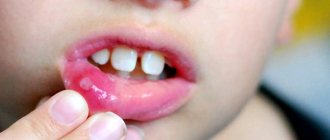
A condition in which damage to the oral mucosa occurs is called stomatitis.
This dangerous and quite serious disease affects neither adults nor children. In medical practice, there are several forms of the insidious disease.
Catarrhal form is one of its common varieties.
Only a qualified specialist can diagnose, and even more so prescribe adequate treatment for this form of the disease.
Causes
The main local cause leading to the occurrence of stomatitis is poor quality or neglect of oral hygiene, which leads to the proliferation of pathogenic flora. The development of the disease is facilitated by the presence of deposits on the teeth, their diseases, and microflora imbalance.
In addition to this reason, there are many others, which are divided into 4 groups:
- Traumatic - damage to the mucous membrane of a mechanical (rough and hard food, sharp objects, tartar, orthodontic construction, chipped tooth), chemical (accidental contact with household chemicals) and thermal (burn with hot liquid or food) nature.
- Infectious – inflammation that develops on the mucous membrane due to the penetration of pathogenic microbes and bacteria accompanying influenza, adenovirus, measles, smallpox, scarlet fever, chickenpox, diphtheria, pneumonia.
- Specific - a lesion that develops against the background of other serious pathologies, such as leprosy, syphilis, tuberculosis.
- Symptomatic – inflammation that manifests itself in general (endocrine, digestive, nervous, cardiovascular) and systemic (pemphigus, streptoderma, immunodeficiency, lichen ruber) pathologies of the body that have passed into the chronic or acute stage.
Knowing the reasons that lead to the occurrence of catarrhal stomatitis, it can be easily prevented.
There are different types of stomatitis; we will be told about its varieties in the following video:
Description
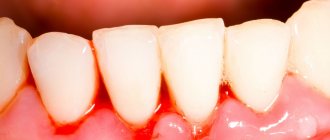
The catarrhal (serous) form of stomatitis is characterized by severe inflammation of the oral mucous tissues and the identification of affected areas on them with the release of serous exudate
. Affected lesions can be localized both over the entire area of the oral cavity and in individual sectors: the inner part of the lips, gums, tongue, palate.
After the first symptoms appear, the disease lasts on average about 10 days. Correctly selected treatment leads to a quick positive result. With poor quality or untimely therapy, the disease often develops into subacute and chronic forms. It can also be accompanied by complications.
The catarrhal form is the most common and easily diagnosed stomatitis.
In order not to confuse this form of stomatitis with others, watch the following video:
Symptoms
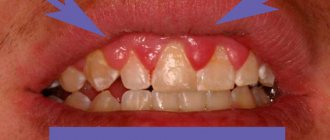
This type of stomatitis differs from all other forms of the disease in that it does not have symptoms characteristic only of it. A clear sign of the onset of the disease is a sharp reddening of the upper epithelial layer of the mucosa and the development of inflammation in it.
Very often in the initial period discomfort and pain appear during conversation and eating.
A doctor can diagnose it during the initial examination of the patient based on the following symptoms:
- increased formation of saliva (at the same time it becomes more viscous, viscous and acquires a grayish tint);
- slight swelling of the mucous membrane;
- temperature;
- bleeding gums;
- a grayish coating found only on areas of inflammation;
- bad breath.
Severe swelling and redness of the gums, the appearance of tooth marks on the mucous membrane, dryness, discoloration of plaque to brown and its spread to the entire surface of the mucous membrane, swelling of the tongue, enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes are signs of stomatitis that has become acute.
Important: if you detect even one of the listed signs of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can differentiate catarrhal stomatitis from other forms of this disease. After a detailed examination of the oral cavity, analysis of all complaints, study of the manifestations of the disease and the patient’s condition, an accurate diagnosis can be made.
If the disease is in an advanced or chronic state, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests:
- mucous membrane - scraping;
- blood - general and biochemical analysis;
- urine - general analysis.
These examinations are necessary to determine the nature of the disease and the patient's health status. If the course of treatment does not lead to positive dynamics, the doctor will prescribe a diagnosis for diseases associated with stomatitis.
Treatment
All therapeutic measures taken are aimed at eliminating the “culprit” of the disease and neutralizing the inflammatory process. In the treatment of stomatitis, 3 directions are used:
- Local anesthesia.
- Use of antiseptic drugs.
- Oral therapy that addresses the root cause of the disease.
In the clinic
The course of treatment in the clinic involves the patient undergoing professional hygienic teeth cleaning in order to remove existing plaque and tartar from their surface. If there are carious cavities in his teeth, the doctor will heal them. Be sure to treat the entire oral mucosa with an antiseptic.
We will tell you in what cases fluoridation of baby teeth in children is necessary in our next article. And in this review you will find a video showing the process of cutting the frenulum under the tongue with a laser.
Medication
The following types of drugs may be prescribed during treatment:
Antiseptics
These are solutions that come in a variety of mouthwash options. Can be assigned:
"Miramistin" is a 0.01% solution of an antiseptic with a wide spectrum of action. It has a pronounced antiviral effect, activates regeneration in affected tissues, prevents the spread of infection, adsorbs purulent exudate without damaging healthy viable tissues. For stomatitis, one rinse will require up to 15 ml of product, the frequency of performing the procedure is up to 4 times.
"Chlorhexidine" is a disinfectant antiseptic solution with a concentration of 0.5%, necessary for disinfecting the mucous membrane. For one application you will need 10 ml of solution, the frequency of rinsing per day is 3 times.
These products can be replaced with inexpensive, but no less effective hydrogen peroxide and aminocaproic acid.
To relieve pain symptoms
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic drug. Its analgesic effect is achieved by blocking sodium channels in nerve fibers and their endings. The analgesic effect usually lasts up to 4-5 hours. For applications, a 10% product, produced in ampoules, is used. For one-time use you will need up to 2 ml.
Benzocaine is a broad-spectrum anesthetic. To reduce pain in dentistry, its 7% paste or 2% oil solution is used. Its duration of action is only 2-3 hours. It is allowed to use no more than 4 times a day.
Important: before you start using these products, you must perform a reaction test, since they show a high degree of allergenicity.
To reduce swelling
"Calcium gluconate" - tablets, they should be crushed before use. Take 2-3 times a day before meals or after an hour and a half. The daily dose of the drug is no more than 9 g.
“Calcium chloride” is a solution for intravenous administration. One injection requires from 0.5 ml to 1.0 ml (depending on the condition). The frequency and duration of use are determined only by the doctor based on the degree of development of the disease and the patient’s condition.
Advice: you cannot delay, let alone ignore, treatment! There is a high risk of the catarrhal form turning into more dangerous types of stomatitis.
Maintenance therapy
Maintenance therapy, which consists in strengthening the immune system, is of great importance in treatment. This is achieved through the right combination of taking vitamins and regulating nutrition. Each patient is recommended to take a complex of vitamins, which necessarily combines A, E, B, C, P.
It is necessary to completely exclude from the diet hot, sour, fried, salty, spicy and cold foods that irritate the organs of the digestive system. Food during this period should be high-calorie and varied.
It must contain meat, milk and milk-based products, and eggs. In order not to irritate the inflamed mucous membrane, food must be ground to a mushy state.
Particular attention should be paid to drinking. During illness, it should be frequent and abundant. Water helps avoid dehydration and reduces intoxication.
Folk remedies
When treating the disease, it is possible to use folk recipes that have pronounced disinfecting and anti-inflammatory effects:
- Rinse with baking soda - dilute 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. soda and 0.5 tsp. hydrogen peroxide. The procedure is performed after meals three times a day.
- Alcohol infusion of propolis - add 1 tsp to 0.5 cups of water. tincture, mix well and use for rinsing 3 times.
- Juice from cabbage and carrots will help cope with swelling. To rinse, the juice is squeezed out of these vegetables and mixed in equal proportions. The procedure is carried out after meals three times a day.
- Decoction of onion peels - pour 100 g of onion peels into 0.5 liters of water and boil for 15 minutes. Then the product is infused for another 6 hours in a warm place. To get results, rinse your mouth for 2 minutes 3 times a day.
It is possible to cope with stomatitis with the help of folk remedies if you start using them at the initial stage of the disease and only after consulting a doctor.
Traditional recipes should not be the only way to treat stomatitis. In order to cope with the disease, they must complement the main drug treatment.
Effective folk methods for treating catarrhal stomatitis
In curing this disease, traditional medicine became widespread. Even ordinary rinsing of the mouth with fairly hot water will help in the fight against the disease. All methods promote rapid regeneration of diseased areas and combat inflammatory processes. If symptoms of an illness are detected, the following folk methods of healing are used:
- First of all, to relieve swelling, you should rinse your mouth with a weak solution of soda and salt.
- Various infusions of medicinal herbs (calendula, St. John's wort, chamomile, sage, etc.) are irreplaceable in use.
- Wounds in the area affected by the disease must be treated with aloe or Kalanchoe juice
- You can give your child yogurt after adding two grated cloves of garlic to it.
- It is worth applying slices of raw potatoes to the site of inflammation, it will help to quickly recover from the disease
With all due respect to these methods of traditional medicine, you should not neglect visits to the doctor. Moreover, the use of folk remedies is appropriate after consultation with a specialist. Without drug treatment, traditional medicine, in this case, makes no sense, and will only worsen the situation.
Possible consequences
With timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. It often happens that the first signs of stomatitis are ignored by a person. Its treatment begins late, when the disease becomes a chronic condition requiring long and serious treatment.
There have been cases where a secondary infection was associated with stomatitis. The result of such a merger is a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition. Children tolerate this “union” much worse.
The presence of infection in the mouth entails the development of diseases of soft tissues and gums: gingivitis, caries, periodontal disease. It is possible for pathogenic microflora to enter the deep layers of tissue, which causes changes in the bone structure.
If stomatitis is not stopped in the initial period, the infection gradually spreads throughout the body, leading to a decrease in its immune defense and the development of sepsis.
Prevention
Timely prevention, carried out to prevent diseases of the teeth and gums, will help prevent the development of catarrhal stomatitis.
The main preventive measures include:
- Regular (at least once a year) visits to the dentist for examination and treatment of identified problems.
- Perform proper oral hygiene procedures (brushing and rinsing) daily.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Treat diseases of internal organs in a timely manner.
- Maintain a balanced and proper diet.
Based on the fact that children under 5 years of age are more susceptible to stomatitis, parents should pay due attention to prevention:
- Disinfect toys, bottles with pacifiers, and objects that the baby comes into contact with.
- Get your child used to brushing their teeth immediately after teething.
- Avoid contact with a child suffering from stomatitis.
- Teach your child to follow the rules of personal hygiene.
We will tell you whether vinylin can be used for stomatitis in infants in a separate review. By clicking on the following link: https://dentist-pro.ru/detskaya-stomatologiya/d-zuby/karies/butylochnyj.html - you can find information about the features of the treatment of bottle caries.
And here you will find out what to do if your child has black plaque on his teeth.
All of these preventive measures are considered standard and are designed to minimize the possibility of developing both stomatitis and many dental diseases.
Differences between aphthous and catarrhal forms
- Catarrhal stomatitis, as already mentioned, is more aggressive. Severe symptoms of intoxication, inflammation, etc. are observed.
- If, with aphthous stomatitis, a few ulcerative defects (aphthae) develop on the surface of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, then the catarrhal form is characterized by massive damage to the entire oral cavity with the formation of inflammation. There are no ulcers.
- Catarrhal stomatitis is characterized by a rise in temperature to subfebrile and febrile levels. The aphthous type of disease almost always occurs without severe hyperthermia, not counting the most difficult cases.
- In children, the catarrhal type is much more common than in adult patients. At the same time, the child’s illness is relatively mild.
Stomatitis of this type is relatively rare, but is highly dangerous to health and life, since it tends to turn into a purulent-necrotic form at the peak of development.