Augmentation is a procedure to restore jaw bone tissue
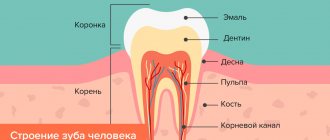
Sinus lifting, or the second name of the term in dental surgery - augmentation (augmentatio), is translated from Latin as enlarge, strengthen. Augmentation is the process of replacing or restoring jaw bone tissue. This procedure was actively practiced back in the 19th century by Walter and Walfform.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the first bone tissue transplant operations were performed by doctors Dyakonov and Deshin. The procedure is quite complex, and therefore requires special equipment and a full study of the patient’s medical history.
Soft tissue augmentation
SOFT TISSUE PLASTY AS A SEPARATE STAGE OF IMPLANTOLOGICAL TREATMENT
It is no secret that with prolonged absence of teeth, atrophy develops not only of the bone tissue of the jaws, but also of soft tissues. The latter is expressed, first of all, in a decrease in the volume of attached gums in the area of the dentition defect.
The absence of keratinized mucosa in the implant area leads to gum recession and permanent inflammation, which, in turn, often ends in peri-implantitis and loss of the prosthetic structure.
In modern implantology, soft tissue augmentation is most often isolated as a separate stage of implant treatment, although in some cases it can be combined with the installation of gum formers and preparation for prosthetics.
The parameters of pink-and-white aesthetics largely determine a person’s perception of the smile profile; therefore, treatment should be aimed not only at restoring the continuity of the dentition, but also at correcting the harmonious contour of the teeth and gums. Based on this, adequate assessment of soft tissue parameters is an important diagnostic step, and the goal of correcting them may be the following:
- achieving sufficient volume;
- formation of an adequate vertical level of the gums around the implant with restoration of full-fledged dental papillae;
- ensuring the natural texture of the mucosal surface without traces of scarring as a result of surgical interventions.
The tissues of the peri-implant area are restored not only for aesthetic reasons, but also to achieve adequate functional parameters: sufficiently formed gums guarantee long-term stability of the implants, and also improve the conditions for supporting the necessary hygienic care. Surgical methods for improving soft tissues are minimally traumatic and eliminate the formation of scars on the surface of the gums. During complex rehabilitation, soft tissue correction in the peri-implant area can be performed at three different points in time: during extraction, during installation of the intraosseous support, and during exposure of the implant. The choice of the most optimal period depends on the degree of soft tissue defect in the peri-implant area, which should be assessed at each stage of treatment.
Before installing the implant
Procedures for preserving the original parameters of the residual ridge are quite effective, especially if the implantation is carried out according to a delayed protocol. The results of many studies have confirmed the positive effect of methods of maintaining the initial parameters of the socket on the retention of the level of alveolar bone tissue. In addition to the use of demineralized bovine bone substitute, the socket cavity can additionally be closed with a free epithelialized graft, thus minimizing the loss of tissue volume in the intervention area and improving the clinical conditions for the subsequent surgical stage of treatment.
During implant installation
If soft tissue correction is necessary, this procedure can be performed simultaneously with the installation of a dental implant. If the vestibular bone plate is intact and its thickness is at least 1 mm, soft tissue augmentation can be carried out in parallel with bone tissue reconstruction during implant placement. To do this, the subepithelial connective tissue graft is sutured into the gap on the vestibular side of the socket along the tunnel tract. When the thickness of the buccal bone plate is less than 1 mm and in cases of its fenestration, it is simply impossible to do without extended surgical interventions.
During exposure of the implant and installation of the healing abutment.
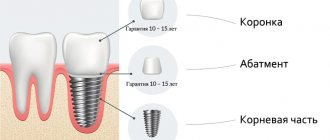
This stage marks the transition from surgery to orthopedics. The shaper is always installed. It helps create an anatomically correct gum shape.
To achieve the best result, it is recommended to separate the time of implantation and installation of additional elements. The former itself looks like a metal cylinder protruding 2-3 mm above the gum level.
How this procedure works:
- The doctor gives anesthesia.
- Then, using a scalpel, an incision is made in the area of the installed implant.
- Afterwards, its head opens and is cleared of overgrown bone tissue.
- The plug that was installed in the implant is unscrewed.
- A gum former is installed in place of the plug.
- If necessary, stitches are applied and removed after 7-10 days.
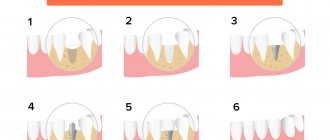
Use of grafts
This is the most popular method of restoring lost soft tissue.
The operations performed are very similar to restoration of gum level during recession:
- Moving the flap from adjacent areas.
- Moving the flap from the same area.
- Harvesting a graft from the palate (Free Gingival Grafts (FGGs) and Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts (SCT))
The first two methods are based on moving a small area of gum.
In this case, gum plastic surgery during implantation proceeds as follows:
- First, the doctor applies anesthesia to the implant and donor area.
- Then incisions are made near the implant, the mucoperiosteal flap is peeled away and space is created for additional tissue.
- Next, the flap is peeled off and moved to the prepared surface.
- At the end, suture material is applied.
The next examination is carried out after 7-10 days, which is combined with the removal of sutures. The doctor checks the degree of engraftment of the graft by assessing its color. If the fabrics take on a pink tint, then everything is fine. Prosthetics can be installed at the surgical site 3-4 weeks after all wounds have completely healed.
The surgical technique for moving the flap from the palate is almost identical. The only difference will be in the size of the wound surface. In this case, the wound will be slightly larger, which will cause slightly more discomfort.
Schematic illustration of graft harvesting from the palate.
Use of membranes
Plastic surgery of soft gum tissue after implantation can occur using resorbable and non-resorbable membranes.
Stages of the operation:
- The doctor administers anesthesia to the intervention area.
- A scalpel is used to make cuts down to the bone.
- Moving soft tissue to a new position.
- Membrane installation.
- Stitching.
- It is also recommended to begin prosthetics no earlier than a month after the manipulation.
Doctor's recommendations
Instructions given to the patient after plastic surgery:
- Brushing your teeth at the site of gum growth should be as gentle and careful as possible. It is better not to touch the seams at all.
- Rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
- Avoid hot, cold, spicy, sour and salty foods.
- Use of medications prescribed by a doctor in the correct dosage.
- Avoid all physical activity for 7-10 days.
- Do not go to the bathhouse, sauna or steam room. If possible, it is better not to overheat or overcool.
What will be obtained as a result
If all interventions are carried out correctly and the doctor’s recommendations are followed, the keratinized gum will be restored to the proper extent. After prosthetics with crowns, its width will be 3-4 mm or more, which is enough to create a high-quality fit.
There is no microdamage to the gums in the prosthetic area, which avoids inflammation in this area and loss of bone tissue with exposure of the implant neck.
Source of information 1
Source of information 2
Contraindications for surgery
The procedure is not carried out:
- during the period of exacerbation of chronic sinusitis;
- if the patient has tumors in the oral cavity, directly in the upper jaw area;
- for pathologies associated with blood clotting;
- history of tuberculosis;
- diabetes mellitus type I.
It is worth noting that doctors also identify relative contraindications. These include: the inflammatory process in the oral cavity, the presence of caries in the patient, as well as the period of pregnancy and lactation.
Possible variations
It is worth noting that there are several types of restoration techniques. The first type is called closed, and the second type is open. In the first case, the procedure is performed when the height of the bone is in the projection of the maxillary sinuses. In this case, the height of the bone should be at least 8 millimeters. If this height is not enough, then an open operation is performed, in which stronger anesthetics are used.
The procedure can be carried out using a variety of materials, it all depends on the degree of complexity of the problem that the patient has.
Autotransplantation involves the growth of the patient's own bone tissue. Before the operation, bone tissue is taken from the patient's chin or hard palate. After which, your own bone tissue is transplanted into the required area of damage.
This type of procedure reduces the risk of infection and improves the healing process.
The second type is also the growth of donor bone material, but only taken from another person. Such material requires additional processing. The disadvantage of this type of operation is the slow engraftment of the material.
The third method is practically not used, since xenotransplantation takes biomaterial from the animal.
Methods and options for bone tissue augmentation
The operation allows you to optimize the bone bed for further implantation.
Augmentation improves the qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the bone tissue area in order to increase the stability of the implantation. The operation can be carried out in several ways:
- autotransplantation (the patient’s own tissue is used for extension);
- transplantation of donor material;
- use of artificial osteosubstitutes.
Depending on the direction of augmentation, bone tissue augmentation in dentistry is of two types:
- horizontal - increase in the width of the alveolar process. This type of bone tissue augmentation is usually performed on the front part of the upper jaw and the back part of the lower jaw. The most common method, standard, with a predictable result. Most often, blocks of the patient's bone are used for horizontal transplantation;
- vertical bone tissue augmentation - increasing the height of the alveolar ridge. The method is technically more complex, labor-intensive, with a relatively less predictable result. It is performed primarily using the sandwich technique—the patient’s bone blocks are fixed with miniature screws, and the gaps are filled with powder or shavings of a bone substitute. The integrated block is covered with a special membrane to prevent the germination of gum tissue, after which the gum is sutured.
In dentistry "SUNNY ISLAND" we perform one-stage and preliminary augmentation of bone tissue. In the first case, bone augmentation occurs simultaneously with implantation. This is possible for small defects, and, as a rule, artificial bone substitutes are used. After 2–3 months and over the next year, osseointegration of the implanted implant occurs.
Preliminary augmentation of bone tissue in our dentistry is carried out when the atrophy of the jaw is significant and a certain time is needed for the formation of sufficient bone volume. On average, it takes 4–6 months for the material to engraft, after which implantation can be performed.
Closed bone augmentation surgery is usually performed to restore bone height in the area of the maxillary sinuses. In this case, the height must be at least 8 mm. If it is insufficient, then open surgery is performed to build up the bone.
Recovery stages
The main stage in preparing for surgery is a complete study and diagnosis of the problem. Therefore, before the procedure, doctors prescribe tests and also examine the oral cavity using X-rays to identify a tumor.
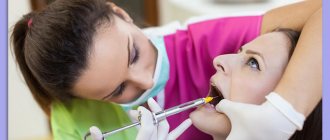
The operation is performed in dental surgery and requires complete sterility.
The patient is seated in the dental chair and anesthesia is administered. The painkiller is selected individually, it all depends on the patient’s medical history.
Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the doctor will insert a special brace to secure the jaw. Using a surgical scalpel, a small incision is made, as a result of which a bone window opens.
Then the cyst is removed and only after that the cavity is filled with biomaterial. At the end of the operation, a cosmetic suture is made.