Inflammation of the gums in children is a widespread disease that requires visiting a dentist for adequate treatment.
In advanced cases, the disease becomes chronic and leads to the appearance of an ulcerative-necrotic stage , and subsequently to periodonitis.
Gingivitis in most cases affects children under 5 years of age who cannot independently perform oral hygiene.
Causes
Inflamed gums in a child primarily occur due to poor oral hygiene. Therefore, to prevent disease, it is necessary to brush your teeth up to 2 times a day. The following factors can also cause the disease:
- Teething in infants.
- Injury to the gums if the baby has a habit of chewing hard objects.
- Red gums in a child can provoke caries of permanent teeth.
- If lip pathology is detected in children.
- If pathology of the frenulum of the tongue is diagnosed.
- If there is an incorrect bite.
- Inflammation of the gums near the tooth may be associated with breathing problems. Most often this occurs due to regular mouth breathing, as a result of which the oral mucosa dries out.
IMPORTANT: Chronic gum inflammation can be associated with infectious diseases.
Ginigivitis can also be observed if the following diseases are detected:
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract,
- liver and gallbladder diseases,
- due to decreased immunity,
- due to a lack of vitamin C in the body,
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus,
- if tuberculosis is diagnosed,
- for allergic reactions,
- for rheumatism,
- blood diseases,
- with hormonal disorders,
- with dysbacteriosis,
- for kidney diseases.
IMPORTANT: Redness of the gums can be caused by a toothbrush with hard bristles.
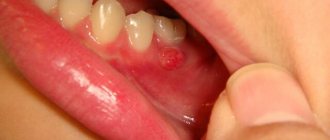
Why do gums turn red in children?
Red gums in a child can appear for various reasons. Most often, this condition of the oral cavity indicates an inflammatory process, which may be accompanied by an increase in temperature. This condition is especially common in children under 3 years of age.
Children, exploring the world, put in their mouths not only toys, but also foreign objects that interest them. At this age, children still have weak body resistance to various infections, so inflammation occurs on the delicate mucous membrane of the oral cavity, which develops due to various reasons.
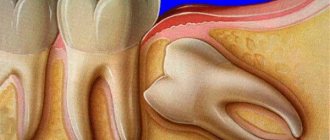
Teething
The appearance of the first teeth in infants is often accompanied by a reaction from the body. The child’s gums turn red and negative symptoms appear, which manifest themselves:
- low mood;
- moodiness, anxiety;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- poor sleep;
- sore gums.
Sometimes teething is accompanied by an increase in temperature, but not higher than 38 degrees and no more than 2-3 days. The inflammatory process can be local.
Gums before tooth eruption
Redness and swelling of the gums are noted only above the tooth that begins to erupt. The timing of the appearance of the first teeth in infants depends on birth weight and type of feeding.
Gingivitis
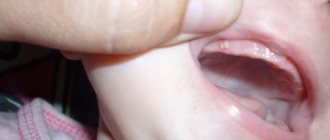
The development of gingivitis in children is associated with the pathological process of periodontium. In this case, inflammation of the marginal part of the gum occurs, which is directly adjacent to the neck of the tooth and the interdental papillae of the gum. The following symptoms are observed with gingivitis:
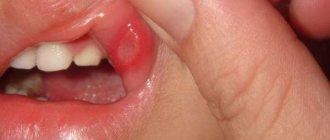
- red, inflamed gums;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the oral mucosa.
Often negative symptoms are accompanied by the appearance of ulcers on the mucous membrane. With physical impact (chewing or brushing teeth), the gums bleed. The main role in the development of the disease is played by bacterial plaque, the pathogenicity of which changes over time. The larger it is and the older it is, the higher and more diverse the bacterial flora (spirilla, spirochetes, gram-negative rods).
Periodontitis
Red gums in a child may appear due to periodontitis, which most often occurs at the age of 10. The pathological process spreads to the periodontal tissues surrounding the tooth, which securely hold it in the socket. As a result of the pathological process, the ligaments weaken, the tooth begins to sway and fall out.
In childhood, periodontitis tends to progress rapidly. Therefore, it is important to promptly notice the following symptoms of the disease:
- hyperemia of the gums, i.e. their redness;
- pain and discomfort after eating;
- bleeding gums, which appears and intensifies when brushing teeth, mechanical pressure on them (biting an apple or pear);
- the appearance of pustular formations on the inflamed gums.
In addition to local manifestations of the disease, the child’s well-being suffers, manifested by increased temperature, general weakness and malaise.
Stomatitis
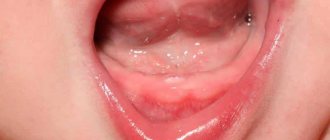
Inflammation of the oral mucosa is a common disease among children. Stomatitis has different etiologies. They often manifest themselves in the form of a chronic course against the background of a decrease in the child’s body’s defenses. Clinically, the disease is manifested by local and general symptoms, such as:
- hyperemia of the oral mucosa;
- looseness and swelling;
- blistering rashes;
- ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Against the background of a pathological process in the oral cavity, the baby’s behavior changes. The child becomes lethargic, capricious, sleeps poorly and refuses to eat. Stomatitis often occurs with increased body temperature and redness of the gums. The infection most often develops in children under 2 years of age.
Depending on the severity of clinical symptoms, the disease can occur in the following forms:
- mild - the child’s general condition does not suffer, and elements on the oral mucosa are presented in limited quantities, which quickly regress;
- moderate – symptoms of intoxication are observed, which are accompanied by multiple rashes on the mucous membrane;
- severe - intoxication of the body is significantly pronounced, against the background of which multiple rashes in the oral cavity can ulcerate.
Important! The appearance of redness of the oral mucosa in a child at any age requires a mandatory consultation with a pediatrician in order to determine the cause and subsequent treatment.
Gum injuries
During play, a child can get gum injuries by hitting their face on a hard surface or getting hit in the jaw with a ball during a game of football or a fight. The most common injury occurs to the gums of the front teeth. It can be minor and manifest itself as redness of the mucous membrane at the site of impact, pain and swelling of the tissues.
Symptoms of mild gum bruising subside within 2–3 days. If there is a violation of the integrity of the gum tissue from a strong blow, accompanied by bleeding, severe swelling and pain, a part of the tooth may be chipped or the tooth root can be driven into the jaw. In this case, a consultation with a dentist is required to determine the nature of the injury, its consequences and treatment.
Burn
The occurrence of a burn is provoked by the action of hot food and tea, aggressive chemical liquids or medications on the oral mucosa. A child can get such a burn due to parental negligence, most often before the age of 3. As a result of the action of aggressive agents, the following symptoms are observed:
- redness and swelling of the oral mucosa;
- sore gums;
- the appearance of blisters.
The severity of clinical symptoms depends on the type of agent and the time of its action on the mucous membrane. In the diagnosis of burns, there are 3 degrees, which are manifested by the following symptoms:
- 1st degree – there is redness of the gums and mucous membrane, pain during mechanical action on it, burning and discomfort in the oral cavity;
- 2nd degree - against the background of hyperemia of the mucous membrane, blisters appear filled with transparent secretion. Damage to their integrity provokes severe pain radiating to the teeth;
- Stage 3 is the necrotic stage, when the blisters ulcerate and cover almost the entire surface of the oral cavity, and the soft tissues die, that is, necrosis occurs.
In pediatrics, the most common thermal burns are caused by ingestion of hot food or household chemicals. A child who has received a burn to the oral cavity, regardless of the type of aggressive agent, must be examined urgently by a doctor.
Caries
80% of children under 6 years old suffer from caries of primary teeth. Common causes of the disease are:
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- improper diet;
- deficiency of calcium and fluoride in the child’s body.
The main symptom of superficial caries in children is pain, which occurs when the affected tooth is exposed to sweet or salty food, or when mechanical pressure is applied to it. The pain is short-term, disappearing when the stimulus is removed.
With average caries, the tooth begins to react to cold or hot food. The resulting carious cavity becomes clearly visible. Sometimes you may experience bad breath when several teeth are affected at once.
With deep caries, pain appears with any irritant. A carious cavity is visible to the naked eye. Food particles entering it cause intense pain. There is bad breath and reddening of the gums.
Kinds
The disease is divided into several types.
- The most common is the catarrhal type.
- With ulcerative lesions, lesions are observed that turn into tissue necrosis if timely treatment is not started.
- Atrophic is characterized by a decrease in the volume of inflamed tissue.
- With hypertrophic, the inflamed tissues greatly increase in size.
Also, red gum around the tooth may indicate an acute or chronic course of the disease. In the acute form, the symptoms are pronounced, while in the chronic form they are blurred.
IMPORTANT: Gingivitis can affect small areas of the oral cavity or the entire mucous membrane.
Symptoms
- The most important symptom is redness of the gums and increased swelling.
- Swelling of the papillae between the teeth may be observed.
- Bleeding may occur.
- While eating, the patient feels painful sensations.
- Plaque is observed on the surface of the teeth.
- If your child's gums are red, they may feel itchy.
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- The baby has a distortion of taste.
- Painful reaction to warm or hot food.
- In the acute course of the disease, an elevated temperature is observed.
IMPORTANT: If there is looseness or thickening of the mucous membrane, or cyanosis of the gums, we can talk about the presence of ulcerative gingivitis.
- Saliva may have increased viscosity.
- There is an increase in lymph nodes in the jaw area.
What to do
- If there are minor complaints of pain or discomfort, parents should examine the oral cavity.
- To determine gingivitis, if a child has gum inflammation, photos can be viewed on the Internet. Even minor symptoms should prompt you to see a doctor.
- If it is not possible to visit a dentist in the near future, parents should help reduce negative symptoms.
- To do this, you need to rinse your mouth with a solution of soda. Pour a teaspoon of the product into a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth up to 5 times a day.
IMPORTANT: The water must be boiled.
- If your baby is an infant, you can purchase a special Kamistad gel at the pharmacy.
- Throughout this time, parents should also constantly clean the mouth of food debris using a sterile cotton swab.
These are the first means of aid that will alleviate the child’s condition. All necessary manipulations and prescription of medications are carried out only by a pediatric dentist.
Therefore, to prevent the disease from becoming chronic, visiting a specialist is mandatory .
How to help your baby during teething
The appearance of teeth is a very difficult and worrying stage in the life of babies and their parents. The child experiences severe pain and discomfort. You can alleviate your baby's condition at home.
- Modern medicine offers many means and methods that will relieve a child of suffering during the appearance of teeth:
- Gum massage. The method helps relieve itching and pain and speed up the process of tooth eruption. You can use simple gauze to massage your gums. It is moistened in water or chamomile decoction, wrapped around a finger, and moved lightly along the gum. Special silicone finger pads are also used for massage. They can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Use of local anti-inflammatory drugs. Gels and ointments with herbal ingredients are widely used. For newborns it is recommended to use “Baby Doctor, First Teeth”. For children over 6 months old, you can use Kalgel with lidocaine, Cholisal and Dentinox.
- Oral use of anti-inflammatory drugs. You can bring down your child’s temperature and relieve pain with the help of children’s “Nurofen” in a convenient suspension form. The drug can be used in children from three months of age.
Teething - inflammation
Some herbal preparations can cause allergies in a child. If a rash or swelling of the mucous membranes appears, you should stop taking the drug and contact your pediatrician.
During teething, special attention should be paid to the baby's nutrition. You should not give sweetened drinks to avoid the development of caries. You also need to pay attention to hygiene. The baby's tongue should be cleaned with moistened gauze in the morning. All procedures should be carried out only with clean hands.
Teething aids
How to treat
This is a complex treatment that involves taking painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. They are not only taken orally, but also used to treat the oral cavity, rinse, and irrigate the mucous membrane.
To rinse the mouth, it is recommended to use decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- pharmaceutical chamomile,
- calendula,
- sage,
- oak bark,
- yarrow,
- plantain,
- birch buds.
IMPORTANT: To prepare the decoction, pour a tablespoon of one of the plants with a glass of boiling water.
To stop the inflammatory processes, the doctor prescribes the following drugs:
- Furacilin solution. To prepare it, a tablet of the drug is diluted in 50 g of boiled water,
- Rotokan contains natural components and has powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects. 5 mg of the drug is diluted in a glass of warm water and mouth baths or lotions are made,
- Kamistad, which has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. It can be used in children from 3 months of age. A 5 mm strip is applied to the inflamed areas and thoroughly rubbed into the gums. The drug works effectively if the patient holds it in the mouth for at least 1-2 minutes up to 3 times a day,
- Romazulan helps relieve inflammation,
- Sangviritrin destroys pathological microorganisms and fungal pathogens. For children under 5 years of age, parents treat their gums. If the child is over 5 years old, he rinses independently up to 3 times a day for 5 days.
IMPORTANT: In case of complications and complex forms of the disease, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Treatment of pathology
If gum hyperemia is associated with teething, then the child does not require special treatment. You can facilitate this process with the help of special toys and gels that will relieve pain. As a rule, the redness goes away when the tooth comes out completely. We bought such a cutter for our baby, it turned out to be enough and we didn’t have to buy special medications. So the child was able to play and scratch his gums.
Gingivitis requires treatment in the clinic and then at home. At the dentist, your child’s teeth will be cleaned, plaque will be removed, and they will be taught how to properly brush their teeth. After this, you will be prescribed irrigation (Rotocan, Miramistin, Chlorophyllipt), and treatment of the gums with drugs to relieve inflammation (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal, Dentinox).
If the cause is caries, they will put a filling or completely remove the tooth.
Treatment of stomatitis will be established after determining the exact diagnosis and type of this pathology - it is possible only after contacting a dentist.
Give your baby first aid
You may not always be able to see a dentist right away. In such cases, you need to know how to temporarily relieve hyperemia. This will help make your baby feel better. For such purposes, decoctions of medicinal herbs are taken, such as St. John's wort, chamomile, and calendula. It is necessary that the infusions be warm. They are used to irrigate the oral mucosa. Also for this purpose you can use a solution of soda, a weak brew of tea, always black. In addition, you can lubricate painful areas with sea buckthorn oil or honey.
Temperature with gum inflammation
Children with severe gingivitis may experience fever. This means that an inflammatory process has begun in the body. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms have spread not only to the oral mucosa, but throughout the body. In this case, you need to take antipyretic drugs:
- Ibuprofen,
- Paracetamol.
It is very important to give children plenty of fluids. This can be warm boiled water or compotes from raspberries, currants, and rose hips. Also in this case, it is necessary to show the baby to a specialist and observe bed rest.
IMPORTANT: It is not recommended to heat inflamed gums without a doctor’s permission.
Definitions of gum disease
Gum diseases in children and adults are divided into 3 categories, in which there are subgroups of ailments:
Gingivitis . Inflammation of the gums around one tooth. This disease does not pose a threat to the tooth itself, since it does not affect its tissue. There are three types of gingivitis: catarrhal, atrophic and ulcerative-necrotic. Despite such terrible medical definitions, curing the sore is quite simple; the main thing is not to miss the moment and start therapy in time so that it does not develop into periodontitis. In children, gingivitis manifests itself during teething; its symptoms are treated with an antiseptic as prescribed by a doctor.
Periodontitis . Guys most often suffer from incompletely treated gingivitis. At the same time, the gums swell, bleed, then the gums recede, and the ligament between the tooth root and the jawbone gradually collapses. A space forms between the gums and exposed roots, where food debris becomes clogged and cannot be removed by oneself.
Important! Periodontitis and gingivitis occur in 80% of children and are the second problem of oral disease after caries.
Periodontal disease . Rarely occurs in childhood, but develops quite quickly. This disease is easily confused with periodontitis, because in both cases the supporting apparatus of the tooth is affected. Periodontal disease leads to degeneration of gum tissue, they recede, exposing the necks of the teeth, and the gaps between them increase. The disease is insidious; it is not localized in one place, but quickly spreads to both jaws. At the same time, the gums do not change color, do not bleed, do not swell, they simply die slowly. Curing periodontal disease is not easy; it requires complex therapy.
Prevention
- To avoid disease, children should brush their teeth at least 2 times a day.
- Brushes must be used with soft bristles.
- It is imperative to treat caries, even if it occurs on baby teeth.
- It is necessary to visit the dentist at least 2 times a year.
- Provide children with adequate nutrition with regular consumption of vegetables and fruits.
To avoid the occurrence of gingivitis, it is necessary to follow preventive measures to prevent the disease. In case of inflammatory processes, immediately visit a pediatric dentist.