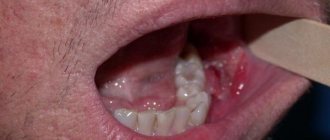
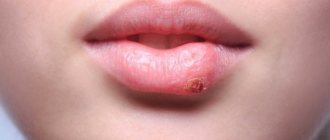
Definition of disease
Tonsillitis in medicine is called inflammation of the tonsils. The disease can take on an acute form (angina) or a chronic form; it can be viral or bacterial. In the second case, the disease is provoked by bacteria (most often streptococci and staphylococci). About 15% of people are carriers of these bacteria. In a passive state, these microorganisms do not create any problems. But some factors (hypothermia, sudden temperature changes, etc.) can activate them, thereby causing an inflammatory process.
Acute tonsillitis in adults
Also, acute tonsillitis in adults can occur due to other inflammatory processes in the pharynx: pharyngitis, rhinitis, rhinosinusitis and caries, as well as due to hypothermia, a general decrease in immunity or a lack of vitamins.
Most often, people get sick with acute tonsillitis during the cold autumn-winter period and when living in dusty and gas-polluted areas. If you often travel on public transport and can easily drink from someone else’s mug, you also run the risk of becoming infected.
“But even in the summer we have plenty of patients with sore throat. Imagine: you sunbathe on the beach, and then, hot, plunge into cold water. Or how nice it is to eat ice cream or drink water from the refrigerator in the heat - and then wonder where the sore throat came from, says otolaryngologist Pyotr Kirillov.
Causes
Bacterial tonsillitis is always caused by bacteria. Most often, hemolytic streptococcus and staphylococcus are activated. The infection can be contracted through contact with sick people or the spread of infection from structures adjacent to the throat. Teeth affected by caries can also cause the spread of pathogenic bacteria. However, not everyone who is exposed to pathogens gets sick. A healthy immune system can protect the body from infection. If the protective forces weaken, then inflammatory processes develop.
Factors contributing to weakened immunity and the development of tonsillitis:
- Chronic colds;
- Hypothermia;
- Hypovitaminosis;
- Severe stress;
- Overwork;
- Transitional age;
- Climate change (from warm to colder);
- Drafts.
As soon as the immune system weakens, streptococcus begins to actively multiply, releasing special substances into the blood that further suppress the immune system. This factor of the negative impact of bacteria contributes to the fact that the infection can spread throughout the body and cause serious complications, for example, glomerulonephritis, cardiomyopathy, arthrosis.
Bacterial tonsillitis
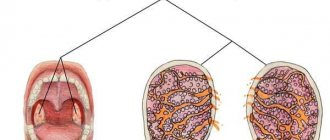
Tonsillitis is classified as an infection of the tonsils. These small, oval-shaped structures are located on either side of the back of the throat. Their role is to protect the body from microorganisms that enter the mouth. Many bacteria that enter the oral cavity can cause bacterial tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis is a contagious disease. Its occurrence is most often provoked by streptococci. When affected by these organisms, a sore throat occurs, while the tonsils remain unaffected by the infection. Less commonly, the disease is caused by staphylococci, mycoplasmas, chlamydia, and nysseria.
It is impossible to say exactly what factor provoked the development of tonsillitis (viruses, bacteria) without special tests. This difficulty in detecting the provocateur of the disease is explained by the similarity of symptoms when the tonsils are damaged by viruses and bacteria.
If one episode of the disease occurs, it is called acute tonsillitis. If the pathology appears regularly (from 5 times a year), then the patient has chronic tonsillitis.
Infection can occur from a sick person. Bacteria are present in tiny droplets released when sneezing or coughing. By inhaling such drops, a person becomes infected.
Streptococci are constantly present in our body, but it does not cause any harm. If the immune system is weakened, they actively multiply, causing inflammation.
How to distinguish a viral sore throat from a bacterial one:
Symptoms
Bacterial tonsillitis can occur in acute or chronic form. The acute form, i.e., sore throat, is characterized by a sudden onset with an increase in body temperature to 38–39 º, headache, and weakness. The main manifestation of the disease is severe pain in the throat, which intensifies when swallowing. Upon examination, the doctor reveals yellow pustules or gray-white plaque on the tonsils. Enlarged lymph nodes can be felt under the chin.
For various reasons (incorrect or untimely treatment, weakened immunity), acute tonsillitis can develop into chronic tonsillitis. With this course of the disease, inflammation in the pharynx is constantly observed. Periodically, the inflammation worsens, showing symptoms similar to a sore throat.
Unlike the viral variety, bacterial tonsillitis is not accompanied by symptoms such as rhinitis and conjunctivitis. The second feature is that bacterial inflammation almost never occurs in a mild form. On the surface of the tonsils of patients, as a rule, purulent accumulations can be found.
Diagnostics
To diagnose inflammation of the tonsils, the doctor conducts an examination, pharyngoscopy, and determines a list of necessary laboratory tests.
To make a diagnosis, examination and pharyngoscopy are performed.
During pharyngoscopy, a specialist examines the mucous membrane of the throat using a special mirror. The photo clearly shows that with angina, there is marked hyperemia and swelling of the tonsils, which does not extend beyond the anterior arches. The surface of the tonsils is covered with purulent plaque. Exudate can also be present in lacunae in the form of microabscesses visible through the mucous membrane.
With streptococcal sore throat, hyperemia of the posterior pharyngeal wall is determined. On the soft and hard palate there may be areas of bleeding into the mucous membrane (hemorrhages).
On examination, an increase and tenderness of the regional lymph nodes is noted; most often, a unilateral change in the submandibular lymph nodes occurs.
C-reactive protein can be detected in the blood
A clinical blood test determines leukocytosis, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, i.e. increase in the number of neutrophils. There is also an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). C-reactive protein is determined in the blood serum.
A general urine test may show traces of protein.
To detect streptococcal infection, a rapid test is performed, which is widely used due to its accuracy (up to 98%) and speed of obtaining results (5–10 minutes).
To further confirm or clarify the causative agent of bacterial sore throat, material is taken from the surface of the tonsils and the posterior wall of the pharynx for bacteriological culture, followed by determination of antibacterial sensitivity.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes electrocardiography
In addition to the basic diagnostic methods, the doctor may additionally refer you for electrocardiography, ultrasound examination of the kidneys, and consultation with related specialists.
Possible complications
Pathogenic microorganisms that attack the tonsils release toxic products that spread throughout the body. As a result, the palatine tonsils turn from a protective organ into a source of poisoning.
Symptoms of intoxication increase gradually. If they last for a long period, then over time functional disorders of the heart, joints, kidneys and brain may develop. The most dangerous complications of tonsillitis are:
- Rheumatism;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Arthritis;
- Myocarditis;
- Glomerulonephritis.
Treatment
The treatment of bacterial tonsillitis should be approached comprehensively. It is necessary to use medications, home procedures and traditional recipes approved by an otolaryngologist.
Medications
Drug treatment of bacterial tonsillitis is carried out using conservative or surgical methods. The choice of treatment method depends on the form, degree of the disease, age and general health of the patient.
Conservative treatment is indicated for acute tonsillitis and in the absence of pronounced signs of intoxication of the body.
In the acute form, a set of measures includes:
- Drink plenty of fluids (warm milk, decoctions, teas, jelly). Drinking fluids not only relieves a sore throat, but also removes toxins from the body.
- Bed rest.
- Diet. Food should be soft or liquid in consistency (porridge, vegetable and meat purees, soups). Sour, salty and spicy foods are prohibited.
- Prescription of antibiotics, which are selected taking into account sensitivity to the pathogen, painkillers (Paracetamol, Nimesulide) and immunostimulating drugs (Immunal, Bronchomunal, Ribomunil). To increase local immunity of the pharyngeal mucosa, the use of nasal sprays (IRS-19) or lozenges (Immudon, Lizobakt, Hexalize) is indicated.
- Regular (every 1–1.5 hours) gargling with antiseptic solutions. A solution of table salt, decoctions of medicinal herbs (sage, chamomile, eucalyptus) or ready-made pharmaceutical preparations (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Hexoral, Stop-Angin) are suitable.
Common antibiotics for tonsillitis
Treatment of chronic bacterial tonsillitis consists of several stages. During the period of remission, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Sanitation of tonsils. This is what is called washing the tonsils with medicinal solutions. Currently, sanitation is carried out using ultrasound using the Tonsillor apparatus. There are also more complex procedures, for example, hydrovacuum aspiration, in which the tonsils are washed, then the purulent contents are pumped out of them using vacuum suction.
- Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, UHF, quantum therapy).
- Drug therapy. The doctor usually prescribes vitamins and immunomodulators (Likopid, Immunal, Polyoxidonium).
Such courses of treatment for chronic bacterial tonsillitis are carried out once every six months for 2 years. In case of exacerbations of the disease, rinsing and taking antibiotics are recommended.
Surgical intervention
Surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is indicated in the following cases:
- If conservative treatment does not produce results.
- In case of complications (rheumatism, myocarditis, nephritis, etc.).
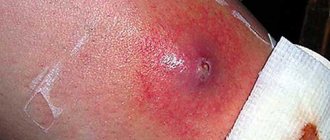
- For paratonsillar abscess (inflammation of the soft tissues located behind the tonsils).
The operation is performed in a hospital setting under local anesthesia. The palatine tonsils are cut out using traditional instruments (scalpel, scissors) or laser, radio or ultrasound.
Treatment with folk remedies
When diagnosed with bacterial tonsillitis, alternative treatment involves performing local procedures: gargling or irrigating the throat.
For rinsing, infusions of calendula, chamomile, sage, and eucalyptus are used. A propolis solution will also help relieve the symptoms of a sore throat. The preparation of the product is very simple: the pharmacy tincture of propolis must be diluted with warm water (1:1) and gargled several times a day. In moments of severe pain in the throat, use a gargling solution based on iodine, salt and soda.
We offer recipes for infusions that are most often used for rinsing:
- Chamomile color (6 parts), linden color (4 parts). One tbsp. Pour a spoonful of the mixture into 1 glass of hot water, leave for 20 minutes, strain, cool, and consume warm.
- Oregano herb (4 parts), marshmallow root (1 part), common oak bark (5 parts). The method of preparing the infusion is as in the previous recipe.
- Marshmallow root (3 parts), Salvia officinalis leaves (4 parts), Black elderberry flowers (3 parts). The cooking method is the same.
- Peppermint leaves (3 parts), sage leaves (3 parts), chamomile flowers (3 parts), fennel fruits (1 part).
For rinsing and inhalation, you can use the following tinctures:
- Fill half a bottle of crushed aloe leaves with sugar, leave for 3 days, then fill the solution with 40% alcohol to the brim of the bottle, leave for 3 days. Use 50 drops per half glass of warm water.
- Infuse 20 g of St. John's wort leaves and flowers in 100 ml of 70% alcohol for 2 weeks. Strain and use 40 drops per half glass of warm water.
For atrophic tonsillitis, it is worth using oils: sea buckthorn (irrigate the tonsils 3 times a day for two weeks), fir oil (apply to the tonsils with a cotton swab or syringe, apply 5 times a day for a week).
Beekeeping products are very popular: For rinsing 1 tbsp. Dissolve a spoonful of honey in a glass of warm water. The following remedy has a very effective effect: squeeze the juice from thoroughly washed and crushed coltsfoot leaves, mix coltsfoot juice, onion juice and red wine in equal proportions. Place the prepared mixture in the refrigerator. Shake before use. Use 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. spoon.
When treating tonsillitis at home, remember that lubricating the throat with kerosene and formalin is unacceptable: this can provoke the degeneration of lymphoid tissue into malignant, which is confirmed by clinical observations.
Also remember: All folk remedies will be effective at the onset of the disease. If you treat from the very first symptoms, when the throat starts to hurt a little or just scratches, then you can avoid more serious manifestations of bacterial tonsillitis.
What is bacterial sore throat and how to treat it
Sore throat is a disease in which the tonsils located in the depths of the throat undergo inflammation. The presented illness can occur in various forms, but the most common are viral and bacterial tonsillitis. They are very similar in symptoms, but they are treated differently. The formation of the bacterial head start of the disease is influenced by bacteria such as streptococcus.
Symptoms
In order for the doctor to prescribe appropriate therapy, he must examine the patient, ask him about his symptoms, and also take a smear to determine the type of microorganism that has affected him. During the diagnosis, the doctor will be able to accurately determine that it was streptococcus that provoked the presented illness.
In the photo - viral and bacterial tonsillitis:
The disease can also be recognized by the symptoms that the patient experiences. These include:
- light yellow coating on the tonsils;
- rise in body temperature;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- sore throat when swallowing;
- swelling of the throat;
- cough.
Sometimes the symptoms presented may indicate a common cold, so many people are in no hurry to go to the hospital for examination. As a result, angina can result in severe complications or the disease becoming chronic.
In the video there is more information about bacterial sore throat:
How to distinguish bacterial sore throat from viral one
How does a viral sore throat differ from a bacterial sore throat? What is the difference? Without additional diagnostics, doctors sometimes cannot distinguish between viral and bacterial tonsillitis. The symptoms of these two diseases are very similar. The difference between them is that the bacterial form of the disease is caused by bacteria (streptococcus), and the formation of the viral form is influenced by viruses.
In addition, when treating a viral sore throat, it is not advisable to use antibiotics, since they will not be able to have their effect. But with bacterial sore throat, antibacterial drugs have a powerful effect and quickly eliminate the cause of the pathology.
How is it transmitted?
- You can become infected with bacterial sore throat through airborne droplets. This happens when a person affected by the disease sneezed, and a healthy person standing next to him inhaled bacteria along with the air.
- Bacteria can also be transmitted through household items. Often this disease affects young children who attend kindergarten. It is there that they become infected from affected children during communication, shared toys, and hugs.
Here you can read how many days a sore throat is contagious. The link shows the incubation period for tonsillitis.
Treatment in adults
How to treat? The unpleasant symptoms of the disease and the very cause of bacterial sore throat in adult patients can be eliminated with the help of complex treatment. As a rule, therapy includes mandatory medication. Here the doctor can prescribe antibacterial drugs, thanks to which it is possible to remove swelling from the inflamed tonsils and bring their size to the desired level. Antibiotics should be taken for no more than 7 days. But there are cases when antibacterial therapy should be increased.
Effective drugs for bacterial sore throat are:
- Penicillin,
- Erythromycin,
- Amoxicillin (treatment of sore throat with amoxicillin is described here)
- Cephalosporins.
To eliminate pain and reduce temperature, the doctor will prescribe Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, and painkillers to the patient.
Local methods of therapy include ultrasound radiation or microwave . Thanks to this method, it is possible to quickly and effectively overcome the cause of the disease and alleviate the patient’s condition. The treatment regimen necessarily includes inhalation and rinsing the mouth with a solution based on soda and herbs.
There are cases when doctors turn to alternative medicine methods. In this case, he prescribes his patients to drink plenty of sugar-free liquids. If you drink teas, you can sweeten it with honey, because it is characterized by excellent antibacterial properties. Propolis also has a positive effect. As a rule, when it is used in the oral cavity, the patient feels a burning sensation. This sign indicates that bacterial asthma will soon leave the patient. The link describes in detail the treatment of tonsillitis with folk remedies.
Laser treatment is considered no less effective. Using a laser, it is possible to achieve effective results. During this treatment, it is possible to partially remove or cauterize the tonsil glands. This procedure must be performed under local anesthesia. To get the desired result, it is enough to do a few manipulations.
Find out if you might have a teething cough.
Here is how to take milk and soda for a cough.
Symptoms of bronchitis without fever: https://prolor.ru/g/simptomy-g/bronxita-u-vzroslogo-bez-temperatury.html.
Treatment in children
When a doctor diagnoses “bacterial tonsillitis,” treatment is most often based on the use of antibacterial drugs of the penicillin group. It is to such drugs that streptococcus is sensitive. Most often, the doctor prescribes the following drugs to young patients:
- Penicillin,
- Amoxiclav for sore throat,
- Amoxicillin.
When a child has an insensitivity or allergy to these medications, the doctor should take care of substitutes, the name of which is macrolides. These drugs are characterized by low toxicity, but they are very effective against microbes.
The most popular macrolides can be considered:
- Sumamed (the dosage of sumamed for angina is indicated here),
- Zitrolide,
- Azicide
- Chemomycin.
An antibacterial drug called Amoxicillin is sold in pharmacies in various dosage forms: tablets, capsules and suspensions. Thanks to this, the medicine is very popular in the treatment of bacterial sore throat in children.
Amoxiclav is a special form of the previous drug. It contains clavulanic acid, thanks to which the effect of Amoxiclav can be enhanced during the treatment of childhood sore throat.
In addition to antibiotics, the doctor may prescribe vitamin therapy to his young patients. This treatment is considered auxiliary; it is aimed at strengthening the immune system, as a result of which the bacteria cannot feel comfortable in the current conditions.
During treatment, vitamins C and B and antihistamines are used. Thanks to them, it is possible to slow down the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Very often, various immunocorrectors can be involved in the process.
The video talks about bacterial tonsillitis in children:
Bacterial sore throat is a disease that primarily affects young children, but adults are also not immune from streptococcal infections. This illness does not entail anything serious if the treatment was prepared correctly and in a timely manner.
ProLor.ru
Prevention
To prevent tonsillitis, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- Carry out complete sanitation of the oral cavity and nasopharynx.
- Cure carious teeth, inflammatory gum diseases, adenoids.
- Perform a massage on the front of the neck in the direction from the lower jaw to the chest (especially in winter before going outside).
- Use natural immunostimulating agents: propolis, garlic, chamomile, echinacea, ginseng.
- Rinse the lacunae of the palatine tonsils and gargle with a warm saline solution.
- Perform daily toileting of the pharynx and oral cavity in the morning and evening.
- Strengthen the entire body and the tonsils in particular. They are hardened by cold (cold drinks, ice cream), but only during healthy periods. They drink drinks not in one gulp, but in small sips. Ice cream is eaten slowly, with a small spoon.
- Good health of the body depends on proper nutrition. The diet should contain foods rich in vitamins and microelements.
All these measures will significantly reduce the likelihood of exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
What is the difference between influenza and ARVI?
Symptoms of ethmoiditis and effective treatment without surgery are described in this article.
Children's “Amiksin”: instructions for use //drlor.online/preparaty/ot-prostudy-i-grippa/amiksin-pokazaniya-k-primeneniyu-i-mery-predostorozhnosti.html
conclusions
None of us like to be sick. Therefore, the easiest way is to prevent a pathological process than to treat it later. Bacterial tonsillitis is a disease that can be prevented and thereby reduce the risk of inflammation. To this end, it is necessary to pay a lot of attention to strengthening the immune system. But even if you are sick, you should immediately begin treatment. At the first symptoms of bacterial tonsillitis, it is useful to start rinsing with medicinal solutions or decoctions. Remember that therapy must be competent, so first of all you need to consult with an ENT doctor. Gargling with decoctions can also provide significant assistance during treatment. An integrated approach to your health is the best prevention of all diseases.