicates the development of an acute allergic reaction to the bite. In this case, it is urgently necessary to give him an antihistamine and call an ambulance.
Read also: Cheek swollen from a tooth, how to remove swelling
Homeopathic treatment
Homeopathic treatment effectively relieves symptoms of neurological, neuralgic and other types of pathology.
The left side of the face hurts: symptoms, causes, possible diagnosis, diagnosis and self-diagnosis, advice from doctors.
A headache is always an unpleasant condition, regardless of its strength and duration. Its appearance is influenced by many factors, and most often the person suffering from it knows that he is dependent on changes in weather or is affected by overwork at work. But what should you do if, for unknown reasons, the left side of your face hurts? To avoid painful sensations from being accompanied by worries about your condition and attempts at unsuccessful self-diagnosis, you need to understand the characteristics of a unilateral headache.
Possible reasons
Headaches of various localizations can be either a disease in itself or a consequence of another serious illness. To understand what caused the discomfort, you need to listen to your body and determine the nature of the pain. After all, it is different for each pathology.
Causes of pain on the left side of the head:
- Migraine. This is a neurological pathology characterized by severe, debilitating pain on one side of the head. Localized on the left side, it covers the temple, forehead, the left side of the face and eyes hurt. In addition, the patient often complains of nausea and vomiting, spots before the eyes, sweating, intolerance to bright light and loud sounds.
If the left side of the face hurts, the reasons causing this condition can be very serious and require medical intervention. Therefore, you should not self-medicate; you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment for facial pain
Self-medication can be dangerous to human health; you should immediately consult a doctor. If you do not contact a doctor, a serious complication may develop. Doctors use anticonvulsants to treat neuropathic pain. These are mainly drugs such as: gabapsepin, carbamazepine (a drug that is used to relieve seizures and to relieve seizures) and others. Non-steroids, vitamin B group drugs, Xefocam, Dicloberp can also be used. These drugs are prescribed in combination with other antibiotics.
If the diagnosis has already been established and the disease is chronic, then self-medication and self-administration of medications is possible. For example: gabapentin, 300 mg, 1 tablet, it is possible to increase the dose of the drug. Recommended frequency of administration is 3 times a day, 1 tablet.
If migraine develops, it is possible to take antimigraine or other similar drugs on your own. In some cases, doctors allow patients to go for home treatment, without their supervision, but in cases where facial pain is not caused by any serious illness.
Reflexology is used in the treatment of neuralgia. They also use acupuncture, acupressure, psychotherapy, tranquilizers, antidepressants and other strong drugs and antibiotics. Much attention is paid to psychological treatment, since the disease can be caused by a psychological disorder or poor mental state.
What do different types of pain mean?
Most often, all that a patient prone to headache attacks can say about his condition is the nature of the pain. It is by how the left side of the head and face hurts that you can determine the diagnosis before the ambulance arrives and provide first aid to yourself or a loved one. What are the sensations?
The nature of pain in various pathologies:
- pulsating - may indicate migraine, hypertension (high blood pressure), vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- shooting - attacks of acute pain occur in many people and can be caused by both minor reasons (stress, hypothermia) and dangerous diseases such as stroke;
- pressing - can be a consequence of various diseases and conditions. Among them are migraines, head injuries, brain tumors, alcohol intoxication, vascular spasms, exposure to changes in atmospheric pressure, and diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Sometimes it can be difficult to understand why the left side of your face hurts. For an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of diseases
To make a diagnosis when complaining of pain on the left side of the head, the patient will be prescribed a comprehensive examination to confirm or refute serious pathologies.
- interviewing the patient and studying the anamnesis;
- measuring blood pressure and pulse;
- CT and MRI of the head;
- electromyography (study of the state of nerves and muscles) and electroneurography (study of the peripheral nervous system);
- blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the brain;
- determination of intraocular pressure;
- consultations with related specialists (neurologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist, dentist, otolaryngologist and others as indicated).
After the diagnosis is made, the patient will be prescribed treatment, but before that, during an acute attack, you can try to help yourself.
First aid
Often, competently provided first aid not only alleviates the patient’s condition, but can also save his life.
Methods of first aid for a patient with a headache:
- take a lying position, relax;
- take a painkiller tablet, carefully studying the instructions before taking it;
- put a cold compress on your forehead;
- apply aromatic oils of lavender, citrus, pine to the points just above the temples (check for allergies before use);
- traditional medicine recommends preparing a decoction of chamomile, St. John's wort, mint, and calendula;
- apply a compress of warm dry salt;
- deep breathing will help saturate the brain with oxygen and relieve pain;
- if there is a suspicion of a stroke, it is necessary to immobilize the patient and wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Consequences of treatment
Sometimes cheek pain and swelling appear after dental procedures. The reasons for this condition may be:
- An allergic reaction, for example, due to the body's sensitivity to the filling material. In this case, you will have to return to the dentist and install a new filling made of hypoallergenic material.
- As a result of treatment of pulpitis, after removal of the nerve. It may not have been completely removed and will require a repeat procedure.
- Pain after tooth extraction is not uncommon. To prevent a tumor from developing, you should abstain from alcohol, hot procedures, and solid food for several days. If swelling appears, then you need to apply cold compresses to the cheek.
- If an incision was made on the gum. This is usually done to drain the pus. In this case, pain and swelling are present for several days.
Quite common explanations for the development of swelling on the cheek inside the mouth include:
- The manifestation of an allergic reaction caused by the body’s high sensitivity to some components of dental materials used in the treatment. As a result, a situation often arises when the tooth does not hurt, but the cheek is swollen. In this case, the dentist will be forced to unfill the treated tooth and redo the work using hypoallergenic materials.
- Sometimes it happens that the tooth does not bother, but the cheek is swollen even after the nerve is removed. This circumstance can be explained by the fact that sometimes the dental canal is located in such a way that the doctor cannot go through it to the end. In this case, after the procedure, a small piece of the nerve remains in it or it is not completely healed. If you ignore this condition, the patient risks losing a tooth.
- An incision on the gum made by the dentist in order to allow the accumulated purulent infiltrate to come out can lead to the fact that the tooth does not bother the patient at all, and the cheek is swollen. This condition will be observed during the first day after the manipulation.
If, due to existing dental problems, the following signs appear, you should immediately attend an appointment with a dentist:
- an increase in the size of the tumor in the mouth, indicating an increase in the inflammatory process;
- if the affected area in the oral cavity continues to hurt and the pain tends to intensify day by day;
- a feeling of fullness in the swollen area on the inside of the cheek, an increase in body temperature.
As you can see, most often cheek swelling is caused by dental problems. A visit to the dentist will allow you to assess the clinical picture and provide timely treatment. Paying attention to your health will help you avoid serious consequences and restore your face to its original appearance. If necessary, assistance from other specialists may be required.
In order to temporarily alleviate the situation, you can resort to traditional medicine, including the following recipes:
- A glass of boiled water with salt or soda diluted in it. They need to rinse their mouth. The procedure should be repeated three times a day until the problem is eliminated.
- Honey and chamomile decoction. These components have strong antiseptic properties. For this, 1 tbsp. l. liquid honey should be mixed in 1 liter of healing chamomile decoction. This product allows you to eliminate harmful bacteria, heal existing wounds, ulcers and other diseases. At the same time, you can moisten gauze in chamomile infusion, apply it to the swollen area for a quarter of an hour and do not wash it off.
- A decoction of oak bark, St. John's wort and sage will also eliminate swelling. To prepare it, mix all the components in equal proportions (their total weight should not exceed 150 g), pour in 1 liter of boiled water and leave to infuse for an hour.
Saline and soda solutions are effective
In order for the body to cope with infection and hidden inflammatory processes, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. To do this, you can take a course of multivitamins and include as many fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet as possible. Traditional medicine also recommends using rosehip syrup.
The problem of swollen cheeks due to or any other pathologies is very common. It can be easily dealt with; the main thing is not to ignore this condition and seek qualified help in a timely manner.
Reason to see a doctor
A headache in itself is already a reason to see a doctor. But there are symptoms that indicate that this needs to be done as quickly as possible.
- constant worsening of the condition;
- sudden onset of unilateral headaches after 50 years of age;
- very strong painful sensations;
- headaches due to head injury;
- serious concomitant problems with vision, hearing, and psyche.
All of these symptoms may indicate a serious illness that should be treated immediately.
Treatment of unilateral cephalgia
Treatment for a condition in which the left side of the face hurts depends on the cause of the pain.
Treatment methods for unilateral headaches:
- If the cause of cephalgia is inflammatory processes in the oral cavity or ear, nose and throat, the pathologies are treated by a dentist and an otolaryngologist, respectively.
- After suffering an injury or with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, massage, painkillers, and exercise therapy will be required.
- If the skin on the left side of the face hurts due to neuralgia, antihistamines, vasodilators, and antispasmodics are prescribed. Physiotherapy is used, and in some cases surgery is indicated.
- To alleviate the condition of migraines, special medications are used - triptans.
- If a tumor is suspected, an examination and consultation with a neurosurgeon, oncologist, or neurologist is prescribed.
- Sometimes, in order to cope with headaches, it is enough to consult a psychologist and avoid stressful situations.
Causes and mechanisms
The infraorbital region is formed by the upper jaw, zygomatic bone and lateral wall of the nose. Therefore, pain in this area can occur due to pathological processes localized in the immediate vicinity. We can talk about the following conditions:
- Acute sinusitis.
- Dacryocystitis.
- Traumatic injury.
- Osteomyelitis of the upper jaw.
- Trigeminal neuralgia.
Thus, pathology can cover various structures - paranasal sinuses, lacrimal ducts, bones, soft tissues, nerve fibers. As a rule, it is necessary to ascertain the inflammatory process, but there are also mechanical damages.
When conducting diagnostics, it is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the overlying eye. Even simple fatigue after prolonged work at the computer can provoke heaviness in the surrounding area, not to mention impaired visual acuity (myopia) or increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma). The probability of each condition is considered so as not to miss the cause of pain.
Only a doctor can determine the source of the disorder. Having carried out a full diagnosis, he will indicate the origin of the pain under the eyes.
The cause of certain symptoms can be discussed based on the complete clinical picture. Painful sensations are a subjective sign, so they need maximum detail:
- Character (sharp or dull).
- Appearance (bursting, aching, shooting, pulsating).
- Intensity (strong, weak, moderate).
- Duration (short-term, long-term).
And when pain is described as occurring under the orbit, this does not mean that the pathology is localized there. After all, an impulse can come from neighboring areas along nerve fibers (irradiate). Factors that provoke pain are also taken into account, for example, tilting the head, touching, hitting, etc. All other symptoms are detailed in a similar way.
Acute sinusitis
The first thing you should think about if a patient has pain under the eye is acute sinusitis, in particular sinusitis. Inflammation of the maxillary sinus quite often manifests itself with a similar symptom. The pain can radiate to the temple or the entire half of the head, they acquire varying intensity (from a simple feeling of heaviness to moderately severe), intensifying when bending over or straining (exudate pressure increases). Local signs of sinusitis also include:
- Nasal congestion.
- Discharge (mucopurulent).
- Impaired sense of smell.
When palpating the infraorbital region, pain is determined. The soft tissues may be slightly swollen and reddened, but this symptom becomes most obvious with the development of complications of sinusitis - an abscess or phlegmon of the orbit. General symptoms of the inflammatory process in the maxillary sinus include fever (up to febrile levels), a disturbance in the general condition (malaise, loss of appetite, headaches).
Acute inflammation of the maxillary sinus is the main cause of pain in the infraorbital region in the practice of an ENT doctor.
Dacryocystitis
The nasal cavity is closely connected with the conjunctival sac through the lacrimal ducts. And they are also susceptible to inflammation. If the removal of tear fluid is impaired, it stagnates in the corresponding sac located at the inner wall of the orbit. This leads to the activation of microbes and provokes a disease called dacryocystitis.
Acute inflammation of the lacrimal sac is quite specific. Patients experience painful swelling and redness below the inner corner of the eye. They can spread to the bridge of the nose and cheek on the affected side. The eyelids are swollen, the palpebral fissure is narrowed. I am concerned about tugging pain in the corresponding area, which intensifies with palpation. The infectious process is accompanied by fever and intoxication.
Read also: Cheek hurts inside the mouth in the corner
After a few days, a softening forms at the site of the swelling, in the center of which a yellow clearing is visible. This indicates the development of an abscess that can break out or into the nasal cavity. In addition to this outcome, acute dacryocystitis in some cases becomes chronic. Prolonged inflammation is accompanied by lacrimation and discharge of pus from the inner corner of the eye. Other structures of the organ of vision (eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea) are often infected.
Traumatic injury
If pain under the eye begins to bother you, then you should find out if there was any injury (direct blow, fall). This symptom is the first to appear after mechanical damage. Then swelling increases, and a hematoma gradually forms. In case of extensive injuries, the eye may be damaged, in which hemorrhages are detected. If the bones of the facial skull are damaged, then the symptoms are more pronounced.
Osteomyelitis of the maxilla
A purulent process in the upper jaw can occur due to inflammation of the teeth and gums, otitis media, injuries, and gunshot wounds. Acute osteomyelitis begins suddenly - the temperature rises sharply with chills, appetite and sleep worsen, weakness and fatigue increase. If the cause is a tooth, then pain is felt in this area, which spreads to the ear, temple and eye socket. An unpleasant odor comes from the mouth, and the gum pockets fill with pus.
With osteomyelitis, the soft tissues of the zygomatic and infraorbital areas swell and turn red. Inflammatory infiltration becomes diffuse. The sensitivity of the upper lip decreases, mouth opening may be impaired, and facial contours are distorted. A purulent process from the bone can move to the maxillary sinus (sinusitis), break into soft tissues (abscess and phlegmon), and become a source of lymphadenitis and thrombophlebitis.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Damage to the middle branch of the trigeminal nerve is also accompanied by pain under the eye. In this case, it is paroxysmal (in the form of an attack), piercing and shooting. A characteristic sign will be the presence of “trigger” zones, the impact of which provokes pain. This is exactly what happens when brushing your teeth or pressing on the infraorbital area. The pain impulse spreads to neighboring and distant areas. And although the attack is usually short-lived, it has an extremely negative impact on the general condition of the patients, disrupting their usual lifestyle and reducing their ability to work.
An attack of pain with neuralgia of the middle branch of the trigeminal nerve covers not only the infraorbital region, but often spreads to the entire half of the head.
Preventive measures
People familiar with headaches know that this condition can make life unbearable. To minimize the likelihood of seizures, you must adhere to the tips below.
Prevention of headaches includes the following measures:
- walks in the open air;
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper nutrition;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- moderate physical activity;
- healthy sleep of at least 7 hours;
- blood pressure control;
- increasing immunity;
- correct posture;
- regular preventative visits to the doctor.
Doctors' forecasts
Most unilateral headaches that are not complicated by severe illness are easily controlled with painkillers and lifestyle changes.
If the pain regularly recurs, intensifies, or changes in character, it is important to consult a doctor to select the optimal treatment regimen.
In cases of serious illnesses, the prognosis is strictly individual and depends on the severity of the disease, the body’s defenses and the correct treatment.
Why does the left or right side of the face hurt?
Why does my face start to hurt? The causes of pain can be different, ranging from an incorrectly formed bite to skin diseases. You can determine exactly why the left side of your face or the right side hurts, or whether there are pockets of pain in the nose area, by consulting a doctor and accurately describing your sensations.
Simultaneous pain in the head and face
When a patient complains that he has a headache in the temporal part and on the face, then in many situations this is associated with migraine.
This diagnosis has a specific feature. A person claims that a certain part of his face hurts.
Symptoms are observed only on one side of the head and rarely spread to the other.
Such discomfort can be described as strong, with a boring manifestation.
It is not able to continue for 1-2 days. Migraines are more common among females in the age range of 20-30 years.
In the future, the symptoms become weaker. In a situation where the right or left half of the face hurts, the main provoking factor will be an emerging cluster headache.
Situations are noted when the patient complains of difficulties with the eyes, at a time when painful discomfort simply radiates to the nerves of the visual organs.
Often males who have bad habits (excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages and constant smoking) come to a specialist with similar symptoms.
The doctor quickly identifies the signs by the mucous membrane of the eye, which is very watery and red.
If the patient complains of pain on the left or right side of the face (notes redness, burning sensation, headache), then this may indicate a hypertensive crisis.
In addition, there are sudden changes in pressure, nausea is felt, a gag reflex occurs, ringing in the ears occurs, the temples begin to pulsate and the heart hurts.
Why does my face hurt?
Pain in the face (prosopalgia) is the occurrence of unpleasant sensations in the facial part of the head. There are several pathologies that indirectly provoke the occurrence of such discomfort:
- Inflammation of the carotid arteries.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Depressive states, neuroses.
In addition, there are a number of diseases in which one or both sides of the face hurt.
Neuralgia is a disease whose main symptom is pain. Considering that there are many nerve nodes in the facial muscles that can become inflamed as a result of infection or hypothermia, or pinched, pain syndrome is divided into several types:
- Neuralgia of the mandibular nerve. It is characterized by burning pain in the cheekbone, temple, and parotid region. Usually the patient has pain on one side of the face, which swells and turns red.
- Neuralgia of the nasociliary ganglion. The pain is localized in the area of the eyebrow, near the inner corner of the eye. The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, discomfort usually appears at night. Periodically there are lumbagoes in half of the nose. The mucous membrane in the nasal cavity noticeably reddens, and a rash similar to herpes appears on the skin.
- Neuralgia of the pterygopalatine ganglion. Accompanied by swelling and redness of one half of the face. The patient's taste is impaired, salivation increases, and lacrimation from one eye. Pain sensations are localized near the eye, root of the nose, or rather the jaw.
- Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. If the nerve node on the left is affected, the left side of the face hurts. At the same time, attacks of intense pain appear under the tongue, in the tonsils, throat, and palate. A burning pain in the lower corner of the jaw, near the ear, on one side of the neck may appear at night, during sleep. An aggravation of unpleasant sensations occurs when chewing, swallowing, or eating too hot or cold food.
Neuralgia can be triggered by a previous cold, flu, sore throat, or Zoster virus. Sometimes the cause of damage to nerve endings is untreated sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, and sinusitis.
Facial migraine is often accompanied by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the pain syndrome causes a disturbance in the patient’s emotional state: apathy, overexcitation, aggressiveness, and a hysterical state appear. During an attack, a person’s face and head hurt, and there are painful shootings in the lower jaw, half of the neck, and under the eye.
The patient has swelling in the area of the carotid artery, half of the neck turns red, and the skin of the face and neck is painful to touch.
Skin diseases
Skin lesions can cause facial pain. Rash and dermatitis dry out the skin, while the upper layer of the epidermis cracks, the patient experiences a feeling of tightness of the facial skin, itching and burning in the area of the rash. Discomfort also provokes:
- Contact with an allergen. A person develops Quincke's edema, the skin of the face swells, begins to ache and itch, and the eyes become watery and red.
- The appearance of deep pimples and boils on the face. At the same time, the skin on the face hurts, point inflammation and redness appear. The purulent contents of acne cannot be removed at home; it is better to go to a beauty salon.
- Degeneration of a mole. Normally, moles do not hurt or itch. If a mole changes color, begins to grow, stand out, become structural, hurt or itch, you should consult a dermatologist.
If necessary, if there is a suspicion of the development of cancer, the doctor will refer the patient for analysis: a scraping will be made from the person’s face and the material will be examined to ensure that the tumor is benign.
Dental problems
As a result of dental disease, pain of odontogenic nature occurs. Discomfort depends on where the diseased tooth is located. If your face hurts on the left side, then the affected tooth is located there. Unpleasant sensations occur when:
- Caries that has deeply affected the tooth.
- Pulpitis – when the soft tissues of the tooth are damaged.
- Periodontitis is a long-term inflammatory process near the root of the tooth.
- Abscess - when the inflamed cavity near the root of the tooth is filled with purulent contents.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
The pain in the face can be twitching and sharp. During the inflammatory process, a person's temperature rises. Cold, hot food, sweet liquids that come into contact with a sore tooth aggravate the discomfort.
The reason that the patient's face hurts may be unsuccessful tooth extraction. Painful sensations appear if the trigeminal nerve was affected during removal, the dental canal was poorly processed, the tooth root was not completely removed, or tooth fragments or parts of dental instruments remained in the socket.
ENT diseases
If a person has pain on the right side of his face, this may indicate the development of inflammation in the ear or nasopharynx. Diseases that provoke pain syndrome include:
- Sinusitis. The nose, cheeks, and cheekbones hurt if the runny nose continues for a long period of time. Swelling of the nose occurs, accumulation of pus in the paranasal sinuses.
- Frontit. Unpleasant sensations cover the forehead and nose. The pain has a pulsating, bursting character.
- Sinusitis. The pain is localized above the eyebrows and intensifies when the person tilts his head forward.
- Otitis. The inflammatory process with the accumulation of purulent contents provokes painful shootings under the lower jaw, in the cheekbone.
Pain can be caused by herpes that occurs on the nasal mucosa or facial skin. In this case, the pain is acute, the temperature may rise, the face “aches,” aches, and burns.
Does a person have pain on the right side of their face? Perhaps the cause is injury. Unpleasant sensations can occur not only immediately after the face has been injured, but also after some time. Pain occurs when:
- Fracture of the nose, jaw, and other facial bones.
- Fracture of the base of the skull.
- Bruise of the soft tissues of the face: nose, cheek, forehead.
- Cutting of eyebrows, lips, chin.
In addition, facial pain may be atypical when the exact cause of the discomfort has not been established. It can appear regularly and have an aching, pulsating character. Some patients report that their face feels like it is burning, drilling, or stabbing. Painful sensations affect not only the skin of the face, but also the neck area and scalp. The pain is not symmetrical and usually appears on only one side of the face.
Cheekbones on the face hurt: causes, types of pain, treatment
Doctors divide the reasons why cheekbones hurt into the following groups:
- Inflammation of the jaw joint, the damage of which manifests itself as pain near the ear. In this case, there is aching sensations, crunching when opening the mouth or when chewing. Their symptoms resemble otitis media and these diseases often accompany each other. The pain varies in intensity from weak and aching to sharp.
- Various dental problems, such as caries, gum inflammation, periodontitis, pulpitis, osteomyelitis, etc. They usually manifest themselves as throbbing, severe pain, which intensifies when chewing solid food or applying pressure. If the patient has osteomyelitis, then this is also accompanied by swelling on the face, fever and particularly intense pain.
- Neurological diseases such as damage to the ear or laryngeal nerve ganglion or facial nerves cause quite noticeable pain when pressed, clicks or noises in the ears, and also increase salivation. Sometimes the jaw even goes numb.
- Migraine is a very common cause.
- Disease of the facial artery - then the pain spreads not only to the cheekbones, but also further along its location - closer to the eyes, near the nose and in the area of the upper lip. This is a very dangerous disease, as without treatment it leads to cerebral hemorrhage.
- Various pathologies of the nasopharynx and throat - these include sinusitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, diseases of the parotid salivary glands or lymph nodes.
- Dislocations and injuries of the maxillary joint, which can occur from mechanical damage to the jaw or too much yawning. In this case, there is a displacement of the chin, a violation of the oval of the face and problems with diction. The pain in this case is aching, not very strong, and the patient knows at what point the problems began.
- Arthritis that affects the upper jaw joint. Especially if left untreated, it will lead to various serious pathologies and irreversible consequences.
- Neoplasms, benign and malignant – osteoid osteoma, osteoblastoclastoma, sarcoma. Each of them manifests itself differently, the pain can be intense immediately or gradually increasing, or even there are no symptoms at all for a long period.
What actions should be taken during an attack?
In this material we looked at why cheekbones hurt, it’s time to talk about specific actions. Before the attending physician takes care of the patient, the following must be done:
- take local antispasmodics, this will relieve the pain at least temporarily;
- provide the jaw with a state of rest, that is, do not eat, do not chew, it is advisable to talk as little as possible;
- the above point does not mean that you should not eat it at all; it is better to use soft food or in the form of purees;
- when the cause of pain is dental abnormalities, rinses like chamomile decoction help greatly;
- If pain occurs due to a dislocated jaw, you can try to straighten it, but it would be safer to entrust this matter to doctors.
You need to understand that self-medication can lead to the development of complications, therefore, after providing first aid, you should show the patient to specialists, they will take further action.
Cheekbones on the face hurt
In the section Diseases, Medicines, the question why do my cheekbones hurt? the hospitable best answer given by the author Points in the area of the temporo-inferior zygomatic joint signal painful sensations when antiviral immunity decreases..
A signal of the presence of a virus in the body and weakened antiviral immunity is a common headache, or pain in the head, which is detected by tapping the head with fists with moderate force or using a half-liter plastic bottle filled with water without air bubbles.
Now let’s look at a way to strengthen antiviral immunity: 1) Find all the painful areas on the head and begin to massage them. Typically, pain accumulates in the area of the occipital protuberances, there are painful temples, the area of the temporomandibular joint, this is the joint in front of the ear canal, the inner upper corner of the orbit, and the forehead area.
Many people note the occurrence of a headache together with pain in the eye, in the eyes, so you need to use the nail of your index finger to influence the pain of the eye through the eyelid. Many will probably find their own special pain points.
All painful points must be massaged day after day until the pain from pressure completely disappears; for this you will need at most two weeks, and perhaps you will have your own time frame. It all depends on your diligence and the degree of neglect of the body.
2) The next technique for strengthening antiviral immunity is tapping the head with fists or a plastic (preferably SPRITE) half-liter bottle of water, day after day, until the pain in the head completely disappears. The number of procedures per day can be increased to ten; the duration of the tapping procedure is different and individual.
To begin with, you can tap for 3-5 minutes with little force. As the pain in the head decreases, the intensity of the effect increases. 3) You can strengthen antiviral immunity if you also use a sneeze.
Spontaneous sneezing during a viral infection is precisely a pure self-healing reflex to the introduction of the virus into the body during a cold. But, when we comprehend this, we can, by consciously irritating the nasal mucosa to the point of sneezing, thereby contribute to strengthening antiviral immunity and getting rid of headaches.
It is advisable to do this during periods of influenza virus epidemic in order to prevent ARVI. The number of sneezes can be increased from 10 to 20 times a day. When sneezing, it is advisable to direct the air flow through the nose. It is convenient to irritate the nasal mucosa with ear sticks or instill 4-5 drops of fresh aloe or Kalanchoe juice into the nose 3-4 times a day; the juices of these plants irritate the nasal mucosa and cause repeated sneezing (up to twenty sneezes per instillation). Some may experience nasal irritation from pepper or snuff. Source: Doctor, more than 25 years of successful massage practice. Source: 22oa.ru