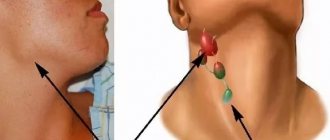
Types of lymph nodes in the neck
There are many groups of nodes in the neck that differ in size, location and protection provided:
- The anterior cervical, which is localized in the jugular part of the neck, is responsible for the condition of the tissues of the throat (posterior wall and tonsils) and the thyroid gland. They can be superficial or deep. The deep cervical lymph nodes cannot be palpated, even if they are inflamed.
- Posterior cervical are located on the back of the head and behind the neck. Inflammation of the occipital nodes can indicate bronchial diseases, as well as meningitis.
- Almond - palpated under the lower jaw and controls, like the anterior cervical, tonsils and the back wall of the throat.
- The submandibular lymph nodes of the neck are located along the lower jaw and become inflamed in the case of infectious dental diseases (periodontal disease, stomatitis, caries, etc.), diseases of the tongue, salivary glands, as well as diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, otitis).
- The lymph node in the neck behind the ear is sometimes classified as a separate group, and sometimes classified as cervical. It is small in size, about the size of a pea, and practically cannot be felt. Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ears may indicate the presence of pathology in the back of the head, in the parietal region.
- The submentals are located under the chin and control the cheeks, lower lip, and teeth.
- The supraclavicular muscles lie in the recess of the collarbones at the base of the neck and are divided into right and left. Controls the lungs, esophagus and heart. Inflammation of this group of lymph nodes in the neck is not a good sign, and often indicates the presence of a serious disease.
Features of the cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are an important organ of the lymphatic system. They are located in a group that includes both superficial and deep lymph nodes. The lymph nodes in the neck react sharply to any colds, upper respiratory tract infections, and inflammation of the ENT organs. Cervical lymph nodes, the location of which allows for palpation on their own, can increase in size and become inflamed due to various pathologies, some of which pose a serious threat to the patient’s life.
Thus, the condition of the lymph nodes of the neck is a kind of marker of the health of the organs located in this area.
This susceptibility to various disorders is associated with the function of the lymph nodes. They are an important part of the immune system. Lymph is cleansed in the lymph nodes, freed from toxins and infectious agents, saturated with useful substances, and then transported into the blood. The lymph nodes produce the main immune cells (lymphocytes), which provide humoral immunity to the whole body, penetrating into the blood with purified lymph. Lymph nodes in the neck, which are located near the most important “gates” for infection (nose, oral cavity), during various infectious processes may not cope with the task assigned to them, as a result, toxic compounds and pathogenic microbes settle in the lymph nodes, disrupting their functioning and causing inflammatory processes.
If the lymph nodes in the neck are inflamed, treatment should begin immediately. Knowledge of the location of these lymph nodes and the symptoms of their inflammation will help you notice the first alarm bell in a timely manner.
Anatomy and functions
Cervical lymph nodes are responsible for processes occurring in the soft tissues of the face and neck, in the mouth, in the ears, so the most common causes of their inflammation can be infectious diseases
The anatomy of the cervical lymph nodes is quite confusing. Each lymph node in the human body is a complex bean-shaped or rounded formation, consisting of two layers and covered with a capsule. Lymph nodes connect to the vessels of the lymphatic system, through which lymph flows into them from nearby organs, and on the other side they have a valve that prevents the reverse outflow of intercellular fluid.
Lymph nodes are located in clusters forming groups. Each group of lymph nodes in one part of the body or near one organ is called regional.
Despite the fact that the location of the lymph nodes is usually symmetrical, it happens that there are more of them on the right than on the left. This is usually observed in areas with a large concentration of lymph nodes, for example, in the groin area or along the mesentery.
There are superficial and deep lymph nodes. The former are located in the subcutaneous fat layer in different parts of the body, the latter are located near vital organs and are hidden by the chest or abdominal cavity. The lymph nodes in the neck are located superficially, that is, shallow under the skin, so they can be felt, which makes it easy to detect their enlargement or inflammation.
The main function of the lymph nodes is to provide lymph flow in the area around the neck. This group of lymph nodes collects lymph from the face, throat, back of the head, neck and supraclavicular region, filters it, saturates it with lymphocytes, and then transports it through the vein located between the collarbones into the circulatory system, ensuring the functioning of the immune system and protecting the body from infections.
Where exactly are the lymph nodes in the neck?
The first thing you need to find out is the location of the lymph nodes in a person’s neck. They are located in groups, with several lymph nodes in each. The following groups are distinguished:
- chin,
- submandibular,
- jugular lymph nodes,
- posterior cervical,
- anterior cervical,
- tonsillar.
An anatomical diagram will help you understand in more detail how the lymph nodes are located in the neck:
Diagram of the location of lymph nodes in the neck
The submental nodes are located directly under the chin. They are distinguished by their small size and deep location, due to which they are not palpable.
The submandibular group of lymph nodes is localized under the lower jaw. These lymph nodes react acutely to diseases of the oral cavity, and can increase in size even against the background of caries. They are small in size, but can grow noticeably in size.
The jugular lymph nodes are located along the jugular vein, in the so-called jugular fossa. This is a small “v” shaped depression located at the bottom of the neck between the collarbones.
The posterior cervical group of lymph nodes, located on the back of the neck, is located on both sides of the vertebrae. The anterior cervical lymph nodes are located near the larynx. These are the largest lymph nodes in the area and are the easiest to palpate.
Tonsillar lymph nodes can be classified as both cervical and facial groups. They are located on the neck, at the corners of the lower jaw. This group of lymph nodes is most vulnerable to diseases of the throat and tonsils.
Having figured out where a person’s lymph nodes are located in the neck, you should know what sizes are considered normal, and in what cases we are talking about a pathology that requires attention.
Dimensions and quantity
Young children often suffer from colds and ARVI, which is always accompanied by enlarged cervical lymph nodes
There has previously been much debate about the normal size of lymph nodes in the neck, but there is no consensus. Size standards are very arbitrary, since normal sizes in adults depend on the physiological characteristics of the body, and in children - on the functioning of the immune system.
The total number of lymph nodes in the neck depends on the characteristics of the body. There can be from 40 to 100.
In general, a lymph node diameter of 1 to 20 mm is considered normal. Moreover, the location of the lymph nodes in the neck largely affects their size. So, the largest are the anterior cervical and tonsillar nodes. Their size in adults can reach 10-15 mm. The smallest cervical lymph nodes are the jugular ones. They are located deep in the subcutaneous fat layer and are therefore difficult to palpate.
The size of the lymph nodes in children is not much different, but quite often, before the age of 3 years, all large lymph nodes are noticeably enlarged. This is due to the peculiarities of the immune system, which in childhood is not yet strong enough to provide full protection for the body. It is because of the imperfection of the immune system that young children so often suffer from colds and ARVI, which is always accompanied by enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
Appearance of healthy tonsils
The healthy state of the tonsils is determined by several parameters:
- They should be medium in size.
- The color of the tonsils should be uniformly pink, without inclusions or furrows.
- The surface has small tubercles and depressions.
- The posterior pharynx is uniform in color and the follicles should not be noticeable.
- When examined with a spoon, no pus is released from the tonsils.
Often the gag reflex does not allow a thorough examination of the patient's throat. Most problems arise when examining tonsils in children due to their refusal to open their mouth wide.
- Choosing the right lighting will help you carefully examine your oral health. A beam of yellow direct light aimed directly at the throat will help give a more accurate picture of the patient's condition.
- During the examination, you can use a teaspoon or a device specially designed for this purpose, purchased at a pharmacy.
- When applying pressure to the tongue, it is important to do this carefully, without causing a gag reflex.
- The patient must breathe through his mouth. This will help make a better inspection.
The symptoms of a sore throat depend on the causes that caused it.
Nevertheless, the main and characteristic features are considered to be:
Other diseases
The main disease of the tonsils is tonsillitis. However, the tonsils can become swollen and inflamed due to other pathologies, including:
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- stomatitis;
- caries;
- staphylococcal infection.
In the case of sinusitis, the tonsils become inflamed due to the entry of infected sinus contents into the throat. Otitis media in general is a consequence of adenoids, but can lead to inflammation of both the tonsils and sinuses.
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. If the disease remains untreated for a long time, the infection can spread to the tonsils.
Advanced caries is a common cause of inflammation of the oral cavity and tonsils. This is due to a general decrease in immunity against the background of a chronic focus of infection, and the subsequent spread of bacteria throughout the nasopharynx.
Treatment
The doctor constantly monitors the process to understand whether there are positive changes in health
Recovery methods are selected according to an individual program, based on the results of diagnostic and laboratory tests.
Treatment also takes into account the underlying cause that contributed to the appearance of characteristic signs of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
The therapeutic effect must be complex - include medication, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and knowledge from traditional medicine.
Drug therapy
Infectious diseases, if they cause enlarged lymph nodes, are treated with special medications - antibacterial and antiviral drugs, which are selected individually for each patient.
It is important to consider the following point - the prescribed antibiotic should be used for at least 14 days to get an effect. The duration of the course is also calculated by the doctor.
If an antiviral drug is present in the treatment program, it should be used from 3 days to 1 week. In this case, the doctor constantly monitors the process to understand whether there are positive changes in the state of health.
If they are not there, the specialist conducts a repeated diagnosis and, if the indicators are correct, changes the drug dosage regimen and dosage. The process of taking medications must be regulated; the course cannot be interrupted without the doctor’s permission.
If the cause of the disease is dental problems, the treatment program includes complete sanitation of the oral cavity. If necessary, treatment of teeth and gums is carried out.
If the therapy is successful, the lymph nodes return to normal, since there is no inflammatory process. No additional specific treatment should be carried out.
The oncological nature of the disease is eliminated by specific treatment - chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Additionally, there are several techniques that help eliminate discomfort and pain. Ointments are used (Vishnevsky, ichthyol). If the presence of a purulent process is noted, then Levomekol is used.
It is recommended to use an iodine mesh, but it can be applied if there are no problems with the endocrine system, and the patient is over 6 years old.
A balm called “Star” helps a lot. It is used exclusively as a complex drug intended to accelerate the healing process. It is important to remember that the drug may cause an allergic reaction.
It is important to remember that any procedures related to warming up should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of specialists.
You also need to remember that in the case of a purulent process, any, especially independent heating, can contribute to the spread of pus to nearby tissues and organs. Warming up can be carried out using physiotherapeutic techniques.
Physiotherapy
If physiotherapeutic procedures are included in the therapeutic effect, then the following procedure options can be prescribed:
- Ultraviolet irradiation - course exposure involves 6-8 procedures. After this, according to indications, the effect can be carried out on the area with the greatest inflammatory process.
- UHF – the procedure takes no more than 15 minutes. Feature - excluded from the treatment program if in the body, in addition to enlarged lymph nodes, there is general intoxication of the body.
- Fluctuarization - the procedure is carried out in a course of 4-5 effects, each lasting 10 minutes.
- Ultrasound – actively reduces the inflammatory process, the mode of exposure is pulsed, the exposure time is 7 minutes. Course impact – 8-10 procedures.
Laser therapy is also used, which helps improve blood flow, which reduces inflammation, relieves pain and accelerates regeneration processes.
Surgical intervention
Surgical interventions are not performed unless indicated. The reason for surgery may be the appearance of pus. During the process, the lesion is opened and the purulent masses are completely removed.
Traditional methods
In 90% of cases, infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs are used in the treatment program. Plants are selected that are able to relieve inflammation and have antiseptic and immune system-strengthening properties.
These include:
- Nettle (flowers).
- Aloe.
- Echinacea.
It is important to remember that traditional medicine cannot be used as the main source of treatment.
Lymph nodes in the neck: which ones and when they increase
Since each group of lymph nodes is responsible for collecting lymph from a certain area of the body, by their enlargement it is possible to determine where the disease process began.
Very simply, we can say that:
- the mental lymph nodes collect lymph from the tongue, teeth and the floor of the mouth;
- submandibular lymph nodes are “responsible” for the bones and soft tissues of the face, as well as for the oral cavity;
- retropharyngeal lymph nodes collect lymph from the pharynx;
- supraclavicular lymph nodes collect lymph from the head, neck, and apexes of the lungs;
- subclavian lymph nodes specialize in diseases of the lungs and upper shoulder girdle;
- the anterior cervical lymph nodes are “responsible” for the tonsils, pharynx and tissues of the neck itself;
- posterior cervical lymph nodes collect lymph from the head and neck;
- The parotid lymph nodes mainly collect lymph from the organ of hearing and nearby tissues.
We invite you to read: Sore gums - what to do at home?
Front
The anterior cervical lymph nodes, which allow the head to tilt and rotate, are located above and below the sternocleidomastoid muscle in front of the internal jugular vein. These are superficial jugular nodes. They are small, but there are many of them. The anterior cervical cleanses the lymph entering the pharynx, throat, tonsils and thyroid gland.
In turn, if you look at the figure, it is clear that among the anterior glands there are groups of preglottic, thyroid, paratracheal and pretracheal. These are deep nodes.
Palpation of the cervical node is difficult, it is impossible to find them, since they are small. In an adult they are smaller than in children.
The lymph node on the left or right side of the neck is inflamed. We need to find out what happened:
- The tonsils are inflamed.
- There was an infection in the oral cavity.
- Bacteria entered the respiratory tract.
The reason could be:
- decreased immunity;
- lack of vitamins;
- freezing of the body;
- long-term stressful situations;
- insect bites;
- inflammation in the ears.
A lump appeared on the front of my neck. Often it is not painful. The anatomy of the appearance of a lump is as follows: depending on the infectious lymph node that first caught the infection, the lump can be in the front, side or under the chin.
The submandibular glands are the first to fight infection of the pharynx, mouth and throat. Changes usually take place at the micro level. The neck remains unchanged. When an infection or viruses enter the gland, the node swells.
The neck can be seen with a lump under the chin. If the lump is on the neck when the glands have returned to normal, then the doctor can answer whether the lymphadenitis has developed into a chronic stage.
Causes
There are many prerequisites for the occurrence of inflammation of lymphoid tissue. Let's focus on the main ones.
- Acute respiratory infection. In the vast majority of cases, the disease is viral in nature, less often bacterial or fungal. It is obvious that the human pharynx is constantly exposed to attacks by foreign microflora. However, inflammation of the tonsils is provoked by a weakened immune system or the absence of antibodies to a particular pathogen in the body.
- Hypothermia. As you know, the height of infectious diseases occurs in the autumn and spring months. It is during this period that pathogenic microorganisms multiply rapidly and acquire resistance. Hypothermia of the body becomes a provoking factor for weakening the immune response from lymphoid organs, such as the lingual and palatine tonsils. That is why drinking cold drinks, being in a draft, and getting wet and cold feet often cause illness.
- The presence of foci of chronic infections. The constant penetration of pathogenic flora from the sinuses or teeth affected by caries into the pharyngeal cavity causes inflammation of the tonsils at the first signs of decreased immunity.
- Congenital or acquired anatomical abnormalities. Such changes in the structure of the nasopharynx interfere with the natural flow of air masses and make breathing difficult. Blood flow in the mucous membranes is disrupted, which causes them to dry out. As a consequence, the impossibility of performing the barrier function and the occurrence of an inflammatory process. Often, anatomical defects require surgical treatment.
Causes of hypertrophy
The tonsils or tonsils perform a protective function in the human body. The organ is located at the intersection of the nasal canals and pharynx, at the base of the tongue (one on each side). The tonsils are palpated from the outer part of the neck (under the jaw), especially if they are very enlarged. Their main function is to prevent infections, harmful bacteria and microorganisms from entering food, water, and air.
With an excessive number of pathogens, the lymphoid tissue cannot cope with its function, becomes inflamed and becomes an independent causative agent of the pathological process, which leads to enlargement of the tonsils. When a child’s tonsils are enlarged, the disease is called chronic tonsillitis or its acute form, in other words, tonsillitis.
Enlarged tonsils in a child are a sign of weakened immunity, dysfunction of the filtering organ, which accumulates pathogenic microbes and gradually becomes inflamed.
Professional treatment
The doctor will conduct an examination and take a swab from the throat to determine the nature of the disease. Then the patient is prescribed antiseptics and symptomatic treatment - immunostimulants, antipyretics, etc. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed.
In the chronic form of the disease, as well as the formation of plugs in the lacunae, sanitation of the tonsils is prescribed - washing the recesses in which plaque accumulates. The procedure can be carried out with a special device or a curved syringe.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Mouth ulcers: causes and methods of treatment
In the chronic form of the disease, physiotherapy is also indicated - UV irradiation, warm compresses and mud applications, UHF therapy. Washing and physiotherapy are prescribed in a course lasting at least 5 procedures. As a rule, the standard course of treatment consists of 10 procedures.
In severe cases, when conservative treatment is ineffective and tonsillitis regularly worsens, the patient may be advised to remove the tonsils.
Indications for removal of tonsils:
- frequent episodes of sore throat - more than 8 times a year;
- the presence of stones in the lacunae;
- tonsil abscess;
- breathing problems due to pathological enlargement of the tonsils.
The operation is also recommended for patients who often experience sore throat and are allergic to antibiotics, which makes treatment ineffective. At the same time, in most cases, regular washing of the lacunae and strengthening the immune system is enough to get rid of the disease over time.
Diagnostics
To determine the type of inflammation of the lymph nodes and find out the causes of its occurrence, you will need to carry out the following diagnostic procedures:
- Study the patient's medical record, conduct an examination and interview.
- Check the condition of the lymph nodes by palpation.
- Take general and biochemical blood tests.
- Conduct an ultrasound of the lymph nodes, CT and MRI of the neck.
- Take a puncture for a biopsy of the affected organ.
One of the ways to diagnose the condition is to perform an ultrasound of the lymph nodes.
Hardware diagnostics are used for damage to the deep cervical lymph nodes. A biopsy is performed in rare cases, if a specific type of inflammation is suspected.
Prevention of inflammation of the lymph nodes
In order to exclude inflammatory processes that occur in lymph tissues, it is necessary:
- promptly treat acute infectious diseases;
- maintain a healthy immune system;
- avoid body hypothermia;
- to harden;
- observe personal hygiene standards;
- use an individual gauze bandage during an epidemic of influenza and other viral infections;
- avoid injury and infection of the lymph nodes.
If all preventive measures are followed, a person reduces the possibility of inflammation of the lymph nodes several times. If you do not know where the lymph nodes are located in the neck, photos of which can be found in a medical reference book, then you can use specialized websites and medical textbooks.
If you have swollen lymph nodes in your neck, be sure to visit your local doctor. In this case, you cannot hesitate, as unpleasant consequences are possible, the treatment and elimination of which can cost a lot of time and money. But, as you know, it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it. Follow preventive measures and lead a healthy lifestyle!
Reasons for the development of inflammation
Damage to the lymph nodes occurs during inflammatory processes, which are based on infection, as well as in a number of non-infectious diseases.
The most significant:
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract (nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx);
- pathology of various parts of the ear;
- diseases of the teeth, soft periodontal tissues, jaw;
- tumor processes;
- disorders in the immune system, autoimmune diseases, allergies;
- venereal diseases;
- infection through damaged skin;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
In addition to infectious processes of staphylococcal and streptococcal nature (inflammation of the tonsils, laryngitis, otitis), so-called childhood infections (chicken pox, mumps or mumps, measles), parasitic infestations (toxoplasmosis, “cat scratch disease”) can cause inflammation of the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) in this area. ).
Neoplasms are accompanied by lymphadenitis, which has a sluggish course and mild manifestations (often there is no pain); one lymph node may be affected. In addition to malignant tumors, the causes may be atheromas, dental cysts, lipomas.
Difference between tonsils and tonsils
The tonsils and tonsils are the same organ. The only difference between them is the area of use of the word. The tonsils are the popular name for the tonsils. And they are an accumulation of lymphoid tissues in the nasopharynx area.
There is a narrow circle of specialists who believe that the tonsils capture only the mucous membrane, and the tonsils also capture the lymphoid membrane. Such differences are not supported by all doctors, so it is not necessary to pay attention to this.
The photo shows plaque on the tonsils.
The question also often arises about what adenoids are and how they relate to the tonsils. If a person is healthy, then he does not have adenoids. This formation is a consequence of an increase in the mucous membrane.
When the adenoids become inflamed, they swell and partially block the nasal passage, which makes it difficult to breathe normally. Sometimes they interfere with the normal perception of sounds. This education brings great inconvenience to a person.
It follows from this that the tonsils are one and the same as the tonsils. And adenoids have their own differences. These are formations that are located on the nasopharyngeal tonsil and interfere with the normal functioning of a person. This is the difference between these tissues of the human body.
Symptoms of tonsil disease
Tonsils are a protective tissue of a person, which contains a huge number of lymphocytes. They are the ones who are able to protect the body from the effects of pathogens that reach people with the air.
They are located on the roof of the throat on the sides of the tongue. The tonsils form the so-called pharyngeal ring. In their shape they are very similar to acorns, only pink. But this is in their normal state.
If the tonsils become inflamed, they change.
The signs that characterize the condition of inflamed tonsils are similar in both adults and children. When examining the patient, the following picture is observed:
- the color of the tonsils changes: from pink it turns into bright red;
- their size increases: when inflamed, the tonsils look not like an acorn, but like a nut;
- tonsils lose their solid structure and become loose;
- cicatricial adhesions form between the palate and tonsils;
- sometimes the tonsils become covered with a yellowish coating;
- ulcers appear on the tonsils, which have an unpleasant odor;
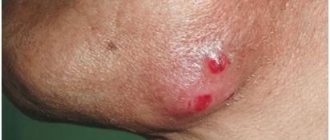
- cervical lymph nodes increase in size and cause discomfort;
Inflammation of the tonsils is accompanied by general symptoms:
- aches throughout the body;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- severe sore throat;
- increase in body temperature.
Inflammation of the tonsils has its own definition in medicine. It is called tonsillitis. This disease can have both acute and chronic forms. The difference between them lies in the severity of the disease and the frequency of inflammation of the tonsils.
We invite you to read Do I need to change fillings in my teeth?
Common pathologies of lymph nodes
It is customary to distinguish between two main pathologies that pose the greatest danger to the body. These include enlargement and inflammation in the nodes. Both violations require attention and a thorough examination in order to identify the provocateur.
The anterior and posterior glands can become swollen and inflamed for a variety of reasons. Only a specialist can determine them. Inflamed groups of nodes differ in characteristic signs.
Reasons to consult a doctor are:
- sudden increase in the size of the lymph nodes;
- pain on palpation;
- discomfort at rest;
- redness of the skin around the formations;
- the formation of ulcers on the skin in the neck area;
- increase in body temperature.
All of the listed symptoms indicate a malfunction of the lymph nodes and the entire immune system. Timely identification of the disease contributes to the rapid normalization of the body’s functionality. Serious pathologies can provoke dangerous consequences. One of them is the formation of a malignant tumor in the lymphatic system.
A common disruption in the functioning of formations is an increase in their size. In medicine, this pathological condition is called lymphadenopathy. According to ICD-10, the disease is designated by code R59, but it is not classified as an independent entity.
Lymphadenopathy is a specific reaction of the lymphatic system to a decrease in the functioning of the immune system due to infection and various inflammatory pathologies. An increase in the size of nodes is an important marker in the diagnosis of lymphoma or laryngeal cancer, as well as tuberculosis.
Lymphadenopathy of the tonsillar and anterior cervical groups is often detected in children under 5 years of age. This is explained by the peculiarities of the functionality of the immune system in this age category. The immunity of infants and older children is imperfect and weak. Children from 3 to 5 years old are prone to infectious pathologies. Lymph nodes become swollen with sinusitis, tonsillitis, and otitis media. They may also swell with diseases such as measles, chickenpox, rubella and mumps, which is a normal reaction of the body.
The main symptoms of lymphadenopathy include:
- swollen lymph node;
- painful sensations on palpation;
- asthenia;
- sweating at night.
Enlargement of size is diagnosed by palpation or visual inspection. If the symptom is pronounced, it is recommended to get tested. Lymph nodes can hurt due to serious pathologies of an acute or chronic nature.
Women and men may be diagnosed with:
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV;
- autoimmune disorders;
- reactions to vaccination;
- ARVI;
- flu;
- malignant tumor.
Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus are types of herpes. In the presence of the latter pathology, the development of infectious mononucleosis is provoked. A feature of the disease is an increase in the size of regional areas in the neck and armpits.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck area can cause infection of the oral cavity. Usually, the provocateur of the enlargement of a certain group is a violation of the functionality of the internal organs that are located near the node.
In the presence of lymphadenopathy of the cervical nodes, the following should be excluded:
- acute and chronic tonsillitis;
- scarlet fever;
- otitis media;
- sinusitis;
- caries;
- stomatitis; fungal infection of the oral cavity;
- cyst and abscess of the jaw.
The pathology itself is not dangerous. Determining the root cause is important. She can be very serious. The disease can be caused by a malignant process in the larynx or lungs. Lymphoma is often diagnosed, which is a malignant degeneration of lymphoid tissue. Also, the enlargement of nodes is provoked by the growth of metastases due to cancer damage to other organs. By examining the lymph nodes, the severity of the pathology can be determined.
A common disease is lymphadenitis, the basis of which is the inflammatory process. The disease can develop on one or both sides. The main provocateur of the pathological process in the neck area of an adult and a child is the entry of an infection into the body. The bacterium can be introduced into the node from the outside, for example, due to mechanical damage to the skin, and can also be transported with the intercellular fluid when nearby organs become infected.
There is a misconception that the inflammatory process in the neck area is caused by prolonged exposure to a draft or hypothermia of the body. The trigger for swelling is always an infection, so if signs appear after hypothermia, it is necessary to establish the source of inflammation from which the microbes entered the lymph node.
A nonspecific inflammatory process can be triggered by the following pathologies:
- Infection caused by toxoplasmosis. Infection occurs through meat products that have not undergone proper processing. It also occurs upon contact with animal waste or when hygiene rules are violated during excavation work.
- Infections of dental tissues. Infection is caused by deep caries, damage to bones and soft structures, and mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. In this case, sharp pain, swelling, unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth occur.
- Suppuration of the palatine tonsils. The pathology causes an increase in body temperature. Swallowing saliva or food is painful for a sick person. Drying of the oral cavity is provoked.
- ARVI. Accompanied by cough, nasal discharge, asthenia. In this case, the inflammatory process covers a number of nodes in the neck area.
- Allergic reaction to external irritants. The pathological process is accompanied by signs characteristic of colds.
Enlarged lymph nodes are caused by several dozen diseases. To identify the root cause, you should undergo tests and consult a specialist.
Degrees of tonsil enlargement
There are four stages of inflammation:
- The first stage is characterized by an increase in the tonsils by 1/3 of the space located at the edges of the anterior arch of the palate and the vomer (middle of the pharynx). The symptoms of this stage are not very developed. During the day, the child breathes normally, but at night some disturbances can be noticed: snoring and breathing through an open mouth.
- The second degree of inflammation is characterized by the enlarged tonsils covering ½ of the vomer. Breathing dysfunction becomes more noticeable.
- At the third stage, the vomer is almost completely covered by the tonsil. The child complains of discomfort during swallowing. He's not breathing well.
- The last, fourth degree, is characterized by complete closure of the pharynx, when the tonsils become greatly enlarged.
Every stage is dangerous. Firstly, the tonsils quickly enlarge with a constant source of infection. Secondly, inflammation develops at a rapid pace and can spread to nearby organs and enter the bloodstream, which spreads the infection throughout the body in a short time. Therefore, it is better to start treatment at an early stage. Otherwise, irreparable changes will occur in the child’s still undeveloped facial skeleton and body systems:
- incorrect jaw bite;
- underdevelopment of the chest;
- anemia;
- mental retardation.
Types of lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis occurs when one or more lymph nodes become inflamed. Pathology can often be accompanied by the discharge of pus. Today there are several types of the disease, the list of which includes:
- Acute lymphadenitis. The development of the disease begins suddenly. This often happens after surgery or wound suppuration.
- Chronic. Occurs as a result of a prolonged course of infection in the body or progression of the oncological process.
- Recurrent. A type of disease can develop due to chronic inflammation.
Lymphadenitis is also classified according to etiology. There are specific and nonspecific diseases. In the first case, it appears when the pathogens of toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis or syphilis spread throughout the body. In the second case, inflammation is caused by bacteria or fungi.
The nature of inflammation also influences the classification of the disease. A person may experience purulent lymphadenitis. In this case, the topology is accompanied by severe pain and general difficulty. If a person develops serous lymphadenitis, the clinical picture may be blurred. This is possible with viral diseases and oncology.
Tonsillitis
When the disease occurs, the tonsils become covered with a white coating.
Sore throat, or tonsillitis, is the most common disease of the tonsils. It occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. In the vast majority of cases, the disease is associated with infection of the tonsils by pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria due to decreased immunity. Children suffer from this disease more often than adults.
Typical symptoms (for acute form):
- sore throat when swallowing;
- temperature increase;
- general malaise;
- redness, enlargement and swelling of the tonsils;
- light plaque on the tonsils.
Having figured out what healthy tonsils look like and knowing that children are susceptible to tonsillitis, every parent will be able to promptly detect the disease in their child.
The chronic form of tonsillitis has more mild symptoms. Plaque and plugs in the lacunae can be observed constantly, but acute pain appears when immunity decreases.
The problem with tonsillitis is that it quickly becomes chronic, which is difficult to treat. Sometimes you have to take radical measures - surgical removal of the tonsils.
How to treat tonsil diseases?
First, you need to figure out why the tonsil may become inflamed on one side. It is best to consult a doctor. The otolaryngologist will examine the patient, prescribe additional examinations, if necessary, and select treatment.
Quite often, swollen tonsils or an inflamed tonsil on one side are only a complication of another disease. Gargling or washing the tonsils in this case will only have a temporary effect if the cause of the disease is not eliminated.
Gargling
How to treat a throat if the tonsil hurts on one side - it depends on the accompanying symptoms. It is recommended to start by rinsing with antiseptic agents. If the cause is a bacterial infection of the tonsils, rinsing will help eliminate pathogenic bacteria, and thereby reduce pain and swelling. In cases where pain is associated with injury to the tonsil, rinsing will reduce the risk of secondary infection and speed up the recovery of damaged tissue. For treatment, you can use both pharmaceutical and folk remedies.
- Sea salt. The simplest and most affordable remedy that you can probably find at home, or at least in the nearest supermarket. Salt rinses are recommended for moderate pain, including tonsil injuries. To prepare the solution, dissolve a teaspoon of the product in a glass of water.
- Soda with salt. Another simple remedy, the so-called first aid for a sore throat. To prepare the solution, mix a teaspoon of baking soda and salt in a glass of water. The water should be at a comfortable temperature, about 37 degrees.
- Iodine solution. This remedy has proven itself excellent for stomatitis on the tonsils and tonsillitis. To prepare the solution, mix 5 drops of iodine in a glass of water and gargle thoroughly.
- Chlorophyllipt. Another effective gargle. Used for tonsillitis and pharyngitis. The product is concentrated, diluted with water in proportions of 1 to 5.
- Among folk remedies, you should pay attention to decoctions of chamomile, sage, and calendula. To prepare the solution, pour 1 large spoon of dried raw material into 500 ml of water and cook for 15 minutes. Then cool and use to gargle.
If the tonsil hurts on one side, treatment should be comprehensive. So, you need to gargle at least three times a day. Additionally, you can use various lollipops for tonsillitis and pharyngitis. Unilateral tonsillitis, or inflammation of the tonsil on one side, is treated with Strepsils, Septefril, Hexoral.
To prevent the gland, which is inflamed due to injury, from becoming infected, you can lubricate the damaged area with Lugol's solution.
Compresses
It is strictly not recommended to apply compresses to the throat at very high temperatures.
Compresses help bring down the temperature, but are generally useless for the throat. If your body temperature has risen to 38 degrees, you can put a cool compress on your forehead. At temperatures above 39 degrees, vodka compresses and rubbing are effective.
Traditional medicine suggests placing compresses directly on the neck. However, this method has many contraindications:
- purulent inflammation of the tonsils,
- heat,
- enlargement or inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
To reduce pain when swallowing, make compresses from warm crushed potatoes, vinegar solution, and vodka. Such remedies help reduce swelling of the tonsils.
Inhalations
To combat the pain inherent in enlarged tonsils, inhalations can be used. This method has proven itself well in the fight against colds, but is ineffective against tonsillitis or pharyngitis. At the same time, inhalations will prevent a sore throat if one (right or left) tonsil is injured, and also strengthen the immune system and prevent infection.
For inhalation you can use:
- drug Pinosol,
- Chlorophyllipt,
- natural pine essential oil (3 drops per liter of water),
- steam from boiled potatoes.
Inhaling warm steam helps relieve cold symptoms and is effective if sinusitis is the cause of swollen tonsils on one side.
Note! The simplest and most affordable inhaler is the Zvezdochka pencil, containing essential oils of mint, eucalyptus, and camphor. The product can be purchased at any pharmacy at an affordable price.
Inhalations are prohibited at high temperatures.
General therapy
If a person has a swollen tonsil on one side, what to do with this symptom will depend on other signs. In the case of a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotic tablets. Such drugs cannot be taken independently, without a prescription.
For viral diseases, special immunomodulators are prescribed. Immune medications may be recommended for a speedy recovery. As a folk remedy, you can take tincture of echinacea or propolis.
For severe tonsillitis, the doctor may recommend rinsing the lacunae of the tonsils. This procedure is carried out in case of accumulation of purulent masses in the tonsils and the formation of plugs.
Eagle-Sterling syndrome is treated with novocaine blockades, glucocorticosteroids or surgery if conservative therapy is ineffective. In this case, only a doctor selects a treatment regimen; self-medication can be harmful to health.
Detoxification
Rosehip tea helps a lot
In infectious diseases, intoxication of the body is observed. At high temperatures, a person loses a lot of fluid through sweat, and dehydration occurs. Due to the inflammatory process, weakness and nausea are observed. In such cases, detoxification therapy is necessary. It is carried out either with special mineral-containing solutions (Regidron, Regidron Bio), or by increasing the consumption of pure liquid.
Decoctions of medicinal herbs with a diuretic effect will also come to the rescue. Traditional medicine advises drinking a rosehip decoction, which not only removes toxins, but also strengthens the immune system due to its high vitamin C content. Herbal teas (chamomile, mint, lemon balm) and a decoction of lingonberry leaves are also useful.
Drinking plenty of fluids when sick
If a tonsil that is swollen on one side is the result of a bacterial infection, for example, with tonsillitis, you must follow several recommendations regarding drinking regime and diet. Doctors recommend increasing the amount of fluid you drink to speed up recovery. Recommended to drink:
- clean water at a comfortable temperature,
- herbal teas,
- fruit drinks and compotes,
- warm milk with honey.
Milk reduces discomfort in the throat and eliminates the sore throat characteristic of pharyngitis. It is recommended to drink at least two liters of clean water per day. It is better to drink half a glass every 20-40 minutes.
Having figured out what to do if the tonsil is swollen on one side, you should pay attention to nutrition. It is necessary to remove from the diet any solid food that can irritate the tonsils. Is it recommended to increase your intake of fruits and vegetables, is it better to puree them or drink them fresh?
Tubal tonsils
Another paired organ is the tubal tonsils. They are located on the lateral walls of the nasopharynx. These are small formations of lymphoid tissue, “hidden” in the pharyngeal recesses on the right and left.
Tubal tonsils can become enlarged and inflamed in response to infection. Swelling of this organ leads to breathing problems and can cause otitis and sinusitis.
This organ is located in the center of the upper nasopharynx. It can become inflamed and swollen, leading to breathing problems and wheezing. Pathological enlargement of this organ causes otitis media and sinusitis. Most often the problem occurs in young children. Enlargement of this tonsil is called adenoids. Starting from adolescence, the organ decreases in size.