Quite often, people pay increased attention to their dental health - they regularly visit the dentist, buy special toothpastes, use special dental floss, forgetting about their gums. But it happens that at one moment, even with light pressure on the gum, a sharp pain is suddenly felt. Why is this happening? Painful sensations are not always the result of poor dental and oral care; gums also have their own, quite serious diseases.
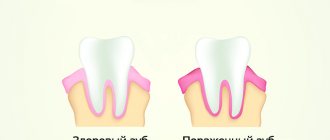
Gum hurts when pressed
Causes of gum pain
Dentists note several causes of tissue pain:
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Poor quality treatment.
All diseases, if left untreated, lead to inflammation and organ loss.
Gingivitis occurs due to poor oral care. The edge of the gum becomes inflamed, swollen and bleeds. The fabric turns pale pink.
Periodontitis appears due to untimely treatment of gingivitis; this is the second stage of the process. The necks become exposed, become mobile, and the tissue festers. If treatment is not started, the organs will fall out and inflammation will spread to the entire oral cavity. The cause of these diseases is poor oral hygiene. Plaque, which is usually removed by brushing, hardens. Microbes found in plaque provoke inflammation. When pressed, the tooth becomes painful and loose.
Periodontitis occurs when an abscess appears near the root tissue. This disease appears due to untreated caries. When pressure is applied to the tooth, the root moves, affecting the abscess and causing pain.
Poor quality treatment. If the root canal is not completely filled, free space remains. Pathogenic bacteria multiply in it, causing pain when pressed. For this reason, an abscess appears on the root. There is another reason for tissue pain, uneven application of the filling to the edges of the tooth. When hardened, the filling injures the adjacent gums, causing pain.
What to do if your gums hurt when pressed?
Only a doctor can localize the disease after determining the causes. Pain when pressing on the gums can occur near one tooth if periodontitis is detected and the root membrane of the tooth is inflamed.
Sometimes an injury causes the gums to hurt when pressure is applied, for example, when biting hard on hard food. The cause may also be a crown or pregingival caries. All this can lead to decay and inflammation.
These diseases cannot be treated on their own, nor are they shelved. The doctor prescribes not only medications, gels and ointments, but also prescribes some procedures that are performed only in dental clinics. Sometimes treatment consists of several courses and takes a long time.
If treatment is not started in time, if the gums hurt when pressed, then over time it will soften, the tooth will become loose and fall out. Moreover, this process can affect one tooth, or a certain part, capturing several teeth. Only an experienced dentist can prevent such a phenomenon. He will also suggest some folk procedures to relieve inflammation of the gums themselves.
How to get rid of pain?
The first thing you need to do when inflammation appears is to contact your dentist for help. He will determine the cause of the disease and, if necessary, carry out the necessary manipulations. Before visiting the dentist, you can relieve pain using available means:
- First you need to thoroughly clean the cavity using toothpaste. If the pain does not subside, you can use auxiliary medications.
- Take a pain reliever. It will not cure gums, but will only temporarily relieve pain, so when it subsides, you should not neglect a trip to the dental clinic.
See also
What is better to choose for the treatment of the throat, “Strepsils” or “Septolete” and comparison of drugsRead
- Rinse your mouth. The cheapest means for cleaning the oral cavity are solutions of soda or salt. To prepare, you need to add a teaspoon of soda or salt to boiled warm water (200 grams or a glass of water) and mix thoroughly. Rinse your mouth every two to three hours for five minutes.
- You can rinse your mouth with herbal infusions - chamomile is best, it has an antibacterial effect, or vodka. Alcohol perfectly disinfects the oral cavity.
- Place a few drops of clove oil on the sore spot. You can find out where it hurts by pressing on your upper lip.
If there is inflammation or suspected purulent periodontitis, it is forbidden to heat the localized area. Bacteria spread faster when heated, causing inflammation in neighboring areas. In this way, the oral cavity is effectively disinfected and the sensations fade away.
What to do when the roots of your teeth hurt
Toothache is considered one of the most severe - it literally pierces through, leaving no chance for a normal life.
But even despite such an acute symptom, some persistently postpone a visit to the dentist, drowning out the unpleasant sensations with pharmaceutical painkillers or, even worse, with the thoughtless use of traditional medicine.
Meanwhile, the pathological process penetrates deeper into the dental tissues, spreads to the nerve and roots, leading to even more serious and sometimes irreversible complications. Today we’ll talk not just about toothache, which usually appears with caries, but about what causes tooth root pain and what to do about it.
Possible causes of pain
So, what can it mean if the root of the tooth hurts when you press on the gums or even without external mechanical irritants? In fact, there are quite a few potential causes, and among them there are both minor ones that are easy to fix and complex ones that require serious treatment.
Pulp ischemia
The pathology is associated with a lack of oxygen in the tissues that nourish the pulp, and this can also cause pain.
The disease usually develops against the background of problems with blood vessels, injuries, infections in the body, disturbances in the endocrine system, oncological processes, contamination with toxins, and disruptions in the nervous system.
Sometimes ischemia is a consequence of diseases of the hematopoietic organs or digestive system. And in this case, it usually becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations.
Pulpitis - inflammation of the nerve
Most often, the disease becomes a consequence of untreated caries, when pathological processes penetrate deeper into the tooth structure and lead to inflammation of the neurovascular bundle. The pain becomes almost unbearable.
In such a situation, it is better to act quickly so that the inflammation does not spread to the periodontal tissues and lead to the development of periodontal disease.
In the early stages, drug therapy may be effective, but more often it is necessary to completely remove the nerve and fill the canals.
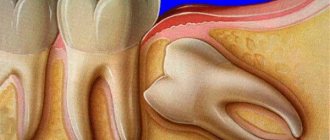
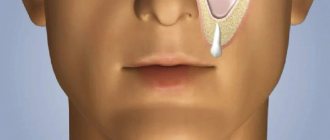
Neoplasm in the form of granuloma
A pathological nodule in the thickness of the gum tissue is formed near the tooth root and most often becomes purulent in nature. The reason for this may be trauma, infection in the tooth or soft tissues, abnormal growth of the wisdom tooth, or medical errors made during endodontic treatment.
Granuloma does not make itself felt immediately. It is better if it can be identified on an x-ray before the surrounding tissues become inflamed and the gradual filling of the cavity with purulent exudate does not lead to severe throbbing pain.
Then the mucous membrane in the area of the causative tooth turns red and swells, the patient’s cheek swells, the temperature rises - the granuloma develops into a cyst.
Extensive cyst
A larger neoplasm in the thickness of the gums, the focus of which is usually localized at the very root and often represents an untreated granuloma. The neoplasm can lead to severe swelling of the mucous membrane and facial asymmetry.
If the gum is swollen and there is a painful lump filled with pus on it, you need to urgently run to the doctor.
Sometimes the removal of such neoplasms must be performed together with excision of part of the root system in order to completely eliminate the pathological focus - resection of the root apex is performed.
Exposed necks of teeth – gum recession
Gum recession is not an independent disease, but only a pathological condition.
If the root of a tooth is exposed, this can be a symptom of a variety of conditions: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, malocclusion, poor hygiene, trauma or excessive subgingival calculus.
In such a situation, the root under the artificial crown may also hurt, and canal treatment and re-prosthetics will be required. If the pathology has become generalized, discomfort may spread to the entire upper or lower jaw.
The symptom itself requires differential diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment. Thus, periodontitis and periodontal disease as its complication are diseases that cannot be cured completely. However, it is always possible to achieve stable remission, and here only comprehensive treatment will be effective, taking into account the stage and individual characteristics of the clinical picture.
Tooth root injury
If pain appears after a blow or bruise, you need to see a specialist as soon as possible. When the cause is a mechanical injury, an accurate prognosis can only be given based on the results of an X-ray examination. Until the doctor examines the broken tooth and sends it for an x-ray, it is better to try not to make sudden movements of the head and jaws.
Associated symptoms
Toothache itself is very severe - this is always a good reason to see a doctor as soon as possible. But usually this is not the only symptom, and with inflammation of the internal structures of the tooth, the general clinical picture has similar features: the pain intensifies with mechanical action, and becomes pulsating in nature if purulent processes occur.
The surrounding mucosa turns red and swells. Lymph nodes often become inflamed, the temperature rises and signs of general malaise appear.
With periodontitis, that is, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root, blood tests show an increased level of leukocytes and ESR.
If the pathology has entered a chronic stage, the causative tooth may darken, and during periods of exacerbation, a lump with purulent contents will appear on the gum.
What treatment is carried out if the roots hurt?
If you experience pain in your teeth, you should first contact your dentist.
Only after a visual examination and appropriate diagnostic procedures will the doctor be able to make an accurate verdict - make a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
One of the most common causes of this symptom is inflammation of the nerve or pulpitis. In such a situation, there are two treatment options at the discretion of the specialist:
- with nerve preservation: the tooth is opened and access to the nerve is provided. Medicine is applied to the pulp chamber, and a temporary filling is fixed on top. After some time, the patient will have to return to see the doctor for a refill or permanent filling,
- with depulpation, that is, with the removal of the pulp: the doctor opens the carious cavity, completely removes the neurovascular bundle, after which he cleanses and treats the root canals, filling them. If necessary, as in the case of periodontitis treatment, the specialist can place medicine in the canals and invite the patient to return after a while for the final installation of the filling. This method is more effective and less dangerous in terms of relapses1.
As for the nerve removal procedure itself, first you need to rinse the canals, and then place a devitalizing paste in the tooth (previously they used arsenic). Killing the nerve is a gradual process, requiring several days.
At your follow-up appointment, the doctor will remove the product, treat the canals, seal them and place a permanent filling. Some people say that the root of a dead tooth hurts, but in reality it cannot bring them any sensation.
If a tooth is without a nerve, but pain is present, this may indicate inflammatory and purulent processes in the periodontium.
If the cause of discomfort is inflammation of the root itself and the tissues surrounding it, as well as the appearance of pathological neoplasms nearby, in such cases surgical intervention is often required. Usually, the inflammatory focus is removed along with cutting off the root apex - its resection. The operation is performed after removing the nerve and filling the canals.
Sometimes it is necessary to completely remove one of the roots along with the crown and additionally restore bone tissue with the help of osteo-replacement chips - when the inflammation has spread to the jawbone and led to its resorption.
If the remaining part of the root becomes painful after some time, this will mean only one thing: the treatment was carried out insufficiently, resulting in a hidden pathological focus.
Is it really necessary to pull teeth?
Many are so afraid of excruciating toothache that they prefer to get rid of the tooth forever, rather than treat it and leave, albeit insignificant, the risk of relapse.
And it’s one thing if it is destroyed, when the crown has crumbled to the very root, and quite another thing if the tooth appears healthy in appearance. In the latter case, the doctor will definitely do everything possible to preserve the nerve.
If this cannot be done, you will have to carry out depulpation, but this is not a reason to completely remove the roots.
Experts take such extreme measures in cases where there is no other way to ensure that the pathological focus is eliminated or the root is severely affected.
But even in this case, pain can occur after removal if the inflammation has spread to nearby tissues or the infection has not been completely eliminated.
In any case, it is better to leave this issue at the discretion of the attending physician - an experienced specialist will be able to correctly assess the clinical picture from X-ray images and choose the correct treatment tactics.
How to reduce pain - home remedies
Traditional medicine is good only in moderation and only after consultation with a specialist. Independent attempts to relieve pain using medicinal herbs can lead to even more serious complications or the development of an allergic reaction. Below are popular folk tips that you need to apply wisely:
- soda-salt solution: mix baking soda and salt in equal proportions and add warm water - a teaspoon per glass. Use the solution for rinsing until the condition eases,
- propolis: the product has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. A piece of pure propolis can be applied to a sore spot. Alternatively, you can rinse your mouth with the prepared tincture,
- compress with honey and cinnamon: mix a teaspoon of honey with a crushed cinnamon stick. Apply the resulting mixture to the gum and hold for a while.
These tips will help to somewhat muffle the acute symptoms, so they are recommended as maintenance therapy, but not the main treatment. Attempts to cure the disease on your own will not lead to anything good - if they do not provoke complications, then they will allow the pathological process to develop into an advanced stage, and then you will have to say goodbye to the tooth.
What medications will help relieve the condition?
It is better to take pharmaceutical painkillers after consulting a specialist. But if the pain takes you by surprise, taking a painkiller pill is a completely reasonable solution. It should be remembered here that the drug will only suppress the symptom, but you still cannot do without treatment under the supervision of an experienced specialist. The most popular and effective means are listed below:
- Ketorol tablets are a powerful drug that quickly relieves even severe pain, but is highly toxic. Using this product too frequently is not recommended.
- Novocaine solution (Lidocaine, Ultracaine) - the product can be used for rinsing or application. In the latter case, it is enough to soak a cotton pad with anesthetic and apply it to the inflamed area,
- gel "Metrogil Denta" ("Solcoseryl", "Cholisal", "Asepta") - a product for external use that effectively relieves acute pain and inflammation. It is allowed to apply the gel at intervals of 2 hours until it becomes easier.
It is better not to bring the situation to a critical state - if a toothache appears, put off everything and run to the doctor. And in order to minimize the risk of such a nuisance, you need to visit the dentist’s office at least twice a year - for preventive examinations and professional procedures. hygiene.
1 Akhmedova, Z.R. Methods of instrumental treatment of dental root canals, 2010.
Source: https://mnogozubov.ru/bolyat-korni-zubov/
Ways to prevent pain
The effects of factors that affect tooth enamel, depleting it, can be neutralized. It’s another matter when the aching tooth suffers from a problem coming from within. So what can you do to protect yourself from complications from a cold? The patient is able to help himself in many ways. Prevention measures:
- Rinse your mouth with plain water after drinking tea with lemon or acid-containing medications. When drinking sour drinks and sour syrups, try not to keep the liquid in your mouth for a long time, hurry to swallow it.
- Drink water to avoid drying out the oral mucosa. Try not to breathe through your mouth; it’s better to put some drops in your nose once again than to suffer with your teeth later.
- Rinsing the mouth after vomiting. To prevent particles of food and stomach acid from settling on your teeth, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
- Maintaining hygiene standards during illness. No matter how difficult it may be to get out of bed to brush your teeth, you cannot do without it. If plaque on your teeth is not removed, they will soon begin to hurt.
How to quickly cure a cold, acute respiratory infection or acute respiratory viral infection in a child
It is better to carry out prevention so that you don’t have to suffer later. Don’t neglect the above tips if you don’t want to regret it when it’s too late.
Toothache is sometimes unpredictable and no one is immune from it. But if you have bad teeth, then they are more susceptible to the negative influence of viruses and bacteria that attack our body during a cold. To reduce the risk of complications such as nerve or gum inflammation, you should visit the dental office promptly when necessary. Unfilled holes in the teeth greatly increase the likelihood that your jaw will ache during a cold. Take proper care of your oral cavity if you don’t want to suffer from pain at night.
Traditional methods of treatment
Any rinses and other folk remedies will not help to completely get rid of the causes that led to inflammation. Especially if the problem is advanced and it hurts to press on the gums near the teeth. However, using folk recipes you can dull the pain and stop (reduce) the rate of development of the inflammatory process. Treatment using traditional recipes gives good results when carried out in combination with medication. Below we present some of the most effective recipes that will help relieve pain and remove suppuration:
- "Indian Toothpaste" This paste has disinfectant properties and is good at soothing the inflamed gum mucosa. For cooking you will need 3 tbsp. spoons of crushed sea salt and 2 tsp. crushed dry banana skin. The powdered ingredients are mixed and diluted with olive oil to a paste. The composition is applied to the tooth and rubbed into the tissue around it in the morning and evening. Leave for at least 10 minutes. After the remains are spat out, the mouth should not be rinsed.
- Tar from an abscess. When gumboil or swelling appears between the teeth on the soft tissues, you can also fight them using folk remedies. One of the most effective is to use a rusty nail. About 5 cm of linden honey (necessarily liquid) is poured into a fireproof container. An old nail, heavily covered with rust, is taken, heated until red and dipped in honey. Rust reacts with honey, forming a dark substance whose composition resembles tar. This substance is lubricated at night on sore soft tissues in the mouth. After several procedures, the abscess should break through and the wound should gradually heal.
- The mixture is wound healing. Mix the yolk with a teaspoon of powdered sugar and a tablespoon of olive oil. A small piece of white, clean cloth is soaked in this mixture and applied as an applique to the sore spot.
Read also: How to treat a tooth at home
Indian toothpaste - sea salt and banana peel
A tooth hurt on one side during a cold
Often such sensations appear unexpectedly, radiate to the ears, temples, and are aggravated by heat or pressure. As for such pain associated with a cold, most often it is pulpitis. The inflammatory process of the soft part of the tooth or the flesh around it brings sharp pain, it can be either constant or occurring, most often only at night. Another cause of such pain is periodontitis. The top of the tooth becomes infected, the sensations are constant and pointing to one specific tooth. In advanced form, the gums swell and the tooth begins to loosen.
When to see a doctor
Toothache during the development of a cold or ARVI is a symptom that worries many. If it is of a mild nature, then there is nothing to worry about. The discomfort will disappear immediately after recovery.
But if the pain in your teeth intensifies, accompanied by high fever, redness and inflammation of the gums, you should immediately consult a dentist.
With the development of infectious processes in the body, bacterial microflora in the oral cavity can become active, which is the cause of many diseases.
It causes inflammation of the pulp (pulpitis), and can also provoke stomatitis, candidiasis, gingivitis, periodontal disease and other diseases of the oral cavity that require immediate treatment.
Complications of gum disease
If you press on your gum and it starts to hurt, this is an important reason to visit the dentist. If the problem is ignored for a long time, without attaching importance to this symptom, the patient risks provoking an increase in the inflammatory process. Advanced gingivitis will develop into periodontitis. Inflamed soft tissues and sunken tartar expose the neck of the tooth, making it mobile, which can lead to their loss. For pregnant women, the consequences of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity can be the development of heart, endocrine and pulmonary diseases. Pathogenic bacteria negatively affect the health of expectant mothers.
If periodontitis is not treated, it can cause intoxication of the body and decreased immunity. The active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria on the teeth and gums leads to their entry into the blood. The infection quickly spreads through the blood throughout the body, causing infection of organs, which can be fatal.
The formation of fistulas and cysts on the soft tissues of the jaw also does not add health and beauty. In severe cases, the fistula can affect the facial muscle, and the defect is difficult to hide from prying eyes. Sometimes granulations dissolve and form a cavity filled with liquid in the gum. Such a cyst, pressing on the jaw, causes acute pain, and if ruptured, it can even provoke a fracture.
Each dental disease from the above list can be eliminated through proper treatment prescribed by a dental specialist. After all, diseases do not disappear on their own; they must be fought with all available methods. If the gums feel painful when pressed, you need to look for the cause of this reaction. Bacteria can enter the oral cavity from the nose or throat and thrive in a warm, moist place, causing an inflammatory process. Advanced diseases in the oral cavity can cause irreparable harm to the human body. Take care of your health regularly and do not miss routine dental checkups.
Gum pain when pressed
Soreness of the gums when pressed is a symptom of inflammation; the cause may be the tooth or the tissues surrounding it. The simplest factor in the appearance of inflammation is mechanical trauma and burns of the mucous membrane. Severe causes - periodontitis, inflammation of the root apex, periodontal disease, difficult teething. When a tooth hurts when pressed, it can be associated with caries and pulpitis, but in this case the gums rarely suffer, and the real cause must be looked for under the tooth.
If the organ wobbles, changes color, the gums around it become pale and atrophy, this may indicate periodontal disease. The same symptoms are typical for complications after pulp removal.
In children, the gums become inflamed and the tooth hurts when biting in case of teething. This can only be affected by pain-relieving dental gels, but it will not be possible to speed up teething to eliminate symptoms. Severe toothache. when the organ is in a resting position and is not given any pressure, it may be a consequence of improper root canal treatment or a cyst. In the case of cystic formation, the gums become swollen, painful, and when pressed, the symptoms intensify.
Gum diseases
Mild deviations that lead to pain include gingivitis, papillitis (inflammation of the gingival papillae),
A systemic disease of the tissues around the tooth, periodontal disease, occurs in a chronic form and can cause pain. The dental ligament weakens, the tissues cease to be nourished normally, and severe degenerative changes occur.
To prevent periodontal disease, you need to treat gingivitis and periodontitis in a timely manner.
What other diseases are manifested by pain around the tooth:
- infectious and traumatic stomatitis;
- cheilitis - inflammation of the tongue;
- increased sensitivity of teeth;
- wedge-shaped defect, fluorosis;
- vitamin deficiency, diabetes mellitus.
The presence of hard dental deposits can also cause pain, then it is enough to carry out professional cleaning in a timely manner. If this is not done, the gums will become infected, and the inflammatory process will progress, involving increasingly larger areas of the oral cavity.
How to treat
Treatment of the mucous membrane in dentistry consists of disinfecting the oral cavity, relieving inflammation with local agents and carrying out complete sanitation. It is important to cure all carious cavities that could cause the disease.
Additionally, radiography may be performed to rule out a cyst or benign formation of the jaw.
Complex treatment includes treatment of the mucous membrane with anti-inflammatory gel and ointment, taking painkillers, nutritional correction, and changing personal oral hygiene products. At home you need to rinse, bath, make medicinal decoctions, compresses. All activities are allowed only after removal of pus in a dental office.
Did the article help you?
Tooth root inflammation: symptoms, treatment by a doctor and at home
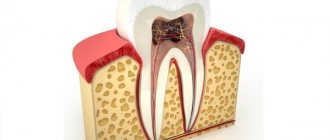
Opportunistic microflora is constantly present in the oral cavity. Being in a comfortable environment, microbes actively multiply. This provokes the development of an inflammatory process that affects soft tissues and tooth enamel. If the root is inflamed, this is a sign of advanced pathology. Without treatment, there is a risk of developing sepsis and loss of healthy teeth.
Causes of inflammation
Periodontal root changes are a consequence of an advanced form of pulpitis. If there is pathology in the oral cavity, and the patient refuses to visit the dentist, pathogenic microbes exit the pulp chamber through the apical foramen and affect the peri-root zone. As a result, the root of the tooth hurts. According to its etiology, periodontitis is:
READ ALSO: what to do if a root remains in the gum after tooth extraction?
- infectious;
- traumatic.
Due to the spread of infection, the tooth root often becomes inflamed due to the patient’s fault.
The soft plaque that forms on the enamel and dentin layers during caries consists of microbes. Their vital activity causes the gradual destruction of the pulp.
The longer the disease develops without treatment, the deeper the bacteria penetrate inside the tooth, affecting the pulp and periodontium.
Violation of the rules or expiration of the life of the artificial crown leads to loosening and displacement of the structure. Gaps are formed into which microbes penetrate. It is impossible to clean the cavity from the inside on your own: bacteria enter the pulp and spread deeper into the periapical region.
Periodontitis due to the fault of the dentist occurs when the rules of root canal treatment are violated. Common reasons:
- insufficient mechanical cleaning before nerve removal;
- failure to comply with antiseptic measures;
- incorrect filling technique.
With marginal periodontitis, infection agents spread directly from the oral mucosa to the root. There are no carious lesions on the crown in the x-ray photographs.
Similarly, ulcers form along the jaw bones and tooth roots. Non-dental infectious diseases also lead to inflammation.
Sinusitis and tonsillitis are frequent “provocateurs” of periodontitis.
The inflammatory process of traumatic etiology is provoked by mechanical and other damage to parts of the tooth. Pathology is caused by:
- fractures and transverse cracks of the root;
- rupture of connective tissue fibers fixing the tooth in the socket;
- increased chewing load due to improper filling;
- sports injuries;
- damage to the neurovascular bundle with increased tooth mobility.
Symptoms of tooth root inflammation
The clinical picture varies for different forms of periodontitis. During an acute attack, the tooth constantly “aches”, regardless of the time of day. The patient feels a “growth” of the tooth and experiences difficulty closing the jaw - the area hurts greatly when pressed and percussed.
The presence of pus in the projection of the root apex is indicated by throbbing pain that spreads in the direction of the trigeminal nerve. Under the influence of heat, attacks are repeated and intensified. There are general signs of the inflammatory process:
- weakness;
- hyperthermia;
- proliferation of lymph nodes in the jaw area.
Chronic periodontitis is accompanied by less obvious symptoms, or there are no signs of pathology. Moderate pain occurs when pressing on the affected tooth.
The penetration of carious bacteria into the pulp chamber and the formation of necrotic masses in it causes an unpleasant odor from the patient’s mouth. With granulating inflammation of the root with frequent relapses, a cyst or fistula with a hole for draining purulent exudate out is formed on the front side of the gum.
READ ALSO: How is a fistula formed on the gum removed?
Chronic periodontitis is prone to exacerbations. The clinical picture is complemented by obvious symptoms of the disease:
- the patient has a fever;
- aching facial bones;
- migraine attacks occur;
- sleep is disturbed;
- teeth hurt a lot when chewing food.
Without proper treatment, the disease leads to an abscess or cellulitis near the root. At this stage, purulent inflammation can spread to the paranasal sinuses, and there is a risk of bone damage or sepsis. The tooth becomes loose, and there is a characteristic taste of pus in the mouth.
Treatment of inflammation in the dental office
The treatment regimen for the disease is determined taking into account the cause and stage, and the condition of the patient. Treatment of the acute form begins with freeing the tissues from purulent exudate. The dentist’s job is to prevent tooth loss.
If the tooth root has become inflamed for a long time and the pain has spread to neighboring chewing organs, the localization of the outbreak is determined using x-rays. Standard tactics involve removing carious lesions. When caries penetrates deeply, the tooth is depulped.
When inflammation of the dental pulp occurs due to improper filling, the composition is removed and antiseptics and instrumental expansion of the root canals are performed. Further inflammation of the gums and tooth roots is relieved by antibiotic treatment. The patient is prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs.
Considering the frequent development of pathology against the background of mixed pathogenic microflora, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in the form of:
- tablets - Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Metronidazole, Azithromycin and analogues;
- injections – Lincomycin, Clindamycin, Oxacillin;
- gels for local treatment - Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal.
After 2-3 days, long-acting preparations are placed into the re-washed root canals and temporary fillings are placed (we recommend reading: what are temporary fillings used for?).
When the formation of pus stops, the tooth is filled with a permanent composition.
To evaluate the results of treatment for inflammation of the gums and tooth root, an x-ray is used (we recommend reading: inflammation of the gums near the tooth: causes and treatment with photos).
If a patient presents with chronic periodontitis, the tactics of action after antiseptics, treatment and innervation of the tooth are different. A cotton swab with an antiseptic drug is placed into the cavity and closed with a temporary filling. Antibiotics are used to stop further infection.
After stopping the process, the dentist cleans the root canals and installs a temporary filling based on calcium hydroxide for 2-3 months. The therapeutic lining provides a powerful antiseptic effect. To enhance the effect, physiotherapy is prescribed using UHF and electrophoresis methods.
If the inflammatory process is stopped, the canals are cleaned and sealed. At the next appointment, the tooth cavity is closed with a permanent filling. If periodontitis does not stop, surgical methods are turned to. The doctor removes the tip of the tooth root along with the inflammatory focus in the canal.
Treatment at home
Acute inflammation of the tooth root begins unexpectedly with sharp pain. If it is not possible to immediately make an appointment with a dentist, symptoms can be temporarily eliminated with folk recipes at home:
INTERESTING: what to do if inflammation begins under the crown of the tooth?
| Main Ingredient | Effect | Mode of application |
| Coltsfoot | Reduces the formation of pus, disinfects the skin and mucous membranes | Smoldering coals and fresh coltsfoot leaves are laid out in a thick layer in a ceramic teapot. Cover the container with a lid and “smoke” without inhaling the smoke. The vapors are kept in the mouth for 10-15 seconds, the procedure is repeated until the leaves burn out |
| Nettle with alcohol | Produces an anti-inflammatory effect, treats mucous infections well | Fresh crushed nettle leaves are ground until the juice is released. Add 50 ml of medical alcohol (76%) and leave for 20-30 minutes. The solution is diluted with water to 300 ml and the inflamed area is rinsed |
| Beet | Suppresses inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, relieves pain | The fresh tuber is cut into slices and applied to the gum. The compress is changed every 20 minutes |
| Sage | Has a wound-healing effect, contraindicated for children and pregnant women | 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs from a pharmaceutical collection are poured with boiling water and steamed. The broth is infused for 2 hours. Rinse your mouth with the resulting liquid every hour until symptoms disappear. |
| Garlic with salt | Eliminates pain during inflammation, kills pathogenic microflora, prevents the formation of pus | 2-3 garlic cloves are crushed to a paste and mixed with sea salt. The composition is applied to the tooth in a dense layer and covered with cotton wool for 20 minutes. The mouth is rinsed with warm water or chamomile solution. |
| Propolis tincture | Accelerates the healing of the mucous membrane, prevents the spread of the purulent process | The tincture from the pharmacy is diluted with 100-150 ml of water. A cotton swab is soaked in the solution and placed on the tooth for 5 minutes. The procedure is repeated every 30 minutes until the pain stops |
Analgesics applied directly to the tooth help relieve pain. The best effect is provided by Ibuprofen, which has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects at the same time. The tablet is crushed to a powder and diluted with a couple of drops of water. The mixture on a cotton swab is applied to the gum and held until the pain stops.
Prevention measures
In most patients, root inflammation occurs due to caries. Therefore, the main prevention is to prevent the formation of carious plaque. To prevent damage to soft tissues and teeth, it is recommended:
INTERESTING: good pills for inflammation of gums and teeth
- Maintain oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day, repeat the procedure after eating sweet foods.
- Limit your consumption of sweets. The greatest threat is the sugar substitute in the composition.
- Strengthen immunity. Vitamin C is essential for teeth and gums. The tablets are washed down with water without dissolving, as the acid destroys the enamel.
- Monitor the condition of your dentures. The accumulation of food debris between “living” tissues and the structure increases the risk of caries.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Preventive examinations are carried out at least 2 times a year. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, you should consult a doctor at the first sign of problems.
Diseases of the oral cavity also provoke general disorders in the body.
To keep teeth healthy, it is important to monitor the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system.
Source: https://AzbukaZubov.com/stomatolog/bolezni/lechenie-vospaleniya-kornya-zuba.html
What pills will help?
As has been said many times, only a doctor can diagnose such unpleasant pain. It is important to call or go to an appointment immediately, but not to kill your body by stuffing it with painkillers, hoping that everything will go away on its own.
- In a situation where the attack happened late at night (as a rule, there is no night dentistry), or on a weekend, it is important to take measures to wait until the doctor’s visit. There are several effective auxiliary methods that can help for a while:
- First of all, you need to check if there are any food residues in the interdental spaces, in the mouth area. Keep your teeth clean in the future.
- Rinse with a warm solution of soda, one teaspoon per glass of boiled water.
- Sometimes using ice helps. Try sucking on a piece, or placing it on a sore tooth or cheek for about fifteen minutes three times a day.
- If painful sensations occur during conversation, reduce the time of communication and try to keep your mouth covered.
How to treat teeth for a cold
This pain can occur when talking, coughing, eating or drinking, or simply when breathing in cold air. It often happens that the upper jaw hurts even with a slight runny nose. The following methods are used to treat toothache:
physiotherapy;
Let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Drug treatment
Modern medicine offers many medications that can relieve raging tooth pain. But they have various contraindications, so you should not take them without consulting a dentist.
You should go to the doctor immediately as soon as pain in your teeth appears. The dentist will conduct an examination and tell you what actions to take. Perhaps the pain arose as a result of increased sensitivity of the teeth and to prevent them from hurting, it is enough to brush them with a special paste.
But if the pain occurs as a result of an infectious process in the respiratory system, then the underlying disease should be treated. Anesthesia is used for the teeth, and surgical measures are required to relieve pressure in the maxillary sinuses. Antibiotics are prescribed to suppress the infection.
To temporarily relieve pain, you can hold an Analgin or Nosh-pa tablet in your mouth before going to the doctor. But you shouldn’t get carried away, they relieve pain temporarily, and constant use can lead to an overdose.
Physiotherapy
In order to relieve pain and inflammation in the dental area, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and UHF are prescribed. To carry them out, a magnetic field, ultra-high frequencies and constant electric current are used. With their help, heat is generated in the affected area and the medicine is delivered to the inflammatory focus. This allows you to achieve better results from treatment.
Doctors and diagnostics
The dentist must determine the root cause, after which he prescribes conservative treatment.
- Examination by a dentist using a mirror.
- Probing – detection of cracks and chips of enamel.
- Percussion is tapping on the tooth with a medical instrument to determine the condition of the tooth socket.
- Laser diagnostics for identifying caries in the early stages.
- Testing for electrical excitability using an electrical impulse. The condition of the nerve can be determined.
- X-rays allow you to view the condition from the inside.
- The use of a diathermocoagulator allows you to see the reaction to heat.
A complete examination will make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Gingivitis and periodontitis require therapy for the inflammatory process caused by bacteria. To do this, remove tartar, which contains foci of infection and various microbes.
Antibacterial therapy is carried out, rinsing with Chlorhexidine is prescribed (10 days). You can alternate with a solution of calendula, oak bark, and sage.
It is recommended to cover the mucous membrane with Cholisal gel and rinse with Rotokan, Stomatofit, Miramistin.
In the case of periodontitis, the root cause must be treated. Take an x-ray to determine the location of the inflammation. If necessary, the doctor opens the filling, removes the nerve, cleans the canals, then places a temporary filling, and after treatment - a permanent one.
Read also: What can pregnant women do for toothache?
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed, most often Amoxicillin, herbal rinses, brushing teeth with special strengthening pastes, and rubbing in gels.
The injured surface is restored by rinsing with sea salt or a solution (salt, soda, 1 tsp + 5 drops of iodine). Use as often as possible.
What to do if the gum under the tooth hurts at night? It's good to have painkillers at home.
You shouldn't get carried away with them. You should visit a specialist as soon as possible. Tablets can help if your gums hurt when pressed for just a short time.
How to relieve pain
Only a doctor can tell you what to do if your teeth ache from a cold. He will prescribe effective treatment based on the cause of the pain syndrome.
If its development is associated with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve or pulp, then in this case anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, in which several drugs are prescribed at once, having different effects.
You may need to take painkillers, antibiotics, use antiseptics and drugs that relieve inflammation. If carious lesions of the teeth are detected, cleaning of the damaged tissues and filling will be required.
In addition to medications, a procedure such as mouth rinsing will help relieve toothache.
In this case, you can use special aseptic medicinal solutions prescribed by the dentist, or other remedies, for example, prepared according to folk recipes. However, when using the latter, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Possible causes of pain
So, what can it mean if the root of the tooth hurts when you press on the gums or even without external mechanical irritants? In fact, there are quite a few potential causes, and among them there are both minor ones that are easy to fix and complex ones that require serious treatment.
Pulp ischemia
The pathology is associated with a lack of oxygen in the tissues that nourish the pulp, and this can also cause pain. The disease usually develops against the background of problems with blood vessels, injuries, infections in the body, disturbances in the endocrine system, oncological processes, contamination with toxins, and disruptions in the nervous system. Sometimes ischemia is a consequence of diseases of the hematopoietic organs or digestive system. And in this case, it usually becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations.
Possible reasons
There are many reasons for toothache, so people can get confused and mistake it for symptoms of other diseases. Sometimes the pain is excruciating even when inhaling, as cool air is directed into the mouth, affecting the sore teeth. It can either be independent or manifest itself from the influence of other stimuli. Temporary pain that occurs when eating or drinking may be a consequence of the development of caries. Also, over time, teeth become even more sensitive and react to too hot and cold foods.
Constant, slightly throbbing pain indicates a disease called pulpitis. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis. Pain is often a signal indicating that the pathological process has gone far and complications have appeared. A spontaneous decrease or increase in pain does not indicate recovery; on the contrary, most likely, a transition to a new stage.
Sources
- https://VipLor.ru/vopros-otvet/bolit-desna-pri-nazhatii
- https://prostudych.ru/prostuda/pochemu-bolyat-zuby-chto-delat.html
- https://prostudoff.ru/sovety/bolyat-zuby-pri-prostude-prichiny-metody-lecheniya-tabletki.html
- https://pulmono.ru/drugie/orz/pri-prostude-bolyat-zuby-osnovnye-prichiny-i-lechenie
- https://respiratornie-bolezni.com/prostuda/kak-i-chem-snyat-zubnuyu-bol-pri-prostude-kogda-stoit-obratitsya-k-vrachu.html
- https://dolgojiteli.ru/vse-o-zubah/bolit-perednij-zub-pod-nosom.html