683
The unique properties of the collagen membrane have significantly facilitated its use in maxillofacial surgery, periodontology and implantology.
The purpose of the material, its advantageous characteristics, and the subtleties of its application will be discussed further.
Origin story
The need to use products is associated with different durations of tissue regeneration.
For example, the periodontal structure includes gums, bone tissue, periodontal ligament and tooth root cement. They all have different regeneration rates, and for the healing process to proceed properly, they must be separated from each other.
The first membranes were created from cardiac tissue (pericardium) and Achilles tendon of calves. However, such products often caused inflammation and rejection, which aggravated the condition of the patient’s oral cavity.
In addition, calf tissue carries the risk of transmitting BSE - bovine spongiform encephalopathy, a dangerous infection - to the patient.
Later, membranes of pork origin began to be used - their protein structure began to cause allergic and inflammatory reactions much less often, and due to this, the effectiveness of dental procedures increased. In addition, products made from pig tissue turned out to be cheaper to produce.
In addition, the thickness of modern products does not exceed the thickness of a paper sheet. Together, all these factors help minimize the risk of an allergic reaction in the patient and speed up healing.
Benefits of use
There are some contraindications to using the membrane:
- the presence of an active stage of the inflammatory process, both in the body as a whole and in the maxillofacial apparatus;
- cannot be used separately, but only with any filler together;
- in the presence of pathologies in the periodontal area (first, stone and plaque are removed, caries is treated).
For quite a long time, bone grafting has been recognized as the most effective method of restoring the width and height of the alveolar process. The technique is constantly modified and becomes safer and less traumatic. In addition, dentists are trying to achieve conditions under which simultaneous implantation will be possible.
There are several basic bone grafting techniques:
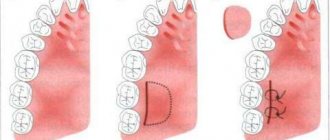
- Sinus lift. Restoration of bone volume in the upper jaw in the area of the projection of the bottom of the maxillary sinus. The operation is performed more often than others, since it is here that bone resorption is predominantly observed. The essence of the surgical intervention is that the dentist, in one of the ways (closed or open), gains access to the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. He disconnects part of the membrane from the periosteum, and fills the resulting cavity with prepared material of natural or synthetic origin.
- Splitting of the alveolar ridge. An effective technique for correcting the width of any jaw. First, the alveolar ridge is cut and spread apart, after which the graft is placed inside. The advantage of the technique is that the structure is immersed in the spongy tissue of the jaw, where regeneration and replenishment of the bone block is actively taking place. That is why the use of expensive osteoplastic materials is not required here.
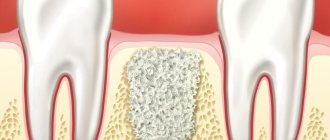
- Guided tissue regeneration. This type of bone grafting includes two components: a graft and a collagen membrane. These two components, interacting with each other, help restore the deficit of both the width and height of the alveolar process in any part of the jaws. The technique is rarely used with simultaneous implantation.
- Bone block grafting. This technique involves the use of a natural, preferably autogenous, graft, which is placed on the area where implantation is planned and where the bone tissue has atrophied. The disadvantage of this technique is that the graft is connected to an area of the bone where there are no blood vessels. Engraftment in such conditions occurs slowly.
Patients tend to be afraid of bone grafting, since it is a full-fledged surgical intervention on the teeth. However, all manipulations are carried out under local or general anesthesia, so they do not cause any discomfort. The risk of complications with this manipulation is minimal, and the benefits are undeniable.
Even if atrophy of the alveolar process does not allow immediate implantation, and patients have to wait six months for the implants to take root, it is still better to give preference to bone grafting rather than alternative methods of tooth restoration. Moreover, in modern conditions there are many designs that increase the benefit and effectiveness of bone grafting, for example, fixation of a barrier membrane.
As in the previous case, the material plays the role of a frame in the restoration of bone tissue. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts are embedded in collagen pores, which stimulates normal bone growth.
To restore the bone, the membrane is soaked in saline, then it is modeled congruently with the bone defect using scissors or a scalpel and placed over it using a sterile instrument. In this case, additional fixation (sutures) is not required.
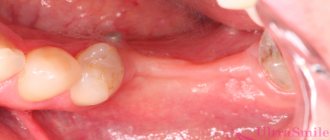
Tooth extraction inevitably leads to destruction of bone tissue. The use of a membrane allows you to prevent this process or minimize its consequences when implanting a new tooth. The membrane can be used in the following stages:
- immediately after tooth extraction, the membrane fixes the space between the bone and gum, preventing further destruction of bone tissue; the technique allows you to avoid lengthy bone augmentation procedures if it is necessary to install an implant;
- when performing operations that involve the removal of part of the gum - implantation of implants or bone tissue. In such cases, the membrane is installed on the new elements of the jaw, and the gum is sutured over it. This technique avoids the entry of unwanted particles and microorganisms into an open wound and ensures successful implantation;
- bone tissue augmentation before installing implants, in which bone blocks or special granules are attached to the bone, requiring reliable fixation until the bone tissue is restored.
DETAILS: No teeth, implantation possible or not
Product purpose
Collagen membranes belong to the category of resorbable membranes - in other words, they dissolve independently in the wound, eliminating the need for repeated surgical intervention, which means additional injuries, the risk of infection, and shortens the healing period.
However, bioresorption of materials in the wound almost inevitably causes an immune response in the surrounding tissues and is accompanied by an inflammatory process. Therefore, it is important that the material is well accepted by the human body, causing a minimal inflammatory reaction, and at the same time retaining the properties of the products for the allotted period.
Collagen perfectly meets these requirements. It has the physical properties necessary for use as a membrane, and during the process of resorption it is incorporated into the structures of the blood clot and surrounding tissues, thereby promoting normal wound regeneration.
Collagen derived from animal sources is essentially the same as human collagen, so it causes minimal rejection.
In addition to creating membranes, collagen is used in dentistry to treat receding gums. It is used together with apatites to create implants, as well as with bone materials to restore jaw bones in case of periodontal disease.
Properties and purpose
Collagen is a component that can be completely resorbed, which is an ideal product quality during the following dental procedures:
- maxillofacial practical surgery;
- implantology;
- periodontology;
- performing operations of varying degrees of complexity aimed at cellular regeneration of both hard and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Such a membrane has a protective function and acts as a barrier to the apical entry of epithelial fragments into the internal cavity of the organ. It ensures self-reproduction of bone areas in the area of augmentation.
At the same time, the participation of soft fragments in the general regenerative processes of bone formation is minimal.
When in contact with a humid environment, the product changes color and becomes almost transparent. The dense fibrous layer inhibits the penetration of gum fibroblasts and promotes the active growth of osteo-forming fragments.
The material is characterized by extremely low antigenic characteristics and the highest tensile strength.
Indications and contraindications for coronoradicular tooth separation, features of the operation.
Read here in which cases surgical removal of a stone from the salivary gland is inevitable.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/operatsii-na-zubah/provedenie-repozitsii-vyiviha.html you will find all the most important things about tooth reposition.
What are barrier membranes?
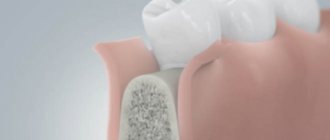
The barrier membrane is one of the most modern and successful inventions in dental practice. Such designs are actively used in almost all surgical interventions. Barrier membranes for bone grafting during implantation can prevent atrophic phenomena in the alveolar process and contribute to the immediate successful fixation of artificial roots.
The membrane for bone grafting is a very thin and fairly elastic plate that is attached to the bone with titanium pins. In this way, the gums are separated from the bone material during the formation of natural jaw tissue.
Types of membranes
There are two types of barrier membranes that are widely used in dentistry:
- Resorbable. This structure gradually dissolves. It does not require separate removal, that is, additional surgical intervention, which means it causes less trauma.
- Non-resorbable. Membranes of this type do not dissolve on their own, which is why patients need an additional stage of treatment - removal of the structure. In most cases they are made of titanium. Such membranes are attached in the presence of a serious deficiency of bone tissue, filled with granules of osteogenic material. Once the alveolar bone and soft gum tissue have recovered, the barrier membrane is removed.
The dentist independently selects the optimal membrane for a specific clinical case. He must take into account that resorbable structures do not fix the grafts well enough, so they are used only for minor atrophies.
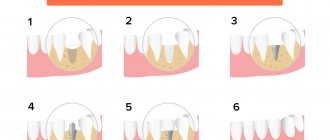
The innovative method of using a barrier membrane requires certain experience from the dentist, as well as clear knowledge of the technique of performing the stage. The structure is fixed as follows:
- Performing local or general anesthesia with the addition of sedatives (the last point is not always necessary);
- An incision in the outer soft tissues of the gums and moving them away from the bone of the alveolar process;
- Replenishment of the required amount of bone tissue using one of the previously selected methods;
- Fixing a modern structure made of collagen or metal with special titanium screws to adjacent teeth or to the jaw bone itself;
- Repositioning the soft gum tissue and securing it with surgical sutures.
When using a membrane that does not dissolve, after a certain time almost all steps are repeated to remove the structure.
A prerequisite for the patient’s successful recovery is careful oral care in the postoperative period. A person must maintain personal oral hygiene and follow all recommendations of the dentist. It is also important to quit smoking a few days before surgery and for the entire rehabilitation period.
Since fixing a barrier membrane is not cheap, many patients are interested in the question of alternatives to this design. In general, the cost of different types and brands of such dental material varies significantly. But if surgical intervention requires the use of a serious and reliable design, then it is not recommended to purchase a cheap analogue, because it still will not bring the expected result.
Performing bone grafting with fixation of barrier membranes is not available to all dental clinics. Refusal to use such structures will increase the likelihood of any complications, but in general will not affect the course of the operation and the recovery stage. But if it is possible to use a barrier membrane for bone grafting during implantation, then it is better to agree to its installation.
COLLOST® Absorbable collagen material ()
Preparing the product for use
Before use, it is necessary to keep a blister pack with a syringe filled with “COLLOST®” gel, as well as a blister pack with an injection needle planned for use, in a thermostat at a temperature of 38-40 ° C for at least 20 minutes until the gel turns into a liquid state, in order ensuring subsequent free passage of the gel through the needle. It is allowed to repeatedly heat the syringe with gel during one procedure for one patient. Before each subsequent heating, the needle must be replaced.
Before using COLLOST®, place the membrane for 10-15 minutes in a sterile solution of isotonic sodium chloride 0.9% to increase plasticity. For better outflow of exudate, the membrane should be perforated.
The tourniquet, ball, powder do not require preliminary preparation. It must be taken into account that the powder upon contact with any liquid increases in volume by more than 10 times.
How the product works
Due to the potential for the development of allergic reactions during routine use, it is recommended to test for the presence of hypersensitivity to the medical device before implantation. To do this, 14 days before using COLLOST®, it is necessary to conduct an intradermal allergy test by intradermal injection into the forearm area of 0.1 cm3 of COLLOST® gel using a 27G gauge needle. If an allergic reaction is detected, the test sample is considered positive, and in this case, COLLOST® should not be used.
The method of application and combination of various forms of the COLLOST® medical product are determined individually for each patient in accordance with the clinical picture, nature, size and shape of the defect.
Features of the use of COLLOST® in surgery
- Clean the wound from fibrin and necrotic tissue, transfer the wound process from the chronic to the acute stage. In some cases, this manipulation does not require local anesthesia, since it is performed on tissues with impaired innervation.
- In the case of using “COLLOST®” gel, inject “COLLOST®” gel in an amount of 1.5-3.0 cm3 into the edges of the wound intradermally along the entire circumference, as well as into the bottom of the wound (if necessary), depending on the size of the wound.
- Place the membrane, tourniquet, ball, powder on the wound bed and model it according to the shape of the wound to ensure complete adherence to all walls and the bottom of the wound. Ensure that KOLLOST® adheres as completely as possible to all walls and the bottom of the defect. If necessary, apply interrupted provisional sutures, which should be removed after 10-14 days. For external use, place a sterile gauze cloth moistened with isotonic sodium chloride solution 0.9% on the wound area, since the best effect of COLLOST® is achieved in a humid environment. Modern interactive wound coverings can also be used as a dressing material - hydrocolloid or sponge dressings, which are selected depending on the degree of exudation.”
- Dressings should be carried out once every 5-7 days. During the process of resorption in the wound, KOLLOST® can take on a gel-like form or remain unchanged. When re-dressing, do not remove any remaining material from the wound.
Features of the use of COLLOST® in dentistry
- In a minimally invasive method of treating chronic periodontitis, “COLLOST®” gel with antibacterial drugs is injected into the periodontal pocket through a syringe with a blunt needle. In this case, no preliminary preparation of the gel (warming) is required. The procedure is repeated after 7 days and then after 6 months.
- In surgical dental practice, a medical device “COLLOST®” is placed into the defect (the choice of shape depends on the defect and the clinical picture).
Features of the use of "COLLOST®" gel in cosmetology
- When correcting nasolabial folds and perioral wrinkles, the patient’s position is “sitting” or “reclining”; when injecting the gel into the skin of the forehead, paraorbital area, the patient’s position is horizontal.
- The area undergoing correction should be cleaned of cosmetics and disinfected with a solution of ethyl alcohol 70% or another antiseptic.
- When correcting wrinkles, it is recommended to use application anesthesia.
Methods for administering COLLOST® gel
Linear injection technique
The needle is inserted into the skin at an angle of 30° along its entire length parallel to the wrinkle line. The gel should be injected into the middle/lower part of the dermis at the back of the needle while pressing evenly on the syringe plunger. As the gel is introduced, the wrinkle/fold should level out and completely disappear by the end of the procedure. The introduction of the gel must be completed before the needle is removed from the skin to avoid leakage of the material or entry into the superficial layers of the dermis and epidermis. It is not recommended to inject more than 0.7 cm3 of material into one area.
Point injection technique
The gel is injected into the dermis, placing injections along the line of the wrinkle/fold being corrected, without allowing any gaps between individual portions of the injected material. After completing the injection, the treated area must be thoroughly massaged to align with the surface of the surrounding tissue. With hypercorrection, the massage should be more active; you can knead the skin with two fingers or press it against the underlying bone structures. If the “whitening” effect appears (the result of compression of blood vessels, impaired microcirculation and ischemia), you should stop the injection and actively massage the skin until it turns pink.
Several treatments may be required to achieve the desired level of correction. A two-stage procedure is especially recommended for patients with severe swelling after injection. An additional injection is given after 3-4 weeks.
Wrinkle correction
To correct wrinkles, linear, targeted gel injection techniques, or a combination of these two methods should be used.
To correct horizontal forehead wrinkles, wrinkles on the bridge of the nose, perioral area, and facial “smile” wrinkles, inject COLLOST® gel 15% into the middle part of the dermal layer of the skin using a 27G gauge needle in a volume of 0.5-1.0 cm3. The duration of the clinical effect ranges from 3 to 5 months.
In the case of very thin superficial wrinkles, when correcting wrinkles in the paraorbital area, inject “COLLOST®” gel 7% into the upper part of the dermal layer of the skin using a 27G needle. The bevel of the needle should be facing down, especially for pinpoint injections. The volume of injected material should not exceed 0.5 cm3 per correction zone. When working with small wrinkles in the paraorbital area, above the upper lip, on the cheeks and chin, you should be careful and introduce the gel evenly, avoiding overcorrection. The duration of the clinical effect ranges from 1 to 3 months. Repeated corrective injections are carried out at intervals of 6-8 weeks.
Shallow wrinkles above the upper lip are corrected by introducing gel along the red border of the lips (the technique is described below). For pronounced deep wrinkles of the upper lip, carry out additional correction by injecting gel under the wrinkle itself.
Correction of folds
To correct nasolabial folds, inject COLLOST® gel 15% into the lower part of the dermis at the border of the dermis and hypodermis using a 27G needle in an amount of 0.5 to 1.5 cm3 using a linear or point injection technique. The duration of the clinical effect ranges from 3 to 5 months. The remaining thread mark from the wrinkle should be smoothed out by introducing “COLLOST®” gel 7%.
Face shape correction
To correct the shape of the face, inject “COLLOST®” gel 7% in a volume of 1.0-2.0 cm3 using a targeted injection technique. After completing the injections, the treated area must be thoroughly massaged to align with the surface of the surrounding tissues. The duration of the clinical effect with a single administration is 3-4 weeks. To maintain a stable clinical result, repeated 3-5 procedures of introducing “COLLOST®” 7% gel are recommended once a month.
Correction of atrophic scars, stretch marks
To correct atrophic scars, inject “COLLOST®” gel 7% for superficial defects, and “COLLOST®” gel 15% for deep ones using a pinpoint injection technique with a 27G needle. The volume of injected material is determined by the size of the scar.
Duration of cosmetic effect
after the introduction of gels is individual and depends on many factors: skin structure, age, lifestyle of the patient, as well as on the injection technique and the doctor’s experience. Typically, a repeat procedure is required after 3-5 months when introducing “COLLOST®” gel 15%, and after 1-3 months when introducing “COLLOST®” gel 7%. Clinical experience shows that with repeated administration of the gel, the effect lasts longer. In areas of the skin involved in constant movement, or in areas where the skin is connected to active muscles (above the bridge of the nose), the duration of the cosmetic effect may be less than usual.
Recommendations for patients after the intervention
After administering COLLOST® to patients, it is recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure, visiting a bathhouse or sauna immediately immediately after the intervention. Carrying out cosmetic or physiotherapeutic procedures in the area of intervention may accelerate the metabolism of the product or provoke the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Indications
Collagen plates are used alone or in conjunction with augmenting material for the purpose of targeted tissue regeneration (slow or instant).
DETAILS: Preservation of tooth root during implantation
Indications for use are the following conditions:
- dehiscence (gap in the bone canal or in the wall of the tooth cavity);
- restoration of post-extraction alveoli (sockets after tooth extraction);
- treatment of fenestration defects (surgery to create an additional hole in the labyrinth of the inner ear);
- augmentation of the jaw ridge (in case of destructive processes due to long-term tooth loss);
- various operations to remove dental units or parts thereof (late temporary teeth, cysts, removal of the apex of the tooth root);
- the need to restore bone tissue around the implant;
- periodontal bone defects;
- the need to restore the jaw ridge for subsequent prosthetics;
- surgical defects of bone tissue and bone wall;
- the need to restore bone tissue at the base of the sinus node and support the nasal mucosa.
Despite the undeniable advantages of collagen and membrane technology in principle, it has a number of limitations for use.
Absolute contraindications to the use of collagen plates are:
- the presence of infected wounds (covering them with a natural product will aggravate the development of infection);
- the patient has a history of allergy to animal collagen (if there is an allergy to a certain animal protein, an alternative is selected).
Relative contraindications are:
- heavy heavy smoking;
- chronic infections;
- autoimmune diseases;
- treatment with radiation or wave therapy;
- long-term hormonal (corticosteroid) therapy;
- metabolic diseases in the degree of decompensation.
Indications for use
– to create a mechanical barrier that prevents the migration of soft tissues into the bone defect during surgical interventions;
– on the periodontium;
– filling of defects after cystectomy, root resection;
– filling defects after cyst removal;
– closing perforations of the maxillary sinus and perforations of the mandibular canal;
– as a mechanical barrier preventing apical migration of gingival epithelium;
– during reconstruction of the alveolar process;
– during maxillofacial operations to close soft tissue defects;
– as a clot stabilizer;
– to hold osteoplastic materials in the defect area;
– to increase the size of the alveolar ridge (augmentation)
What are barrier membranes?
Types of membranes
The barrier membrane performs several functions at once that contribute to the patient’s recovery. The design reliably fixes the osteogenic material in the place and position where the dentist installed it. Also, the membrane does not allow bone-destroying cells - osteoclasts - to pass through, which are normally responsible for the balance of metabolic processes in the alveolar process.
Indications for use of barrier membrane:
- Preventing the resorption of bone tissue in the alveolar ridge after tooth extraction (if treatment is not performed immediately and the patient will have to remove the load from this area for some time);
- Any type of bone grafting (retention of bone grafting material);
- Dental implantation with one-stage bone grafting (reinforcing function);
- Performing flap surgical interventions for periodontitis.
Barrier membranes appeared not so long ago, and therefore their cost remains high. Dentists make decisions based on the patient's financial status and may sometimes refuse to use them. In general, the use of a barrier membrane allows for better control of the outcome of bone grafting and reduces the likelihood of adverse treatment outcomes.
Application for tissue regeneration
The use of the product for regeneration purposes is based on the main advantage of the material - its ability to activate natural restoration processes in the human body at the cellular level.
In this case, the membranes almost never peel off from the walls of the restored fragment , which makes the effect of such therapy an order of magnitude higher.
The therapeutic result is achieved through:
- chemotactic fibroblast effect on surrounding wound fragments;
- being a high-quality hemostatic agent, the element stimulates hematopoietic processes, accelerates their coagulation and quickly stops bleeding;
- activates cell proliferation, migration and adhesion.
Different in structural composition, number of fiber fragments, resorption time, collagen membranes cope well with their regenerating function, which fully justifies their use in this area of dentistry.
Reasons for performing sequestrectomy for osteomyelitis and the essence of the method.
In this article we will talk about the indications for osteosynthesis of the jaw.
Follow the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/operatsii-na-zubah/udalenie-kapyushona-mudrosti.html to find out in which cases removal of the hood over the wisdom tooth is inevitable.
Benefits of use
Modern materials are easy to use, do not require sutures, retain their barrier function throughout the entire period of wound healing, and are strong enough to be successfully used in surgery. The multilayer structure simultaneously allows the product to be thin and maintain its barrier function.
Due to the fact that collagen becomes a natural part of the surrounding tissue during the healing process, the risk of inflammation and infection is minimal, and repeated surgery to remove the product is not required.
This is comfortable for the patient and allows wounds received during dental procedures to heal faster.
Collagen is a natural substance for the human body, so it practically does not cause rejection and allows the gum tissue to recover into a stronger and healthier structure.
Advantages
Due to a number of specific factors, collagen is considered one of the most compatible materials with natural tissues for the production of membranes. Moreover, biocompatibility concerns not only the component itself; the products of its decomposition also have the same characteristics.
Few people know that the presence of this material in its natural form in the human body is quite common - about 60% of the total volume of protein formations of gingival connective tissues is made up of it.
In this case, the substance is characterized by minimal manifestation of antigenic properties. This feature allows collagens, for example, from animals, to be transferred to humans without consequences.
Their breakdown is possible only under the influence of rare enzymes. The element takes an active part in hemostatic processes , which promotes rapid healing of the wound and stabilization of the structural content of the surrounding tissues.
Another, no less important plus is the chemotactic effect on the activity and qualitative state of periodontal cell fragments. As a result of the membrane being exposed during natural marginal dehiscence, the material breaks down faster without interfering with healing by secondary intention . Inflammatory manifestations are not observed in this clinical situation.
In addition, being a natural hemostatic agent, the component has a binding effect on damaged walls of capillaries and blood vessels , directly interacting with platelets at the surface receptor level.
Flaws
In rare cases of using a collagen membrane, allergic reactions may occur, since collagen is of animal origin.
Like any surgical intervention, surgery followed by installation of the product may lead to some complications - for example, pain, swelling, material rejection, necrosis, etc.
These consequences are not related to the peculiarities of collagen products - they are due to the qualifications of the doctor and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Contraindications
Contraindications for which the use of the product is strictly unacceptable are:
- infectious processes in the oral cavity in the acute stage of progression , as well as any manifestations of an inflammatory nature in the area of implantation - both acute and chronic course of the disease;
- general diagnoses , when maxillofacial surgery is not performed for objective reasons, as well as in the presence of contraindications to periodontics, surgical dentistry, endodontology and prosthetics by implantation;
- individual intolerance to elements of pork collagen , which can cause an acute allergic reaction.
Upgraded Bio-Gide Materials
One of the most widely used membranes in dentistry is the Bio-Gide two-layer design, which is absorbable. It is made from collagen fibers that have undergone many different treatments, making it ideally compatible with the human antigenic structure. Such membranes are made from specially selected cattle tissues.
Features of this membrane:
- The presence of two layers with different surfaces;
- Turning the porous surface towards the bone tissue, which improves the restoration of the alveolar process;
- The presence of a dense surface in the soft tissues of the gums prevents the ingrowth of fibrous (rough connective) tissue into the operated area;
- High biocompatibility of the membrane with natural tissues of the body;
- Gradual (over six months) resorption of the membrane through enzymatic action, without the formation of acids harmful to the body and irritation of the operated area;
- Swelling of the structure after installation and formation of the basis (base) for the regenerating bone tissue of the alveolar crest;
- There is a low probability of developing an inflammatory process (but it still exists, so you should follow the rules of oral care).
DETAILS: Bone augmentation during dental implantation
After fixing this type of membrane, treatment is continued only after 5-6 months. It is necessary to wait not only for the resorption of the structure of the structure, but also for the complete engraftment of the osteoplastic material.
Installation of the Bio-Gide barrier membrane does not cause any side effects, and complications are no different from those with bone grafting. Contraindications include an active inflammatory process and the lack of use of osteoplastic material during implantation, which is a prerequisite for attaching the membrane.
Dental, or barrier, membranes are a thin film of collagen fibers that are specially attached to damaged areas of bone in the jaw. The use of this material makes it possible to avoid further destruction and leaching of bone tissue, to fix materials used to build bones, and to strengthen mobile teeth during various operations.
Application of membranes in dentistry
Today, the membrane used for dental implantation is included in the list of modern medical achievements. Its use makes bone augmentation reliable and safe. It is especially in demand when restoring large volumes of bone, as it effectively prevents bone atrophy and loss. It is no secret that bone tissue takes a long time to recover, and this film construction accelerates this process.
Its main task is to prevent the osteotropic drug that is placed on the bone from coming into contact with the inner gingival side. Otherwise, there will be no full growth of bone tissue. Bone augmentation uses materials such as bone tissue from a patient or animal, as well as donor hard tissue or artificial materials.
If surgery is performed to remove a section of gum, the film is placed on new areas of the jaw and the gums are sutured over them. Thus, microorganisms do not penetrate the open wound. The use of barrier-type films requires the dentist-surgeon to have both excellent operating skills and experience working with special dental equipment.
To restore soft tissues, the product is used without pre-treatment, straight from the package.
The doctor evaluates the area of the defect and trims the flap of the product to the appropriate size. The material is applied to the defect area and spontaneously adheres to the tissue. If necessary, stitches are applied.
The material can be used as a soft tissue replacement if it is not possible to install an autogenous graft (for example, if there are increased risks associated with taking soft tissue from the patient).
The product in this case provides the structure of the guide splint, increasing the volume and promoting the ingrowth of soft tissue.
Tissue cells occupy space in the porous structure of the product, and with its absorption they fill all the necessary space.
Popular manufacturers
Today there are many companies producing collagen products. We will list the most famous of them, which use veterinary control and guarantee the high quality and safety of the material produced.
Collprotect
Collprotect is a material of natural origin with a rough three-dimensional structure. Its use allows for controlled, optimal tissue regeneration.
The material takes approximately 2-3 months to completely absorb, allowing for predictable and controlled wound healing and blood clot support.
Jason products are naturally derived and optimized for dental use.
The barrier function is maintained for 3-6 months, and the material itself has a small thickness while maintaining its natural structure.
It can be used both dry and wet, adapts perfectly to the contours of the surface and does not stick together after rehydration. Jason is highly durable and resistant to tearing and other damage.
Alpha-Bio's GRAFT Collagen Membrane is derived from porcine heart tissue and undergoes a standardized purification process to ensure its high compatibility with human tissue.
When completely saturated with blood and exudate, the product completely follows the contours of the wound, securely fixing and promoting the formation of a blood clot.
The disadvantage of the material is the need for sutures. The period for complete resorption of the material is 12 months.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Use for bone restoration
Being a highly purified natural component, membranes made from this material are successfully used in bone restoration.
Having a three-dimensional matrix structure and excellent biocompatibility, its natural composition helps to efficiently restore hard bone fragments.
The product has two sides - smooth and rough. A smooth surface intensively heals wounds, and a rough surface activates cellular bone growth.
Can be used either independently or in combination with patient cellular material.
The main advantage of use is improved bone formation and minimal trauma to the working area . In addition, it is an obstacle to the growth of surrounding soft fragments, in which these processes occur much faster.
The video shows the process of using a collagen membrane in bone grafting.
conclusions
Collagen turned out to be a real godsend for dentistry. Possessing exceptional biocompatibility and low antigenicity, it allows for controlled and effective tissue healing after various manipulations, avoiding trauma due to the absence of the need for repeated intervention to remove the barrier material.
Collagen is a natural hemostatic agent that forms a blood clot while leaving sufficient space for bone tissue growth, which implies a more physiological regeneration process.
The use of collagen membranes significantly improves the patient’s quality of life and comfort, and also ensures the safety of the postoperative period.
- Membrane for dental implantation in St. Petersburg – Price for installing a titanium membrane for implantation
- Dental implantation under anesthesia
- Dental instruments for implantation - Buy dental instruments for implantology in Moscow
- Computed tomography for dental implantation; CT scan of teeth in Moscow; What it is?