Types of antiseptic solutions for external use at home and in the hospital
- Group of halogens. These include aqueous and alcoholic tinctures of iodine, potassium iodide, and Lugol's solution. Used for treating and washing wound cavities. They have a cauterizing effect. Sutures are treated with iodine preparations no more than once per knock.
- Salts of heavy metals. Currently, bandages and ointments with the addition of silver nitrate are widely used, as well as a 0.1-0.2% solution of silver nitrate for the external treatment of postoperative wounds. At a concentration of 5%, this solution has a cauterizing effect, so it is used only in cases of severe inflammation and weeping of the wound.
- Alcohols. Ethyl alcohol in solutions with a concentration of 40% is used extremely rarely. It is not recommended to use it on a dry, non-inflamed seam. It is used primarily for treating wounds that are in the phase of active inflammation.
- Dyes. This group includes the most widely used solution - brilliant green, better known as brilliant green. For external use, an aqueous or alcoholic 1-2% solution is used. It is used both on mucous membranes and on the skin. The wound is treated daily, at least 2 times a day.
- Acids. Here, a weak solution of boric acid (2-4%) is most often used. Boric acid is a good antiseptic that is used in the form of solutions, ointments, powders, and powders. Local treatment with boric acid is applicable to both mucous membranes and skin. Treatment of postoperative wounds is carried out at least 2 times a day: in the morning and in the evening.
- Oxidizing agents. Also widely used in medical practice. The most well-known drugs from this group are potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide.
Hydrogen peroxide is an active oxidizing agent used for the treatment and treatment of purulent wounds.
It is more often used in hospitals to separate purulent contents and completely clean the wound surface. Potassium permanganate has cauterizing properties. In low concentrations it is suitable for washing sutures in the oral cavity, in higher concentrations - for treating postoperative wounds. It is used for processing no more than 1 time per day.
- Detergents. 0.1-0.2% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine is one of the drugs in this group. It is used externally for processing and washing postoperative sutures, at least 2-3 times a day.
- Antibiotics. To combat bacterial infection, ointments have been developed with the addition of antibiotics and hygroscopic agents. They are used to apply bandages to purulent postoperative wounds. Use at home only in case of suppuration of the sutures. An example of such ointments is Levomekol ointment, Vishnevsky ointment.
The first signs of suppuration
Treatment of purulent wounds will be radically different from those cases where the lesion is not infected. The onset of the inflammatory process can be determined by the following signs:
- local increase in temperature;
- slight redness and swelling of the damaged area;
- unpleasant pain, pulsation in the wound;
- general increase in body temperature.
If a yellowish, white or even greenish substance oozes from the wound, this is purulent exudate. Under no circumstances should such a phenomenon be ignored. The best thing in such a situation is to seek advice from a specialist.
Chlorhexidine solution: instructions for use in gynecology
There are several types of bacteria and viruses against which this remedy is effective. These are mainly gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and some viruses. Unfortunately, Chlorhexidine does not completely affect bacterial spores, but only at high temperatures, and therefore is not able to destroy them.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Pulmicort for inhalation for adults instructions
Chlorhexidine solution, instructions for use in gynecology:
- Vaginitis caused by Trichomonas
- Bacterial erosion of the cervix
- Unpleasant burning sensation in the area of the external female genitalia
- Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. Among them are syphilis, ureaplasma, chlamydia
Cotton-gauze swabs were soaked in Chlorhexidine and then inserted into the vagina for two hours. Similar manipulations were carried out twice a day, morning and evening. Please note that vaginal tablets or suppositories with Chlorhexidine are now used. They are much more convenient to administer, which simplifies the treatment process. Before suppositories were made, irrigation of the vagina and cervix was used for erosions, as well as vaginitis of various etiologies.
Solution
Sequence of treatment of a purulent lesion
It is worth paying special attention to removing the old bandage. In most cases, it dries to the affected area. If you abruptly tear off an old bandage, the victim may bleed, which will only increase the healing period of the wound. To prevent this, before removing the bottom layer of the dressing, it should be generously moistened several times with hydrogen peroxide or manganese solution. Only after making sure that the bandage has softened can you remove it from the skin.
After the old bandage is removed and the gloves are changed, you need to thoroughly disinfect the skin around the festering wound. The patient may experience pain, but it is extremely important to clean the wound thoroughly. To do this, take a gauze swab with tweezers, moisten it with hydrogen peroxide and wipe the entire skin around the affected area. This procedure must be repeated several times, constantly replacing the tampon with a clean one.
When the skin around the suppuration is cleansed, you can begin to treat the wound itself. The festered area must be washed thoroughly. To do this, use hydrogen peroxide and a gauze swab. The patient must endure the pain. A poorly cleaned wound will significantly slow down the healing process.
To wash the wound and free it from accumulated pus, you can use both peroxide and potassium permanganate. The compositions can be alternated. For convenience, both products are poured into small containers. After each contact with the wound, the tampon must be changed, and the used one must be thrown into a container.
What is necessary first of all for treating sutures and wounds?
For dressing, you will need an antiseptic, cotton wool or gauze pads, cotton swabs (can be replaced with regular cotton swabs), and tweezers.
After cleansing, immediate processing is carried out:
- When using an ointment, take a gauze pad and apply the product to the surface. The napkin is placed on the wound surface, and a bandage is applied on top for fixation.
- If an antiseptic is used in the form of a solution, take a cotton swab and soak it in the liquid. Instead of a tampon, you can use a regular cotton ball or gauze, but you cannot grab it with your hands; use tweezers to grab it. Treat the wound surface with a thin layer, then wait for the solution to dry completely.
To treat a wound you must have:
- Antiseptic;
- Gauze pads or gauze;
- Tweezers.
Before treating the wound, it should be thoroughly washed so that the wound surface is completely clean. In case of contamination, the first action to be taken is to remove all foreign objects and wash the seams using a weak antiseptic solution. Next you can start processing:
- If ointment is used as an antiseptic, it must be applied with a gauze pad, which after application can be secured with a bandage.
- In the case when the antiseptic drug is in the form of a solution, it is necessary to use cotton swabs, first dipping them into the liquid. The wound surface should be treated with a thin layer.
- After treatment, the wound should not be wetted for three hours. Also, during the first three days after discharge from the hospital, it is also not recommended to wet scars and sutures.
If during treatment it is visible that the seam is oozing, you should immediately consult a doctor for examination and prescription of suitable antiseptic drugs, possibly containing antibiotics. You can speed up the healing of wounds after surgery if you properly care for them, following all the recommendations of doctors.
Rules for caring for wounds after wart removal
The photo shows a wound after wart removal
If all the rules are followed and the most effective treatments are used, wound healing after wart removal occurs in several stages. First, a crust of damaged tissue and dried blood forms, which protects the wound from infection and any other negative impact. From this moment, the process of tissue regeneration under the crust begins. Over time, it disappears, which indicates that healthy tissue has been restored.
To ensure that this course of the rehabilitation period is not overshadowed by complications, it is worth not only treating the wound correctly, but also adhering to certain precautions.
Precautions to take when caring for wounds after wart removal:
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Normalization of diet;
- Keeping the wound clean;
- Refusal to use pumice stones and washcloths when carrying out hygiene procedures;
- Refusal to visit public swimming pools, saunas, spas, gyms;
- Refusal to swim in bodies of water;
- Using sunscreen and reducing sun exposure;
- Prevention of mechanical, chemical, thermal effects on the wound to avoid damage to the crust;
- Refusal to use cosmetics, for example, fatty creams, scrubs, lotions, at the site of tumor reduction;
- Minimizing contact with aggressive household detergents;
- Ensuring constant access of air;
- Abstinence from intimacy after removal of a wart in the intimate area;
- Wearing comfortable clothes made from natural fabrics.
During removal, it is quite difficult to predict how quickly the scar will heal and the skin will recover, because Each case is individual and the result depends on the characteristics of the disease and the general health of each patient.
Possible reasons for prolonged tissue regeneration after wart removal:
- Incorrect removal procedure . Removing skin tags at home often leads to negative consequences in the form of excessive damage to healthy skin. Against this background, the rehabilitation period increases.
- Accompanying illnesses . First of all, diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalance and decreased blood clotting inhibit wound healing. That is why before the procedure you should undergo an examination and exclude possible contraindications.
- Weakened immunity . A depressed body is not capable of rapid regeneration, so skin restoration may take longer. In such cases, complex vitamins and immunomodulators are usually prescribed.
- Wrong rehabilitation . Failure to follow the doctor's recommendations for wound care - improper treatment of the wound after wart removal - leads to undesirable consequences and prolongation of the recovery period.
- Bad habits . This factor ensures constant weakening of the body and a deficiency of nutrients. Among other things, smoking and drinking alcohol disrupt the functioning of the circulatory system, impairing the supply of oxygen, vitamins, and minerals necessary for the normal functioning of each cell. This course of events provokes the formation of an irregular structure of the integument.
- Re-injury . By scratching the crust or slightly tearing it off, you can not only prolong the recovery time, but also provoke the addition of a secondary infection.
It should be noted that the rehabilitation period and the rules for treating the wound after wart removal depend on the choice of removal method. The fastest recovery occurs after radio wave removal. In second place is laser evaporation, and then, as recovery time increases, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, removal with chemicals, and surgical excision.
Chlorhexidine digluconate solution: method of application
They are actively used in dentistry for care after surgical interventions, and in the treatment of certain bacterial lesions.
Chlorhexidine digluconate solution, method of application:
- Chlorhexidine is effective for gingivitis and stomatitis. In addition, the drug is often used when rinsing drainage in sepsis. Often used to process dentures and bridges.
- Often used in ENT practice, for the treatment of sore throat, and treatment of the nasal passages and ears after surgical interventions. However, this is not the entire list of ailments for which Chlorhexidine is used.
- It can also be used when treating burns to disinfect the surface of the skin. The product is often used by surgeons and medical staff to disinfect their hands. Chlorhexidine is often used to treat not only hands, but also thermometers, that is, medical equipment that cannot be sterilized.
For external use
Treatment and healing of weeping wounds
Weeping wounds represent damage to soft tissue structures. The skin is the body's natural barrier and performs many functions.
The superficial skin is exposed to aggressive environmental influences.
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
↑
There are different degrees of damage. Localization: skin, blood vessels, bones, sometimes internal organs. When a wet injury does not heal, inflammation occurs. During the healing process, scars form. Treatment consists of regular dressings, antibiotics and disinfectants.
↑
Ointments for drying
Treating with drying agents means using ointments and gels.
Products that protect the skin from infection:
Source: https://GidPain.ru/ranenie/moknushhaya-lechit.html
How to properly treat a wound and suture
Before the sutures are removed, the dressing is changed daily with solutions and ointments of silver nitrate, antibiotics, and hydrogen peroxide. Sutures are removed mainly on the 7th day after surgery. Immediately after this, the scar is cauterized with a solution of potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide.
We suggest you read: For burns caused by quicklime, several answers are needed
On the day of discharge, the attending physician gives recommendations for further management of the postoperative suture and recommends a suitable antiseptic. Treatment at home is carried out 1-3 times a day, depending on the properties of the disinfectant solution. Cauterizing solutions are used no more than once a day. Treatment with water and alcohol tinctures is carried out 2-3 times a day.
Chlorhexidine: use in urology
Chlorhexidine is most often used at home to prevent sexually transmitted diseases. Usually, within 2 hours after contact, the vagina, as well as the external genitalia, are treated with a solution with a concentration of 0.05%. In addition, irrigation of the thighs and pubis is also carried out. It is advisable after the manipulation not to go to the toilet for two hours and not to wash off the solution. It must be allowed to dry completely.
Chlorhexidine, use in urology:
- Urethritis and prostatitis are often treated with Chlorhexidine. To do this, it is necessary to take approximately 3 ml of a solution with a concentration of 0.05% into a syringe without a needle.
- The syringe rod is inserted into the hole in the head of the penis and the medicine is injected. Irrigation is carried out twice a day. 10 days are enough for treatment.
- It is also prescribed for the treatment of trichomoniasis and vaginitis caused by various bacteria.
Solution
Peace and cleanliness
This depends on many things: on the size and location of the wound itself (for example, damage to the mucous membrane heals faster), and on the state of local and general immunity (for example, with diabetes and some other diseases, as well as with hypovitaminosis, healing is often difficult).
Lifestyle is also important - it is not for nothing that doctors after operations warn about the need to avoid increased physical activity - do not lift heavy objects, do not run, do not jump, so that the stitches do not come apart. In addition, you need to protect fresh post-operative scars from the sun and water.
But perhaps the main reason why a wound may not heal for a long time is non-compliance with asepsis rules. Therefore, the importance of modern dressings is especially great - various healing dressings, which, thanks to their fine mesh structure, reliably protect the wound not only from dirt and microbes, but also from unnecessary injury. Wounds are especially sensitive to bacteria within two days after suturing, and already on the third day this risk decreases. Therefore, in the first days, applying a bandage is simply necessary. Indeed, in addition to protecting against bacteria, dressings also play another important role: they immobilize a certain area of the wound, which slows down the lymph flow in this area and minimizes the spread of wound microflora. In addition, they create the necessary pressure on the underlying tissues, and also prevent moisture from evaporating from the surface of the wound, maintaining the required degree of moisture in it. Due to this, healing goes better.
Dry scar care
If healing is successful, a scar will form almost immediately after discharge from the hospital. Signs of a dry scar:
- The absence of pus, exudate, and serous fluid discharged from the wound.
- Pink or pale pink color.
- Normal temperature of the skin above the surface of the scar.
- Absence of keloids (pathological growths of scar tissue).
Such a scar is treated with ordinary brilliant green 1-2 times a day for 7 days. During the procedures, the condition of the scar tissue is checked and signs of inflammation are identified. The final healing of the scar should take place in the open air; it is not recommended to cover the defect with bandages and plasters.
Primary wound treatment
In medicine, wounds are usually called mechanical damage to tissues that affects the skin or mucous membranes. This distinguishes them, for example, from ruptures of internal organs. Wounds are the most common type of injury, and there are quite a few types of them:
- chopped;
- cut;
- torn;
- chopped;
- bitten;
- firearms;
- poisoned.
This is not the entire list of possible wounds that healthcare workers constantly encounter.
Any open wound is a gateway for germs. They easily penetrate the body through it and begin their subversive activities after 6-8 hours. Microbes multiply rapidly and strive to penetrate blood vessels, tissues and spread throughout the body. After about 12-24 hours, if the wound is not treated, the infection will spread beyond its boundaries.
Chlorhexidine solution for rinsing teeth: method of application
Chlorhexidine is also used in dentistry.
Chlorhexidine solution for rinsing teeth, method of application:
- This is usually done in both the adult and children's departments, when performing surgical procedures to remove teeth.
- To do this, approximately 10 ml of a solution with a concentration of 0.5% is poured into the gums and cheeks and left for 3-5 minutes.
- After this, the solution is spat out and surgery is performed.
Solution
What to do if the seam festers
The onset of weeping is the first sign of serous inflammation. The exudative fluid is clear or yellowish. Wetting is accompanied by inflammation of the wound surface: the forming scar is red, hot to the touch, painful on palpation.
Inflammation is a complication of the postoperative recovery period, so it is necessary to inform your doctor about this as soon as possible and seek medical help. As first aid, drying agents are used: salicylic ointment, boric acid solution, lotions with oak bark decoction, ointments and solutions based on silver nitrate.
We invite you to read Salipod instructions for use for calluses
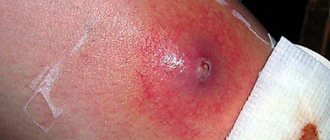
The separation of thick, yellow or greenish liquid from the wound cavity indicates the addition of a purulent infection - a serious complication of the postoperative period. Treatment measures should be started immediately, as early as possible.
Purulent inflammation occurs with a clear clinical picture. In addition to discharge from the wound, the patient is worried about weakness and fever. The temperature rises to 39-40C. The wound surface is bright red, hot to the touch, sharply painful on palpation. The skin around the seam is shiny and tense.
If such symptoms appear at home, the patient should immediately contact the emergency room of the hospital or a surgeon at the clinic at his place of residence. As first aid, wash the seams with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, bandages with Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment. Cauterization with potassium permanganate or brilliant green is not recommended, as this will make it difficult for the doctor to work when treating sutures.
Products for treating sutured wounds
The treatment consists of 2 stages - cleaning the skin adjacent to the scar. The epidermis is cleaned with a soap solution and hydrogen peroxide. It is necessary to avoid contact with liquid on the damaged area. After manipulation, a sterile bandage is applied to the sutured wound.
Antiseptics used during processing:
- Hypertonic solution or sodium chloride with a concentration of 10%. For external use only. The drug has a detoxifying, disinfecting, drying effect. There are no contraindications.
- Potassium permanganate solution. The crystals need to be dissolved in boiled water. The color of the liquid should be pale pink. The drug has an antiseptic, drying effect. Avoid contact with eyes, do not use high concentrations, as this may cause burns and a low rate of tissue regeneration.
- Hydrogen peroxide. The drug softens and removes remaining pus and blood. Does not have a bactericidal effect. Apply using a gauze pad. Blasting is allowed. After the release of oxygen ceases, the sutured wound should be dried with a cotton swab.
- Brilliant green has antibacterial and fungicidal effects. Does not relieve inflammation and does not irritate the epidermis. The product is applied to a previously cleaned seam using a cotton swab. The drug is incompatible with iodine and alkaline solutions. May burn after application.
- Chlorhexidine is a ready-made solution for external treatment of tissues. Has an antibacterial effect, is not active against fungal flora. Apply in a stream. The medicine is incompatible with soap and alkaline solutions.
- Miramistin is a ready-made solution. Active against pathogenic and fungal flora. Apply using a cotton swab or jet.
- Betadine based on povidone-iodine. Acts on bacteria, fungi, viruses and protozoan microorganisms. Apply to the seam using a cotton swab. The product should not be used for diseases of the thyroid gland, imbalance of thyroid hormones, or in early childhood.
There is a wide selection of antiseptics on the shelves of pharmacies, from expensive to budget ones. You should buy the drug recommended by the doctor based on the patient’s condition and medical history.
Reviews
Now there is even a solution for treating hands. Additionally, it contains vitamin D, vitamin E, as well as vitamin A, Panthenol. This is necessary to moisturize your hands. The solution is effectively used as a regular antiseptic if it is not possible to wash your hands before eating. It is very convenient on the road, and in camping conditions, when it is not possible to wash your hands properly. Additional components included in the product moisturize the skin, preventing it from drying out.
Antiseptics
Recently, the solution has not been used in gynecology due to the fact that convenient methods of using the substance have been developed. Nowadays in gynecology suppositories with Chlorhexidine are mainly used. It is enough to use them for treatment for 10 days, in the amount of 2 pieces per day. This product was used for tampons, as well as for treating the cervix.
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Special dressings
Accelerated healing is greatly facilitated by the use of ready-made special dressings, which are excellent for both clean and purulent wounds. The composition of such dressings varies depending on the stage of healing.
Dressings intended for the initial healing phase are impregnated with antibacterial and absorbent substances, thanks to which the wound heals quickly. In the middle and last phase, it is necessary to use dressings that protect the developing scar and contain substances that stimulate regeneration. The use of special dressings is the best way to speed up the recovery of the wound surface after surgery.
A very convenient way to treat postoperative sutures is to use special ready-made dressings. They are effective in treating the healing of clean and purulent wounds. Depending on the regeneration phase, dressings of different composition are used.
Dressings for the first phase contain antibacterial and adsorbent substances that help cleanse the wound, including necrotic tissue. Dressings for the second and third phases of healing are designed to protect delicate granulations (forming scar), and also contain substances that stimulate regenerative processes.
This method is very convenient for the patient, as it does not require any effort other than changing the bandage daily. The most common dressings are Vaskopran, Algipor, Sorbalgon and others.
It will heal until the wedding! How to properly care for a wound
Before healing and turning into a barely noticeable scar over time, any wound goes through three stages. First comes the stage of inflammation, then - cleansing and preparation for scarring, and finally comes the stage of epithelization, which ends with the formation of a scar. And, although these stages are the same for everyone, the time they take to complete them can differ significantly. Why do some people’s wounds heal easily and quickly, while others heal poorly and slowly?