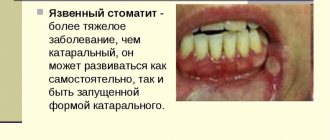
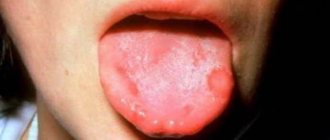
Description of ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis
This disease refers to infection with a spindle-shaped rod or spirochete, which is called Vincent. World medical dictionaries describe the disease under terms such as trench mouth, sore throat and stomatitis with the presence of various types of ulcers. If the bacterium affects the gums, then doctors interpret the diagnosis as Vincent gingivitis. In practice, there are situations when the infection affects several parts of the human body. For example, the palatine tonsils may be affected, and then this disease is called Vincent's angina.
Differential diagnosis of ulcerative stomatitis
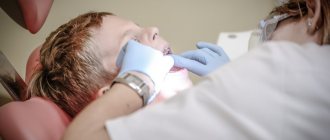
The clinical picture of ulcerative stomatitis is so characteristic that making an accurate diagnosis is not difficult. Diagnosis is based on anamnesis and visual examination of the patient. When examining the oral cavity, it is customary to evaluate the condition of the mucous membrane, the hygiene index, the nature of ulcerations, as well as local factors that can act as irritants.
It is mandatory to take a scraping from the oral cavity, and the following studies are carried out, which have important diagnostic value:
- PCR - research;
- microbiological studies;
- cytological studies, etc.
Differential diagnosis with symptomatic stomatitis is required. For this purpose, various studies are carried out to help establish the patient’s immune status, identify hormonal imbalances, endocrinological disorders or diabetes mellitus. In order to diagnose concomitant pathologies, the patient may need consultations with a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, allergist, immunologist, etc.
Causes of infection
The main cause of the disease is resident flora. It is this that causes Vincent’s stomatitis in most people. Microorganisms are found in the oral cavity of every person, but there is a maximum permissible limit. Exceeding the optimal number of bacteria is observed when the rules of caring for teeth and gums are violated. Unsanitary conditions contribute to the proliferation of infectious microbes, which cause necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis. We have looked at the most common cause of painful symptoms, however, there are also the following pathogens:
- Borrelia or Fusobacterium infection
— these microorganisms appear when a person’s immunity and ability to resist infections decrease. You can get stomatitis if you are frozen, have a cold, or are regularly overworked and in stressful situations. As you can see, this type of bacteria can multiply for many reasons;
- damage to the oral cavity, trauma, improper hygiene care
— if the integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised, then optimal microflora conditions are created for bacterial invasion. Very often observed in patients who have experienced periodontitis. The second reason for the manifestation of Vincent symptoms can be careless oral hygiene. So, if there are wounds or cracks, they become clogged, which leads to the development of infectious bacteria;
- complications of viral infection
— if stomatitis is not treated in time, treatment in adults or children may result in serious health complications. As a final result, the disease will move to a new level of danger, for example, leukemia, scorbuta, syphilide and others will form.
Systemic treatment
An acute period of inflammation implies strict adherence to bed rest. In severe cases of the disease, additional systemic treatment is prescribed. In particular, antibiotic therapy is used. For this, the following drugs are prescribed:
- "Metronidazole";
- "Trichopolus";
- "Flagyl";
- "Klion".
In addition, broad-spectrum antibiotics may be prescribed, such as:
- "Sumamed";
- "Levomycetin";
- "Rulid."
Additionally, antihistamines and vitamin complexes may be prescribed. With properly selected therapy for adults, normalization of well-being is observed approximately 1-2 days after the onset of the disease. With a mild form of stomatitis and satisfactory condition of the oral cavity, healing of ulcers occurs in approximately 3-6 days. In some cases, surgical treatment of the affected area of the mucosa may be required - removal of necrotic tissue. In addition, affected teeth may be removed. In this case, constant irrigation with anesthetics and antiseptics is carried out. Treatment can also be supplemented with traditional therapy, but this requires prior consultation with a doctor.
Timely treatment always guarantees a positive result. The doctor must keep a protocol for the treatment of Vincent’s ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis, as this will allow him to determine the correctness of the therapy.
In the absence of proper, timely therapy, the disease can lead to very serious complications, in particular, bone destruction, the development of osteomyelitis, periodontitis, and tooth loss. With irrational therapy, inflammation can last for several months. Relapses are also possible.
Types of stomatitis for treatment
There are four levels of classification of the disease, each of which has its own subtypes. To determine treatment methods, you must know the correct diagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the types of Vincent’s infectious disease:
- In the division regarding the nature of the course of the disease, acute, subacute, chronic ulcerative-necrotic degrees and relapse are distinguished.
- Regarding the complexity of the disease, stomatitis is mild, moderate and severe.
Each type manifests itself in different symptoms, so in the next section we will look at what the patient feels at each stage of the disease.
The main symptoms of stomatitis in adults
The main symptoms should be considered at different stages of the disease. It is worth noting that the disease progresses and becomes more pronounced over time. When affected by an infection, a person begins to feel weak, he regularly has headaches, there is an increase in temperature and brittleness in the joints. The patient may notice blood on the gums, feel burning and drying of the oral mucosa. Such symptoms torment a person for several hours, and sometimes for several days.
When examined by a doctor, the stage of stomatitis, symptoms and treatment are described. In this case, the optimal course for the stage of the disease is selected. The disease progresses and gradually all its manifestations intensify. The person’s general condition becomes weaker, headaches become more frequent and severe, which affects performance. Over time, the patient feels a sharp pain even with slight contact with the tongue. Brush your teeth
and it becomes more and more difficult to eat, as sharp convulsive bursts of pain occur. At the same time, the patient notices increased secretion of saliva, and also an unpleasant smell of rot from the oral cavity. If a wisdom tooth becomes infected, the ability to open the mouth decreases. This phenomenon in medicine is called trismus.
Some facts about the symptoms of the disease at different stages:
- the first manifestations of the disease are pain in areas of damaged teeth and damaged gums;
- Mild stomatitis is characterized by a limited spread process. At an early stage, only certain types of teeth are affected. The general condition of a person does not undergo significant changes, so performance does not suffer either;
- Severe stomatitis occurs with a body temperature of up to 40 degrees. At the same time, the person feels very bad. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is especially severely affected. In some situations, the infection affects muscle mass and bones. If you do not seek help from a hospital in time, complications of the disease can lead to melting of the jaw bones. You can easily see the image of stomatitis in the photo, the treatment that was started;
- if the infection gets to the site of the palate or tonsil, then this disease belongs to the category of angina ailments;
- in the acute form of stomatitis, the disease can progress to the chronic stage.
- Males are most often susceptible to infection at a young age, namely from 17 to 30 years. The season of exacerbation of the disease is observed in the autumn.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear gradually:
- first there is weakness, high body temperature, headache, weakness, cracking in the joints, bleeding gums, dryness and burning of the mucous membrane. The duration of the stage varies from several hours to several days, it all depends on the form of the disease;
- As stomatitis develops, general weakness accumulates, body temperature rises, capacity decreases, and headaches intensify. Pain in the oral cavity increases from a light touch, the tongue becomes numb and stiff. Difficulties arise when eating and brushing teeth, up to complete impossibility, salivation increases, and a strong putrid odor appears from the mouth. Inflammatory processes in the area of wisdom teeth are accompanied by difficulty opening the mouth (trismus);
- damage to the mucous membrane spreads from the gums and areas where local irritant factors are observed: broken teeth, tartar, dental crowns that injure the gums;
- the process is accompanied by pain, redness, loosening, swelling of the gums , which begin to bleed for no reason;
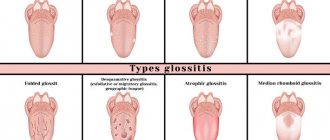
Find out about candidal glossitis on the tongue here.
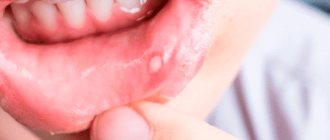
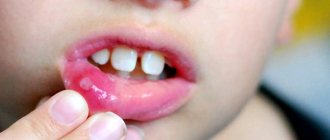
- necrosis affects the tops of the interdental nipples, spreads over the entire surface of the gums , over time the gum tissue becomes covered with a coating of white-gray, yellow or gray-brown shades;
- the mild stage is characterized by a weak prevalence of the process , most often the death of the apex of tissues in one group of teeth is observed, the general condition does not change, the capacity is preserved;
- at a severe stage, body temperature can rise to 38.5-40°C , a sharp deterioration in general health occurs, and ulceration appears over a large area of the mucous membrane. Ulcers can reach muscle tissue, bones, tendons, and alveolar ridge. This course of the disease can lead to the development of osteomyelitis of the infected area of the jaw, the disease is accompanied by destruction of bone tissue;
- when the lesion spreads to the tonsils and palate, stomatitis transforms into Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent angina;
- If the acute form of stomatitis is not treated sufficiently, it can recur and become chronic. This phenomenon is often observed against the background of pathologies of the oral cavity and in chronic somatic pathologies.
In some cases, there is pronounced facial asymmetry resulting from tissue swelling. In severe cases, necrosis affects the soft and hard palate, the lateral surface of the tongue. The formation has soft edges of irregular shape, a dense plaque has a blue-green tint, and after its removal a loose, bleeding bottom is formed. Processes on the hard palate quickly provoke necrosis of all layers of the mucosa, and as a result, bone tissue is exposed.
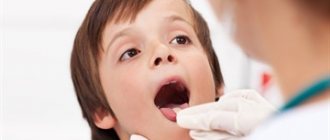
Diagnosis of stomatitis in children for treatment
As we said earlier, young men and young children under 3 years of age are most often affected by the disease. Diagnosing the disease is only possible in a clinical setting. When analyzing, they try to find symbiotic organisms. If their presence is detected, then a course of treatment is prescribed. It is especially important to timely diagnose the presence of infection in young children, since their bodies are still weak to resist infection.
If stomatitis turns into a sore throat, then it is necessary to take an analysis of a sample from the surface of the necrosis or a deeper layer, in case of a complicated form. It is worth noting that Vincent’s illness very often accompanies other dangerous diseases, including HIV, leukemia, syphilis, gingivitis, scorbuta and others. It is for this reason that the examination often includes procedures to screen out the above diseases. When stomatitis is detected in children, treatment is prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment methods for stomatitis
In order to successfully get rid of the disease, it is best to perform sanitation of the oral cavity. After eliminating the pain, doctors can begin to remove ulcers and unwanted deposits. In practice, a course of antibiotics is most often prescribed. So, an adult should drink about 4-5 tablets a day; for a child this norm is reduced to one. Also effective methods of treating the disease include:
- antiseptic substances
- it is recommended to rinse your mouth with them at least 4 times a day; - trichopolum
- for optimal treatment, it is enough to take half a gram per day; - antihistamine therapy
- this method helps to suppress microbial sensitization; - in the vitamin complex
- to maintain the tone of the body, as well as strengthen it, it is recommended to consume vitamin C at least one and a half grams per day; - keratoplastic ointment
- it is used to lyse infectious plaque.
Local treatment
Local treatment of Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis involves the removal of necrotic tissue and the use of stimulating epithelial restoration processes. Partial sanitation of the oral cavity is performed even during the acute period of the disease. Anesthesia is first required by using local applications with solutions of Lidocaine, Anestezin or Trimecaine.
The dentist then carefully removes existing plaque and tartar. Teeth with caries are treated with antiseptic agents. This entire process is carried out after the ulcers are completely cleansed.
Proteolytic enzymes are used to clean the ulcer surface. The oral cavity is treated every day with antiseptic solutions, as well as antimicrobial agents. To speed up the healing of ulcers in adults, local applications are used.