Blisters in the throat and on the back wall are encountered quite often in the practice of an otolaryngologist - in most cases we are talking about different types of sore throat, but not in 100% of cases.
Bubbles in a general sense appear as small fibrous capsules filled with exudate: serous or purulent. Depending on the type of disease and the severity of the process.
In all cases, it is necessary to undergo urgent diagnostics and prescribe adequate treatment: we may well be talking about abscesses, which pose a danger not only to health, but also to life. What should you know about blisters in the back of the throat?
Angina
A sore throat is defined as an infectious-inflammatory lesion of the oropharynx with possible involvement of the velopharyngeal arch and even the soft palate in the pathological process (this is no longer a pure sore throat, but a complex disease).
The formation of red blisters on the back of the throat does not occur with all types of tonsillitis, but only with infections of enterovirus and herpetic origin. In 100% of cases, the disease has an infectious etiology, as already mentioned.
The culprits are herpes viruses from types one to six, Coxsackie viruses, and other enteroviruses.
Interesting:
Bacterial agents almost never provoke the development of this kind of sore throat (not counting follicular, complex forms of pathology).
Symptoms of viral tonsillitis develop rapidly, sometimes the full clinical picture unfolds in a matter of hours. Among the characteristic manifestations of enteroviral and herpetic sore throats are:
- Intense sore throat. The severity of the pain is such that the patient cannot eat, drink, or even speak normally. The pain syndrome weakens after drinking warm liquid and intensifies in the opposite cases. The localization of the discomfort is the pharynx. The pain can radiate (radiate) to the neck, spine and even the face.
- Exudation. In other words, the release of a large amount of pus from the throat. Exudate can also be serous in purely herpetic sore throat.
- Burning, itching in the throat.
- Increase in body temperature to 39 degrees and beyond. This is a nonspecific sign of a pathological process, but in acute forms of the disease it is common.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the body. Weakness, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, headaches (cephalalgia), dizziness, nausea, vomiting, etc.
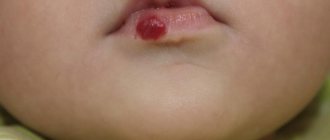
- The formation of red or white blisters filled with bloody or purulent-serous contents. Business card of herpetic and enteroviral tonsillitis.
Symptoms must be considered in their entirety. In any case, differential diagnosis will be required.
The treatment is classic. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, broad-spectrum antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine), antiviral drugs, antibacterial agents (antibiotics) for follicular tonsillitis, etc. are used.
It is possible to use immunomodulators to normalize the functioning of the body's defenses.
Self-medication is strictly unacceptable. This will lead to aggravation of the situation and chronicity of sore throat. Consultation with a specialized specialist is required.
Probable Causes
Red spots in the throat are the main sign of the occurrence of pathological processes in the mucous membrane of the airways. The following factors can trigger their development:
- dry air;
- inhalation of volatile chemicals;
- hypothermia;
- vitamin deficiency;
- allergic reactions;
- decreased body reactivity;
- infectious diseases;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine disorders;
- bad habits.
The cause of the appearance of red spots on the throat and palate can be identified by their location, number and accompanying manifestations.
Most often, the causes of the occurrence lie in the development of bacterial and viral infections. However, in order to make sure that such suspicions are correct, you need to seek help from a doctor.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity as a whole. Most often the tongue, lips, cheeks are affected and, of course, the mucous membrane of the throat is often affected.
The infection begins to spread expansively in the absence of proper treatment.
In total, there are three types of stomatitis: herpetic, aphthous, necrotic. The first two affect the throat more often.
The causes of the disease are infectious. Herpes viruses of all types are responsible for the development of the inflammatory process in the vast majority of cases. Somewhat less frequently, stomatitis occurs when infected with enteroviruses, in particular the Coxsackie virus.
Symptoms are varied. There are such signs of stomatitis:
- Pain in the oral cavity of a burning nature. When the pathogenic agent reaches the pharynx, the pain syndrome remains the same, but changes location.
- Itching in the throat, desire to scratch the affected area.
- White blisters form on the back of the throat. They are filled with serous exudate. They open on their own. As a rule, the main difference between stomatitis and tonsillitis is the absence of multiplicity. Papular rash is limited to 5-8 blisters.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the body.
- An increase in body temperature is also possible, but only in severe cases of the underlying disease described.
Antiherpetic treatment. Broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed: antiviral, specific antiherpetic medications, antiseptics (primarily Miramistin). Additionally, the use of immunomodulators is indicated.
Throat abscess
An abscess is colloquially called an abscess, which quite accurately reflects the nature of the pathological process. As a result of tissue infection, purulent melting and destruction occur. Read more in this article.
The body strives to delimit the lesion, forming a fibrous capsule around the pathological site. This allows you to stop the expansive spread of the process.
The causes of development are infectious in one hundred percent of cases.
The culprits are bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus primarily), streptococci, herpes viruses, enteroviruses, rotaviruses, adenoviruses, and some other types of agents.
Symptoms are specific:
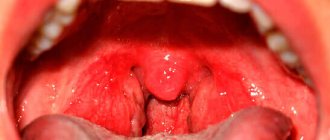
- Visually, a white or reddish, convex lesion is detected in the throat. The sizes vary from small 2-3 mm to significant 2-4 cm. Large lesions pose a danger to the patient’s life.
- Pain. It has an intense character. Pecking, burning, aching. Usually all together. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the throat, neck, face, spine.
- Symptoms of general intoxication of the patient’s body.
- Hyperthermia. The increase in body temperature is significant and occurs almost always. The numbers vary, but in general we can talk about an increase in temperature to 39 degrees and a little more.
- Changes in the relief of the pharynx. The throat becomes grainy and unevenly colored.
Treatment is mainly surgical. A surgical opening of the lesion and drainage of the resulting cavity is performed.
Next, specialized medications are prescribed. Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin, antiseptic solutions, antiviral and antibiotics (in some cases).
Pharyngitis
Red blisters in the throat can also appear with pharyngitis, especially granulosa.
In medical practice, it is defined as an infectious-inflammatory or allergic disease affecting the palate and velopharyngeal arch.
The prevalence of the pathology is quite wide. Up to 8% of the entire human population suffers. At least once in a lifetime.
The reasons for the development of the disease process are multiple:
- Infections. Mainly herpetic and staphylococcal agents.
- Allergy. Occurs when taking certain medications, eating certain foods, or inhaling other agents. These factors may well provoke the development of acute allergic pharyngitis. Moreover, determining the etiology of the process is not so easy. Because the symptoms are the same in all cases. Diagnosis required.
There are also provoking factors: alcohol abuse, smoking, working in hazardous industries.
The signs of the disease are as follows:
- Pain in the throat. Burning, aching, pulling. It is quite possible that it will intensify after eating food. Radiates to the neck and throat itself.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat. Develops in 90% of clinical situations. Caused by a significant inflammatory process and swelling of the pharyngeal tissue.
- Disappearance of voice. Speaking is almost impossible due to swelling of the vocal cords. The voice may disappear entirely or partially. In the latter case, hoarseness and hoarseness are observed.
- Sore throat.
- Non-productive cough. Sputum is not produced at all or comes out in small quantities in the morning.
- Increased body temperature and symptoms of general intoxication.
The treatment is specific. It consists of eliminating inflammation and destroying pathological flora and agents.
Angioma of the pharynx
The disease can affect not only the pharynx. This tumor can occur in other parts of the human body or in the liver. It is important that such tumors, which form against the background of changes in the vascular walls, do not develop into malignant ones. Therefore, usually a trip to the doctor reveals the problem; all that remains is to treat it correctly.
Throat angioma, which appears from blood vessels, has a red-blue or purple tint. The tumor arising from the lymphatic vessels is pale yellow. The color in this case is due to the lymph filling the neoplasm.
So what is angioma in the pharynx? How does the disease manifest itself? Is this condition dangerous for humans and how to treat it correctly? Let's find out!
Types of throat angioma
Otorhinolaryngologists distinguish two types of such neoplasms depending on the vessels where the throat angioma forms:
If the tumor grows from blood vessels, it is called a hemangioma. Hemangiomas, in turn, are divided into simple (capillary), cavernous (cavernous) and branched.
All these types of hemangiomas differ in appearance from each other. Capillary ones look like red-blue spots filled with blood. Cavernoses look like nodular new growths of a blue hue. Branched ones look like bubbles consisting of pulsating vessels.
Lymphangiomas also have their own classification. They are divided into simple, cavernous and cystic. As with simple hemangiomas, simple lymphangiomas are composed of capillaries, but these capillaries are filled with lymph.
Cavernous formations have several cavities, like a sponge, where each of the cavities is filled with lymph.
Cystic, as the name suggests, is one cyst or several cysts fused together.
Laryngeal angioma may not manifest itself for a long time, remain dormant and appear, for example, already in adulthood.
Symptoms
A small angioma does not cause the patient any discomfort. Only by growing and reaching large sizes does it make itself felt. At this time, the patient begins to feel a lump in his throat. The constant feeling of a foreign object in the throat causes discomfort. The patient has difficulty swallowing food or saliva.
Growing to the ligaments, the tumor can cause slight hoarseness in the voice.
An increase in the size of angioma is accompanied by:
- sore throat;
- cough;
- problems swallowing food;
- the presence of blood clots in saliva;
- pain in the throat area.
As a rule, the first “bells” appear at the age of twenty. A sign that makes it easy to identify an angioma is that when pressure is applied to the tumor, it disappears and then reappears.
Hemangiomas usually reach large sizes. Injuring them can cause severe bleeding. Lymphangiomas do not grow to large sizes and cannot lead to bleeding.
Despite the fact that these neoplasms do not develop into malignant tumors, they cannot be left without attention and medical care.
The symptoms expressed in the presence of angiomas adversely affect the patient’s quality of life, and the risk of bleeding threatens with more serious consequences.
Therefore, it is important to pay great attention to your throat and, when the first signs of illness appear, seek medical help.
This pathology often occurs in pregnant women: neoplasms appear against the background of changes in hormonal levels and reduced immunity. The difficulty of therapy in this case lies in the inability to use the entire range of means to combat the tumor. But medicine knows of cases where after the birth of a baby the tumor disappeared by itself.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of this disease is carried out by an otolaryngologist. Small neoplasms are more often diagnosed during a routine examination of the pharynx, when the patient comes to be treated for tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or when diagnosing adenoids. It is not difficult for an experienced ENT doctor to identify a neoplasm by its characteristic color and appearance.
Large angiomas force patients to purposefully go to an ENT doctor, since unpleasant symptoms interfere with their usual way of life.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is sent to undergo pharyngoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), X-ray examination, and stroboscopic examination of the larynx (study of the ligaments).
It is noteworthy that the collection of tumor tissue cells (biopsy) is not performed in this case, since such measures can provoke severe bleeding.
In some cases, a swab is taken from the throat to rule out the presence of foreign bodies, scleromas, or other cancers.
Treatment
It is possible to cure lymphangioma and hemangioma of the larynx at an early stage without resorting to surgical methods. If the tumor is small, conservative therapy is used: radiation or hormonal therapy. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor your health and pay attention to the body’s first warning signals as early as possible.
Treatment of lymphangioma and late-stage hemangioma involves surgery to remove the tumor. The following methods are used to remove angioma: laser removal, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, surgical removal.
The ENT doctor chooses which method to use in a particular case, based on the degree of growth of the angioma and the patient’s health condition.
Sclerotherapy has a good effect. During this procedure, alcohol is injected into the tumor. But because of its pain, this procedure is performed extremely rarely and in cases with small, hard-to-reach angiomas.
If you are faced with an angioma or suspect that you have this pathology, do not delay - make an appointment with us!
After conducting the necessary examination, we will correctly diagnose the problem and offer the optimal solution!
Please, come!
We will be happy to help you!
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5ab4a825fd96b102b0c8c3e2/angioma-glotki-5c9de430f5372a00b34d1705
Chickenpox (internal form)
Chickenpox, or in common parlance chickenpox, is defined as an infectious, predominantly dermatological disease of viral origin. In 100% of cases, the pathological process is provoked by a strain of herpes type 3 (Varicella-Zoster virus).
Mostly children get sick, but adults are not completely safe, especially if there is no immunity to the disease.
In the absence of proper treatment, an expansive spread of viral damage to internal organs and structures occurs. Including on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and pharynx.
In general, chickenpox can be suspected based on the following signs:
- The formation of small blisters (papules) on the skin, transparent or slightly reddish in color. This is the calling card of chickenpox, defining the whole essence of the disease. The acute phase, subject to treatment, does not last long: up to 3-5 days, after which the papules themselves open and the wounds heal.
- The lesions may become ulcerated when scratched. If treatment is not started, an expansive spread of the disease to the oral cavity is observed. In this case, papules are extremely difficult to distinguish from dental ones. It is necessary to judge all the symptoms as a whole.
- Itching and burning of the dermis.
- The throat becomes red, covered with a small papular rash, the blisters are red or whitish.
- Increase in body temperature to pyretic levels. This is extremely dangerous. This temperature (40 degrees) needs to be brought down urgently.
- Symptoms of general intoxication.
Complicated herpes is treated in a hospital, especially if an adult is sick. The use of a complex of drugs is required: first of all, antiviral therapy is prescribed, then the immune system needs to be strengthened.
There are other diseases in which a papular rash forms in the pharynx: diphtheria, throat angioma. But they are much less common, and therefore do not have great epidemiological significance.
Rashes in the throat of a child: types, clinical manifestations and treatment features
With many infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, both viral and bacterial, a rash in the throat may appear. In medical practice, any rash is called enanthem.
For some diseases (for example, ARVI or influenza), pink or red spots on the pharyngeal mucosa are not a characteristic sign of the disease and do not always appear. But for certain diseases, based on the nature of the rash in the throat, a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist can clarify the diagnosis and determine the tactics of treatment and observation of the child.
By the appearance and characteristic changes of the rash in the throat, it is possible to determine what pathogen is causing the infectious process and prescribe the correct treatment.
There are rashes on the mucous membrane of the throat due to viral (respiratory infections, influenza, measles, rubella, chicken pox, herpes simplex) or bacterial infectious processes.
In adults
The disease is rarely activated, but has dangerous consequences. After entering the body, the herpes virus begins to actively multiply, contributing to the appearance of characteristic rashes. The infection can become generalized, affecting the nervous system and internal organs. Treatment in this case is carried out in a hospital setting.
In children
Herpes in a child’s throat is a type of viral stomatitis. It is important to be able to distinguish it from a sore throat. Despite similar symptoms, infections are caused by different pathogens. Therapeutic regimens will also be different. And it is precisely the distinctive features of the disease that allow an experienced doctor to easily identify it.
Treatment of herpes in the throat in children should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
During pregnancy
Primary infection is considered the most dangerous. The risk of fetal infection depends on the stage of pregnancy. In the first weeks, the infection can cause spontaneous abortion. Type 1 virus contributes to the occurrence of congenital pathologies. In the first trimester, the formation of the nervous system occurs, which is often damaged by infection.
After the 13th week, internal organs develop - herpes during this period leads to hearing loss and decreased vision. A viral infection causes pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Damage to the central nervous system in the future manifests itself as epilepsy.
In the 3rd trimester there is a high risk of developing gestosis and perinatal infection of the child, so the woman needs hospital treatment.
During the period of exacerbation, natural childbirth is replaced by cesarean section, since this operation significantly reduces the risk of infection of the fetus.
Diagnostics: what needs to be examined?
Diagnosis is carried out by otolaryngology specialists (ENT doctors, in other words). The preliminary list of studies looks like this:
- Visual assessment of the pharynx using a specialized mirror and spatula.
- Interviewing the patient for complaints.
- Anamnesis collection.
- A general blood test to detect inflammation or an allergic process.
- PCR diagnostics. Allows you to determine the type of virus and its activity in the body. The essence of the study is to search for the genetic material of the agent in the biomaterial.
- ELISA. It makes it possible not only to determine infection, but also to understand its stage.
- Serological examination, bacteriological culture of a throat smear on nutrient media. Allows you to identify the type of bacteria causing the disease.
In general, this wave is enough to make a diagnosis, but additional studies by specialized specialists may be required.
Red and white blisters in the throat are what is called a papular rash. It is formed as a result of the development of infectious or allergic diseases and requires quick and adequate treatment.
Self-medication is unacceptable. You need to see a doctor.
Therapeutic measures
Timely therapy will help avoid the development of complications in the form of septic inflammation. However, success in treatment can only be achieved with a correct diagnosis.
When the first signs appear, you should immediately consult a therapist or pediatrician. At the initial appointment, the doctor assesses the nature of the rash and its location. After making a preliminary diagnosis, the patient is redirected to specialized specialists - an infectious disease specialist, an oncologist, an otolaryngologist.
Antiseptic solutions used for gargling help reduce the number of vesicles in the throat and relieve pain. For children, aerosols are most often prescribed: Hexoral, Orasept and others, used for irrigating the throat.