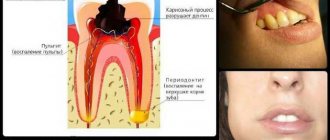
What does a white coating on the tongue indicate?
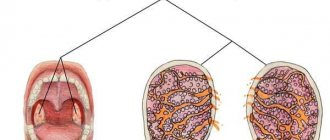
Normally, the mucous membrane of an adult’s tongue should be moderately moist and have a soft pink color. A thin layer of light plaque may form, which can be easily removed with a scraper or the back of a toothbrush.
The cause of development is a disruption of the natural process of keratinization of the smallest cells in the papillae of the tongue. It is difficult to get rid of plaque formation. If you brush it with a toothbrush, it will form again after a while.
The disease may occur without any symptoms. But when a thick, white layer coats your tongue, you should not delay seeing a doctor. Every person should understand that problematic changes in most variants become provocateurs for the development of serious complications. Delayed therapy can cause complications.
More often, the formation of white formations is associated with various disorders of the digestive system. The same defect may also indicate the introduction of a viral or bacterial infection into the body. Plaque is often formed due to non-compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene.
Oral soft tissue injuries in cats.
Mouth injuries can cause severe inflammation but are usually treatable.
Cheek bite.
A wound on the inside of the cheek can be caused by the cat itself while chewing food. To prevent the injury from worsening, “extra” cheek tissue is surgically removed.
Mouth burn in cats.
There are thermal, chemical and electrical burns of the mouth. In the case of a burn, the cat must be examined for damage to other organs of the body, which in some cases can be life-threatening. Cats with burns in the mouth exhibit “hesitation” when trying to eat or drink, may drool, and resist examination of the mouth.
Inflammations and wounds may appear in the mouth, which can easily become infected. If the burn occurred in front of your eyes, tell your doctor all the details. If the burn causes only redness, without tissue damage, treatment will consist of a diet of soft or liquid food until the condition returns to normal.
Mouth burn in cats.
Classification of white plaque
Pathological changes are classified according to the specific color, as well as the location.
Nuances that are important to consider:
- how long does it persist (plaque continues to cover the mucous membrane for a day or longer);
- time of formation (morning, afternoon or late afternoon);
- the presence of a specific odor.
Other signs:
- the appearance of an unpleasant bitter or sour taste or characteristic odor;
- changes in the characteristics of the tongue - it swells, changes its normal size;
- viscous, thick saliva is formed;
- the surface of the organ changes - it becomes dry, loose, heterogeneous, small cracks or wounds appear on it;
- itching begins, pain appears, the tongue often burns or stings, and the organ may also become numb;
- the ability to sense tastes is lost;
- constant dryness appears.
A common occurrence is the simultaneous formation of other defects: pimples, small ulcers, red spots or rashes, liquid blisters.
When assessing the severity of the disease, it is important to consider the area of distribution:
- middle of the organ - gastrointestinal pathologies;
- at the root - problems with intestinal functionality;
- ending - heart disease;
- along the edges - pathologies of the spleen or liver;
- area near the throat - inflammation of the pancreas;
- on the palate - a fungal infection;
- plaque on the tongue, as well as on other areas of the mucous membrane - sore throat.
Plaque does not always have a rich white color. Its tint range may contain greenish, yellowish, light brown or grayish shades.
The plaque can be light, small and quickly removed, dense and unevenly distributed, and also have a cottage cheese-like structure.
Forms of the disease
A severe form of the disease is the plasmacytic-lymphocytic form . It is caused by various viruses - rhinotracheitis, panleukopenia, hyperreaction of the immune system. This form has complications. The gums begin to bleed and swell. Without treatment, complications develop.
The dental form of the disease is accompanied by sore gums, bleeding and swelling. Diseased tissues become bluish in color. The submandibular lymph nodes begin to swell. Unlike the plasmacytic form, the disease is caused not by a virus, but by accumulated plaque. The dental form is treated faster and rarely causes complications.
Juvenile gingivitis is a form of the disease characteristic of cats under the age of 1.5 years, also called “juvenile” gingivitis. Inflammation of the gums and pharynx occurs immediately after the eruption of permanent teeth. If left untreated, periodontitis may develop.
Reasons for formation
Often, a white coating on the tongue becomes a temporary defect and disappears on its own after a couple of hours or after a few days. But you cannot be inattentive to the formation of an unpleasant defect.
Doctors often associate the formation of a defect with disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Also, in addition to changes in the shade of the tongue, patients also exhibit other deviations.
Gastritis in the acute stage
The disease is diagnosed in people of different ages. Symptoms include heartburn, periodic acute pain in the abdomen, periodic or constant nausea, unbearable dry mouth.
With an exacerbation of the disease, a plaque with the presence of gray shades is formed. It spreads along the edges of the organ, but the root remains clean.
An accompanying symptom of the pathology is a specific smell from the mouth.
Chronic gastritis
The signs of the disease are similar to those of the disease described above, but for the patient they occur in a less intense form. In the chronic form, patients notice that they are often bothered by belching and discomfort after eating.
The plaque with this disease acquires a yellowish tint. The taste buds of the tongue often become enlarged and cause noticeable discomfort to the patient. Reddish spots that cover the oral mucosa also become a frequent occurrence during exacerbation of pathology.
Ulcer
Very serious pathologies that can cause serious complications. Symptoms of an ulcer include cutting pain in the middle of the abdomen, constant nausea, and a feeling of heaviness. The intensity of pain may decrease after eating, or, on the contrary, may increase.
It is not uncommon for ulcers to experience bleeding, which is very dangerous due to complications.
Plaque is located on the root of the organ. The color of the formation becomes gray, and the structure becomes thick. It is not possible to clean the tongue on your own, since the formation is tightly attached to the papillae.
Pancreatitis in the acute stage
The disease is associated with an inflammatory process developing in the pancreas. Symptoms of the pathology include loss of sensitivity, dry mouth, and pain in the left rib area.
Plaque in acute pancreatitis has a yellowish tint.
Chronic pancreatitis
The symptoms are not as pronounced as in the previous case. The formation of defects is a consequence of the development of candidiasis, also due to disruption of metabolic processes due to a deficiency of fortified components.
Oncological processes in the stomach
Symptoms of a serious illness include physical weakness and apathy, sudden weight loss, and the appearance of sharp and prolonged pain in the abdominal area.
In oncology, the formation envelops the tongue with a rich white layer that has a dense structure.
Dysbacteriosis
In patients, the tongue is covered with a white coating. In a mild form, the defect has a white and uniform structure; in a severe form, it becomes yellowish.
The plaque is characterized by a light structure; it can be easily removed from the tongue. But after some time after removal it appears again.
Plaque due to dysbacteriosis predominantly forms in the left region of the organ. It can cover the surface of the organ so heavily that it is impossible to visually detect taste buds under the thick and dense layer.
Poisoning
Vomiting is a common symptom of poisoning. The patient is also concerned about constant nausea and stool upset. In complex forms of poisoning, a person’s body temperature rises, severe pain in the stomach appears, and signs of intoxication of the body appear.
A white coating on the tongue due to food poisoning is not uncommon. It forms on the mucous membrane of the organ. In case of digestive disorders, a specific odor from the mouth is formed.
If poisoning was caused by exposure to toxic or harmful substances on the body, then erosions, ulcers and cracks additionally form in the oral cavity.
Not only pathologies of the digestive system provoke the appearance of a defect. Other root causes of the formation of an unpleasant formation are:
- colds in a complicated form (a defect of a rich yellow tint covers the entire surface of the tongue);
- syphilis (a white defect with the presence of grayish inclusions forms at the root of the organ and on the upper back wall of the throat);
- HIV infection (white formation, simultaneous presence of painful cracks);
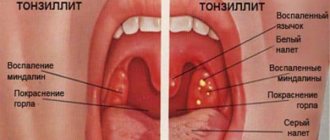
- tonsillitis (a dense white defect forms at the root);
- scarlet fever (white formation, it spreads over the entire surface of the mucous membrane);
- gonorrhea (yellow-white defect + purulent ulcers);
- pharyngitis (a white defect forms on the back wall of the throat, the mucous membrane of the tongue);
- sore throat (covers the oral mucosa with a thick layer of rich white formation);
- candidiasis (the defect is dense and thick, has a rich white structure similar to granular cottage cheese);
- galvanic stomatitis (white defect with a heterogeneous structure + pimples and ulcers on the tongue).
A layer of white formation can form as a result of dental diseases. Such formations are not always provoked by various pathological phenomena. A white coating on the tongue can form after taking medications, as well as as a result of eating certain foods (fermented milk foods, sweets).
Non-pathological reasons for formation:
- individual sensitivity to toothpaste components;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene;
- harmful addiction (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
Language and symptoms
- anxiety
- shortness of breath, rapid breathing
- abdominal breathing (the cat “breathes with its belly”) with its mouth open
- cyanosis, that is, blueness of the mucous membranes - the tongue and gums are blue (in normal condition - from pale pink to pink), sometimes blueness of the skin is noticeable
- first, adopting a pose with widely spaced limbs (an attempt to enlarge the chest), then a lying lateral position
- coughing up fluid (sometimes)
- wheezing in breathing
Edema, depending on the cause, can be cardiogenic or non-cardiogenic.
First of all, no stress(!), the cat should not worry, it needs peace. You should not try to force her to sleep, feed her or give her water. You should take your pet to a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment of pulmonary edema largely depends on the severity and the cause that caused it. The main methods used are diuretics (diuretics) and oxygen therapy. Then, after the condition has stabilized, the disorders that led to the swelling are treated.
To provide the animal with oxygen, it is placed in a special chamber or allowed to breathe oxygen using an oxygen pillow and mask, sometimes artificial ventilation or surgery is used.
Simultaneously with the provision of first aid, the underlying disease is diagnosed: an X-ray, general and biochemical blood tests and other studies are taken.
The condition of pulmonary edema requires constant monitoring (listening, monitoring heart function, blood composition, color of mucous membranes), the use of oxygen therapy and intensive anti-edematous therapy with diuretics, the use of painkillers, cardiac medications, etc., if necessary. Therefore, it is more advisable to place a pet diagnosed with pulmonary edema in inpatient veterinary clinic.
Unfortunately, the body of cats, like other animals that live on land, is not adapted to do without oxygen, so its lack is life-threatening. If your cat has breathing problems, a visit to the doctor cannot be postponed! Often the animal requires emergency assistance with minutes counting down!
Although cats are speechless, a pet's language can tell a lot about her health. For example, a cat’s white tongue, covered with plaque, indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract, intoxication, fever, and constipation. If the tongue itself turns pale, shock, anemia, vascular disorders, heart disease, and hypothermia are suspected. Yellow plaque - check the kidneys and liver. Grayish, brownish - lungs, intestines, stomach.
An ulcer on a cat's tongue can form as a result of trauma - biting, stabbing with a twig, or scratching with a claw. Usually, when you can look into the mouth, the damage is easy to notice. In this case, it is enough to treat the wound with an antiseptic and ensure that the sore heals quickly. No improvement within two to three days - see a doctor. If there are several ulcers, stomatitis, a bacterial or viral infection is suspected - a reason for an immediate visit to the clinic.
Viruses, severe pain or fever are suspected if the cat is breathing heavily with its tongue hanging out. In this situation, it is important to carefully examine and feel your pet, measure its body temperature and, of course, consult a doctor immediately.
If your cat has spots, strange grooves, or pimples on his tongue, be sure to show your pet to the veterinarian. There are many reasons for changes in the color and structure of the surface of the tongue, from fungi and bacteria to all kinds of viruses and chronic diseases of internal organs. Without treatment, necrosis of a cat's tongue may begin - tissue necrosis at the cellular level, an irreversible process. In this case, part, or even all, of the language will be removed. And you will be very lucky if the tissue of the oral cavity is not involved in the process.
A black tongue in a cat may be a symptom of an acute deficiency of vitamin PP. Although more often the pet simply licked something colorful - a fur collar of a jacket, a belt, etc. Sometimes a cat gets dirty with something, and then, while licking itself, scares the owners with a tongue of an unnatural color: particles of the substance, licked from the fur coat, get stuck between the papillae, turning the pinkish tongue into black, blue, green or bright red. The latter, that is, a red tongue, may be the beginning of an inflammatory process or a sign of high blood pressure.
We suggest you read: Causes, symptoms and treatment of vitamin deficiency in cats
If the owner notices that a cat has been bitten on the tongue by a wasp - this usually happens when the pet gnaws out a caught wasp stuck between its fingers - action must be taken immediately. The tongue has many nerves and blood vessels. Poison that gets into tissue spreads quickly. If an allergic reaction (swelling) begins, the pet may die.
To be on the safe side, you should give an intramuscular injection of diphenhydramine (or suprastin, but diphenhydramine is preferable). Dosage – 0.5 for a medium cat, 1 ml for a large pet weighing more than eight kilograms. Now all that remains is to observe your pet: if swelling still becomes noticeable, consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnosis of possible pathologies
The appearance of various defects and formations in the tongue cannot be ignored. You need to contact a gastroenterologist or another specialist (dentist). Additionally, consultation with an infectious disease specialist or endocrinologist may be required. Specialists will examine the oral cavity and prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests for the patient:
- blood, stool and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- gastroduodenoscopy;
- bacteriological culture;
- tests for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV and gonorrhea.
Based on the results of the studies, the diagnosis is clarified and the correct treatment is prescribed.
Treatment: what to do with flux?
Traditional methods
During surgery, an incision is made and pus is removed, after which drainage is installed.
To rid your cat of gumboil, the following methods are used:
- Surgical intervention. The purulent cavity is opened, the wound is cleaned and drained. In particularly difficult cases, the diseased tooth is removed.
- Drug therapy. To suppress the activity of pathogenic bacteria and prevent the development of sepsis, antibiotics are prescribed. The veterinarian determines the medications and their dosage individually. They also use steroid medications (Prednisolone) and painkillers (Novocaine).
- Physiotherapy. To improve tissue regeneration and relieve inflammation, warming applications with paraffin or ozokerite and ultrasound treatment are effective.
Treatment at home
Veterinarians remind that it is not recommended to treat a cat with flux on your own, as this is dangerous due to complications.
Home therapy can be carried out after consultation with a veterinarian and therapeutic procedures. External warming alcohol compresses can be applied. It is recommended to treat the cat's oral cavity with decoctions of antiseptic herbs - chamomile, string, calendula. To do this, pour 5 g of the plant into 200 ml of hot water, let it brew, cool, and filter. Pour into the cat's mouth slowly through a syringe without a needle.
How to get rid of it?
If the formation is caused by pathological changes in the body, then the underlying disease must first be cured. After a course of therapy, the plaque disappears on its own.
The treatment method is prescribed individually. The doctor may prescribe both medication treatment and a strict diet. Traditional methods of eliminating the problem should be used only in consultation with a doctor.
Additional measures include sanitation of the oral cavity, treatment of dental caries and removal of tartar.
To clean the mucous membrane of the tongue, you can purchase a separate toothbrush or a special scraper. Do not clean your tongue with metal objects, iron spoons or other objects dangerous to the thin and sensitive mucous membranes.
Cleaning your tongue with a brush and toothpaste:
- Rinse your toothbrush thoroughly under running warm water. Additionally, the brush can be dipped in boiling water for a couple of seconds.
- Squeeze a small amount of toothpaste onto the brush.
- The cleansing procedure begins from the root of the organ, then it is gradually recommended to “move” to the tip.
- Movements should be soft and slow.
- Completion of the procedure is irrigating the mouth with any disinfectant.
Drug treatment
If plaque on the surface of the tongue is a consequence of pathological changes in the body, then the doctor prescribes therapy for the patient that corresponds to the diagnosis.
- Candidiasis - antifungal drugs (Fluconazole). For local irrigation of the oral cavity - antifungal sprays and ointments (Nystatin ointment).
- Dysbacteriosis - drugs that normalize intestinal microflora (Bifiform).
- For sore throat and other serious diseases - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Tantum Verde Forte).
- Gastrointestinal diseases and infections - antimicrobial agents (Romazulan).
- Colds - antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen).
- If a coating on the tongue has formed while taking antibacterial agents, the patient is prescribed prebiotics (Linex).
- To prevent the development of fungal infections, sanitation of the oral cavity with a disinfectant solution is prescribed.
- Analgesics (Kalgel) are used to relieve pain in the oral mucosa.
- Antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine) for treating the oral cavity.
- Enzymes (Festal) to stimulate the proper functioning of the digestive tract.
- To cleanse the body of toxins and pesticides, the patient is prescribed sorbents (Polysorb).
- To strengthen the body's immune forces, multivitamin complexes are indicated.
Diet
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs often become provocateurs of various pathological changes. For the same reason, a white coating may form on the tongue. Along with drug treatment, the patient is advised to adhere to the basics of a healthy diet.
You should exclude from your diet:
- canned, fatty, salty, smoked and fatty foods;
- sweets;
- baked goods, various baked goods;
- alcohol;
- carbonated drinks;
- chocolates and bars;
- fast foods;
- dishes with flavors.
Useful dishes for abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract are: low-fat meat soups, vegetable broths, porridge with the addition of a small amount of milk, fermented milk products, fresh vegetables and a variety of fruits.
Therapeutic techniques
Treatment directly depends on what exactly caused the whitish coating on the tongue. If there is a suspicion that this is the result of poor oral hygiene, all measures must be taken to correct such a sad situation. Buy a special toothpaste and a brush for children (with the softest bristles), and clean your mouth and tongue from plaque at least once every two days.
If tests carried out in a veterinary clinic reveal the presence of an infectious disease, it is “pressured” by prescribing broad-spectrum antibiotics. For fungal diseases of the oral cavity, it is more difficult - it is necessary to use systemic antifungal drugs. The problem is that such drugs are quite toxic and can have a bad effect on the health of the animal if used for a long time.
Features of plaque formation in children
In infants, the cause of the formation of whitish formations on the mucous membrane of the tongue may be thrush.
Other factors can also be the root causes of the disease: hypothermia, the birth of a child ahead of schedule, a serious violation of the basics of caring for the baby. Thrush can develop in a newborn if a woman who is breastfeeding eats a lot of sweets and fatty foods.
In children over the age of 2 years, the formation of problematic formations on the tongue can be associated with non-compliance with basic rules of oral hygiene. You can prevent the appearance of unpleasant formations by maintaining a healthy diet for your child. The baby should not get carried away with sweets, snacks, and carbonated drinks.
Diseases of the digestive organs can also cause the formation of an unpleasant defect. If signs of pathology appear, you should not hesitate; it is important to contact your pediatrician in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations.
Oncological diseases
If you look into a cat’s mouth, you can see black dots on the gums that weren’t there before, and the animal is already many years old, you can sound the alarm. Such spots may be a manifestation of melanoma, a dangerous cancer associated with pigmentation.
The tumor is sometimes located on the oral mucosa or metastasizes here, being located in another part of the body. The second option is sadder than the first, because it speaks of an advanced stage of the disease and the futility of treatment.
Melanoma in cats does not only appear as dark spots. The animal loses its appetite, looks exhausted, and apathetic. As soon as the first alarming signs appear, the pet needs to be shown to a veterinarian. In the case of oncological tumors, it is extremely important to start treatment in a timely manner.
However, cancer is not common in furries. In most cases, spots on a cat's lips or mouth turn out to be normal pigmentation.
. The doctor will examine the animal and, if necessary, prescribe a diagnosis and explain why the color of the mucous membrane has changed. After this you will be able to sleep peacefully.