What is important to know about herpetic rash in a child’s mouth
Adults who are carriers of this disease can infect children. But there are cases when newborn babies are infected with the virus during intrauterine development, so their disease is considered to be congenital.
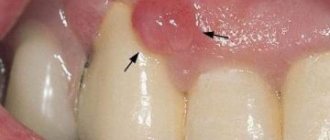
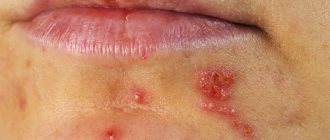
Infection with the herpes virus type 1 is typical for children. In medicine, this disease is called herpetic stomatitis. It manifests itself as inflammatory processes on the lips, surface of the tongue, gums, and the inside of the cheeks. In these areas, the child first develops characteristic pimples, which eventually burst and small ulcers form.
This whole process is accompanied by intense pain, causes discomfort while eating and talking, so children with this disease become capricious, nervous, and need special attention from adults.
Having discovered symptoms characteristic of herpes in the mouth in a child, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor in order to begin treatment on time and alleviate the condition of the little patient.
Herpetic stomatitis
Herpes in the oral cavity also has another name - herpetic stomatitis. The fact is that this virus produces symptoms similar to typical stomatitis. Given the similarity of manifestations, to ensure proper treatment it is necessary to differentiate these 2 diseases.
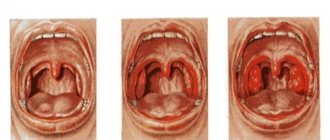
Diseases can be distinguished by the extent of the lesions. The herpes virus is characterized by ulcerations throughout almost the entire oral cavity, while with stomatitis only the inner surfaces of the cheeks and lips are affected. In addition, herpetic ulcers are formed from small blisters with liquid, which is not the case with stomatitis.
Why do children get oral herpes?
A child can become infected with the herpes virus due to the use of shared utensils when feeding. This also often happens during contact with a carrier of herpes, for example, when kissing sick people. The virus spreads through airborne droplets and is very difficult to protect yourself from.
The nature of herpes is such that children aged 1–2 years are at risk. At this age, antibodies received from the mother during the prenatal period cease to function in their bodies. It is during this period of a baby’s life that the herpetic virus can be transmitted to the child even through microtraumas on the mucous tissues of the mouth, and it also takes root well with the slightest weakening of the immune system.
The virus activates its activity when the following conditions are present in the child’s life:
- acute respiratory infections;
- stressful conditions;
- poor nutrition;
- menstruation in girls;
- avitaminosis;
- weak immunity;
- postoperative period;
- prolonged exposure of the body to high or low temperatures.
More often, herpes in children appears in the autumn or spring, when the air temperature fluctuates.
It is important to know! Children with herpes can infect other children. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent healthy and sick children from feeding with common utensils, using the same pacifier, and playing with objects that children can put in their mouths.
Reasons for appearance
Disease occurs in the mouth and throat for the following reasons:
- Hypothermia . The child may catch a cold while walking. This happens especially often in autumn and winter.
- Stress . Frequent stressful situations for a child negatively affect health and cause this disease.
- Colds . If your baby is already sick with the flu or acute respiratory viral infection, there is a high probability of herpes.
- Weakened immunity . With a lack of vitamins, physical and psycho-emotional overload, and colds, immunity decreases. This allows the virus to develop.
- Drinking cold drinks . It has a negative effect on the tissues of the throat mucosa, causing inflammation and the occurrence of herpes.
- Infection of a child with herpes by airborne droplets or contact. People around you can infect a child in everyday situations. For example: when a child kisses, the virus enters the body through saliva from the mother, which happens quite often. When the immune system weakens, the virus will make itself known.
What to do if an abscess appears on a child’s gum? Find out the answer right now.
Signs indicating the development of the disease in children
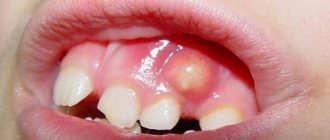
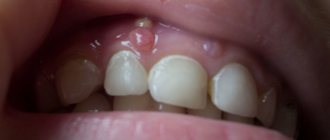
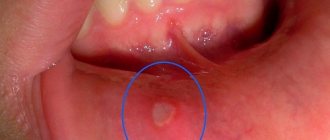
The most important symptoms of oral herpes in children is the appearance of small blisters containing cloudy liquid on the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity. They burst after a few days, resulting in the formation of areas covered with a yellow-gray film. It gradually peels off, and ulcers appear in its place. The mucous membranes of the child's mouth become bright red. After about two weeks, the wounds heal.
In addition to rashes, there are other symptoms indicating the development of the disease:
- child's moodiness and irritability;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- pain in the mouth;
- itching of the affected areas;
- increased salivation;
- bad breath;
- weakness;
- enlarged submandibular lymph nodes;
- bleeding gums;
- increase in body temperature to 39°.
These symptoms are very similar to the clinical picture of other diseases, therefore, having noticed them, you need to contact a specialist who will determine the correct diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of mild forms of herpetic gingivitis in children is carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a physician. In severe cases of the disease, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. The patient is prescribed a diet with a predominance of pureed food that does not irritate the oral mucosa. It shouldn't be hot. There is no need to give your child solid food to prevent additional injury to the gums.
For mild forms, local treatment is used.
The following drugs are used:
- antiviral agents (Acicovir, Ganciclovir) - destroy the DNA of the virus, use ointment to lubricate the gums up to five times a day for two weeks;
- local anesthetic gels and ointments (Lidochlor gel, Kamistad) - they anesthetize, disinfect, have an anti-inflammatory effect, are used three times a day, two weeks;
- local antiseptics (Iodinol, Miramistin, Hexoral) - these agents rinse the mouth every four hours, two weeks;
- reparative preparations (Solcoseryl-gel, Methyluracil ointment) - applying ointments to ulcers promotes their epithelization and rapid healing, applied three times a day for two weeks.
Herbal infusions (chamomile, rose hips, calendula, sage, St. John's wort, licorice) are widely used for rinsing when gums are damaged.
In severe cases, the baby is prescribed oral medications.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Zovirax) - taken according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, the drug must be taken to the end, otherwise there will be a relapse;
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil, Citrine) - reduce swelling of gum tissue and reduce pain;
- antipyretics (Panadol, Nurofen) are used to reduce high fever.
Parents should monitor the baby’s oral hygiene; during illness, it is carried out especially carefully. To prevent gum injury, it is recommended to use toothbrushes with soft bristles. It is necessary to treat toys and objects that the baby uses with antiseptics.
Herpes severity
The disease develops quickly, causing a lot of problems for both the baby and his parents. You need to react immediately, without triggering the disease, so that the process does not turn into an acute or, even worse, chronic form.
Herpes, localized in the mouth of children, comes in three degrees:
- Mild: often goes away almost unnoticeably. A few pimples appear in the mouth, but they heal quickly. In some cases, body temperature rises slightly.
- Moderate: profuse rashes form on the mucous membranes of the mouth. Clinical tests confirm changes in blood composition. If treatment is started immediately, the disease will pass quickly and will not leave any traces.
- Severe: characterized by numerous rashes on the mucous tissues of the mouth and lips. This form of the disease occurs suddenly.
If herpes has entered a moderate or severe phase of development, even with proper treatment, doctors do not rule out frequent relapses.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of herpes gingivitis is quite easy for a child to make, since the disease has characteristic clinical manifestations. The diagnosis is made by the dentist based on an examination of the baby’s oral cavity and data on the course of the disease. Characteristic formations on the mucous membrane and manifestations of inflammation in the mouth clearly indicate that this is a specific lesion. To clarify the nature of the lesion, the doctor prescribes general blood and urine tests. If the disease is severe, it is necessary to clearly identify the type of pathogen. In this case, specific laboratory research methods are used.
These include:
- virological study;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- HSV test for the determination of immunospot G-specific glycoprotein;
- serological test with immunoglobulin M.
These methods determine with a high degree of accuracy the type of pathogen in the blood and discharge from ulcers. But they are very expensive and labor-intensive, so they are used quite rarely.
Effective treatment of the disease using medications
Treatment of herpes in a child should be comprehensive. In addition to taking the necessary medications, the patient must remain in bed and also adhere to a special diet. It is necessary to exclude sour, salty, bitter foods from food. Eating hot or cold food is not allowed. In addition, the patient needs to drink a lot of water, with the help of which toxic substances will be removed from the body.
Herpes in children can be successfully treated with the following medications:
- Acyclovir.
- Penciclovir.
- Diolin.
- Zovirax.
An important point in the fight against this insidious virus is taking vitamins and microelements (vitamin C, fish oil, calcium-containing preparations), as well as products that help increase the child’s immunity.
Immunostimulating drugs for herpes:
- Decaris.
- Immunal.
- Taktivin.
- Histaglobin.
- Groprinosin.
- Imudon.
- Eleoterococcus tincture.
- Arpetol.
Antiseptic and painkillers are used in the form of sprays and solutions:
- Trimekain.
- Furacilin.
- Lidocaine.
- Chymotrypsin.
- Dimexide.
- Rotokan.
It is important to know! Not long ago, a medical vaccine against herpes appeared. The vaccination course consists of 5 doses of the drug with breaks between injections of 4 days. Such vaccination is necessary for the treatment of patients suffering from frequent relapses of the disease. But it is carried out only when the child does not have any problems with the functioning of the kidneys or liver, and he normally tolerates taking tetracycline antibiotics.
Symptoms of the disease
Specific bubbles appear in the child’s mouth, which quickly burst, and there is redness around them. It all bakes unbearably, burns, itches, hurts, and is accompanied by increased salivation.
The condition is usually of moderate severity, sometimes severe. The thermometer shows febrile numbers, a temperature of 39-40 degrees, which lasts up to a week. Characterized by pain, sweating, moodiness and nervousness. The child refuses to eat, which further aggravates the severity of his condition.
The use of folk remedies in the fight against herpetic virus
Mothers, when starting treatment for their children, very often look for an alternative to medications. If a child has herpes, doctors recommend complex therapy using both medications and traditional medicine. It is the latter that can significantly improve the patient’s condition and speed up recovery, but only as auxiliary drugs.
Decoctions from medicinal plants
Chamomile, wormwood, and lemon balm are used to prepare healing infusions and decoctions. They help stop inflammatory processes. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. medicinal herbs and pour a glass of boiling water. The product should sit for 20 minutes, then it should be strained. The child needs to rinse his mouth after meals 5-6 times a day.
The healing effect of propolis
This bee product relieves inflammation well, being a natural antibiotic. The mouth should be rinsed, and the affected areas should be lubricated with alcohol tincture of propolis, previously diluted in water in a ratio of 1:10. Such procedures are carried out 3–4 times a day.
Ointment made from honey, garlic and ash
This ointment is easy to prepare at home. You need to take 1 tsp. honey, 1 tbsp. l. ash (you can get it by burning regular paper), 2-3 cloves of garlic, passed through a garlic press. All ingredients must be mixed. The resulting ointment is applied to the affected areas. Even if a child swallows part of such a product, it will not cause harm, since it consists of natural products and ash.
Characteristic signs of infection
Symptoms of oral inflammation include:
- discomfort on the tongue, cheeks and gums,
- change in color of the mucous membrane,
- swelling appears in painful areas,
- a rash appears
- bubbles appear at the final stage of the disease.
Obvious signs are tingling and burning sensations. At first they are rare, but each time they become stronger and more frequent. The pain predominates when eating and talking, especially when the infection occurs on the gum.
During infection, the color of the mucous membrane is distinguished between light pink and dark brown, which depends on the stage of the disease. Bubbles from a millimeter to one centimeter may also form on the affected area. If it ruptures, extensive inflammation develops and there is a high probability of developing stomatitis. You should not delay treatment so that the infection does not spread to the entire oral cavity and cause diseases such as pharyngitis or sore throat.
People most susceptible to oral herpes are those who:
- smoke,
- have had viral or bacterial infections,
- have caries,
- do not perform good oral hygiene,
- suffered a nervous breakdown,
- in case of hypothermia or overheating,
- suffered poisoning
- had contact with the patient,
- have weakened immunity,
- malnourished
- with excessive physical exertion.
Prevention of disease in children
Protecting children from the herpes virus is difficult, but still possible. By taking the following measures you can reduce the likelihood of your child becoming infected to a minimum:
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the cleanliness of toys.
- It is necessary to strengthen children's immunity.
- Pacifiers and nipples should be boiled.
- It is necessary to provide adequate nutrition.
- Limit your child’s contact with people who have herpes.
- In windy weather, you need to apply a special hygienic lipstick to your baby’s lips.
Herpes in a child’s mouth is a serious problem that causes severe pain and discomfort to the baby. If parents, after detecting the first signs of this disease, immediately contact a specialist for advice, he will correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary therapy. This means that it will be possible not only to quickly eliminate the alarming signs of herpes, but also to protect the baby from re-infection with the virus in the future.
5 / 5 ( 3 voices)
Treatment of HSV on the oral mucosa
Complete destruction of the virus after initial infection, even with a full course of therapy, is not possible. Once a herpes virus infection has entered the human body, it remains there forever.
A person becomes a carrier of the infection for life. Relapses of the disease occur against the background of decreased immunity in the human carrier and require adequate treatment.
The doctor decides how to treat herpes in the mouth. Medicines with the active substance known as acyclovir can stop the development of the disease and suppress the active reproduction of the virus in the body:
- 100 mg – children under 2 years of age;
- 200 mg – adults, as well as children over 2 years old.
Important!
The medicine is taken 4-5 times a day exclusively under the supervision of a doctor and in tablet form.
Treatment of herpes in the mouth of a child is carried out using the drug Valtrex with the active ingredient valacyclovir.
Prescription of medications (based on acyclovir or valacyclovir) by the attending physician is carried out only for moderate and severe disease.
Medicines in the form of ointments are used to treat herpes in the corners of the mouth. Using ointment for herpes in the mouth is not advisable.
Rinsing with dental rinses helps prevent infection and the development of complications in a sick child.
Doctors often recommend using Miramistin for herpes in the mouth, chlorhexidine, decoctions of oak bark and chamomile. Hexoral has a good antiseptic effect.
Important!
Antiseptics do not affect the progression of a viral infection.
Symptomatic therapy
herpes on the roof of the mouth photo
Oral herpes in children is accompanied by severe pain. Medicines with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects can help reduce unpleasant symptoms:
- Solcoseryl dental adhesive paste;
- Kalgel;
- Tantum-Verde spray, as well as analogues of the drug;
- Kamistad-gel;
- antipyretic medications for fevers elevated to febrile (paracetamol or ibuprofen);
- herbal decoctions with anti-inflammatory effects.
Important!
It is not recommended to use Analgin or Aspirin to reduce fever due to herpes in the mouth during pregnancy. These drugs are also not prescribed to children and adults due to the high risk of serious adverse reactions.
Before treating herpes with medications, it is necessary to provide the child with bed rest. It is important to adhere to the diet recommended by your doctor, since hot, sour or spicy foods can harm the patient, increasing pain.
In addition to a gentle diet, treatment also includes drinking plenty of warm drinks, taking ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
Preventive actions
It is impossible to prevent primary infection. Most children by the age of 3 are already carriers of the herpes virus. Prevention of the disease is aimed at preventing relapses that occur when immunity decreases.
In order to prevent repeated episodes of rash in the child’s mouth, it is necessary:
- promptly treat somatic diseases;
- avoid injuries to the oral cavity and infection;
- engage in physical education and hardening;
- eat natural foods;
- spend more time outdoors.
Compliance with the basic rules of personal hygiene and sanitation is essential in preventing relapses.
Complications and relapses
20-30 days after infection with the herpes simplex virus, the child’s body produces antibodies (immunity), which protect against complications and relapses in the future. In the absence of characteristic symptoms, the pathogen is in an inactive form. Re-activation of the virus is possible due to mental/physical overload, stress, hypothermia or weakened immunity. Bubbles can form on the throat, tongue, oral mucosa and lips.
The child’s strong immunity is not able to eliminate the virus, but it suppresses it in the tissues. In a latent state, herpes lies dormant in certain parts of the human body. Periodically, the pathogenic virus awakens and multiplies again.
To prevent the formation of ulcers, you should regularly strengthen your immune system and follow the following recommendations (if one of your relatives has herpetic stomatitis in the mouth):
- Avoid kissing until complete recovery.
- Avoid the possibility of the child touching the wounds.
- When ulcers are healing, it is contraindicated to tear off the scabs. Otherwise, this leads to re-infection.
- To apply antiviral ointments, it is better to use disposable cotton swabs.
- Use personal hygiene items and cutlery.
- After treating inflammation, wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
In children with a weakened immune system, relapses are severe, with blisters spreading throughout the skin and internal organs.
You should not self-medicate. If symptoms of herpes appear, you should immediately take your baby to the doctor.