Inflammation of the parotid gland is popularly called mumps. And in medicine, the term mumps is used for this pathology. What kind of disease is this? What causes inflammation of the parotid salivary gland? How to treat it correctly and effectively? We will try to cover these and some other questions in as much detail as possible. We will look at the mechanism of development of mumps, its types, causes, symptoms, complications and methods of treatment.
Mumps is an inflammation of the parotid gland. Very often it happens in childhood and with proper treatment it goes away quickly.
Inflammation, treatment
Inflammation of the gland that produces saliva can have unpleasant and dangerous consequences for the patient. Let's first understand what saliva is and what its functions are. In the mucous membrane of our oral cavity there are as many as three pairs of salivary glands. They are supplemented by many small tributaries. Their entire function comes down to the production of a special secretion - saliva. Without it, the normal course of many important processes associated with digestion is impossible. It is she who wets and softens pieces of food, forms a food bolus and participates in its direct swallowing. In addition, saliva has bactericidal capabilities, that is, it can suppress infection. But if the salivary glands become inflamed, saliva begins to lose its usual properties. Problems begin with the production of the required amount of secretion, the patient feels difficulty swallowing. Due to the penetration of the virus and the development of the inflammatory process, the parotid salivary gland loses its ability to function normally. In general, inflammation of the salivary glands becomes a real test for the body. If the salivary glands are affected, inflammation and symptoms will not immediately manifest themselves.
Large glands of the digestive system.
Using lectures (presentations and text of lectures are posted on the department’s website), textbooks, additional literature and other sources, students must prepare the following theoretical questions:
1. General morphofunctional characteristics of the major salivary glands and their classification.
2. Features of the structure of the final secretory sections (acini) of the parotid, submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
3. Basic microscopic and submicroscopic features of muco- and serocytes.
4. Excretory ducts of the major salivary glands.
5. Secretory products and hormones of the salivary glands.
6. Morphogenesis and regeneration of the salivary glands.
7. Secular changes in the salivary glands.
8. Sources of liver development and general morphofunctional characteristics.
9. Fine structure of the classic lobule of the liver. Liver beams. Hepatocytes, their microscopic, histochemical and ultramicroscopic characteristics and functions.
10. Vascular system of the liver and features of blood supply.
11. Features of the structure of intralobular hemocapillaries and the significance of Visokovich-Kupffer stellate cells.
12. Perisinusoidal space of Disse, its meaning.
13. The concept of the hepatic acinus and the portal lobule.
14. Biliary tract and their morphological characteristics. Microscopic structure of bile capillaries and bile ducts.
15. The structure and role of the gallbladder.
16. Regenerative abilities of the liver.
17. General plan of the structure and development of the pancreas.
18. Morphology and functional significance of the exocrine part of the gland.
19. Microscopic and ultramicroscopic structure of the acinus. Cytophysiology of the secretory process.
20. The relationship between the terminal secretory sections (acini) and the intercalary duct. Centroacinous epithelial cells. The structure of the excretory ducts.
21. Endocrine part of the pancreas. Pancreatic islets, their cellular composition, histophysiology.
22. Morphofunctional characteristics of insulocytes (A, V.D, D1, RR).
Blood supply and innervation of the pancreas.
The digestive system unites a number of organs, which together ensure the body’s absorption from the external environment of substances necessary to fulfill its plastic and energy needs. It includes the digestive tube and the glands located outside it, the secretion of which helps digest food particles: three pairs of large salivary glands, the liver and the pancreas.
The ducts of three pairs of large salivary glands - parotid, submandibular and sublingual - flow into the oral cavity. The secretion of the minor salivary glands - labial, buccal, palatal and lingual - also gets here.
Based on the secretion of secretions, the salivary glands are divided into glands of the vestibule of the mouth and the oral cavity itself. The former include the parotid, labial, and buccal glands; the latter include the submandibular, sublingual, palatine and lingual salivary glands.
In structure, all major salivary glands are complex alveolar or alveolar-tubular glands.
Between neighboring serocytes lie intercellular secretory tubules, which remove the products of the synthetic activity of serocytes. Part of the secretion leaves the cells through their apical surface. Myoepitheliocytes, or basket cells, have processes that, like tentacles, cover the bases of serocytes. The contraction of myoepithelial cell processes promotes the removal of secretions from the final secretory sections.
All salivary glands secrete according to the merocrine type, i.e. without destruction of secretory cells. According to the nature of the synthesized substances, the secretory cells of the salivary glands are divided into protein, mucous and mixed. Protein cells (serocytes) synthesize predominantly enzyme proteins. The molecules of the latter contain a high content of the peptide component and relatively little of the carbohydrate component. The products of the synthetic activity of mucous cells (mucocytes) are predominantly mucus-like mucin proteins and proteoglycans, in which the carbohydrate component predominates, and peptide chains make up a relatively small part of the molecules. Cells with a mixed type of secretion (seromucocytes) simultaneously produce enzymes and mucus (glycoproteins and proteoglycans).
The secretory products of all types of salivary glands collectively form saliva. About 1.5 liters of saliva are produced per day, which is 99% water; dry residue includes inorganic and organic components. Among the inorganic components, sodium, potassium and calcium ions predominate. The organic components of saliva include a number of enzyme proteins (amylase, maltase, hyaluronidase, pensin- and trypsin-like enzymes, lysozyme, acid and alkaline phosphatase, nuclease), as well as (glycoproteins, mucins, proteoglycans). In saliva one can also detect leukocytes (so-called salivary bodies), epithelial cells, as well as a number of excretory substances - uric acid, creatine, iodine.
Saliva moistens food, makes it easier to process and swallow, and promotes articulation. Through the presence of enzymes in saliva, the primary chemical processing of food is carried out. Saliva has a bactericidal effect due to the presence of lysozyme and leukocytes. It rinses the structures of the oral cavity and thereby promotes the rejection of dead epithelial cells and the removal of food debris. The salivary glands secrete into the external environment a number of intermediate and final metabolic products - uric acid, creatine, iron, iodine, and play a significant role in maintaining the body's water-salt homeostasis.
In addition to external excretory activity, the large salivary glands secrete a number of biologically active substances directly into the blood, that is, they perform an endocrine function. Hormones produced by the salivary glands include parotin, insulin-like protein, nerve growth factor, epithelial growth factor, thymocyte transforming factor, etc.
In structure, all major salivary glands are complex alveolar or alveolar-tubular glands.
The submandibular salivary gland (glandula submandibularis) is a paired organ located near the inner surface of the lower jaw. The mass of each gland is 10...15 g, the shape is elliptical. This is a complex alveolar-tubular branched gland with a protein-mucosal type of secretion. Connective tissue septa extend from the connective tissue capsule into the gland, dividing the parenchyma into lobules. The organ consists of terminal secretory sections (acini) and a system of excretory ducts.
The final secretory sections of the submandibular salivary gland are of two types - protein and mixed. Protein acini form the vast majority of the parenchyma of the gland. Each protein acini is built with 10-15 serocytes; myoepithelial cells surrounded by a basement membrane are located along its periphery. Serocytes are conical cells with basophilic cytoplasm and a round nucleus.
Types of inflammation of the salivary glands
We have three pairs of large glands in our mouths. They produce saliva. Most often, with mumps, the parotid salivary gland becomes inflamed. The infection reaches a person in the most common way - airborne droplets. At the same time, the parotid gland increases significantly, and saliva production decreases. In addition, there is a blockage of the small ducts through which saliva enters the oral cavity. Mumps is very common in children, although there are many cases where adults also get it.
In most cases, there are cases of viral mumps. Mumps is transmitted by contact. The virus infects the gland tissues in the body. Most often the salivary gland is affected, but the genital glands can also be affected. The central nervous system is also affected. In addition, the pancreas and thyroid may suffer from the virus. But the virus destroys them to a lesser extent. Doctors note a fairly high susceptibility to the mumps virus. Faced with it, more than every second. Moreover, boys aged 3-6 years suffer more from this disease. They tolerate the disease more difficult than girls. The surge in the mumps epidemic is seasonal. It's cyclical. The maximum surge usually occurs in early spring - in March-April. A couple of times a year, doctors note outbreaks of epidemics of this disease.
Most often, mumps occurs in children in a fairly mild form. But do not underestimate the danger of this disease. The main problem of mumps is that it can lead to quite serious complications and consequences.
Inflammation of the salivary gland: treatment at home, recipes – Denta-smile
Pain in the ear and throat does not always indicate otolaryngological problems. The problem may be due to other causes, including inflammation of the salivary gland. The disease has several forms and manifestations. Each type of disease requires its own approach to therapy.
Diagnosis of the disease
Which doctor treats sialadenitis? A dentist can treat sialadenitis. Diagnosis of the problem begins with an external examination of the submandibular, parotid and sublingual glands.
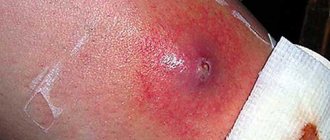
During an external examination of the patient, the doctor pays attention to several criteria: soreness of the lump; redness and swelling of the skin over the damaged area; lack of fluid secretion; the presence of purulent discharge when pressing on the gland.
Laboratory methods are necessary to confirm developing inflammatory processes in the body. The patient is prescribed:
- General blood analysis. The presence of pathologies in the body is indicated by a reduced erythrocyte sedimentation rate (up to 30 mm/h) and a shift to the left in the leukocyte formula.
- Biochemical blood test. Inflammation is indicated by the appearance of a C-marker in the body.
- Oral swab analysis. Using the procedure, the type of causative agent of sialadenitis is determined. This study allows you to create a competent treatment regimen.
- Serological tests (ELISA, PCR). They allow you to identify the degree of accumulation of antibodies in the body to the causative agent of the disease.
Sometimes purulent discharge from the salivary gland goes directly into the mouth. The condition indicates an infectious problem. If the attending physician suspects a complication of the disease, he suggests the patient undergo a set of instrumental studies:
- The CT method is based on X-ray radiation. The tomograph produces a series of layer-by-layer images, with the help of which the condition of the salivary glands and the presence of tumors in them are assessed.
- MRI. Gives the same clear images of the salivary glands. The method is considered less safe for the human body due to the lack of x-ray radiation.
- Ultrasound is the most common way to diagnose sialadenitis. The method has a number of advantages over other studies - accessibility and speed of implementation.
MRI is considered the most reliable way to determine sialadenitis, especially if the disease is associated with neoplasms in the oral cavity
General principles of treatment
Treatment of sialadenitis includes medication, physiotherapy, folk remedies and surgery (in severe cases). Only a doctor can select a suitable treatment regimen after determining the cause of the problem and studying the symptoms of inflammation of the salivary gland. A special diet will help strengthen the results of treatment and speed up recovery.
Diet for sialadenitis
Nutrition during illness should consist of crushed foods, since it is difficult for the patient to chew and swallow large pieces of food. The menu is allowed to include: well-cooked porridge; puree soups; vegetable stew; vegetable purees. It is important to consume enough liquid to periodically moisturize the mucous membranes of the mouth.
In addition to regular still water, you can drink juices, compotes, decoctions and milk
Limit consumption of soda and sour drinks. It is forbidden to drink alcohol, strong coffee, tea.
In case of inflammation of the salivary gland, dry compresses with dioxidine and alcohol solutions in combination with UHF therapy effectively help. In addition to compresses, antibacterial ointments are used. A suitable drug is selected after obtaining a swab from the oral cavity.
If sialadenitis is infectious in nature, preference is given to antimicrobial agents: Kamistad, Cholisal, Solcoseryl. Ointments are used to treat areas under the tongue.
Fungal infections are eliminated with Nystatin ointment. The course of therapy and frequency of use of antifungal ointments is determined by the dentist, since their components in large dosages are toxic to the body. After treating the affected areas, refrain from eating and drinking for 30 minutes so that the components of the drug have time to penetrate the mucous structures.
Drug treatment for inflammation of the salivary gland should be supported by maintaining a healthy lifestyle: quitting smoking, adjusting the diet, and refraining from the habit of pulling foreign objects into the birth.
Tobacco smoke is especially dangerous for a person with sialadenitis. A bad habit leads to the fact that the acute form of the disease becomes chronic
Drug treatment
Depending on the cause of inflammation of the salivary glands, patients are prescribed: antihistamines, antibiotics and antivirals, anti-inflammatory drugs. Sialadenitis of viral origin is treated with interferon drugs. In case of a bacterial type of disease, the introduction of antibiotics into the ducts of the gland is indicated.
Biochemical analysis of saliva
Antimicrobial therapy is supplemented by treating the mouth with solutions of potassium iodide and pilocarpine. The products stimulate salivation. Lemon juice and chewing gum are used for the same purpose.
Dry compresses and physiotherapeutic procedures can help relieve pain. To reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process, take Ibuprofen orally. The drug is also suitable for reducing the temperature that occurs in complicated forms of sialadenitis.
If there is no effect from conservative treatment within 5-7 days, the patient is prescribed surgical intervention. Its essence is to open and cleanse the abscesses and drain the wound.
In rare cases, antibacterial agents are used for mumps: solutions of antibacterial agents (about 1 mm of solution) are injected into the affected gland.
What antibiotics are used? Combined solutions, for example, streptomycin and benzylpenicillin, are injected into the ducts of the gland. This treatment regimen can be used to treat the acute and chronic stages of the disease.
There may be several indications for surgical intervention for inflammation of the salivary glands:
- blocking of ducts with a foreign body;
- formation of an abscess in the gland;
- narrowing of the ducts;
- stone formation.
In chronic forms of sialadenitis, the salivary gland is completely removed.
The photo shows the types of incisions used for damage to the parotid salivary glands
Treatment depending on the form of the disease
When drawing up a treatment regimen, the nature of the pathology must be taken into account. Acute sialadenitis is treated on an outpatient basis, following all the doctor’s recommendations. Viral forms of the disease are useless to treat with antibacterial drugs.
The acute form of viral sialadenitis is eliminated with the help of immunomodulators and drugs with Interferon. Additionally, medications are used to alleviate the symptoms of the problem: anti-inflammatory, wound-healing, antipyretic.
To reduce the concentration of viral pathogens in the body, plenty of warm fluids are required.
Acute bacterial sialadenitis requires adherence to a salivary diet and the use of antibacterial drugs. This type of illness is treated in a hospital. The drugs are administered to the patient into the affected gland 2 times a day. For home treatment, antibiotics are used in capsules or injection solutions. The oral cavity is rinsed with a warm solution of Dioxidin.
Acute forms of sialadenitis in a child are treated with compresses on the affected area. The procedure is performed once a day for 30 minutes
Of the physiotherapy procedures used to treat calculous sialadenitis, UHF is noted. For difficulty eating and severe swelling, blockades with Novocaine and Penicillin are used. To prevent the formation of adhesions during inflammation of the salivary gland, intravenous injections of Contrical or Trasylol are prescribed.
Chronic forms of the disease are treated in almost the same way as acute ones. In this case, it is important to maintain active saliva formation to prevent the occurrence of purulent plugs.
For chronic disease, treatment includes:
- massage the affected area with the introduction of antibacterial agents;
- novocaine blockades;
- electrophoresis with Galantamine;
- galvanization;
- course intake of potassium iodide;
- periodic injection of Iodipol into the gland (once every 3 months).
Iontophoresis is a modern physiotherapeutic procedure to combat inflammation of the salivary glands.
Folk remedies
Drug treatment of sialadenitis is supported by home treatment. To do this, they use natural ingredients, the effectiveness of which has been tested by generations of people. You can make compresses, decoctions, etc. from natural ingredients. The main goal of this method of therapy is to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and increase the body's resistance.
Therapeutic compresses
A compress made from homemade cottage cheese is effective. The milk product is evenly distributed over a gauze bandage and applied to the problem area for 1 hour. The procedure is performed once a day, replacing the old cottage cheese with a new one.
A decoction of celandine works well for signs of inflammation of the parotid salivary gland: 3 tbsp. l. vegetable raw materials are poured with 300 ml of water and simmered for 15 minutes over low heat. A cotton pad is moistened in the decoction and applied to the lesion. Instead of celandine, you can use other plants: hemlock, calendula.
A good addition to therapeutic compresses is daily consumption of carrot juice. The product promotes the healing of affected areas of the submandibular gland. It is recommended to drink at least 200 ml of the product per day
Herbal infusions
Medicines increase the secretion of saliva and contribute to the death of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. You can treat sialadenitis:
- chamomile – has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves swelling;
- mint – activates the salivary gland and eliminates bad breath;
- raspberry leaves – have a regenerating effect.
Before using each of the listed remedies, it is recommended to consult a specialist, especially if multicomponent medications are used for therapy. The means that help one person are not always effective for another. In addition, the treatment of sialadenitis in children and adults requires a different approach.
Source:
What to do if the salivary gland is inflamed - effective treatment at home
Among all diseases of the salivary glands, inflammatory processes (sialadenitis) predominate. Inflammation almost always develops in an acute form with pronounced swelling, purulent formations, tissue necrosis, and infiltration.
The main symptom of the disease is pain in the throat and swelling in the neck.
General concept of treatment and prevention
- Most doctors, after a detailed examination and diagnosis, prescribe a number of medications, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of inflammation of the salivary gland, but at the same time they do not resist the patient’s desire to be additionally treated at home using unconventional methods and folk remedies.
- As auxiliary therapeutic measures, it is useful to use various herbal decoctions, juices, and fruit drinks.
- When treating sialadenitis, drink plenty of fluids, and it is better if it is fortified.
It is best to eat acidic foods and drinks. You can take a slice of lemon and dissolve it in your mouth, or use chewing gum. This promotes salivation very well, and along with it, pathogenic microorganisms will also be eliminated from the body faster.
All recommendations given by the attending physician must be strictly followed to avoid complications with the formation of pus in the sinuses.
As preventative measures, it is necessary to adhere to simple preventive measures:
- regularly carry out wet cleaning with mandatory ventilation of the room;
- systematic daily procedures for maintaining oral hygiene, including cleaning the gums and tongue;
- give up harmful foods such as chips, crackers, sucking candies, which can damage the mucous membrane;
- strengthening general immunity;
- during the cold season, take immunomodulators and multivitamins;
- If suspicious symptoms appear, do not resort to self-medication.
Inflammation of the salivary gland spreads very quickly and threatens with serious consequences.
ethnoscience
Inflammation of the salivary glands is one of those diseases for which patients often practice treatment with folk remedies. For this, various medicinal plants are used: roots, herbs, berries. Aromatherapy, which uses essential oils, also helps to cope with the inflammatory process.
Before using any of the methods of traditional medicine, you should definitely consult with your doctor about the safety and effectiveness of such treatment.
Tincture recipes:
- Hemlock tincture , has a good effect . The first day is to start with one drop one hour before breakfast. Then repeat the procedure at 15.00 and 21.00, three hours after meals. And so every day increase the amount of tincture by one drop until there are 30 of them. After this, the countdown begins, every day the amount of tincture should decrease by one drop. The treatment course lasts three months, followed by a five-day break, and again according to the same scheme.
- Take celandine roots - 300 g (pass through a meat grinder), St. John's wort flowers - 50 g, yarrow - 50 g . Mix all ingredients, pour vodka (0.7 l). Leave at room temperature in a dark place for one week. After infusion, strain and you can apply compresses with the resulting liquid.
Causes
It is very easy to get mumps. It is enough to simply contact someone who is already sick. The carrier of the virus is highly contagious. Almost 50% of those who come into contact with him may get sick. Already at the stage of the incubation period, such a person is infectious and poses a danger to others. This is why it is so important to monitor the health of children, for example, in a kindergarten group. If nannies and teachers do not notice that there is a sick child in the group, he can infect almost half of the children. But the difficulty lies in the fact that at the stage of the incubation period no symptoms of the disease are yet observed. Moreover, a person will be dangerous to others even a week after the first clinical signs of the disease appear.
How does such an aggressive pathogen enter the body? It penetrates through the respiratory system. It is the respiratory tract that becomes the gateway through which the infection instantly penetrates into the body. Some deterrent for it may be the nasal mucosa, which prevents microorganisms from penetrating further. Therefore, during epidemics, it is useful to rinse your nose at least once a day with a solution of ordinary table salt (1 teaspoon per glass of warm water). But this method is not suitable for small children, since they will not be able to perform this procedure correctly and efficiently. They can simply instill one drop of the same saline solution into their nose.
So, mumps enters the body through airborne droplets. For infection to occur, a sick person simply needs to sneeze or cough nearby. It is also possible to become infected through a kiss. But we should not forget about the household method of transmission of infection. After all, a sick person grabs objects around him: towels, pens, dishes, toys, etc. Accordingly, his saliva, which already contains the virus, falls on them. It is enough for a healthy person to handle the same object for the infection to pass to him. Therefore, you need to wash your hands as often as possible and try to handle objects less in public places. If we are talking about children, then you need to wash their toys, wash their towels, and wash their hands more often. And the dishes must be kept almost perfectly clean.
Prevention of mumps
The only way to prevent mumps is the triple vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella. The vaccine is called MMR, from the first letters of the English names of these diseases. The vaccine contains a weakened live virus. Its effectiveness is about 97%. It refers to compulsory vaccination. It is first performed between 13 and 14 months of age and is free.
Unfortunately, the vaccine does not provide lifelong protection, i.e. only works until school age. At school age, re-vaccination is carried out. It is important that even a vaccine does not completely protect a child from mumps, it significantly softens the course of the disease, and the risk of complications is also significantly reduced. It is imperative to remember not to vaccinate sick children.
Mumps vaccinations are not used in pregnant women, patients receiving treatment with glucocorticoid drugs, or other immunocompromised patients. However, there are no contraindications to vaccinating children infected with the HIV virus.
Shortly after vaccination against mumps, in rare cases, unwanted reactions are observed, such as fever, mild inflammation of the parotid salivary glands.
Allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, rarely appear after vaccination and, as a rule, are minor and disappear spontaneously. It has also been proven that vaccinated children have an increased risk of brain inflammation over the next month.
Symptoms
In order for mumps to proceed without complications, it must be identified and treated promptly. What are the symptoms of mumps? It all depends on how severe the disease will be. We will describe the most typical clinical picture. Approximately 11-23 days of the so-called incubation period will generally pass without any symptoms. A person will go about his usual activities, but the virus will already multiply in his body. At this stage, he already poses a danger to others and can easily infect them.
When the first symptoms appear, they will differ little from the usual manifestations of viral diseases.
The first symptoms of mumps:
- Headache.
- Lethargy.
- There is a feeling of aching in the joints and muscles.
- Lost appetite.
- The temperature rises.
After about a day, the characteristic symptoms of mumps appear: noticeable swelling and soreness appear in the ear area, and dryness of the oral mucosa is observed. In this case, the salivary parotid glands are affected. This may soon be accompanied by inflammation of the submandibular and sublingual glands. Visually, it is difficult not to recognize the pig. The child experiences swelling of the glands, and the area under the chin may also noticeably increase. On the side where the swelling appears, the ear may even protrude. Due to the inflammatory process, it becomes difficult for the child to swallow and chew.
It is by swelling that mumps can be easily identified. They are formed due to the fact that tissue damage begins around the gland. In this case, the excretory ducts of the glands are affected and then blocked. The swelling will not have clear boundaries and is soft to the touch. With mumps, salivation is impaired. This happens because inflammation of the salivary sublingual glands begins. Because of this, the patient may develop stomatitis. This is explained by the fact that during the inflammatory process in the gland, saliva loses its antibacterial properties and can no longer effectively fight infection. This can even cause disruption of normal bowel movements and may cause pain in the abdominal area. All this is explained by the fact that an infection has entered the body. And since the body is already weakened by the action of the mumps virus, it is doubly difficult for it to cope with an intestinal infection. The form of the disease largely influences the severity of mumps.
Inflammation of the parotid salivary gland in adults
The inflammatory process in the parotid salivary gland affects both adults and children with equal frequency. And if in young patients this pathology is more often caused by the penetration of a viral agent into the blood (causing the so-called “mumps”), then in older patients the range of possible etiological factors in this situation is much wider and has a number of specific symptoms.
The course is divided into acute (newly occurring and proceeding with a clear clinical picture) and chronic (sluggish, with vague symptoms and periodic relapses) inflammation of the parotid salivary gland.
You should not try to treat sialadenitis yourself by seeking help from unqualified specialists. In this case, the patient risks not only not achieving the desired results, but also significantly aggravating the existing situation.
If stones are detected in the parenchyma of the organ, the doctor diagnoses calculous sialadenitis (as well as inflammation of the parotid duct), which in advanced stages requires surgical treatment (the duct is “cleared” of a foreign body).
Severe form
The symptoms are pronounced. The patient suffers from high fever (about 40°C). It hasn't subsided for quite some time. There are even disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. The patient may experience a significant drop in blood pressure, tachycardia, and disturbed sleep. In severe cases, all sorts of dangerous complications often occur.
How severe the disease will be depends on a number of factors. First of all, it depends on the age of the patient. It has long been noted that children tolerate mumps much easier than adults. And they get mumps much more often than adults. That’s why this disease is sometimes considered a childhood disease. In children, the salivary glands can be affected on one or both sides. If an older person has mumps, they will likely experience more severe symptoms and the disease will be much more severe. Most often, in adults, the salivary glands are affected on both sides, which causes their health to worsen.
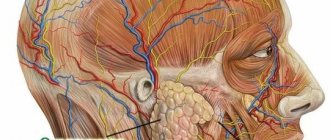
Localization of the parotid salivary gland
The parotid gland is the largest of all glands and has an irregular oblong shape. It is located immediately under the skin in the parotid-masticatory area. The anatomical formations that make up the boundaries of the gland are as follows:
- above - zygomatic arch;
- below - the angle of the lower jaw;
- behind - the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the sternocleidomastoid muscle;
- in front - the posterior edge of the masticatory muscle.
The parotid salivary gland is covered with a rough, dense capsule, the processes of which penetrate into the thickness of the organ, giving it a lobular structure.
You can get the most complete idea of the location of the parotid gland from the photo below:
Non-mumps
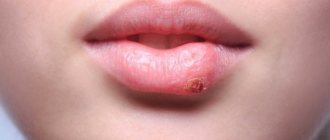
The non-epidemic form of mumps occurs much less frequently than the viral form. Its main causes are blockage of the duct that removes saliva by various foreign bodies, salivary stone disease, and trauma. The cause may also be surgery or previous infectious diseases (influenza, typhus, pneumonia, encephalitis). Symptoms will be similar to viral mumps:
- A swelling will appear near the auricle. It's quite painful.
- The earlobe begins to protrude.
- The skin around the ear turns red.
- Saliva of the usual consistency is not produced. It is replaced by a liquid that resembles pus or cloudy secretion.
- The temperature rises (up to 39-40 degrees).
- There is pain when swallowing.
Often the area of inflammation is so painful that the patient has difficulty opening his mouth. As soon as the diagnosis is made, comprehensive treatment should begin. It is important that the patient strictly follows all the doctor’s advice. Otherwise, the inflammatory process may intensify and purulent melting of the glands will occur.
Clinical picture
Sialadenitis is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- shooting pains in the area of the affected gland - they can radiate to the ear, mouth or neck;
- pain when swallowing and chewing;
- swelling and redness;
- the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, there is a risk of pus formation;
- dense formation in the affected area;
- feeling of fullness;
- temperature increase to 39 degrees;
- general weakness.
A particularly dangerous form of the disease is mumps, which can lead to damage to other glands - mammary, pancreas, and genitals.
If the pathology is not treated in time, there is a risk of purulent complications.
Treatment
If inflammation of the salivary gland has begun, symptoms and treatment should be determined by a doctor. Therefore, at the first sign that there is a problem in the body, you need to consult a doctor. He will conduct a thorough examination, prescribe tests and a treatment regimen. The entire course of therapy will be prescribed only when the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. If the case is typical, then it will not be difficult for him to make the correct diagnosis, since mumps is easy to recognize by its characteristic symptoms. But there are times when additional examination techniques are required. But such cases happen quite rarely.
If the case is typical and mumps occurs without complications, then it is most often treated at home. There are no special medications for the mumps virus yet. Therefore, all treatment will be aimed at maximizing the relief of the patient’s condition, as well as preventing the occurrence of any complications. But even with a normal course, the patient must be under the strict supervision of a doctor. It is important to remember that even in mild cases, dangerous complications are possible. And since children most often suffer from mumps, it is necessary to constantly monitor the health of the little patient.
It is important that the patient is isolated. Do not forget that the mumps virus is very easily transmitted by airborne droplets and through household objects. If a child in the family gets sick, parents should also take care of protection from the virus. After all, in adults, mumps occurs in a more severe form. The doctor will most likely advise the patient to remain on strict bed rest for about a week. If this recommendation is ignored, serious complications are possible. For example, boys often experience orchitis, an inflammation of the testicles. If you do not comply with strict bed rest and expose the weakened body to stress, then the risk of orchitis increases more than 3 times. To alleviate the general condition of a patient with mumps, the doctor will prescribe:
- Painkillers and antipyretics (ibuprofen, paracetamol).
- A dry warming bandage should be applied to the affected gland (but such a bandage cannot be applied at a high temperature. Only when the temperature drops to 37.2 C is such a dry bandage allowed to be applied).
- Drink more. An increased drinking regimen should help relieve inflammation as quickly as possible.
- The oral cavity requires careful care. This is due to the prevention of stomatitis. It often occurs with mumps, as the antibacterial properties of saliva are reduced. After eating, it is better to rinse your mouth with a soda solution.
- A special diet with a high content of dairy products and fiber.
- To make food easier to swallow, it is better to grind all dishes. You should exclude sour, spicy, fats, sour juices, pasta, cabbage, white bread.
- To increase salivation, you can periodically dissolve a piece of lemon in your mouth. But this is only if there is no high temperature.
- Your doctor may prescribe physical therapy methods, such as ultraviolet or UHF radiation.
- It is useful to drink herbal teas and decoctions. They have a good general strengthening effect and relieve inflammation.
- It is useful to drink linden infusion and rosehip decoction.
- The mouth can be rinsed with infusion of sage and chamomile.
If the course of mumps is complex, then the patient is recommended to be treated in a hospital.
Inflammation of the salivary gland treatment at home – ProfiMed – aesthetic dentistry
The parotid or salivary gland belongs to the digestive system and is responsible for the secretion of saliva. Humans have large salivary glands, as well as several hundred small glands scattered in the mucous membrane of the mouth, as well as in the throat, larynx and nose.
The largest is located in the parotid region on the lateral surface of the faces, accessible for palpation between the mastoid process and the lower jaw. The second largest is the submandibular gland, in third place is the sublingual gland.
Mumps, as mumps is colloquially known, is an inflammation of the parotid gland. This disease is predominantly of childhood, but can also affect adults and cause serious complications.
How to treat the salivary gland at home? Using tinctures
In addition to modern traditional medicine, folk remedies help to gradually get rid of sialadenitis. A variety of tinctures that are made independently from plant components have proven effective. To prepare the tincture at home, you need to take the following ingredients:
- wild raspberry root – 0.5 kg (it is recommended to collect the component before flowering and bud opening);
- young pine shoots – 1 kg;
- honey – 500 g;
- granulated sugar – 1 kg;
- water – 500 ml;
- alcohol or vodka.
You can find plant materials yourself among forest plantations or purchase a ready-made version. When all the components are prepared, you need to grind the raspberry root to medium-sized granules. Next, boil water, immediately pour in the pine shoots, allowing the mixture to brew for 4 hours.
After time, add raspberry root, honey, and sugar. Place the bowl with the tincture in a water bath and simmer over low heat for 8 hours. As soon as the mass is ready, it is poured into a glass jar and left to infuse for 2 days in a dark place.
The infused mass is filtered through cheesecloth or a fine sieve, without discarding the remainder. The strained mixture is diluted with alcohol or vodka in a ratio of 1:10. The remains are also poured with alcohol until the liquid completely covers the mass. Close and leave for a month, just like the strained composition.
The prepared tinctures must be mixed and a solution of 1 tbsp taken. three times a day. If you do this half an hour before meals, the composition will be absorbed better. The course of treatment lasts 10 days.
If you plan to take the tincture for preventive purposes, it is recommended to do this in the fall or spring, when the body experiences a lack of vitamins.
In another topic: inflammation of the salivary gland in a child. A detailed analysis of the symptoms of the disease in children - from mumps and mumps to acute nonspecific sialadenitis.
For information on edentulous diseases in children, see here.
Read about the treatment of wedge-shaped dental defects here.
Sialadenitis of the parotid gland in children
In children, parotid sialadenitis occurs as a result of mumps. The pathogen is transmitted by airborne droplets. When a virus enters the body, it penetrates the gland, causing its inflammation. Accompanied by fever, vomiting, severe headache.
Complications
Mumps is dangerous due to its unexpected complications. But most often they are associated with the fact that some patients have reduced immune function. Complications are also observed in those patients who suffer from any chronic diseases. It’s bad if the patient’s weak point is precisely those organs and systems that mumps most often affects. After the first symptoms of mumps, after a few days, symptoms may appear that indicate a complicated course of this disease:
- The headache gets worse.
- There is severe nausea and vomiting.
- Dizziness and loss of coordination appear.
- Visual disturbances are observed. There may be double vision.
- Abdominal pain.
- Hearing may be impaired or a strong ringing may be disturbing.
- Urine darkens.
- There may be numbness in any part of the body.
- Cramps.
- Loss of consciousness.
- In boys and men, the disease may be accompanied by scrotal pain.
- Orchitis often occurs in men. It makes itself felt either immediately after the salivary glands are damaged, or after 1-2 weeks. In this case, the patient suffers from severe pain and redness in the scrotum area. It becomes inflamed. The temperature rises to 39-40 C. Orchitis is especially dangerous for those boys who have entered the puberty phase. It can even lead to infertility. In severe cases of orchitis, even testicular atrophy is possible. Infertility occurs in cases where two testicles are damaged at once.
If inflammation of the salivary gland has begun, it is important to prescribe treatment as early as possible. This will protect you from all sorts of complications. You should also strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. If he prescribed bed rest, then it must be observed. The fact is that the mumps virus is quite insidious and dangerous to the body. Therefore, you should not subject an already weakened body to additional stress. In girls, mumps most often occurs in a milder form, but this does not mean that their treatment will be less important. You need to take all the medications prescribed by the doctor. If you have doubts about any of the prescribed medications, you should immediately consult a doctor rather than canceling it yourself. Remember that the child’s health largely depends on how responsibly his parents treat the treatment process.
In girls, complications are most often associated with menstrual irregularities. In more severe cases, ovarian atrophy is observed. Also, with complications, mumps can develop:
- Meningitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Hearing loss and even deafness may develop.
But if you seek qualified medical help at the first symptoms of the disease, the outcome of mumps is most often favorable, even in the presence of complications.
Unfortunately, it is quite difficult to protect yourself from mumps, especially during an epidemic. But if you follow our simple tips, you can still minimize the risk of infection. And if the virus has entered the body, it is important to immediately begin comprehensive treatment. Always try to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat rationally, exercise, walk more in the fresh air and your body will be as prepared as possible for a possible viral attack. If you do get sick, contact your doctor immediately. Moreover, it is worth clarifying that you do not need to go to the clinic on your own, because you pose a real threat to others. To avoid infecting anyone, call a doctor at home. Well, your relatives will be tested to see how well they can observe the rules of personal hygiene. Remember that the virus is very easily transmitted through saliva. If the patient touched dishes, towels, pens and other objects, it means that a dangerous virus has settled on them. Therefore, wet cleaning should be done more often, and the patient should have his own dishes and hygiene items. It is also important not to neglect bed rest. Strictly follow all doctor's recommendations. If complications arise, it is better to continue treatment in a hospital.
Video about salivary glands
Clinical significance
A sialogram is a radiopaque examination of the salivary duct that can be used to examine its function.
Due to the formation of stones in the ducts, they can become blocked, causing pain and swelling due to the cyst.
Salivation can be stimulated pharmacologically by salivary agents (eg, pilocarpine, cevimeline). It can also be suppressed with antisalivation medications (eg, tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, antihypertensives, polypharmacy). Many cancer treatments can worsen salivation, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Radiation therapy can lead to irreversible hyposalivation due to trauma to the oral mucosa, resulting in dry mouth or xerostomia, while chemotherapy may only cause temporary deterioration of salivary flow.
After allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, dry mouth and many small mucoceles are possible due to graft-versus-host disease.
Tumors of the salivary glands are possible.
In other species
However, in some species these organs have changed to produce enzymes; salivary amylase is found in many, but not all birds and mammals (including humans). In addition, the venom glands of venomous serpentine snakes and some shrews are modified salivary organs. In other organisms, such as insects, they are often used in the production of biologically important proteins such as silk or glues, and in flies, these organs contain polytene chromosomes that have been useful in genetic research.