Symptoms
Signs that you need specialist help include:
- painful and unpleasant sensations when touching the gums or teeth below;
- lump on the gum;
- painful to swallow or open your mouth;
- pain radiates to the throat or ear
- elevated temperature.
If you notice these signs, you need to call and make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. If you need to wait a long time, for example, a day or more, you can take a painkiller, but in no case just before the visit, as this reduces the effect of anesthesia and even nullifies it.
If your gums hurt
When your gums hurt, what should you do in this situation? If you have pain in your teeth and jaws, you should not self-medicate. Whatever the cause of the pain, it must be diagnosed and treated by a dentist.
Elimination of pain consists of sanitizing carious teeth, removing dental plaque, and careful oral hygiene.
In extreme cases, surgical treatment may be necessary. This condition should be treated with anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, and antibiotics. In any case, you need to find out and eliminate the cause of pain in the gums, and this should be done by a dentist.
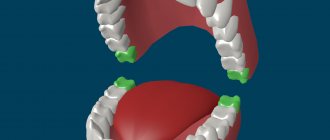
Wisdom tooth eruption
If the gums at the end of the lower or upper jaw are swollen, it is very often associated with a wisdom tooth. Acquaintance with “eights” occurs in the period from eighteen to thirty years. The problem is that they always erupt with a lot of trouble, because a person’s bones are already fully formed by this time.
The space allotted to it is often not enough for a tooth; sometimes it tends to squeeze out the neighboring teeth. They become curved and grow inside the gums, making it not only painful for the owner to swallow, but even to open his mouth or exhale sharply. At the same time, the temperature often rises, soreness of the gums radiates to the head or ear. But this is not the only problem for the G8s. Very often they begin to collapse as soon as they are born, and sometimes even inside the gums.
That is why the problem cannot be dealt with without the help of a dentist, and sometimes a dental surgeon. The doctor will examine the oral cavity, prescribe an x-ray examination, and if the tooth is simply being cut, without “surprises,” then the patient will have enough painkillers. But in the case of impacted (grown inward) “eight” or signs of destruction, the teeth are removed under local, less often general, anesthesia. There is no need to be afraid of this; modern anesthetics guarantee a complete absence of pain and discomfort.
Important: modern dentistry does not involve treating wisdom teeth; if pathologies are detected, they are immediately removed. You can find out more detailed information about wisdom teeth in the article “Everything about the wisdom tooth removal procedure.”
The gums at the end of the lower jaw hurt during pregnancy
Pain in the gums at the end of the lower jaw during pregnancy is not uncommon. The reason for this is most likely a hormonal imbalance in the body, a weakened immune system and a lack of vitamins .
Even with constant gum care, a pregnant girl can develop gingivitis and periodontitis. During the course of these diseases in a pregnant woman, therapy will be reduced to traditional medicine, since not all drugs can be taken by pregnant women. The gynecologist must create the correct diet for a woman preparing to become a mother, which will include fruits, vegetables, dairy products, fish and lean meat.
Herbal infusions of chamomile, sage, and linden, which should be used to rinse your mouth, will help alleviate the condition of sore gums at home. Also, you should be careful when treating your teeth on your own while breastfeeding. Only a dentist can help you find the optimal treatment path.
If the cause of gum pain is microbes, then pain relief alone will not be enough. It is necessary to treat the gums with antiseptic agents and clean the enamel from tartar and plaque .
If the gums near a tooth covered with a crown are swollen, this means that the crown was placed poorly or has shifted and caries is developing near the tooth. To get rid of the disease, you should go to the dentist as soon as possible.
Gingivitis
The term “gingivitis” refers to the inflammatory process of the gums. It is characterized by swelling of the gums, erosion, small wounds, and often bad breath.
The main cause is plaque and tartar. It is also provoked by long-term use of hormonal contraceptives.
To treat gingivitis, antibacterial pastes and rinses are prescribed. If no action is taken, it can spread further and develop into periodontitis, in which the necks of the teeth are exposed, the teeth become loose and quickly fall out.
Cause of gum pain at the end of the jaw
The gums hurt and swell at the end of the upper and lower jaw for various reasons:
- with the eruption of a wisdom tooth and its abnormal growth;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- periodontitis;
- caries and pulpitis;
- tooth cyst.
To know why your gums hurt, you need to make an appointment with a doctor, he will examine the lower and upper jaws and prescribe treatment.
Wisdom tooth eruption
This condition is accompanied by itching at the site of tooth eruption, swelling and redness of the gums in the back of the jaw, and pressing pain. Body temperature rises to 37.5–40 degrees. Appetite decreases and insomnia begins. The lymph nodes in the neck area become enlarged, and in rare cases their size interferes with head movement. My head hurts and my cheek sometimes swells.
Incorrect growth of wisdom teeth
In such a situation, the symptoms of teething are more pronounced. This condition is called dystopia.
The tooth erupts towards the cheek and tongue. My gums hurt a lot. The pain can radiate to the ear, temple, end of the upper or lower jaw. The gums are inflamed and food is difficult to chew. This provokes complications. Pus accumulates at the site of eruption, blood and bad breath appear. Swelling of the face occurs, the temperature rises, and the pain is stabbing in nature.
Complications occur when a tooth fails to erupt, a condition called retention.
Caries and pulpitis
Caries is tooth decay. It damages its walls, and holes form. Pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental nerve.
With pulpitis, the pain is pulsating and intermittent. The gums become inflamed and red, and the jaw hurts. The attack of pain lasts 5–10 minutes, then stops.
With caries, sensitivity to cold and hot foods appears. To eliminate the pain, you need to be examined by a doctor who will order an X-ray and conduct treatment. When the nerve becomes inflamed, the gums become swollen and red.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. If left untreated, gingivitis will lead to complications. It most often occurs in adolescents and during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Occurs for the following reasons:
- injury or burn;
- taking medications;
- disease of the salivary glands;
- infection;
- incorrectly applied filling.
The disease is accompanied by redness, pain and inflammation of the gums in the back of the jaw, and the mucous membrane of the mouth swells. Bleeding appears. In advanced forms, necrotic ulcers appear on the gums, body temperature rises, and lymph nodes enlarge.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is inflammation of the area around the tooth. Accompanied by redness, swelling and pain in the gums and jaws, plaque appears on the crowns, discharge of pus, bad breath, loosening of teeth, and rarely tooth loss. Periodontitis occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- decreased immunity;
- leukemia;
- intestinal diseases;
- increased tone of the masticatory muscles;
- incorrect position of teeth;
- penetration of infection;
- oral trauma.
Periodonitis
The disease is acute and chronic. There is an increase in body temperature, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, pain when chewing, swelling and redness of the gums at the end of the jaw. The pain radiates to the ears, adjacent crowns, and jaw. Pus is released and the gums bleed. It has the following causes:
- advanced caries complicated by pulpitis;
- improper filling and poor treatment of caries;
- malocclusion;
- jaw injuries;
- arsenic poisoning;
- smoking.
Sore gums after dental treatment
After dental treatment, the manifestation of pain is considered normal, since the nerve endings are affected. This pain lasts no more than 3 days after treatment. If it persists, then the procedure was carried out incorrectly.
Problems arise when the filling placed is too high for the bite. It only appears when biting. This problem can be easily solved, the dentist will correct the filling and everything will return to normal.
It happens that some of the fragments of dental material remain in the dental canal. This problem is more difficult to identify. Swelling of the gums, redness, inflammation and severe pain occurs. The filling should fill the entire space of the resulting hole. If the space is left unfilled, bacteria begin to develop in it, which causes inflammation and pain in the back of the jaw.
After tooth extraction, if treatment is improper or food debris gets into the wound, inflammation occurs. It must be eliminated so that complications do not develop.
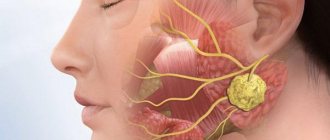
Periostitis
Periostitis is an inflammatory process of the periosteum of the tooth. Accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and redness of the gums. The pain is aching and throbbing in nature and can radiate to the temples, ears, and eyes. Weakness and intoxication of the body appears. The cervical lymph nodes become enlarged, swallowing food becomes difficult, and an abscess forms on the gum. It has two forms of flow: acute and chronic. Occurs as a result:
- untreated periodontitis;
- deep caries;
- jaw injuries;
- broken crown;
- non-compliance with oral hygiene rules.
Develops as a concomitant disease with:
- diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2;
- actinomycosis;
- tuberculosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- constant stress.
Tooth cyst
A cyst is a formation filled with fluid and has dense walls. Located in the gum of the upper or lower jaw, around the root of the tooth.
If measures are not taken to eliminate the cyst, the affected crown will fall out. The disease is accompanied by tissue growth in the back of the jaw, discomfort when chewing food, swelling, redness and aching pain.
Occurs for the following reasons:
- oral trauma;
- chewing nuts or other hard objects with teeth;
- incorrect filling;
- penetration of infection;
- after sinusitis or other infectious diseases.
Periodontitis
An increase in the periodontal pocket and the inflammatory process of the tissues surrounding the tooth are leading among all periodontal diseases. When the disease occurs, the fixing tissues lose their ability to hold the tooth; they weaken, exposing the necks of the teeth, which then become loose and fall out. If the disease is ignored, it leads to periodontal disease, which requires much more complex treatment.
The following signs are characteristic of periodontitis:
- itchy gums;
- increase in pockets;
- pain when pressing on a tooth or gum;
- unpleasant or painful chewing;
- bloody or purulent discharge from under the gums (more advanced stages).
Periodontitis can be treated quite easily on its own - antibacterial ointments and rinses are prescribed. With systematic adherence to the rules of oral hygiene, it goes away quickly. The problem is that this scourge never develops on its own, as they say, out of nowhere. It is usually provoked by a number of factors:
- plaque;
- tartar;
- dental problems, including orthodontic ones.
By removing plaque and tartar, regularly undergoing professional dental hygiene procedures, sanitation of the oral cavity and correcting the bite, the disease is completely cured. In general, the prognosis is favorable, but if the disease is neglected, it develops into periodontal disease and leads to tooth loss.
How is the treatment carried out?
You should immediately contact a specialist if your gums and teeth hurt. A qualified dentist knows what to do. After making an accurate diagnosis, the specialist will be able to prescribe effective treatment. If the disease is not advanced, you can manage with medications. The specialist cleans the tartar and also prescribes medications that will help relieve inflammation. Propolis and chamomile have a good effect on the gums. There are many herbal rinses available at the pharmacy.
Physiotherapeutic methods can also be used to treat gums. Removing inflammation with laser is popular today. Electrophoresis and massage also have a good effect. The specialist will show you how to properly massage your gums to strengthen them. Just a week of treatment will relieve pain and bleeding if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Periodontitis
The fear of drills has been preserved among many citizens from Soviet times to the present day, when no one is afraid of dentists for a long time. However, caries, if left untreated, develops into pulpitis, and then into periodontitis - a disease in which the inflammatory process from the pulp passes to the root of the tooth. The gums swell, hurt, gumboil appears, sometimes a fistula appears, pus comes out, the swelling subsides and it seems that the danger has passed. It's not like that at all. Yes, in this case the pain often goes away, because tissue necrosis is noted along with the nerve endings, but in the end the matter can end in tooth loss.
After making a diagnosis, the dentist prepares the affected tooth cavity, then cleans the periodontium, after which a filling or stump inlay is installed, and then a crown.
Prevention of pain
In order not to encounter such unpleasant symptoms, you need to follow a few simple and clear rules:
- Take good care of your oral hygiene. You need to brush your teeth 2 times a day, but it is better to rinse them after each meal. This will help reduce the risk of developing tooth decay.
- Consume enough vitamins and microelements, especially calcium, because it is a building material for teeth.
- Treat your teeth in a timely manner and prevent complications from developing.
- Visit your dentist twice a year, even if you think everything is fine and all your teeth are healthy. A timely examination with the help of special instruments will help to identify caries at the earliest stage and quickly treat it without waiting for complications.
Inflammation of the periosteum
This disease is most often referred to as “puffed cheek.” The gums swell, then the lip, then the swelling spreads to the neck and even eyelids. However, the wind has nothing to do with it, although it, coupled with cold, can act as a provocateur of inflammation. Periostitis, which is the scientific name for inflammation of the periosteum, occurs as a result of pathogenic bacteria that enter the alveolar process from untreated teeth, as well as from injured areas. Sometimes the cause of periostitis is poor quality work of the prosthetist dentist or general systemic diseases.
If the gums at the end of the upper jaw hurt (no matter whether it has swollen or not), you should also not delay a visit to the dentist. Perhaps these are the first signs of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. What to do? The worst thing that can be recommended is to warm the swelling with a compress or hot rinses. Rotting of tooth tissue cannot be cured with baths or heat. This will only aggravate the inflammatory process, and then the problem will have to be solved in the department of maxillofacial surgery.
For treatment, the doctor either sanitizes or removes the tooth, applies medicine, then (usually after a few days) cleans the canals and installs a permanent filling or crown.
Pain after treatment
Often discomfort between teeth occurs after treatment. This may indicate poor-quality filling and the development of infection inside the canal. In this case, you need to take an x-ray, with which you can immediately detect the pathology.
Important! Trauma to the gums can occur due to an “overhanging” filling that comes into contact with the gingival papilla.
You can detect a filling defect by using dental floss that gets stuck or breaks. Treatment requires correction of the filling or its replacement. Microtrauma from a filling or crown can cause discomfort in the first days after dental treatment. The pain goes away on its own after a few days.
Video - Gums hurt: what to do?
How to escape from pain?
While the time passes before your visit to the dentist, you can take a pain reliever. However, you should not get too carried away with them, as this causes an overdose or can significantly reduce the effectiveness of the anesthetic from the doctor.
To relieve pain, Ibuprofen, Ketonal, Ketorol, Nurofen, Analgin, Solpadein, Paracetamol are used.
Traditional methods
They can be used as a preventive measure, but not as an alternative method of treating gums. They can only provide temporary partial improvement.
Traditional methods include rinsing:
- soda;
- chamomile decoction;
- sage infusion
Sometimes the affected gums are rubbed with garlic or a chewed apple is applied to them. Such remedies will not cause harm, but it is better not to expect any benefit from them. The only effective treatment can be prescribed only by a dentist.
What to do if there is pain and swelling of the gums in the area of the last tooth?
Traditional treatment
Treatment is prescribed according to the cause of discomfort. If the disease is not in an advanced stage, you can get by with medications that relieve inflammation and cleaning tartar.
When discomfort is caused by the appearance of a third molar, there is no need to panic. If the wisdom tooth grows normally, then you can relieve the unpleasant symptoms:
- rinse your mouth with Chlorhexedine and Miramistin;
- apply pain-relieving gels Cholisal and Kamistad to the gums;
- contact a dental surgeon to make an incision in the gum (if a hematoma forms to ensure blood outflow).
In case of severe discomfort, you need to take a painkiller. To reduce pain use:
- Adolor tablets - the effect occurs after 20 minutes and lasts 4-5 hours;
- drugs Ketanov, Ketorol, Nise, Nurofen - act from 1-2 to 4-5 hours.
It is worth remembering that medications temporarily eliminate the unpleasant symptom. At the first opportunity, you should seek help from a specialist. Taking medications in excess of a dose can cause poisoning.
Physiotherapeutic methods are very helpful in treating gums for any disease: laser, electrophoresis, massage. Such methods of therapy relieve inflammation, relieve pain and bleeding.
Sometimes you can’t do without contacting a surgeon:
- Flux is a condition that requires urgent treatment (we recommend reading: how to remove a tumor and treat gumboil at home?). The doctor releases the fluid that has accumulated in the gum by making an incision in it. The outflow of pus and ichor is ensured by the installed rubber drainage. Therapy is accompanied by taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexedine or another antiseptic.
- Treatment of periodontitis involves removing tartar and plaque, after which a specialist will reduce the gum pockets.
- "Eight" is subject to removal according to indications. These include the inclined condition of the tooth, the presence of carious cavities, purulent inflammation, and cysts. Also, the bone unit is pulled out if it provokes the development of sinusitis.
Folk remedies
If it is not possible to see a specialist in the next couple of days, then the pain can be eliminated with home remedies:
- apply an ice cube to the affected area for 10 minutes;
- rinse your mouth every 2 hours with a solution of salt and soda (1 tsp per glass of water);
- chew a piece of propolis.
Rinsing with herbal decoctions copes well with inflammation and discomfort:
- 2 tbsp. sage, pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for an hour. Rinse as often as possible, after eating - be sure.
- 6 tbsp. oak bark, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, leave for 10 minutes over low heat. Irrigate the mouth several times a day. The product has a bactericidal effect, reduces inflammation and swelling.
- Add 2 tbsp to a glass of boiling water. chamomile, leave for 30 minutes. Rinse your mouth 5-6 times a day.
It is worth remembering that pain is often associated with infectious diseases, which can lead to serious consequences. It is almost impossible to completely get rid of discomfort and inflammation with topical agents.
Main reasons
There are many reasons that can cause gum discomfort. Some of them are harmless, and when the unfavorable factor is eliminated, the unpleasant symptom goes away on its own. If the pain is caused by diseases of the oral mucosa or teeth, treatment is required.
The following may cause temporary discomfort:
- Using a low-quality or hard brush.
- Traumatization of the gums by solid food.
- Taking certain medications.
If, after changing the brush to a softer one, your gums still continue to hurt, and trauma and medication are excluded, you can suspect one of the diseases of the oral cavity. In such cases, it is necessary to urgently visit the dentist.
Signs and consequences of tartar
The main causes of pain:
- Plaque. It contains a large number of pathogenic bacteria that cause inflammation and pain.
- Improper cleaning. “Plaques” are formed on the enamel, which are colonies of bacteria.
- External damaging factors. Various microtraumas can cause pathogenic microorganisms to penetrate into periodontal tissue, causing inflammation.
- Some diseases. Failure of the digestive and endocrine systems, as well as blood diseases, often cause pain in the gums.
If the pain spreads in the area of several teeth, then the cause most often lies in caries or an inflammatory process. In this case, it is important not only to relieve the unpleasant symptom, but also to cure the disease that caused it.
How to brush your teeth correctly