X-ray of teeth: what the study shows
Panoramic
Find out the dose received when X-rays pass through selected organs using a modern digital device, and compare the indicators with the natural background. Go to “Dosimeter”.
Dental radiography is often prescribed because it is informative in case of pathologies of the oral cavity. In complex cases, doctors promptly recommend that patients undergo x-rays to eliminate guesswork and make an accurate diagnosis. X-rays of the jaw can reveal the presence of the following diseases:
- root fractures or cracks in the root - such damage occurs after a serious injury, a blow to the jaw. Typical signs of a fracture include gum inflammation and pain when chewing or biting. In this case, the tooth itself will become mobile and will wobble in the gum. For a final diagnosis, an x-ray will be needed;
- periodontitis is a pathology of bone tissue in which atrophic processes occur, gums become inflamed, bleeding appears, and the tooth itself begins to become loose;
- Periodontitis is a disease of the apex of the tooth root, manifesting itself in the form of a granuloma or cyst. Accompanied by an inflammatory process and pain in the area of the affected tooth. As the cyst increases in size, a fistula tract may open, and if the suppurative process begins, the person faces the loss of the crown and root. A dental x-ray will help make a diagnosis in a timely manner;
- hidden caries is a big problem for all people, since the disease does not reveal itself and even with the most thorough examination of the oral cavity, the patient will not see signs of caries, but nevertheless it is there. Often caries develops under the crowns, so the problem can only be visualized by taking an X-ray of the teeth;
- Anomalies in the location of the dentition are rare, but can be so significant that they sometimes change the previously planned treatment regimen. Only x-rays will help determine this;
- neoplasms or foci of inflammation - they are not visible outwardly, but the treatment of pathologies requires the earliest possible diagnosis.
These preliminary diagnoses are direct indications for an x-ray. X-rays of the jaw are also taken in other cases, for example:
- before the implantation procedure;
- if necessary, prosthetics;
- before orthodontic treatment;
- to make a decision about bone grafting;
- if it is necessary to treat dental canals (in order to check the quality of canal filling).
Dentists recommend taking an X-ray for preventive purposes every year, even if the patient is not worried about anything and there are no visible indications. This will help to timely diagnose pathologies that can lead to crown loss and prevent pathological processes.
Doctors recommend taking preventive photographs for those patients who have already had implants placed, have pulpless crowns, or have undergone extensive restoration of the jaw (osteosynthesis, prosthetics, basal implantation, etc.).
Using an X-ray of the oral cavity, you can not only determine the pathology, but also a clear localization, as well as complications caused by the destructive process - cracks, inflammation, cysts.
Carefully collected data on the condition of the crowns, roots and bone tissue of the jaw will help the doctor make a correct diagnosis and outline a treatment plan.
When is radiography prescribed?
X-rays of the TMJ area are usually indicated in the following cases:
- presence of severe dislocation;
- for mechanical and other injuries to the TMJ area;
- for gout;
- before implantation of prostheses;
- with ankylosing spondylitis;
- to find out the exact causes of malocclusion;
- before prescribing plastic surgery in the head or face area.
Most often, disorders in the TMJ area appear as a consequence of lack of treatment or complications of diseases such as mumps or otitis media suffered in childhood.
X-rays may also be prescribed if TMJ arthritis is suspected if there are the following complaints:
- pain when talking, chewing;
- the presence of swelling in the projection of the joint;
- elevated temperature (this is a sign of the body’s reaction to an existing inflammatory process).
The study is also indicated for suspected arthrosis of the TMJ, especially after microtrauma, occlusion disorder, visual deformation, visual displacement of the jaw. Indications for research in this case are severe pain, deformation and decreased mobility of the TMJ. If treatment is not prescribed for a long time, serious hearing loss is possible.
The first signs of the development of destructive processes are:
- clicks, crunching while talking, chewing;
- visual violation of symmetry;
- the mouth cannot be completely closed or opened;
- When closing or opening the jaws, discomfort and sharp pain are felt.
How is an X-ray done?
The examination is carried out quickly. For the x-ray, the patient is escorted into the x-ray room, where a technician places a lead apron on the client to protect them from harmful radiation. The technician explains how to hold your head to get an image. If a circular picture is taken, the patient’s head is fixed with additional fasteners.
Once the patient is ready, the technician brings up the X-ray machine and comes out to take the picture. This takes a matter of minutes, after which the patient’s apron is removed and escorted to the doctor’s office. After a few minutes, the doctor receives either a snapshot or a digital image on the screen.
Features of preparation for diagnostics
X-rays are not recommended more than once or twice a year because the dose of radiation a person receives is too high for frequent examinations. But the method has a number of significant advantages. There is no need to prepare for it. X-rays are performed very quickly. The results will be ready in just a few minutes.
Depending on the age of the patient, the examination is carried out in different ways. For adults, X-rays are performed using the survey method. For children, close-up photography is most often used. During the examination, photographs are taken in two ways: with the mouth open and then with the mouth closed. In particularly difficult cases, a contrast agent is used.
You can get a referral for an examination from specialists such as an arthrologist, traumatologist, surgeon, or dentist. Radiography is performed on an outpatient basis; it does not require a hospital stay or special preparation of the patient. The duration of the examination is short, everything takes a couple of minutes, results can be obtained in ten to fifteen minutes.
Pros and cons of jaw x-rays
The benefits of the study are obvious. In a short period of time, the doctor can clarify the picture and confirm or reject the proposed diagnosis. X-rays will show even those complications that you may not suspect. For example, if osteosynthesis is necessary, an x-ray of the upper or lower jaw is always taken, and if the jaw has pathologies, the doctor will postpone the procedure until a later date. It is impossible to detect this without x-rays. X-rays have become a common procedure in dentistry due to the ease of taking images and obtaining important results.
The disadvantages include certain diagnostic features when it is not possible to establish pathology. However, the fault here is not with the equipment itself, but with the processes that occur in the bone. When certain areas are darkened, the doctor already receives indirect information about the disease. Radiation should not be considered a disadvantage of X-rays, since the doses are small and do not pose a danger.
The essence of radiography of the temporomandibular zone
If previously patients received black and white photographs in their hands, with which they had to walk throughout the hospital, for fear of accidentally crushing them, today progress has stepped far forward. Now the received visual information is sent to the computer memory of a new generation X-ray machine. From there it can be recorded on any digital media.
Content
- The essence of radiography of the temporomandibular zone
- Indications for use
- Diagnosed anomalies
- Procedure algorithm
- X-ray in dentistry
From an anatomical point of view, the temporomandibular joint is a connection between the lower jaw and the temporal bone of the skull, formed by the ellipsoidal fossa of the temporal bone of the skull and the head of the condylar process of the mandible.
Often, diseases of this area are based on pathologies of the articular disc, or destabilization of the intra-articular ligament.
No less often, the primary source of all problems is the inability to perform its functional duties as a capsule. Even arthritis does not bypass this joint.
Despite the fact that radiography is not always able to provide a 100% clear image of the area being examined, it is the most popular way to find the root cause of the disease.
Types of X-ray of the jaw
There are several types of X-ray examination of the jaw. Depending on the goal pursued by the doctor, x-rays can be:
- bite - detects the presence of tartar and caries;
- targeted - the coverage of the image is from one to three teeth, as a result of which the condition of the roots, the quality of canal filling, pathologies and complications in neighboring teeth are visible, which can affect the chosen treatment regimen;
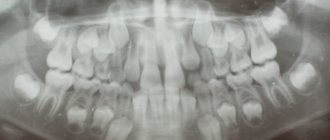
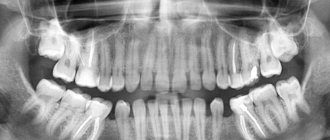
- panoramic - with this image you can see the condition of the jaw. An x-ray of the lower jaw and upper jaw is taken, and the latter even makes it possible to visualize the maxillary sinuses and determine the pathology there. Such a study is carried out during the patient’s initial consultation when visiting the clinic and, if necessary, to monitor the situation during therapy;
Panoramic shot
Sight shot
Depending on the technique of the procedure, there are:
- intraoral x-ray - during the procedure, a film is installed on the inside of the jaw. A periapical photograph helps to see up to three teeth, capturing gum tissue, and an occlusal photograph “sees” the entire dentition, since the film is clamped between the teeth and visualizes the entire row;
- cephalometric - an image is taken to evaluate a specific area of the oral cavity. It is possible to obtain information about the relative position of the jaws and draw a conclusion about the need for orthodontic care;
- panoramic - the picture is taken in large clinics or diagnostic centers. Using a circular image of the teeth, information about the condition of the entire jaw is obtained at once.
Cephalometric image
The type of image that needs to be taken is determined by the doctor, who also gives a direction for the study.
Types of dental x-rays
You have already understood why dental x-rays are necessary, and also when it is prohibited to do it, now let’s look at the main types of this study. The variety of types is based on the fact that various devices can be used, here are the main types:
- Bitewing X-ray. This examination allows you to diagnose tartar and caries.
- Targeted X-ray. This procedure allows you to study the condition of the gums, as well as the insides of the teeth;
- Panoramic X-ray. This study is used by specialists to obtain the most accurate images of the entire jaw joint;
- Digital X-ray. This type of procedure is the most modern; it involves the use of modern technologies.
- X-ray in 3D. Such diagnostics are rare, but they are the most effective, as they allow you to create a panoramic image that can be viewed on a computer.
Important! During an x-ray, the patient must follow certain rules, which the dentist will tell you in more detail. If you do something wrong, you will most likely have to redo the pictures.
X-ray during pregnancy and lactation
Dentists prefer not to treat the teeth of pregnant women in the first three months of gestation, since there is a risk of adverse effects of anesthesia on the fetus. X-rays are not performed for the same purpose. Nevertheless, the second and third trimesters are safe in terms of therapy and diagnosis, so all non-urgent cases of dental care are postponed to this time.
If there is an urgent need for dental treatment, then it is carried out and x-rays are taken, which are necessary during the therapy process. Modern X-ray machines help minimize radiation, so pregnant and nursing mothers do not receive a large dose of radiation.
Additionally, doctors take the following measures:
- the woman's body is covered with a lead apron to protect it from X-rays;
- the doctor carefully examines the problem area and indicates the best position in which the picture is taken. This is done to get a complete picture at one time and not to irradiate the patient again.
Since the woman was covered with a lead apron during the X-ray of her mouth, this allows her to continue feeding as usual; there is no need to express milk.
X-ray of teeth for children
Dental X-rays are performed frequently for children. This is due to increased bite problems, because children often develop an incorrect bite and to eliminate the problem it is necessary to diagnose and prescribe treatment. An X-ray of the teeth will show the rudiments of the roots, which will be useful in case of abnormal eruption or incorrect position.
Parents worry whether x-rays will affect the child’s health. There is no need to worry about this - a low-dose x-ray of one or even several teeth will be safe for the baby. But the benefits of timely diagnosis of pathology far outweigh the possible adverse consequences.
Why do dental x-rays take place?
Questions about whether it is possible to take an X-ray of a tooth should not arise, since taking an X-ray of a tooth in dentistry is very important, and it would not be so widespread if it posed any danger to the human body. The question, rather, is how many times can an X-ray of this kind be taken per year, because in many situations it can be in demand, especially if you go to the dentist to correct a large number of problems.
Taking dental x-rays is necessary in many situations because it allows specialists to diagnose the following possible complications:
- cyst;
- various cracks in the teeth;
- inflammatory processes accompanying periodontitis;
- latent caries;
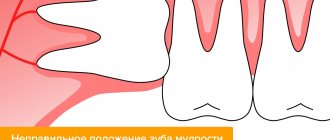
- disturbances in the arrangement of teeth (most often wisdom teeth);
- overhanging fillings;
- the degree of damage to the tooth by caries.
X-rays can also be used simply to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment, usually this concerns root canals, namely, their filling. To answer the question why take several x-rays, you can give an example with the process of adjusting the bite. The fact is that x-rays will help in this process at all stages, because with its help it will be possible to establish the cause and monitor the correction of the problem. Fused teeth are another problem that can be diagnosed and corrected using a series of x-rays; this must be done.
Sometimes radiography of this kind is used outside dentistry. We are talking about completely different problems associated with the jaw apparatus, for example, an abscess or some kind of injury. Children are sometimes prescribed dental x-rays even more often than adults, because baby teeth are much more vulnerable. The fact is that such research is not so harmful, since the radiation dose is very small, and a lead apron will help reduce the danger to a minimum. Let us also mention that the procedure can be carried out right at the first appointment, that is, at the consultation, and in some situations it may not be limited to one image; the doctor may need several x-rays.
The examination procedure is extremely necessary for a complete dental diagnosis.
Diagnostic frequency
Dental x-rays can be taken frequently. The body receives an insignificant dose of radiation, and even then in a strictly designated local zone, because the rest of the body is covered with an apron. The total dose per year is 5 mSV, determined by sanitary rules and regulations. No more than eighty film studies can be carried out per year, and digital photographs (harmless) can be taken up to five hundred per year. It is clear that patients do not exhaust this limit, so dental x-rays are considered one of the safest.
Dental X-rays are a safe procedure performed in dental clinics and offices. It has a high diagnostic value and helps the doctor make the correct diagnosis.