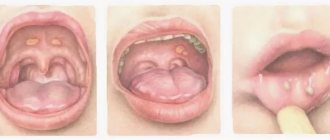
For stomatitis, treatment necessarily includes the use of local antiseptics, which destroy infectious pathogens and suppress the inflammatory process. One such drug is iodinol. It is based on the use of molecular iodine. It has a bactericidal effect. An additional component is polyvinyl alcohol, which increases the duration of tissue contact with iodine. The use of iodinol for stomatitis makes it possible to quickly extinguish the inflammatory reaction and prevent complications.
For what symptoms should I use iodinol?
Iodinol is a universal antiseptic that is used to irrigate the oral mucosa and destroy pathogens. Antiseptic rinsing has a detrimental effect on staphylococci, E. coli, streptococci and pathogenic fungi. Iodinol can be used for any form of stomatitis, except traumatic. Iodine can increase swelling caused by thermal and mechanical stress.
The antiseptic Iodinol is effective even for periodontitis and other diseases of the oral cavity, accompanied by the risk of pathogens spreading to healthy tissue.
The main symptoms for using iodinol for stomatitis:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of tissues;
- formation of ulcerative defects against the background of stomatitis;
- pain in the area of inflammation when chewing food;
- putrid odor from the mouth.
The presence of alcohol reduces the irritating effect of iodinol on the delicate tissues of the oral cavity. But before rinsing stomatitis, it is necessary to determine the causative agent in order to select an effective treatment. The instructions for use provided by the manufacturer provide complete information about the options for using the drug.
It is better not to use iodinol for rinsing in case of childhood stomatitis in the mouth. In a child, the mucous membrane is sensitive and may react with increased inflammation to the use of iodine. To treat childhood stomatitis, it is better to use other antiseptics (miramistin, chlorhexidine), decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile).
Treatment of stomatitis in children
Stomatitis in children is a signal of a decrease in the protective mechanism and it will be difficult to get rid of inflammation only with local drugs. The instructions for use state that Iodinol can be used as a rinse for a child, diluting the drug and preventing its accidental ingestion.
For very young children, it is better to omit rinsing and instead apply to areas of inflammation. Thus, the risk of ingestion is reduced to a minimum, and the effectiveness will only increase.
But the instructions for use also warn that this solution is contraindicated in children with hypersensitivity and dermatosis. Young children may experience a chemical burn or an allergic reaction as a result of using a highly concentrated iodine solution.
In order for Iodinol to be truly useful for treating a child, you need to monitor the dosages, smear it only after preliminary treatment of the mouth, that is, brush your teeth or rinse your mouth with warm water to get rid of food debris and remove soft plaque.
Advice! If a child has thyrotoxicosis, treatment with iodine solutions is strictly prohibited, even if it is a local treatment.
How to dilute iodinol for stomatitis
The drug cannot be used without prior dilution.
A concentrated product can burn the mucous membrane and dramatically worsen the patient’s condition. Iodinol is diluted in water in a ratio of 1:2 before rinsing the mouth. The product is prepared immediately before use. If you have aphthae, you can use iodinol for spot treatment. In this case, the drug is diluted 1:1, applied to a cotton swab and applied to the ulcers for a few seconds.
Iodinol for stomatitis dries out ulcerative areas and inhibits the spread of infection to the tonsils. But the drug in no case replaces other drugs prescribed by a doctor. Treatment should be comprehensive, aimed at both the symptoms and the causes of stomatitis.
Adverse reactions during treatment with Iodinol
Returning to the drug Iodinol, it should be said that the medicine, like any pharmacologically active substance, can have side effects. Undesirable effects are usually associated with individual reactions of the body or improper use of the product. These include:
- skin rashes;
- increased salivation;
- tearfulness;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- sneezing;
- burning and itching at the site of use.
All of the above symptoms may indicate an overdose or “iodism.” Treatment in this case consists of discontinuing the medication and symptomatic therapy. Poisoning can occur if the drug is accidentally ingested, especially in pediatric patients . If the first signs of overdose appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Timely measures taken will help avoid serious complications.
Why does stomatitis develop?
Stomatitis most often occurs in childhood. In a child under 8-10 years of age, the activity of the immune system is reduced. This contributes to the rapid occurrence of inflammatory processes under the influence of unfavorable factors (ARVI, injuries, poor personal hygiene, caries).
In adults, stomatitis occurs less frequently, mainly in people who damage the mucous membrane with dental prostheses and braces. Also, the mucous membrane often becomes inflamed due to overheating by excessively hot dishes and drinks. Strong alcohol also has an aggressive effect on oral tissue and can provoke a local inflammatory process.
Mode of application
You can rinse your mouth and throat with undiluted Iodinol and diluting it with distilled or filtered water. Pure Iodinol is indicated for adults and adolescents over 12 years of age with sore throat, tonsillitis and extensive or ulcerative stomatitis. Rinse is repeated no more than 2 times a day. If you rinse your mouth more often, there will be no special effect, and excess iodine intake into the body is quite possible due to the inevitable accidental ingestion of the solution with saliva.
For catarrhal stomatitis, characterized by the absence of deep erosions, Iodinol is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 1. This concentration is quite sufficient for the planned destruction of pathogens in areas of inflammation.
For stomatitis in children, the instructions for using Iodinol recommend diluting it in a ratio of 1 to 2, and for children - generally 1 to 4 (a stack of the drug per glass of water). If the baby does not yet know how to rinse his mouth, the mucous membranes are treated with a cotton swab dipped in diluted Iodinol. You can make lotions if erosions are localized on the lips, gums, and tongue.
Treatment of stomatitis with Iodinol should not be continued for more than 7–10 days.
Contraindications
The main contraindication to the use of Iodinol and other iodine preparations is hyperthyroidism, excessive secretory function of the thyroid gland. The drug should not be used for tumors and other diseases of this organ.
Iodinol is contraindicated in patients with tuberculosis, because it increases the inflammatory process in the lungs.
Individual intolerance to iodine is observed quite rarely, however, with constant use of antiseptics, iodism can develop - aseptic inflammation of the mucous membranes caused by a complete disruption of the natural balance of microorganisms.
When using undiluted Iodinol, the instructions for use warn of the possibility of chemical burns to the skin and epithelium of the mucous membranes.
Storage of the drug
The aqueous solution of Iodinol should be stored out of the reach of children and in a dark place. The solution must not be frozen.
If Iodinol is accidentally spilled on fabric or wooden surfaces, difficult to remove stains will form. Iodinol must be used with extreme caution.
Price
Iodinol is one of the most affordable antiseptics. A bottle of regular Iodinol for rinsing costs no more than 30 rubles. Iodinol spray is more expensive. For a package of spray with a 50 ml bottle you need to pay about 100 rubles.
Reviews about Iodinol
- I treat it with great respect, and it is always kept in my first aid kit; if I go anywhere, I take it with me. Over the past 15 years, I have discovered unlimited possibilities for treatment with iodinol.
- Doctors hid the truth about this remedy.
- Many years ago I became very ill with a sore throat, I couldn’t even talk. One friend advised me to buy iodinol at the pharmacy and gargle. Two days later I was fine.
- An excellent antiseptic, it really helps a lot with sore throat, chronic tonsillitis and exacerbation.
- Iodinol is a “first aid” in my house; I always have it at hand.
Types of stomatitis
Main types of stomatitis:
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative;
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- Vincent's stomatitis;
- allergic;
- traumatic.
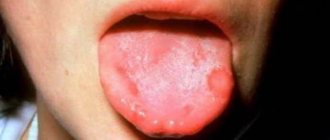
In most patients, inflammation of the oral mucosa begins with catarrhal symptoms. Local swelling appears, the tissues become hyperemic and painful. In adults and children, salivation increases and gums bleed due to stomatitis. If you start treatment in a timely manner and carry out regular antiseptic rinses with iodinol, chlorhexidine or miramistin, complete recovery occurs in a few days.
The ulcerative form of the disease is more severe. In a person, the lymph nodes located in the face and neck become inflamed, body temperature rises, and severe pain occurs. Because of it, appetite almost completely disappears. The patient complains of sharp pain while chewing food. Ulcerative stomatitis is especially acute in young children and people with weakened immune systems.
With aphthous stomatitis, the mucous membrane is covered with single or multiple aphthae. The disease is accompanied by increased body temperature and malaise. The mucous membrane in the area of ulcers is painful, swollen and hyperemic.
When the herpes simplex virus becomes active, herpetic stomatitis develops, treatment of which should begin immediately. The disease occurs mainly in children in closed preschool institutions. The child's temperature rises sharply, he becomes capricious, refuses to eat and complains of pain in the mouth. After a few days, ulcerative defects appear, which can become covered with plaque. Salivation increases. The disease lasts 5-7 days, longer in weakened patients.
Vincent's necrotizing stomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of ulcerative defects on the mucous membrane. Lack of vitamins and decreased local immunity contribute to the development of the disease. During the formation of erosions on the oral mucosa, body temperature rises. Soreness of the gums appears, from which blood may periodically bleed. Breath becomes foul-smelling, which indicates the development of an infectious process.
Allergic and traumatic stomatitis differ in severity and can occur both in the form of a catarrhal inflammatory process and ulcerative-necrotic. Patients complain of dry mouth, itching, and moderate pain. The mucous membrane is red and swollen. With a long course of allergic stomatitis, atrophy of the papillae occurs, local immunity is greatly reduced, and the risk of developing tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other ENT pathologies increases.
Description of the drug
Iodinol is a liquid product with powerful antiseptic properties. Its composition contains molecular iodine, potassium iodide alcohol and purified water. The solution has a deep blue color. When shaking the bottle, bubbles form in it. Polyvinyl alcohol, which is contained in the medicine, is characterized by a delayed therapeutic effect of iodine. Moreover, the medicine itself is absolutely non-toxic. But this does not mean that it can be used in large quantities. Otherwise, it may result in a burn.
Iodinol has a detrimental effect on fungi, bacteria and microbes that lead to the development of stomatitis. If a one-time use of the drug did not have an effect on the microbes, then with repeated sessions a positive effect is guaranteed.
The peculiarity of Iodinol is that it is able to completely cover the affected areas with a protective film. This prevents the subsequent spread of the virus and contributes to its complete elimination. After using the solution, relapses rarely occur, since Iodinol has an effect on aphthae caused by stomatitis for a long time after application.
Useful properties of the drug:
- does not allow pathogenic microbes into the body;
- allowed for young patients over 5 years of age;
- fights various pathologies;
- saturates the body with the necessary amount of iodine;
- contributes to obtaining quick and high-quality results;
- stops inflammation by covering the affected areas;
- prevents harmful microorganisms from multiplying if the oral cavity is not kept clean and hygienic.