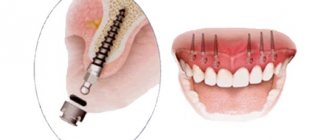
The importance of bone grafting in dentistry
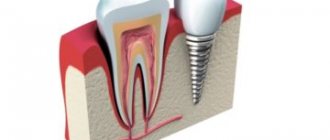
One of the main advantages of implantation over classical prosthetics is that it prevents bone loss in the area of missing teeth. The jawbone constantly needs stimulation, which occurs as a result of the pressure exerted on it during the chewing process. However, after the loss of a tooth, the bone ceases to receive the proper load, as a result of which it begins to decrease. Conventional dentures cannot prevent bone tissue resorption, since they mainly put pressure on neighboring teeth, and not on the area of the missing tooth. Only an implant can stop this natural process. During dental implantation, bone tissue receives the necessary load and does not lose volume, which allows you to avoid numerous negative health consequences and maintain the aesthetics of your smile. In case of prolonged absence of a tooth, as a result of which the jawbone has begun to atrophy, bone grafting comes to the rescue.
Plastic methods
Soft tissue grafting uses several methods. Here are the most common methods of intervention.
- Tunnel. In this case, trauma to the oral cavity is minimized. The surgeon makes small incisions in the mucosa to access the tissue. The wound heals quickly, since the soft tissues of the oral cavity have an increased regeneration rate. The rehabilitation period is minimal.
- Soft tissue grafting uses an autograft. Healthy tissue is collected from the patient himself. This is the most reliable method, since the probability of engraftment tends to 100%.
- For deep correction of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, the method of free plastic surgery with a displaced flap is used.
The dentist chooses the methods of influence based on the characteristics of the situation. All procedures do not require general anesthesia. If you think you need soft tissue plastic surgery, contact our dental clinic in Tula.
Source: smilespa.ru
The factors that cause resorption even in the presence of an implant are not completely clear. Most authors are inclined to believe that the reason for the remodeling of the bone plate is the presence of a large number of Sharpey fibers, which are derivatives of the periodontium. Accordingly, the operation of tooth extraction triggers the mechanism of resorption of the outer cortical wall.
And the degree of resorption depends on the thickness of the cortical plate and the number of fibers in it. In this case, atrophy of the alveolar walls occurs to a greater extent due to the vestibular part of the socket. The presence of an implant in the socket often does not affect the resorption of the outer cortical plate.
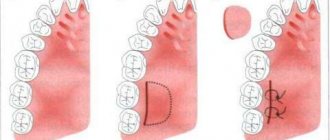
In this regard, when planning treatment, a computed tomography (CT) scan is necessary. Based on CT data, a classification was proposed (Kan, Roe Kit, etc.), thanks to which one or another method of treatment can be chosen (Fig. 1).
Depending on the clinical situation, they can be conditionally divided into techniques that preserve the volume of the socket and soft tissues when planning implantation in the near future and techniques aimed at restoring the lost volume of bone tissue. In the first case, the hole heals by secondary intention, in the second - by analogy with the membrane augmentation technique - it requires hermetically sealed closure and delayed implantation for at least 6 months.
CLINICAL CASE No. 1
Removal of the 11th tooth due to long-term chronic inflammation, constant exacerbations, extensive periapical lesion and, as a consequence, resorption of the outer cortical plate. In this situation, immediate implantation has certain risks and unpredictable results. Therefore, the 11th tooth was removed while preserving the volume of soft tissue for subsequent implantation after epithelization of the socket.
The socket heals by secondary intention (Fig. 2-10).
This technique was proposed by Dr. Alfaro.
CLINICAL CASE No. 2
Removal of the 12th tooth. The vestibular wall of the alveoli is preserved throughout its entire length, with the exception of the periapical third, due to the inflammatory process. A decision was made to delay implantation. Sanitation of the apical lesion from the vestibular surface through a semilunar incision in the projection of the root apex. An osteoplastic material is placed in the socket, which is isolated by a resorbable membrane.
The socket is covered with a free mucous full-thickness epithelial graft. The absence of vertical incisions and the need for flap mobilization in case of socket suturing is of great importance for future aesthetics. The implant was installed after 6 months with immediate restoration with a temporary crown, followed by correction to obtain an optimal gingival contour (Fig. 11-18).
Source: ohi-s.com
What is bone grafting for dental implants?
Bone grafting in dental implantology is the augmentation of bone tissue, which is often necessary to perform turnkey dental implantation. On average, 3 to 6 months after the loss of a tooth, the process of bone tissue atrophy begins at the site of its removal, due to the fact that the bone ceases to bear the load. This process reaches its peak after about a year, and if you do not contact an implantologist immediately after removing unhealthy teeth, there is a high probability that additional bone augmentation surgery will be required later. It should be noted that plastic surgery, even in situations where there is a lack of jaw bone tissue, is not always required and not for everyone. The decision on the need for it will be made by the doctor, based on the situation of the individual patient.
There are cases when the bone tissue in the place of a missing tooth remains unchanged for many years, but this is rather an exception to the rule. More often, quite pronounced bone atrophy and even tilting or displacement of teeth towards the defect are observed.
Photos of bone grafting at various stages of its implementation
Advantages and disadvantages of bone grafting
The main advantage of bone grafting is the ability to completely restore the volume of bone tissue even with severe atrophy. Bone augmentation guarantees further reliable fixation of the artificial root and long-term trouble-free wearing of the implants.
The disadvantages of bone grafting include the following:
- 1. Pain (as after any operation). When healing without complications, they are easily relieved with painkillers and disappear within 2-3 days.
- 2. Long-term rehabilitation. Some bone grafting methods require long-term healing and regeneration of the operated jaw. Sometimes the gap between osteoplasty and implantation itself can be several months.
- 3. The risk of complications, which include inflammatory processes and the likelihood of bone block rejection. However, if the operation was performed efficiently and the patient followed all the doctor’s recommendations, then the risk of complications is minimal.
Prices for bone grafting in Moscow
Bone augmentation surgery requires skill and extreme precision from the surgeon. The price of bone grafting depends on the qualifications of the surgeon, the materials chosen for transplantation, as well as the volume of additional services included in the clinic’s package. Very often, the price of bone grafting in dentistry is overpriced, because doctors do not have the proper level of professionalism and perform the operation much longer than it requires. It is not surprising that the prices for bone grafting for dental implants discourage patients.
What types of bone grafting are there?
Bone grafting of the lower jaw in the lateral regions is necessary in case of a decrease in the height and width of the alveolar process and a reduction in the distance to the mandibular canal. Significant loss of bone volume in the lower jaw can result in a change from the normal bite to a mesial bite (where the lower jaw moves forward).
Bone grafting of the alveolar process of the upper jaw is associated with bone resorption and the formation of a thin and sharp alveolar ridge. The difficulties of plastic surgery in this area are associated with the task of achieving an optimal cosmetic result.
Bone grafting of the lateral sections of the upper jaw is called sinus lifting, since the maxillary sinuses, or sinuses, are located in this area. There are closed and open sinus lifts, and they differ in the way they penetrate the bone.
Types of operations performed on soft tissues
Gumplasty
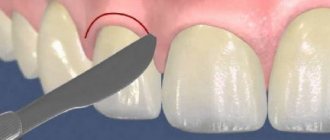
Asymmetrical gum contour is one of the most common cosmetic problems identified in the dentist's chair. With this defect, not only the beauty of the smile suffers. An uneven edge of the gum can cause many oral diseases. Gingivoplasty, an operation performed on the gums, will help eliminate the problem and possible risks. The surgeon makes a shallow incision in the area of the unevenness, carefully moves the gum to the desired position, and then sutures the tissue.
Correction of the gum margin
Changing the shape of the lip frenulum
Too short a frenulum on the upper and lower lips stretches the mucous tissues of the jaw when talking and chewing food. This phenomenon provokes malocclusion, exposure of teeth as a result of gum detachment. The result is the appearance of “pockets” in the gums into which food gets trapped. In the worst case scenario, the tooth may fall out. In rare cases, patients may notice a complete absence of the frenulum, or several at once. But if there is a threat of tooth loss, doctors recommend surgery at any age.
Correction of the frenulum of the upper lip is necessary
Plastic surgery of the oral vestibule
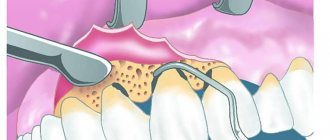
Too small a vestibule of the oral cavity can cause the development of many dental problems. Bleeding gums, exposure of roots, gingivitis and other unpleasant phenomena can be eliminated by plastic surgery of the vestibule. The operation is performed using different methods. The most common is a tissue incision at the junction of the gums and the moving part of the mucosa. The surgeon removes the mucous layer, lowers it into the incision site and sews it to the periosteum.
Tongue frenulum surgery
Frenuloplasty helps to avoid the formation of malocclusion and many speech defects. In adults, this part of the mucosa can shorten as a result of mechanical trauma. The specialists of the One to One clinic have extensive practical experience in performing operations on this area of soft tissue.
Before surgery for plastic frenulum of the tongue in adults
Surgeries to remove tumors
Inflammatory processes occurring in the gums can cause the formation of cysts, tumors and fibroids. These phenomena are painful and interfere with talking and eating. Any unpleasant tumors can be quickly and painlessly removed in our clinic.
Fibroma in the oral cavity before surgery
Any operations performed on the oral mucosa can have unpleasant consequences. A surgeon, when prescribing a particular type of intervention for a patient, carefully analyzes the possible risks and the degree of need for plastic surgery. Modern materials and instruments, high professionalism and experience of doctors allow us to minimize negative consequences. The patient does not feel any discomfort during the operation.
What materials are used for bone grafting in dentistry?
Both natural and synthetic materials, which have similar capabilities for engraftment and replenishment of bone volume, can be used as a bone tissue implant. Synthetic materials are made based on hydroxyapatite or calcium phosphate. As a rule, they are produced in powder form and are successfully used in world practice.
Autogenic
For bone tissue augmentation, the best material is autogenous, that is, your own bone sections taken from the donor area. Such an area, as a rule, is the chin or the area of the lower jaw in the area of the wisdom teeth. An autogenous graft takes root better than others, but its use is associated with an additional operation to collect donor material.
Allotransplantation
In addition to autotransplantation, in some cases allotransplantation is used, when bone material is taken from another person who bequeathed his organs for medical purposes. In this case, the donor material is carefully selected, sterilized and processed, and the recipient’s body eventually accepts such bone material as its own and successfully restores the lost bone.
Xenotransplantation
When people talk about xenotransplantation, they usually mean the transplantation of bone tissue from animals, usually cattle. The bones of cows and bulls are carefully processed, sterilized, and manipulated to make them compatible with the human body. Such transplants also take root well.
To adequately complete this task, we have developed and patented an original method of performing bone grafting in the oral cavity using bone material obtained from extraoral areas, which is the “gold standard” in world medicine. This allows us to subsequently install the required number of implants and subsequently carry out prosthetics of varying degrees of complexity.
Materials used to perform bone grafting
A large number of materials have been developed for jaw bone augmentation. They are called grafts, they are obtained from human or animal bone tissue, and materials obtained synthetically are also used.
For bone grafting, materials from a human or animal donor are used; they are also artificial and have a high survival rate.
There are the following types of such materials:
- Autografts - they are obtained from the patient’s bone tissue (usually from the area where the “wisdom teeth” are located or his bone on the chin), this transplant material is the most reliable, it will take root with a 100% guarantee and will not be rejected by the body, because it is “our own”
- Alloplasts are artificial materials, but with high survival rate, widely used for bone grafting
- Allografts - materials for augmentation are prepared from the tissues of another person, most often these are cadaveric bones treated in a special way, they do not contain living cells, for this reason such material takes a long time to take root
- Xenografts – bone tissue taken from cattle
When is soft tissue plastic surgery necessary?
- Deficiency of soft tissue volume, as a result:
- long-term absence of a tooth (with edentia, atrophy occurs both in bone tissue and soft tissues);
- wearing a Maryland prosthesis (mechanical impact on soft tissues, even in a short period of time, leads to a loss of gum volume);
- thin biotype of the mucosa (here we are talking about the prognosis of future restoration and prevention of volume deficit of hard and soft tissues).
- Lack of attached keratinized mucosa due to:
- the need for directed bone regeneration or an already performed GBR operation (the suturing technique afterward is such that part of the keratinized mucosa is often lost, not counting the already existing atrophy);
- past mistakes during implantation or soft tissue plastic surgery.
- In order to improve the prognosis of treatment. Creating a reserve of soft tissue in the frontal region increases the favorable prognosis of treatment.
To achieve success, it is necessary to comply with parameters that must be taken into account at the planning stage. Some factors may influence directly, others indirectly. Factors such as the accuracy of sampling the SDT or SST, the processing method, the quality of the graft, the preparation of the material fixation zone and the quality adaptation to the receiving bed directly influence.
Indirect ones include careful planning and compliance with the surgical protocol (position, inclination and size of implants, correct choice of suprastructures, compliance with the necessary timing and stages of treatment).
Before we go any further, let's refresh our memory a little. The purpose of dental implantation is to restore a functionally and aesthetically missing element of the dental system. In the dental system, we are interested in bone tissue, mucous membranes, and adjacent teeth. The function of bone tissue is support, retention of the implant, perception and distribution of load. The function of the mucosa is to protect and nourish bone tissue and ensure adequate hygiene.
Based on the above, it turns out that for high-quality implant treatment it is necessary to have high-quality bone tissue in the right volume and the right place (if there is not enough, create it), and high-quality soft tissue (not only in volume, but also of the desired histological structure). Below are examples in different clinical situations.