.
In dentistry, there are many different diseases of the oral cavity and teeth. If you notice a red spot on your gum, do not be alarmed, it could be gingivitis, periodontitis or periostitis. It sounds scary, but don’t be afraid - all these diseases are easily treated in modern medicine.
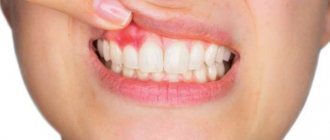
Abscess in the mouth - red abscess
Why do red spots and dots appear on the palate and other mucous membranes in the mouth?
If a person, who suddenly once felt unwell, has red spots in his mouth (on the palate, lips, gums and other mucous membranes), it may well be that this is not a reason to panic, but just a hint that it is worth contacting the nearest dentist . For in the name of this profession, the first part of the word: “stoma” means not only teeth, but also the mouth in general, while the word dentist itself is a specialist in oral diseases. Including those that are accompanied by the appearance of spots and rashes of any color.
Prevention
The main means of preventing oral diseases is careful control over hygiene. In relation to diseases of the gums and other soft tissues of the oral cavity, attention should be paid not only to brushing the teeth, but also to the personal hygiene of the child:
- Regularly disinfect toys that your baby puts into his mouth and thoroughly wash and sterilize/steam feeding accessories.
- The baby should be given a few drops of water after each breastfeeding or formula feeding to “wash away” the remaining milk or formula and prevent the formation of a breeding ground for microbes.
- Monitor your child's general health - a strong immune system protects against many diseases, not just dental ones.
Causes of occurrence and mechanism of occurrence
The appearance of red spots in the oral cavity and in areas adjacent to it can be due to various reasons.
For example, a vascular reaction due to:
- cerebral or vascular accident;
- acute poisoning;
- entry into the body of an acutely infectious infectious agent (virus) or activation of its own chronic flora (microbial, fungal, mycoplasma or protozoal infection of the pharynx).
The second category of reasons for the appearance of spots within the oral cavity is cases of allergies.
Thirds include damage to the mucous membranes with discoloration of their surface layers. As in the case of exposure to too high or too low a temperature, and in similar situations.
Strictly speaking, all episodes of changes in tissue color in the area under the dentist’s control, perceived as the appearance of red spots and dots in the mouth, are caused by vascular disorders in it, occurring at different rates.
Thus, hyperemia when exposed to excessively high temperatures appears almost instantly due to vasomotor paresis of the capillaries, while cyanosis with a purple tint when exposed to extremely low temperatures develops after some time necessary to slow down the blood flow or complete stasis of the blood in the damaged area.
Red spots on the palate due to acute infections
Despite the common mechanism for the appearance of red spots on the palate due to injury, chronic intoxication (smoking) or due to acute infection in the mouth, their characteristics will be significantly different from each other.
If the spots on the palate of a smoker are similar to spider veins and are not accompanied by a clinical picture of acute damage to the body, then during an infectious process it is a rash characteristic only of a specific disease in combination with general clinical symptoms.
Thus, with chickenpox, the rash has the appearance of bubbles on a hyperemic conical base, located not only on the palate, cheeks, tongue and other mucous membranes in the mouth, but also protruding to the surface throughout the body.
In addition to red spots and a polymorphic rash in and around the mouth, stomatitis of herpetic etiology manifests itself:
- regional lymphadenitis;
- hyperthermia;
- symptoms of intoxication in the form of headache, body aches, weakness and similar phenomena;
- pain in the mouth from eating.
In a flu-like state, toxic effects come to the fore, but the appearance of a rash is also common.
Unlike a viral rash, when a chronic microbial or fungal infection is activated, the spots will have a less impressive appearance. If a viral rash is like a volcano exploding the mucous membranes from the inside, then a microbial and fungal rash looks less militant.
Despite a significant burning sensation in the areas where painful points are located and discomfort during eating, candidiasis does not occur as violently as chickenpox. Its distinctive feature is a typical white yeast coating on the formed elements of the rash.
The characteristic appearance of a scarlet fever (streptococcal) rash is red pinpoint spots not only in the mouth, but also around it, in the corners of the mouth, on the lips and cheeks, as well as on the skin of the body, with a tendency to merge. The nasolabial triangle is free of rash.
The sequence of appearance of the rashes: face, arms, upper body. A skin test is indicative: when a hard object is passed over the surface, a white stripe remains, then the rash appears again, confirming the diagnosis, as well as symptoms of severe intoxication.
If the cause is poisoning
A classic example of a poisoning rash is a meningitis rash.
With this disease, which is infectious in nature, capillary paresis occurs with the appearance of hemorrhages of various sizes and shapes (red, black, white dots) in various parts of the body, including in the mouth.
The difference between hemorrhages and spots of a different nature is that when the affected area of the skin or mucous membrane is pressed or stretched, they turn pale and disappear, only to appear again after the end of the exposure.
Allergy sign
Due to the expansion of the geography of travel of citizens abroad and the approaching of East Asian and other exotic cuisines closer to the consumer, as well as the introduction of artificial and herbal food additives into food, rashes with a complex etiology may appear.
These are symptoms of poisoning in the form of pain and colic in the abdomen, but with signs of allergy coming to the fore: severe skin itching against the background of more or less significant swelling of the tissues of the extremities, face and oral cavity with protrusion of rash elements of varying degrees of hyperemia to the surface.
A fairly typical concomitant manifestation of allergies is suffocation and nasal congestion of varying severity due to
swelling of the respiratory system.
The appearance of hyperemia (spread or in the form of red spots and dots in the mouth and lips), similar in appearance to a burn, is possible not only with food allergies, but also with:
- household allergies;
- with the mistaken use of liquids of unknown composition and in similar situations, especially by children.
Traditional methods of treatment
Folk remedies help get rid of white mouth sores faster, and they are also widely available.
- Dilute 1 teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth.
- Add a teaspoon of calendula tincture to half a glass of water; you can apply this solution to the affected area.
- Squeeze carrot juice and dilute it 1:1 with water, rinse your mouth.
- Grind 1 clove of garlic, mix with sour cream (1 tsp), apply to the aftertaste.
- Chop raw potatoes and make a lotion on the sores.
- Grind the burdock seeds, add a little salt to the resulting juice, evaporate over heat, adding a little butter to make an ointment. Use this ointment to lubricate all aphthae that appear in the oral cavity.
Traditional medicine is not the ultimate truth; all the remedies described should only accompany the main treatment, and not be independent remedies for aphthae. Before using them, it is important to consult a doctor.
If your gums are red and painful, you should seek help from the hospital as soon as possible. At home, you can only relieve unpleasant symptoms, but not eliminate the cause of their occurrence. Therapy is prescribed only after a comprehensive diagnosis. The most effective and common treatment methods will be discussed below.
If the disease has caused a large amount of plaque and stone, this procedure is necessary. Recently, ultrasonic or laser cleaning has been used for this purpose. The advantages of mechanical cleaning are that there are no side effects.
After professional cleaning, teeth become white and gums become healthy.
If the gum above the tooth is red, and the reason lies in the inflammatory process, dental products can be used, namely, ointments and gels.
| Name | Description |
| The gel is used in dentistry and has several effects: analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial. There are two forms: children's and adults. |
| The combined action agent is used in dentistry. The release form is liquid, the smell is reminiscent of menthol. It is used both as a preventive measure and for the treatment of oral diseases. |
| The drug accelerates regeneration processes, relieves inflammation and pain. In addition, the oral mucosa is cleansed of pus and pathological bacteria. |
| The drug relieves inflammation in the oral cavity. It is not a bad analogue of other means. |
In particularly advanced cases, Solcoseryl or Actovegin may be prescribed.
Physiotherapy
They can be either auxiliary methods of treatment or primary ones. In case of gum disease, manual or hardware massage, electrophoresis or darsonvalization are performed. The main advantage of such methods is that there are no contraindications and can be used even for children and pregnant women.
The procedure is indicated if there is pus in the gum pockets. The patient is given local anesthesia, after which the deposits are scraped out. It is extremely rare to have to dissect the gums.
Splinting
If teeth are loose, the procedure is considered necessary. The teeth are secured with a removable or non-removable splint, this reduces the likelihood of complications. During chewing, the load is evenly distributed.
Example of the procedure
Implantation
The gums are red and painful, what should I do? If this is associated with periodontitis or complicated periodontal disease, implantation is required. After the procedure, it is possible to eliminate malocclusion, and the condition of bone tissue improves.
In folk medicine, there are enough methods to eliminate redness on the gums, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms. The most effective way is rinsing.
| Name | Mode of application |
| Lemon is the main ingredient in traditional medicine recipes. To relieve the inflammatory process, you can mix lemon juice and water, and then treat problem areas with the resulting liquid. Do not allow the product to come into contact with tooth enamel. |
| To prepare the solution, take part water and ten parts alcohol tincture and rinse your mouth twice a day. |
| Soak a cotton swab with oil and treat the gums. Rinse your mouth with water after ten minutes. To achieve results, it is recommended to carry out the procedure every day before bed. |
| The juice of the plant has an anti-inflammatory effect and is often used in folk medicine. Clean the leaf from the film and wipe it on the sore spot of the gum. |
| To relieve the inflammatory process, you can use lemon balm tincture. Pour half a liter of boiling water over a spoonful of herbs and let it brew for three hours. Strain the cooled product and rinse your mouth several times a day. |
| Grind several lemon peels in a blender, mix the resulting pulp with a small amount of vegetable oil. Let it brew for two days and apply the resulting ointment to problem gums several times a day. |
If you are experiencing severe pain, but there is no way to visit a doctor, you can take a pain reliever.
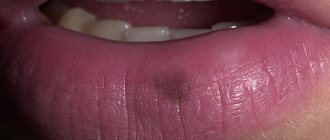
Red spots and sores on the gums and cheeks
The most common cause of such localized redness is gingivitis, which does not necessarily have to be of viral, bacterial or mycotic etiology.
It may also be a consequence of slowing down the healing processes of microdamages as a result of conditions that weaken the body:
- tuberculosis;
- AIDS;
- oncological pathology;
- aging.
The morphology of its manifestations is varied - from flat spots to deep narrow holes in the gums and ulcers with undermined edges, painted in various shades of red.
Red, inflamed areas of the mucous membrane on the cheeks are often the result of biting, which can be either a random one-time act or a habit that has become a system.
About red spots on the tongue and red tongue
Red spots that appear on the tongue can be a signal of disorders in the body when:
- allergic reactions;
- eating food that hurts the tongue physically and chemically;
- presence of bad habits;
- lack of oral hygiene;
- dental diseases;
- oppression of the body, physical or mental.
A separate category of causes consists of diseases with changes in the surface of the tongue.
Read also: Tumor on the gum in a child With mononucleosis, this is the appearance of pinpoint hemorrhages on it, which are also present on the soft and hard palate. The disease has all the features of an infectious process: lymphadenitis, hyperthermia up to 40°C, symptoms of severe intoxication.
The same violent symptoms are also characteristic of exudative erythema, which ends with the transformation of red spots into blisters filled with serous fluid, after opening of which ulcers are formed that merge together. The process develops with the involvement of the lip mucosa.
Changes in both the color and the tongue itself are characteristic of a variety of pathological processes: with syphilis it is a crimson chancre, with Kaposi's sarcoma - moderate pain and the presence of non-protruding red spots with a bluish tint in the area of the tongue root, with anemia, red spots stand out in contrast on an almost white tongue spots accompanied by pronounced pallor of the gums.
Establishing diagnosis
Due to the various causes leading to the appearance of red spots, rashes and spots in the oral cavity and adjacent areas, a thorough investigation of the case with diligent history taking is necessary when the patient's condition allows. In the case of incapacitated persons and children, an interview with the mother or other caregiver is necessary.
If an infectious process is suspected, in addition to a physical examination, there is a need to analyze scraping material from the mucous membranes, culture it on nutrient media to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
It will be useful to participate in the diagnostic process of an ENT doctor, endocrinologist, mycologist, oncologist, each of whom will offer their own range of studies to determine the causes of the syndrome or disease.
Methods for treating redness
If inflammatory processes appear in the oral cavity, it is better to immediately seek qualified help. In this case, folk remedies can only eliminate obvious symptoms, but the cause of the disease will not be solved. Qualified assistance includes the following:
- hygienic cleaning of teeth from plaque and stone;
- carrying out anti-inflammatory therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- curettage of the contents of periodontal pockets;
- splinting teeth if they are very loose;
- implantation for partial tooth loss.
Hygienic teeth cleaning
You can treat red gums at home using well-known pharmaceutical products or folk methods.
Pharmacy products for the treatment of red gums
Pharmacies sell products that will help relieve the symptoms of inflammation in the mouth. The most common among them:
- Periodontocide;
- Holisal;
- Polyminerol;
- Maraslavin;
- Dental;
- Parodium;
- Asepta.
Cholisal
These products are available in different forms. To relieve redness of the gums, it is recommended to use balms, rinses and gels. They have hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
If you notice a rash in your mouth
Each case of a rash in the mouth, regardless of the primary or recurrent occurrence of the phenomenon, should be carefully examined by a dentist, even without life-threatening symptoms. Because one family member may have a sore throat
a highly contagious disease that will put the whole family to bed.
Under no circumstances should you delay an independent visit to the doctor, and if hyperthermia appears, increasing signs of swelling of the respiratory tract (even minor difficulty breathing), and especially nausea, vomiting and other cerebral phenomena, an ambulance must be called without fail and immediately .
In no case should the patient make an independent decision about his condition, much less attempt self-medication - all diagnostic and therapeutic measures must certainly be agreed upon with medical specialists.
For a painless and harmless-looking formation in the mouth can become the beginning of an oncological pathology.
Is treatment always necessary?
The general approach to treatment depends on the provoking cause.
If in the case of an allergy to toothpaste it is enough to replace it with another, then Kaposi's sarcoma requires radical surgical excision followed by radiation and chemotherapy.
In cases where the appearance of red spots is a symptom of an acute infectious disease, a course of therapy is carried out aimed at destroying or suppressing the pathogen that caused it.
Considering that the causative microorganism may be a representative of one of the many classes of pathogens, therapy is carried out using the following means:
- antimicrobial;
- antiprotozoal;
- antiviral;
- antifungal.
That is, the drug is selected taking into account the anatomy and physiology of the pathogen and its sensitivity to a particular category of active substances of medications.
These may be substances from the group:
- antibiotics;
- sulfonamides;
- nitrofurans;
- anti-tuberculosis action and others.
Considering that the changes produced in the body by the invasion of a pathogen are great and varied, in addition to means to suppress the cause of the disease, there may be a need for means with the effect of:
- antihistamine;
- painkillers;
- decongestant;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antipyretic or complex.
A separate category consists of emergency aid and resuscitation means, including the use of Euphyllin, Prednisolone, Adrenaline and others.
Most often, outpatient treatment is used using a complex of multidirectional agents. In cases that raise uncertainty about the possibility of outpatient therapy or present diagnostic difficulties, the patient is hospitalized in the department of the appropriate profile.
Conditions that cause depletion of the immune system and the entire body as a whole are treated with appropriate methods, starting with vitamin therapy and detoxification methods, including immunomodulators and replacement therapy, and ending with hardening procedures and exercise therapy, massage and similar measures for overall health improvement.
Chronic diseases require particularly persistent and methodical treatment using various categories of drugs, including hormonal ones.
Preventive measures to prevent the appearance of spots and rashes in the oral cavity and adjacent areas are also aimed at maximizing health promotion from childhood and imply timely and careful care of this area of the body, competent, nutritious and varied nutrition, elimination of harmful addictions, and in the presence of chronic diseases of any nature and their treatment.
Visiting a dentist at least twice a year who knows what to do with stains in the mouth and outside it should become the same habit as brushing your teeth twice a day.
Complications
Any problems with oral health are a direct threat to the respiratory system and digestive system.
In the first case, infection or inflammation quickly spreads to the pharynx, throat, trachea, vocal cords, since the oral cavity and oropharynx have a “common” mucous membrane.
And the constant presence of infection in the mouth leads to the fact that the child regularly swallows infected saliva, which can cause problems with the digestive system.
In addition, pain and discomfort, which always accompany inflammatory and infectious lesions of the oral mucosa, lead to sleep and appetite disturbances - a child, especially in the first year of life, may begin to lose weight, which negatively affects its development.
Treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the oral cavity in children is carried out using products approved for use in pediatric practice.
The child may be prescribed rinses, irrigations or lotions on the affected areas using the following means:
Which drugs to use and how exactly - in the form of rinses, irrigations, applications - is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the child’s age and the characteristics of the clinical picture.
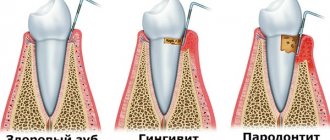
Gingivitis and its types
Gingivitis is one of the most common diseases in dentistry. Its characteristic features are inflammation of the gums, the appearance of red dots on them, and in some cases bleeding. The appearance of these symptoms signals that you need to visit a doctor and under no circumstances self-medicate, as this can lead to the next disease – periodontitis.
Erosion on the gums with advanced gingivitis
There are several types of gingivitis, which are determined by the nature of its course. We show them in the table below.
If your gums are red or strange spots appear on your gums, this is due to catarrhal gingivitis, which can be treated quickly and does not entail complications or the appearance of more serious symptoms, such as an increase or decrease in the volume of the gums, bleeding or desquamation of the epithelium of the oral cavity.
Fistula on the gum due to inflammation of the root
Suspicious symptoms
Many symptoms may indicate the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process; they appear gradually. As inflammation progresses, the intensity of the symptoms increases.
Appearance of redness
Red spots on the gums immediately catch the eye. If you notice this condition, but there are no other symptoms, this is still a reason to go to the hospital.
In the second stage of inflammation, bleeding appears. You can notice the release of blood during mechanical impact or while brushing your teeth. The phenomenon is serious and indicates that the disease is severe and long-lasting. Even slight palpation can cause severe pain.
The next stage is the formation of swelling, the accumulation of pus in the gum pockets, which causes an unpleasant odor.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Bright red dots on the tongue. Red dots on the tongue: causes and treatment
Red dot on a child's gum
Very often, mothers find red dots, pimples or strange spots in their child’s mouth. It is considered normal if the child’s oral cavity is pinkish in color without any abnormalities: cracks, redness of the gums, redness around the teeth, etc.
Read also: How does a dental cyst manifest itself?
Red dot - petechiae, tissue hemorrhage
But there are clinical cases that are caused by a number of reasons:
- Neglect of hygiene rules. Don't forget about brushing your teeth - even at an early age, when your child's teeth are just beginning to grow, and about rinsing the mouth after eating. In infants, a white coating may form on the gums. The reason for its appearance is mother's milk. There is nothing wrong with this - the plaque can be easily cleaned off using a special brush that is placed on your finger.
- Lack of calcium in breast milk can contribute to the appearance of spots or spots on the gums. All a nursing mother needs to do is balance her diet.
- HIV infection. In rare cases, HIV is detected in a newborn. This infection can be transmitted both from the mother and introduced in the maternity hospital.
- Bon's knots. These are formations of salivary gland tissue that contribute to the appearance of white spots on the child’s gums. Most often, these cysts go away on their own.
- Congenital teeth. It happens that a child is already born with teeth that rather resemble a white spot. With such a diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a doctor to remove them, since they may not be baby teeth, but additional ones, which in the future will lead to curvature of the teeth.
- Sometimes a pimple may appear on a baby's gum. Mothers think that this is a phenomenon of teeth sprouting, but this is not the norm, and it is necessary to show the baby to the pediatrician. It's probably stomatitis. The cause of a pimple in an infant may be a hormonal imbalance. This is due to its adaptation outside the womb.
Gingivitis in a child before teething
- In addition, the child may experience the appearance of white or red spots and dots on the gums. These growths can develop into growths that can be painful. The reason for this process may be:
- Teething. It happens that a pimple appears in the place of a missing tooth. This is not an anomaly and will pass over time.
- Viral stomatitis caused by herpes.
- The appearance of pus due to gum damage.
To prevent your child from having red spots on his gums, you can give him one teaspoon of boiled water after each feeding.
Stomatitis on a child's gums
Home Remedies
If you notice red dots on your child’s gums, but you are unable to see a doctor immediately, use available home treatment methods:
- Wipe the affected areas in your child's mouth with a fresh infusion of black tea cooled to body temperature. If the child already knows how to rinse his mouth, let him do this procedure with tea every 3-4 hours. You can also use oak bark, chamomile flowers, calendula flowers (provided that the child is not allergic to these plants).
- Eliminate sweets and fresh baked goods from your child’s diet, which form a breeding ground for microbes in the mouth. It is also necessary to remove from the menu pickles, smoked foods, hot and spicy dishes that irritate the mucous membrane.
- Preference should be given to soft, pureed foods heated/cooled to body temperature. If your child has severe mouth pain, switch him to liquid food that can be drunk through a straw until he visits the doctor.
- To relieve pain and burning in the mouth, you can give your child Efferalgan, Panadol, Paracetamol or any other painkiller appropriate for the child’s age.
The methods listed will slow down the spread of infection or inflammation, but they do not eliminate the need to visit the dentist.
Symptoms of gum disease
75% of people suffer from gum problems. To determine the disease, it is necessary to identify the symptoms. The main signs of gum disease are:
- red or swollen gums;
- bleeding gums;
- increased sensitivity of teeth;
- bad breath.
However, it is not always possible to immediately determine the disease. Thus, with gingivitis, the symptoms are barely noticeable, so you should visit the dentist twice a year for a routine examination so that the doctor can promptly identify abnormalities, make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
Red purulent ulcer
Symptoms accompanying the appearance of plaque on the gums with photos
White aphthae in the oral cavity can periodically appear and become chronic, which causes a lot of discomfort to a person.
To prevent their occurrence, it is important to remember about preventive measures that will allow you to forget about this disease for a long time.
- Avoid injuring the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- Visiting the dentist should become your habit.
- Be sure to maintain good oral hygiene and try to prevent plaque from accumulating on your teeth.
- Very hot foods can cause aphthae, so you should not eat them; wait until they cool down.
- Stress can have an impact on a person’s immunity; try to develop stress resistance in yourself.
- Try to increase your immunity by any means, take vitamins, eat fruits and vegetables.
- During seasonal illnesses, try to protect yourself from viral attacks; you can take immunostimulating drugs for prevention.
Preventing the occurrence of aphthae is not difficult. It is important to systematically monitor your health, then white sores will not often or never bother you.
Dysfunction of the oral mucosa leads to complications in the structure of the entire body. Firstly, the presence of a focus of infection contributes to its spread to nearby organs and tissues: teeth, with the formation of caries, sinuses, conjunctiva of the eyes, membranes and substance of the brain. It would seem that an inconspicuous white film on the palate can lead to severe diseases, for example, meningitis and encephalitis with a high risk of death.
Fungal plaque. For etiotropic treatment, antifungal drugs such as Fluconazole and Ketoconazole are used. The tablet form is purchased at the pharmacy and used for 2 weeks, 2 tablets each. In the presence of systemic manifestations on the skin, ointments are applied topically in the form of applications.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Anti-tartar toothpaste, anti-tartar toothpaste
After a course of antibiotics, in addition to drugs for the growth of bacteria in the intestines, antifungal agents should be prescribed.
When treating a sore throat, the choice of drug depends on the type of pathogen that caused the infection. For streptococcal or staphylococcal sore throat, antibiotics are prescribed. New synthetic broad-spectrum drugs are used in combination: cephalosporins, protected penicillins, glycopeptides. In case of viral etiology, it is advisable to prescribe antiviral drugs Anaferon, Arbidol, etc.
For the treatment of lichen planus, the drugs of choice are glucocorticosteroids - Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. They are used in the form of a spray, the effect is local. To avoid side effects, the dose of steroids is gradually reduced and then completely discontinued. Local treatment consists of prescribing Anastezin for pain relief and drugs that enhance tissue regeneration. These include vitamin E and methyluracil.
A fairly common complication after taking steroid medications is a fungal infection; the above drugs are prescribed to prevent it.
Prevention
- Strict adherence to personal hygiene rules: use only a personal toothbrush and toothpaste, preferably for sensitive teeth. Once a day, thoroughly clean the dental spaces with dental floss. Use brushes to clean the palate and tongue.
- Fractional rational nutrition - a variety of foods, with an increased amount of food intake. Washing vegetables and fruits before eating.
- Prevent the development of vitamin deficiency by taking complex medications in the autumn-winter period.
- Timely treatment of dental caries and chronic infections in the body to avoid decreased immunity.
In some cases, white spots are interpreted as markers of precancerous diseases. For verification, it is necessary to monitor laboratory parameters of tumor markers in the blood. Next, a consultation with an oncologist is scheduled.
White plaque on the surface of the gums rarely becomes the only symptom of a developing disease. As a rule, it is accompanied by a whole complex of signs that greatly facilitate the correct diagnosis. What the accompanying symptoms and white plaque may look like can be seen in the photo with explanations for the article.
If the mucous membranes turn white, this symptom cannot be ignored. When, in addition, the gums hurt, and red spots appear on their surface, and the clinical picture is complemented by the appearance of plaque, then in most cases the symptoms indicate the development of gingivitis. With the catarrhal form of the disease, multiple small dots or red spots may also appear on the surface of the gums.
A pale spot on the gum often represents a kind of channel through which purulent masses emerge. If, in addition to the white spots, they are puffy or swollen, the tooth next to the formation hurts, pus is released, and the mouth smells unpleasant, then we are talking about a pathology such as a fistula.
A dot or spot often accompanies mechanical damage - it can occur after an injection. However, in some cases, such a sign indicates the development of such a serious pathology as leukoplakia. In the latter case, the characteristic symptoms will look like this:
- painful white spots rising above the gums - they can have clear, even outlines or be blurred;
- usually the surface of the formations is smooth, sometimes slightly rough;
- As the disease progresses, the affected areas crack, followed by the formation of ulcers.
Pale gums
Sometimes the gums change shade to a less saturated one. This is a symptom of periodontal disease. With this disease, the blood supply to the gums is disrupted and they turn pale. In some cases, if the gums suddenly turn white, this may indicate other pathological conditions. One of the most common is anemia. It is not difficult to confirm or refute such a diagnosis - a general blood test is sufficient, which will show deviations in hemoglobin levels.
If you experience redness on your gums, it is recommended that you visit your dentist immediately. The doctor will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment.
In cases of infection, it is first necessary to undergo drug treatment, and then undergo a course of physical therapy, which will bring the oral cavity to full working condition. In some cases, it will be necessary to remove tartar, which can cause periodontal disease or periodontitis.
Often, during treatment, patients also have time to treat their teeth or simply clean them, so a visit to the dentist can also add additional expenses. For mechanical damage, all treatment consists of treating the gums with special gums, which relieve swelling and pain in the patient.
Moreover, such drugs not only treat damage, but also restore the deteriorated condition of the gums in general, stop bleeding and cover them with a protective coating that prevents infections from entering your body.
Red dots near the tooth
If you see red dots or spots near your teeth, then this is definitely an alarming signal. Most often, such symptoms cause toothache, and people think that this is the problem. But in fact, such pain can signal gingivitis or even oral cancer.
It is important to know that signs of this type of cancer may include:
- a white or red spot or dot that quickly progresses and increases in volume;
- an ulcer on the gum that has begun to bleed;
- severe toothache or unexplained tooth loss.
However, only a dentist or oncologist can find out whether this or that formation and deviation from the norm in the oral cavity is cancer.
Leukoplakia is a precancerous condition
It is worth remembering that these symptoms may not necessarily signal cancer. Do not make hasty conclusions and consult a doctor.
Causes of red gums
Redness of the gums
The causes of gum hyperemia can be varied. In addition to the inflammatory process, there are several other significant factors in the appearance of this problem. Among them:
- decreased immunity;
- poor oral hygiene;
- avitaminosis;
- bad habits;
- mechanical injuries;
- chronic systemic diseases;
- accumulation of tartar;
- diseases of the connective tissue of teeth;
- deep caries, periodontitis, stomatitis.
Often people do not go to the doctor if their gums are red. They blame everything on damage during brushing or the wrong toothpaste. If treatment is not started in time, the gums become loose. Pathogenic bacteria accumulate at the site of inflammation, teeth become loose, and the gingival margin atrophies.
Why is there red gum around the tooth?
The gums around the tooth turn red not only due to trauma. The cause is chronic diseases, which often manifest themselves as inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Preventing gum disease
To avoid gum problems, which can lead to serious diseases in the future, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- Maintaining hygiene rules.
- Regular visits to the doctor.
- Proper nutrition for nursing mothers and babies.
- Creating a favorable atmosphere for the baby.
Remember that any abnormality in the mouth is a threat to your health or the health of your baby. If any symptoms appear, contact your dentist immediately and under no circumstances resort to self-medication. Any incorrect actions can aggravate the disease and worsen your overall physical condition.
In our age of the Internet, when a person notices symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis or another problem that worries him, the first thing he does is not go to the doctor, but to a professional dental forum. But postponing a visit to the periodontist when bleeding and inflammation of the gums appears is not the wisest decision. You should not engage in self-diagnosis: entrust the health of your teeth and gums to professionals.
The content of the article
Gingivitis: my gums hurt
The process, which is characterized by gum inflammation, swelling, redness and bleeding, is called gingivitis and is one of the most common periodontal diseases in both children and adults. Only 3% of people can boast of absolutely healthy gums. How to get into such a small percentage of lucky ones? The answer is simple - follow the necessary measures to prevent gum inflammation, regularly visit the doctor and not let even seemingly harmless signs of an incipient disease take their course.
Gingivitis is the last of all diseases in periodontology in which the inflammatory process can still be stopped. Next comes periodontitis, a disease in which inflammation spreads to other periodontal tissues. From this point on, treatment is based only on bringing the disease into remission and attempts to relieve symptoms as much as possible at the time of relapses, as well as in the future when it is necessary to resort to tooth extraction. Therefore, gingivitis in children and adults requires increased attention in order to avoid serious periodontal problems.
Why do gums turn red?
The inflammatory process is initially asymptomatic, but over time, in addition to redness, the gums begin to bleed and other signs appear. Redness can be caused by various diseases that differ in their causes.
Redness of the gums due to gingivitis
In adults
The most common diseases that cause gums to become red are:
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease;
- gingivitis;
- diabetes;
- viral diseases;
- leukemia.
Inflammation can begin due to improper brushing of teeth, bad habits, and lack of vitamins and minerals. The most common cause is poor oral hygiene. The resulting dark plaque, consisting of microbes, eventually turns into a hard stone that must be removed.
Periodontal diseases
It happens that the reason is:
- using a brush with stiff bristles;
- chemical and thermal burn of the gums;
- poor quality filling or prosthetics.
In some cases, redness is caused by cracks and scratches into which microbes penetrate, causing inflammation. Women often face this problem during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and weakened immunity.
In children
Inflammatory processes, in which children's gums become red, in many cases are hereditary. In children, the cause of this disease is the habit of putting various objects in their mouth. During teething, this problem may arise. The child’s oral hygiene must be constantly monitored and caries treated promptly. With leukemia in children, gum tissue begins to be affected, which is largely influenced by reduced immunity.
Types of gingivitis
Gingivitis differs in the nature of its course:
- Acute gingivitis is a disease whose symptoms appear suddenly and progress quite quickly.
- Chronic gingivitis is a sluggish process, the symptoms of which increase gradually.
- Aggravated gingivitis (recurrent stage of a chronic process) is an increase in the symptoms of a chronic disease.
- Gingivitis in remission is the moment of complete relief of all symptoms.
The form is:
- catarrhal gingivitis, which is manifested by swelling and redness;
- ulcerative (ulcerative-necrotic) gingivitis, with necrotic (dead) areas of the gums;
- hypertrophic gingivitis, in which there is a significant increase in the volume of gum tissue and its bleeding;
- atrophic gingivitis, on the contrary, is characterized by a decrease in the volume of gingival tissue;
- desquamative (geographic) gingivitis, which is manifested by intense redness and abundant desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
Read also: How to treat gum disease during pregnancy
According to its distribution in the oral cavity, gingivitis can also be local (affects some areas of the teeth) and generalized (the process affects the gums of the entire jaw or both jaws). And according to severity - mild, moderate and severe gingivitis.
Causes of gingivitis
Most often, gingivitis develops as an independent disease, but sometimes the causes of its occurrence are acute and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, hematopoietic organs, infectious diseases, and changes in hormonal levels. In this case, gingivitis is one of the symptoms of the underlying pathology. The causes of gingivitis can be internal or external.
Internal reasons include:
- tooth growth that injures the gums - the eruption of wisdom teeth;
- vitamin deficiency, hypovitaminosis (most often lack of vitamin C and zinc);
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic disease;
- allergic diseases;
- diabetes;
- stress, mental illness;
- anomalies and various deformations of the gums;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
External reasons are a number of factors:
- physical (injuries, burns);
- chemical (the influence of aggressive substances);
- medical (incorrectly applied fillings, incorrectly installed veneers, traumatic wearing of braces);
- bad habits (smoking, mouth breathing);
- biological (infectious process);
- hygienic (insufficiently thorough hygienic procedures).
Toxins from microorganisms that enter the oral cavity with food and water, as well as those that live there permanently, form dental plaque (plaques) due to insufficient hygiene measures. They are the most common cause of the inflammatory process.
Inflammation can develop differently depending on the cause. Chronic catarrhal gingivitis occurs most often due to unsatisfactory hygiene measures or as a result of gum injury or burns. Hypertrophic gingivitis is caused by crowded teeth, incorrectly installed fillings or dental crowns, as well as changes in hormonal levels, for example, during pregnancy (pregnant gingivitis) or puberty (adolescent or juvenile gingivitis). Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (Vincent gingivitis) is usually caused by an infectious process. It occurs due to the activation of two microorganisms (Vincent spirochete and spindle bacillus) against a background of weakened immunity, hypothermia, stress or malnutrition.
Gingivitis, photo
Localization of sores on the oral mucosa
Considering the location of the tumor in the mouth, we can guess what kind of disease the person is facing. White spots on the inside of the cheek and tongue may indicate thrush. Formations on the inside of the lip indicate probable herpes. Multiple points near the gums provoke suspicion of leukoplakty. The lesion on the palate is associated with a cyst.
The health of internal organs is assessed based on the condition of the oral cavity, in particular the tongue:
- white small dots on the sides sometimes indicate a disease of the gallbladder or liver;
- growths at the root indicate intestinal diseases;
- damage to the center is associated with kidney pathology;
- a whitish coating at the tip of the tongue indicates problems with the respiratory system;
- the tip of the tongue damaged by white pimples is observed in diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Regardless of the location of the white, painless dots in the mouth, you should seek help from a doctor. This will eliminate the possibility of improper home treatment and worsening the condition.
We suggest you read: ᐉ How to treat gumboil - what to rinse with to remove swelling at home
Forms of gingivitis and symptoms
Signs of gingivitis directly depend on the nature of the disease and its form. Let's look at each form of gingivitis separately. So, complaints and visual inspection.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease usually occurs without obvious pain. Its immediate symptom is bleeding gums when brushing teeth, eating solid foods and other mechanical effects on the dental system.
Ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis
This is one of the most unpleasant forms of gingivitis, which is characterized by a feeling of itching of the gingival papillae, severe pain, copious flow of saliva, fever, inflammation of the lymph nodes and the formation of necrotic areas of the gums.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
Patients suffering from this form of gingivitis complain of severe pain, constant bleeding of the gums and a significant increase in the volume of the gums, which can partially cover the crowns of the teeth from the outside (not from the tongue). At the same time, the patient’s gum remains quite hard and under it, on the teeth, tartar forms, which creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of microorganisms. With hypertrophic gingivitis, teeth may move slightly.
Atrophic gingivitis
The last and most advanced stage of gingivitis, often leading to periodontitis, is atrophic gingivitis. With it, the gum tissue becomes thinner, decreases in size, the necks of the teeth, and sometimes their roots, are exposed. Teeth become more sensitive to temperature changes (cold or hot drinks, frosty air), to sour or sweet foods, to the mechanical impact of a toothbrush.
Desquamative (geographic) gingivitis
The symptoms of this form of gingivitis differ from others by pronounced red spots on the gums, desquamation of the upper layer of the epithelium, the appearance of blisters on the gums and the formation of mouth ulcers and erosions.
Features of the treatment of red gums in children
Treatment of red gums consists of cleaning teeth from plaque and mandatory removal of tartar. Ultrasonic cleaning and polishing with special brushes are recommended for children. This procedure is highly effective and completely painless. To combat inflammation, the doctor prescribes rinsing with antiseptics. Miramistin is suitable for children under 3 years of age. Rinsing with infusions of medicinal herbs, such as:
- sage;
- chamomile;
- eucalyptus.
Diagnostic tests
- Schiller-Pisarev test
This test is based on determining the level of glycogen in the gum. Its amount increases significantly during inflammation, while healthy gums do not contain glycogen. Lubricating the inflamed gums with Schiller-Pisarev solution gives a color change reaction from light brown to brown. This research method is used to make diagnoses of both periodontitis and gingivitis.
- Assessment of oral hygiene level
A solution (2 g of potassium iodide, 1 g of crystalline iodine, 40 ml of distilled water) is applied to the outer surface of the six lower front teeth.
The assessment is carried out using a five-point system and each tooth is assessed separately:
- 5 points – complete staining of the entire tooth surface;
- 4 points – staining of ¾ of the tooth surface;
- 3 points – staining of half the tooth surface;
- 2 points - staining of a quarter of the tooth surface;
- 1 point - absence of any staining of the tooth surface.
Then the scores of all examined teeth are summed up and divided by their number (usually the test is carried out on six teeth). This is how the hygiene index is obtained.
As a result, the quality of hygiene is assessed:
- 1.1-1.5 points – good hygiene index;
- 1.6—2.0—satisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.1—2.5—unsatisfactory hygiene index;
- 2.6—3.4—poor hygiene index;
- 3.5-5.0 - very poor hygiene index.
- Vacuum test according to Kulazhenko
Using a Kulazhenko vacuum apparatus, it is possible to determine the time of hematoma formation when a vacuum is applied to the gum area. Typically, the test is carried out in the incisor area by placing a tube of the device on the gum. The formation of a hematoma in 60 seconds indicates the normal condition of the gums, while the appearance of a hematoma in 29-30 seconds signals an inflammatory process.
- Oxygen tension in gum tissue
The sensor of the device is applied to the gum, and the device records the level of tissue hypoxia. Reduced oxygen tension indicates a prolonged inflammatory process.
Differential diagnosis of gingivitis
It is based on the complaints presented to the patient, a visual examination of the patient, the results of functional tests and laboratory tests. The goal of differential diagnosis is to distinguish gingivitis from other periodontal diseases, such as periodontitis and periodontal disease.
The main feature that distinguishes gingivitis from other periodontal diseases is that the inflammatory process affects only the gum tissue, the remaining structures (muscle ligaments that hold the tooth in the jaw and bone tissue) remain unchanged.
Along with this symptom, gingivitis is not characterized by periodontal pockets, exposure of the necks of teeth, or their mobility. And the x-ray shows no signs of bone resorption.
Identifying gingivitis in a timely manner, determining its form and prescribing the correct treatment is the task of a periodontist. But not to forget about prevention and regularly visit the dental clinic is the maximum program for the patient. This is the only way to avoid a more serious periodontal disease – periodontitis.