Treatment of periodontitis
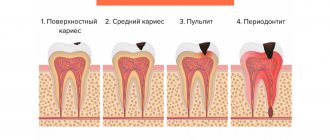
If during caries microbes are found in the hard tissues of the tooth, during pulpitis - in the tooth cavity (pulp chamber) and root canals, then during periodontitis - they extend beyond the boundaries of the tooth root.
This complication is called periodontitis , i.e. periodontal inflammation. Periodontium - the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth - is the connective tissue that fills the narrow space between the tooth and the bone bed of the jaw (these are ligaments, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels). The main functions of periodontal tissue are shock-absorbing and nutritional. When chewing food, the periodontium absorbs the load on the tooth and evenly redistributes it to the bones.
When a tooth remains untreated for a long time, there is a risk of a serious complication of caries - periodontitis. First, cariogenic microorganisms destroy hard tooth tissues (enamel and dentin), then penetrate into the pulp chamber, infecting the vessels and nerves located in it and causing pulpitis. When pulpitis is asymptomatic and is not treated for any reason, the inflammatory process deepens and, passing through the canals, extends beyond the root apex.
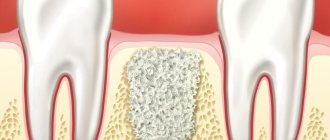
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root tip. The periodontium itself is a complex of tissues located in the gap between the tooth root and the jaw bone. Behind the root, the infectious process creates a focus of increased pressure, which causes spontaneous pain in the tooth, which sharply intensifies when biting on it. Patients often complain of the feeling of a “grown tooth” or “lengthened root”. Sometimes on the gum, or less often on the skin near the causative tooth, a “swelling” occurs - a fistula, from which contents from the source of infection are periodically released. Under certain circumstances, periodontitis is asymptomatic, without causing pain or complaints; periodic exacerbations of the disease are possible. In any case, the infectious process causes rarefaction (loss) of the bone tissue behind the root, which ultimately leads to the formation of a large cavity in the bone tissue - a cyst.
- Penetration of infection from the root canal through the hole at the apex of the root: untimely treatment of caries or pulpitis;
- poor-quality root canal filling;
- incomplete elimination of foci of infection during the treatment of pulpitis;
According to the nature of the course, periodontitis is divided into acute and chronic.
Acute periodontitis is manifested by sharp pain in the tooth area, aggravated by touching it. Swelling of the lips, cheeks, gums is enlarged, the tooth is mobile. Sometimes there is a hole in the gum from which pus flows. This is a fistula, i.e. a channel that has formed to drain contents from an infected cavity.
Chronic periodontitis can manifest itself in the form of unpleasant and mild pain (feeling of heaviness, fullness, awkwardness, pain when chewing load on this tooth). Chronic periodontitis may not manifest itself for a long time and may be discovered by chance on an x-ray during the treatment of neighboring teeth.
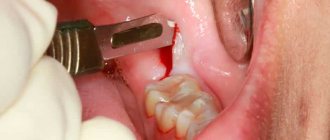
The first measure in the treatment of periodontitis is to release the impurities that have accumulated behind the roots. To do this, it is necessary to remove the softened carious tissues of the tooth and go through the entire length of the infected canal. Typically, the patient then experiences immediate pain relief. Next, it is necessary to expand the root canal, which contributes to the rapid drainage of infection and recovery of the tooth. Rinses are prescribed, and medicine is placed into the diseased canal. When the inflammatory process behind the root subsides, the tooth canals are filled, after which the coronal part can be restored with a filling.
The photographs can be used to trace the dynamics of bone tissue restoration behind the root of a chewing tooth after high-quality endodontic treatment of periodontitis.
What is atrophy
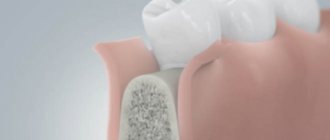
Jaw bone atrophy is a pathological process that leads to a decrease in cell size and loss of the normal volume of bone structures (both in width and height). With atrophy, negative changes begin to occur in the body and the full functionality of the maxillofacial apparatus is disrupted.
Atrophy is a decrease in bone volume
Treatment result
The inflammation behind the root has been eliminated, the tooth is not bothered, the fistula tract has been healed, tooth mobility has disappeared, chewing has been restored.
During initial root canal intervention, after the cessation of anesthesia, there may be minor discomfort of a short duration, and, if necessary, relieved with mild painkillers. After a permanent root canal, the tooth may be sensitive when eating very hard foods. This phenomenon does not cause much discomfort and goes away after a few days.
Be healthy!
The information was prepared by dentist Smirnov E.S.
The cost will depend on the chosen treatment method, the complexity of the work and the number of canals of the diseased tooth.
The following services may be required to treat periodontitis:
- Anesthesia 300 rub.
- Processing 100 – 300 rub.
- X-ray 250 rub.
- Unsealing the canal 400 – 800 rubles
- Canal filling 800 – 1000 rub.
- Drug therapy of the canal 250 rub.
- Ultrasonic treatment of the canal 250 rub.
- Temporary filling 150 rub.
Total : the average cost of treating periodontitis of a single-canal tooth will be 2100 rubles
See also:
Loss of bone tissue in the hip joint. Mechanical properties of skin and bone tissue. Is it possible to return bone tissue? Increased androgen levels in women are treated with folk remedies. What does bone tissue consist of?
Order on Aliexpress with delivery from Russia and up to 25% discount
Loss of bone tissue in tooth and jaw
For the success of treatment, it is important how long the clinic has been in existence, what experience the doctors have, and whether they undergo advanced training courses. Our clinic’s specialists have more than ten years of work experience and regularly participate in scientific and practical conferences, training programs, and other educational events.
Thus, all SMILE-AT-ONCE implantologists have valid certificates from the International Implant Foundation, which confirms their right to work in this field. The clinic is part of the international community of implantologists (International Team for Implantology. ITI), which has existed for 30 years. We provide a full range of services for dental prosthetics using implants in seven days and provide a lifetime guarantee on implants, and also offer a convenient treatment regimen for both patients from Moscow and non-Moscow patients.”
Periodontal disease with bone destruction - folk remedies
Dear reader, here you can read about folk remedies for the treatment of periodontal disease with significant destruction of bone tissue. Why is this necessary? A periodontist can eliminate almost all, or most, symptoms of gum disease, but if you suffer from a chronic disease, then it is necessary to treat it, because the body is a single whole. It is not for nothing that in the old days, a person’s health was judged by his teeth and gums.
Therefore, it is necessary to regularly visit a periodontist (preferably once every six months) to monitor the condition of the gums over time and individually select treatment methods for periodontal disease and periodontitis.
Reduction of bone tissue represents the greatest difficulty in the treatment of periodontal disease. This is due to the structural features of the alveolar bone: its low regenerative ability, the peculiarity of the structure of the spongy substance.
In the initial stage of periodontal disease, demineralization of the alveolar bone occurs. Then pronounced destructive changes occur in the compact plate and cancellous bone.
At this stage of periodontal disease, under the influence of targeted therapy, remineralization and bone restoration are possible. In the initial stage of development of destructive changes, the real result of stimulating therapy, at best, can be the stabilization of periodontal disease, stopping the rapid loss of bone tissue and reducing tooth mobility.
The group of general and local therapy for periodontal disease consists of drugs with various effects (desensitizing, stimulating, anti-inflammatory, increasing the regeneration of periodontal tissues). All these drugs prevent the further development of periodontal disease; to a certain extent, they can stimulate the restoration of periodontal tissue.
One of the few herbal remedies that increases bone tissue regeneration is comfrey.
It promotes the rejection of non-viable tissue and the growth of young tissue, stimulates cell growth. In addition, comfrey has antimicrobial, enveloping and tonic effects. The roots of plants contain essential oils, pectin, tannins and mucous substances, alkaloids, choline and other compounds.
In order to prolong the action of the active substances of comfrey, prepare a 25% solution of dimexide in its decoction, which promotes more intense diffusion of medicinal substances into periodontal tissue. The course of treatment for periodontal disease is 7-10 applications of a 25% solution of dimexide in a decoction of comfrey.
To treat periodontal disease, this infusion is also used in the form of irrigation, for oral baths, which are done 3 times a day. Data from clinical and special studies indicate the high effectiveness of comfrey and dimexide and allow us to recommend it for use in the complex treatment of periodontal disease.
Phytin drug
, obtained from plant materials, stimulates hematopoiesis, enhances the growth and development of bone and dental tissues.
Kohlrabi
contains many minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus. Useful for children to strengthen bones and teeth, and for pregnant women.
During menopause, calcium is leached out of bone tissue especially strongly. As a result, the bones become less strong, which causes frequent fractures, joint disorders and, as a result, gait in old age. This occurs due to a lack of vitamin E.
It is prescribed: for osteoporosis - 500 mg per day. during menopause - 1000 mg.
Calcium preparations are also recommended: - Ca carbonate (40% Ca content in the preparation), possible complications: constipation, gases.
— Ca lactate (13% Ca content in the preparation). — Ca gluconate (9% Ca content in the preparation).
Comments
Can I take any vitamins to prevent bone atrophy?
Marianna (04.10.2020 at 14:36) Reply to comment
- Dear Marianna, taking vitamins as an independent measure will not solve the problem. However, vitamins, in particular vit. D, help improve the quality and structure of bone tissue. This vitamin is often prescribed in postoperative periods, for example, after tooth extraction or after installation of implants, also after bone tissue augmentation.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (07.10.2020 at 09:24) Reply to comment
I want to install mini-implants, because... they have a very good price. Will they save you from atrophy?
Makarchenko (10/29/2020 at 6:27 pm) Reply to comment