Causes of candidiasis in pregnant women
Candidiasis during pregnancy is becoming more common, despite the development of diagnostic and therapeutic trends in medicine. The main reasons are the adverse effects of external factors in combination with reduced immunity.
While expecting a child, a woman's body undergoes a restructuring. The intestinal microflora changes, and a deficiency of vitamins and minerals appears.
Dysbacteriosis leads to increased proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, including Candida fungi. From the intestines they can spread to the vaginal mucosa.
Hormonal levels change. This factor acts in several directions at once.
Firstly, increased levels of progesterone inhibit the activity of the immune system, so adverse external influences such as hypothermia, overwork, and unbalanced nutrition can easily lead to the development of candidiasis.
Secondly, the action of hormones changes the vaginal mucosa, making it more susceptible to infections.
Thirdly, changes in hormonal levels lead to emotional disturbances, reduce resistance to stress, which provokes a decrease in the body’s protective functions and the development of thrush.
In addition to these specific features, candidiasis in pregnant women can develop for reasons common to all women:
- chronic infectious diseases, including genital diseases;
- the presence of thyroid pathology, diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- chronic diseases of the intestines (colpitis, dysbacteriosis), liver or kidneys;
- taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs;
- unbalanced diet with a predominance of sweet foods.
Candidiasis is a sign of trouble in the female body, a decrease in general immunity. Therefore, treatment of the disease should be aimed not only at destroying the fungus, but also at strengthening the immune system.
Thrush during pregnancy: how to treat? Effective treatment of thrush in pregnant women
The harmless word “thrush” is the popular name for candidiasis.
The disease occurs not only on the genitals, but also on other mucous membranes, for example, in the mouth, intestines, and even on the skin and nails. Thrush often appears during pregnancy.
How can expectant mothers treat this disease so as not to harm the fetus? And in general, does it need to be treated? What's dangerous about it? To correctly answer the questions posed, let’s take a closer look at thrush.
What is candidiasis
The disease received its medical name from the Candida fungi (Candida albicans), representatives of the group of opportunistic pathogens. “Conditionally” means that they begin their harmful activities only under certain circumstances, for example, a decrease in immunity.
This is not as good as it seems, because the disease can occur at any time, as a response to taking antibiotics, severe stress, even poor nutrition. In every second case, thrush is registered during pregnancy. How to treat her in this case and why is she so “indifferent” to pregnant women? The answer is simple.
Pregnancy is a condition in which a number of changes occur in a woman’s body that are favorable for the growth and development of candida. But where do they come from if they weren’t even there before pregnancy?
Routes of infection
Candida fungi live harmlessly in each of us, entering our body in the womb or during childbirth. In the future, we can pick them up with food (milk, raw meat, unwashed vegetables and fruits) and with household items.
The habitats of candida are the oral cavity, vagina, and colon. As long as these microorganisms are present in controlled quantities, they help the normal functioning of the body. The disease begins when abnormal growth of fungal colonies occurs.
This is one reason. The second is unprotected sexual intercourse with a patient with candidiasis. If the second reason is absolutely excluded, but thrush still suddenly appears during pregnancy, the woman should not panic and look for the culprits.
In most pregnant women, fungal colonies begin to grow rapidly on their own under the influence of certain factors.
Thrush: causes, treatment of the disease in pregnant women
Many expectant mothers did not suffer from thrush before pregnancy. The appearance of the disease was facilitated by:
– changes in hormones and, as a result, changes in the acidity of vaginal secretions;
– decreased immunity due to increased stress on the body;
- psychological condition;
– performing heavy physical activity during this period;
– change in diet (pickles, marinades, sweets);
– unreasonably frequent hygiene procedures, during which the necessary microorganisms are washed off from the mucous membranes;
– some diseases (hemorrhoids, dysbacteriosis, constipation, colitis);
– use of antibiotics.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of thrush are mild and, as a rule, go unnoticed. These include minor itching of the external genitalia and an increase in the amount of discharge.
Nowadays, almost all women use sanitary pads, which make it difficult to control the amount of vaginal discharge.
Therefore, candidiasis can be detected at the initial stage of the disease only by doing a smear bacterioscopy.
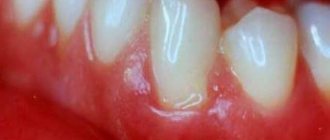
If the first symptoms of thrush are somewhat blurred, then it is difficult not to pay attention to the further development of the disease. Women experience persistent itching of the external genitalia due to the penetration of candida mycelium into the mucosa. This itching usually intensifies when wearing synthetic underwear, after washing and urinating, and during sleep.
Subsequently, the walls of the vagina become inflamed, react painfully to any touch, urination occurs with a sharp burning sensation, pain, and vaginal discharge becomes significant. Their color is white, with an unpleasant odor. In appearance, they resemble thick kefir or curds. Hence the name – “thrush”.
If left untreated, pain in the lower abdomen may appear.
Danger for women
Many people have no idea what the dangers of thrush during pregnancy are. Your doctor will tell you how to treat the disease. The expectant mother must strictly follow all instructions.
Failure to take the problem seriously leads to the following complications:
1. Threat of miscarriage. Continuous itching causes irritation, insomnia, headaches, increased blood pressure and increased tone of the uterus.
2. Complicated childbirth. The inflamed walls of the genital organs have little elasticity, which is why numerous ruptures occur during childbirth, and the sutures are poorly tightened.
3. Based on candidiasis, other, more dangerous diseases may arise.
4. In those who gave birth to their first child by cesarean section during a second pregnancy, the suture may diverge due to thinning of the scar on the uterus.
Danger to the fetus
Thrush during pregnancy also poses a serious threat to the baby. How to treat a mother so as not to make things worse for the unborn baby? Some women fear that treatment will do more harm than good. It is not right. Thrush can cause:
1. Delayed development of the fetus and pathological diseases of its internal organs.
2. Infection of the fetus with more dangerous microorganisms that appeared in the mother against the background of candidiasis.
3. Candidal sepsis, often leading to the death of the fetus and the already born baby. An autopsy shows that in such children many internal organs, including the brain, are covered with a mycelium web.
Treatment
We told you what causes a disease such as thrush. Treatment of this insidious disease should be carried out only with drugs prescribed by a doctor. To determine which of the dozens of existing drugs will be most effective, special studies are conducted.
Biomaterial taken from a woman’s smear is placed in an environment that promotes the growth of fungal colonies. In the future, they are influenced by various means, selecting the most effective, and from them the safest for the fetus.
At the initial stages of the disease in the first trimester of pregnancy, Nystatin, Zalain, and Natamycin are recommended, used exclusively topically, in the form of suppositories and ointments. In advanced cases, doctors prescribe tablets, as well as Clotrimazole.
The price for this Russian-made medicine ranges from 40-50 rubles for an ointment, 60-100 rubles for a cream and 70-120 rubles for a solution. There is also an imported drug that differs from the domestic one only in price.
Safe drugs to treat thrush
Like any medicine, antifungal agents have contraindications. Some drugs have more of them, others have less.
For example, Nystatin is practically non-toxic and is poorly absorbed into the blood, which is why it is prescribed even to newborns. It is contraindicated only for people with increased hypersensitivity to the components.
The same can be said about “Zalain”. This drug is expensive, but with its help, the symptoms of thrush go away in just one or two applications.
“Nitamycin” or “Pimafucin” are among the most harmless, so there is no need to be afraid to use them. Their disadvantages include longer treatment periods and low effectiveness in advanced cases.
Clotrimazole has excellent results. The price allows it to be used by any category of pregnant women. However, this drug has a number of side effects, such as irritation of the mucous membranes, pain in the lower abdomen, and rashes on the body.
It is advisable to use it only at the final stage of pregnancy.
Folk remedies
If you are diagnosed with thrush, home treatment using only folk remedies will only bring harm. It is impossible to get rid of the fungus without the use of medications. Traditional medicine suggests making baths and douching with decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, calendula, nettle, garlic, solutions of baking soda and iodine.
These remedies only temporarily reduce discomfort without affecting the further development of fungi. This apparent well-being helps the growth of candida colonies and the exacerbation of the disease. In addition, frequent douching during pregnancy can result in miscarriage.
Treatment with folk remedies is advisable only in combination with the use of medications prescribed by a doctor.
It is important to remember that not only the expectant mother, but also the future father should be treated. Otherwise, the disease returns again after a short period of time. After completing the course of therapy, both spouses are required to pass control tests.
How to avoid candidiasis during pregnancy
Everyone will agree: it is better not to need to use any remedy at all, even the most effective and harmless one for thrush.
To do this, the first and most important thing that needs to be done before conception is for both spouses to take tests to detect any sexually transmitted infection in the body. This especially applies to those who have already encountered similar diseases.
In addition, there are a number of simple but effective recommendations for pregnant women:
1. To support your immune system, eat more fruits and vegetables.
2. Monitor your stool, avoiding constipation or dysbacteriosis.
3. During the day, be sure to find time to rest, avoid lack of sleep and stress.
4. Perform hygiene procedures without fanaticism, using only natural products.
5. Avoid wearing synthetic underwear and pads in hot weather.
6. During periods of a surge in colds, avoid visiting crowded places.
How not to treat candidiasis
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, thrush during pregnancy is not so bad. Reviews from patients who have successfully dealt with the problem are excellent confirmation of this. They all gave birth to healthy children. However, there are still women who trust the advice of their friends and ancient recipes more.
There is also a category of very shy women who cannot overcome themselves and consult a doctor if genital itching occurs. Such people prefer to be treated at home on their own.
I would like to remind you that “grandmother’s” remedies relieve symptoms only temporarily, thereby driving the problem inside, complicating its further treatment and jeopardizing the birth of a healthy baby.
Buying medications without a prescription is also wrong, because only a doctor can determine which medicine is suitable in each specific case.
And it is completely unreasonable to leave candidiasis unattended, planning to get rid of it only after childbirth, so as not to harm the fetus with unnecessary medications. Such “care” for the baby can lead to his death.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/174452/molochnitsa-vo-vremya-beremennosti-kak-lechit-effektivnoe-lechenie-molochnitsyi-u-beremennyih
Symptoms and diagnosis of candidiasis
Vaginal candidiasis during pregnancy does not have symptoms that are different from those at any other time in a woman’s life. As a rule, patients complain of itching, white cheesy (flaky) discharge with a sour, unpleasant odor.
Itching and pain intensify during sexual intercourse and disappear for a while after hygiene procedures. On examination, irritation and redness of the external genitalia are noted.
But all these symptoms can indicate not only candidiasis, but also a number of other diseases (including STDs).
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor writes out directions for diagnostic examinations:
- Microflora smear. During the procedure, a tampon is inserted into the vagina and the contents (mucus, discharge) are collected on it. The material is then dried on a viewing glass and examined under a microscope. The laboratory technician counts the number of bacteria, fungi and leukocytes. With vaginal candidiasis, the smear reveals fungi, a large number of leukocytes, characteristic of inflammatory reactions, and a predominance of pathogenic bacteria over beneficial ones. Read more: what a gynecological smear shows→
- Bacterial culture. It is not always carried out; it allows us to identify exactly which bacteria and fungi inhabit the vagina, as well as determine effective drugs for treatment.
Since it usually takes several days to obtain diagnostic data, the doctor prescribes therapy after the first examination and then, if necessary, supplements and adjusts it.
Symptoms
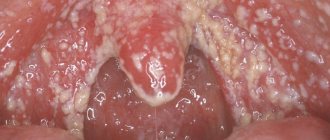
The most obvious sign of thrush in a pregnant woman is the formation of a whitish, cheesy coating on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It can form on the roof of the mouth, gums, tongue, inside of the cheeks, or everywhere at once. When plaque is scraped off the affected area, bright red spots with a shiny surface become noticeable.
In addition to cheesy formations, oral thrush has other symptoms, such as:
- itching and burning in the mouth,
- feeling of unpleasant taste
- constant bad breath,
- pain while eating,
- change in taste perception.
In pregnant women, due to weakened immunity, colonies of the fungus quickly spread to other areas: the nasopharynx, intestines, and genitals. At the same time, the clinical picture of the disease will change.
Diagnosis of oral candidiasis in a pregnant woman
To make a more accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of the disease, the doctor will need to carry out a number of diagnostic procedures:
- external examination of the mouth and throat,
- examination of other mucous membranes and skin,
- scraping plaque from the affected area,
- blood and urine tests.
If necessary, other studies may be prescribed.
Treatment of candidiasis during pregnancy
Candidiasis is a fungal disease associated with decreased activity of the immune system. Therefore, its treatment includes the use of antifungal and immunostimulating agents.
Antifungal drugs, in turn, are divided into systemic (tablets, capsules for oral administration) and local (creams, suppositories, etc.).
Treatment of candidiasis during pregnancy should be comprehensive. Tablets and capsules destroy the fungus in the intestines, where its main focus is located, and local preparations act on the surface of the vaginal mucosa, quickly eliminating unpleasant symptoms.
Most often, the following are prescribed for the treatment of thrush in pregnant women:
- Systemic antifungal drugs: Nystatin, Pimafucin. They are allowed both during pregnancy and during breastfeeding, they are effective and non-toxic. More popular antifungal agents, for example, Diflucan and Fluconazole, are contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Local preparations: “Epigen Intim” (spray), “Pimafucin” (cream, suppositories), “Nystatin” (suppositories). The spray is used in combination with Nystatin or Pimafucin, quickly relieves inflammation and restores normal vaginal microflora. The selection of drugs in each specific case should be done by a gynecologist, since there are drugs that are contraindicated in the first trimester, but acceptable in the later stages.
- Local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic drugs. During pregnancy, the use of a solution of borax in glycerin (sodium tetraborate in glycerin) and brilliant green (brilliant green) is allowed. These products are applied to a gauze swab and mechanically clean the vaginal walls of fungus. This prevents its growth and relieves inflammation. In addition, the drugs are approved for use in the first three months of pregnancy, when other drugs are contraindicated.
- Immunomodulatory and restorative drugs. Excessive proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the intestines and vagina begins with a decrease in immunity, or in the presence of a chronic disease. To treat thrush during pregnancy, it is possible to prescribe multivitamins, Viferon suppositories, as well as probiotics with bifidobacteria (Bifidin, Bifidumbacterin).
When deciding how to treat candidiasis during pregnancy, you should first consult with a gynecologist.
All groups of drugs must be prescribed by a specialist, as they have their own contraindications. It is necessary to take into account the woman’s general health, tendency to allergies and other factors.
It is important to undergo therapy together with your sexual partner. Otherwise, the infection will manifest itself again. Men can use any antimycotic drug: Fluconazole, Nystatin, Diflucan, Nizoral, etc.
Folk remedies
In combination with medications, candidiasis during pregnancy can be treated with traditional methods:
- Baths with iodine and soda. For the first procedure, you need to dissolve 1 tsp in a liter of boiled warm water. soda and sit in the basin for about half an hour. For the second and subsequent procedures, add 1 tsp to the soda solution. Yoda. Do baths once a day until complete recovery.
- Douching with salt, soda and iodine. In one liter of boiling water you need to stir 2 tbsp. l. salt, boil the solution, cool until warm. Then, add 1 tbsp. l. soda and 0.5 tsp. Yoda. The douching procedure is carried out twice a day for 5 days.
- Irrigation with herbal infusion. To prepare the infusion, you need to mix 3 tbsp. l. chamomile, yarrow, calendula and sage. 2 tbsp. l. pour the resulting mixture with a liter of boiling water, leave for several hours, strain. Irrigation is carried out using a syringe bulb. The procedure is repeated twice a day for two weeks.
You cannot rely only on folk remedies; they are all local and do not completely eliminate the infection.
Treatment nuances
During the treatment of thrush during pregnancy, most antifungal drugs are contraindicated. They can lead to various developmental disorders of the fetus, including heart defects and pathologies of skull formation.
The drug Betadine, which is often used outside of pregnancy, should not be used; it affects the development and functioning of the thyroid gland of the unborn child.
Sometimes, having heard that taking probiotics is recommended for candidiasis, women begin to use drugs with lactobacilli, which create a favorable environment for the development of a fungal infection. It is important to remember that for thrush it is bifidobacteria that are needed.
With properly organized treatment, improvements become noticeable already on the second or third day. In some cases, by this time the symptoms have completely disappeared, creating the appearance of recovery.
In fact, a significant amount of fungus is still present in the body, and the positive effect is due to local elimination of the causative agent.
It is necessary to continue the course of treatment until the end, regardless of how you feel. This will help avoid relapses and the transition of candidiasis to a chronic form.
Safe treatments
During pregnancy, ideal conditions are created for the occurrence or recurrence of thrush. A woman’s body works to preserve the fetus, but often against herself. The following factors contribute to the activation of the fungus.
- Estrogen. Along with progesterone, during pregnancy there is an increase in the concentration of estrogen. This leads to increased accumulation of glycogen in the vaginal epithelium. Glucose should serve as a nutrient medium for lactobacilli, which play a protective role. But the fungus also feeds by processing glycogen.
- Immunity. A natural decrease in the body’s defenses is necessary for bearing a child, which is 50% genetically foreign to the mother’s body. But suppression of the immune system leads to the activation of a latent infection.
- Vaginal environment. Increased blood flow to the genitals leads to an increase in temperature. Pregnant women may also experience an increase in vaginal discharge. Warm and humid environments are ideal for fungal development.
In non-pregnant women of reproductive age, the symptoms of thrush are pronounced and cause anxiety and discomfort. In pregnant women, the disease usually progresses mildly, but with frequent relapses.
Depending on the reactivity of the body, thrush can occur in several clinical forms.
- Carriage. Before pregnancy, this condition is considered as a normal variant, but only in the absence of symptoms and detection of no more than 104 CFU/ml of fungi in the smear. In this case, the main flora should be represented by lactobacilli, there are no signs of inflammation. But such an analysis in the early stages of gestation should be a reason for increased attention.
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis. The disease is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture. The smear reveals more than 104 CFU/ml of candida, lactobacilli is normal (more than 106 CFU/ml), no other flora is detected.
- Thrush and bacterial vaginitis. The disease is caused by a combined infection - a fungus and opportunistic flora. This form is most often observed during pregnancy: decreased immunity contributes to the proliferation of not only the fungus, but also facultative flora.
Sometimes thrush is combined with bacterial vaginosis. Microorganisms create a special film on the surface of the vaginal mucosa that protects them from the action of antibacterial agents.
According to the nature of the course, three forms of thrush are distinguished.
- Spicy. The disease occurs once, the duration of the disease does not exceed two months.
- Chronic relapsing. There are more than four cases of exacerbation of thrush per year, despite treatment.
- Persistent. The woman is bothered by constant symptoms of thrush; periods of improvement are observed only with the use of antifungal drugs.
Symptoms
The main symptom of thrush is discharge. They can be curdled, milky or creamy. The amount varies from moderate to heavy. Leucorrhoea usually has a sour odor.
Itching and burning in pregnant women may be absent or minor. Sometimes women don't give them any importance. Symptoms may worsen after sexual intercourse or hygiene procedures. Severe vaginal lesions are accompanied by dyspareunia. Sometimes the urethra is involved in the process, causing pain when urinating.
Thrush is dangerous during pregnancy due to possible complications for the child and additional changes in the immune system. Fungi can be present in different forms - in the form of individual cells, filamentous forms. In response, B lymphocytes are produced that cannot produce specific immunoglobulins. Therefore, gradual sensitization occurs - an increase in sensitivity with the development of an allergic reaction.
Pregnancy may be complicated by the following conditions:
- termination of pregnancy (in the 1st trimester);
- intrauterine infection;
- malnutrition and low fetal weight;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- premature birth (in later stages);
- early rupture of amniotic fluid;
- complications during childbirth (bleeding, trauma to the birth canal);
- infection of the child during childbirth.
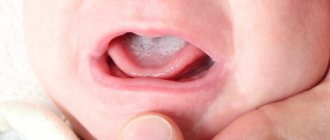
Women who are not treated for thrush during pregnancy are more likely to develop postpartum endometritis. Newborns infected by their mother may develop oral candidiasis. Girls have vulvovaginitis, and boys have balanoposthitis. The increase in the number of sick children has led to the fact that, according to German standards of therapy, all pregnant women with diagnosed candidiasis must undergo a course of antifungal treatment.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Oxygen face mask - it will enrich your skin with pure oxygen
A pregnant woman's body is susceptible to infections. Candidiasis, which is known as thrush, develops especially often. According to statistics, more than 70% of women suffer from fungal infection during pregnancy.
This is due to the fact that when carrying a baby, hormonal changes occur in the body, and the protective forces are reduced. In addition, a woman experiences stress at this time and changes her diet. This causes changes in microflora and proliferation of fungi.
As soon as a woman feels itching and notices a cheesy discharge, she needs to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will answer: is thrush dangerous during pregnancy? He will tell you how to properly treat candidiasis and what measures to take to prevent exacerbations.
The main task of the gynecologist in this case is to explain to the woman that she should not panic and worry about the baby’s health. After all, there is minimal risk for him and for the mother, especially if the treatment is carried out on time and according to the rules.
Any inflammatory processes affect the woman’s condition. Mild forms of the disease can go almost unnoticed, but in many cases they complicate the course of pregnancy. Since candidiasis is a frequent companion of women at this time, gynecologists are constantly asked the question: “Does thrush affect pregnancy?” What doctors can tell you about this:
- advanced candidiasis can cause premature birth or threatened miscarriage;
- it can cause inflammation of the placenta or postpartum infections of the birth canal;
- The amniotic fluid may break earlier, which will negatively affect the baby.
How dangerous is thrush during pregnancy for the mother? Although candidiasis does not cause serious complications, inflammatory diseases of the uterus may develop during the postpartum period. Damage to the genital organs and disruption of the vaginal microflora leads to the appearance of ruptures during childbirth, and then adhesions form.
In addition, candidiasis is a potential cause for the occurrence of other infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract. And severe itching from thrush during pregnancy leads to insomnia and irritability in women.
- When planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to check for infections and fungi. After all, thrush is most dangerous in the first trimester of pregnancy. Therefore, it is advisable to treat it before conception.
- The danger for the baby is that in the first three weeks of pregnancy the fetus is not yet protected. Therefore, the fungus can penetrate the uterus and affect its intrauterine development.
- You need to know that if thrush was present long before the woman decided to conceive, a recurrence may occur during pregnancy.
- In the early stages, the fungus easily penetrates the uterus, especially if it has multiplied greatly. This leads to damage to the umbilical cord, skin and mucous membranes of the baby. Often such infection is fraught with miscarriage and other complications.
After a couple of months, the placental barrier is completely formed. How does thrush affect the fetus at this time? It is believed that the fungus is no longer dangerous for him. The fetus is reliably protected by the mucous plug in the cervix and the placenta. He cannot become infected with the fungus, but thrush during pregnancy still causes him harm. Why is it dangerous for the fetus?
- at birth the baby will have a small weight;
- the fetus develops hypoxia, which leads to deviations in the development and formation of organs;
- in very rare cases, a child may also develop an infection - the fungus penetrates the umbilical cord and affects not only his skin, but also his internal organs.
This is the most dangerous time of the disease. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, it is necessary to stop infection of the fetus by sanitizing the vagina. For example, using suppositories with Chlorhexidine.
Statistics show that if a woman is sick with candidiasis, then no matter what type of birth she has, the fetus becomes infected in 80% of cases.
This happens because two weeks before birth the mucus plug comes out and the cervix opens slightly. Fungi can get inside and infect the child. How do they affect the fetus? Most often, he develops candidal stomatitis or a fungal infection of the skin. But in premature and weakened newborns, the disease can lead to death. This is the main danger for a child from thrush during pregnancy.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Treatment of thrush with folk remedies: kefir, herbs, soap
Most often this happens during childbirth. Infection can affect the normal growth and development of the baby. To prevent this, a woman should know how dangerous thrush during pregnancy can be for the health of the child. In newborns, the fungus affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, genital tract and even the eyes.
Most antifungal drugs are prohibited for women who are expecting a child. Therefore, treatment of the disease at this time is very difficult and must be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor.
For pregnant women, it is best to use topical medications. In some cases, it is also possible to use traditional methods of treatment.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor takes into account the duration of pregnancy, the condition of the mother and fetus, and possible contraindications. And only after that he chooses an acceptable treatment. The most commonly prescribed drugs are those that will not harm the fetus:
- in the early stages, Pimafucin suppositories or the low-toxic drug Natamycin are prescribed;
- after 20 weeks you can already use stronger agents - “Butoconazole” or “Isoconazole”;
- from the second trimester, use “Clotrimazole” in cream or vaginal tablets;
- Terzhinan suppositories are effective and safe for the fetus;
- you can use a soda solution or chamomile decoction for baths and washes;
- before childbirth, if other treatment does not help, use Hexicon suppositories containing Chlorhexidine;
- in the most extreme cases, under the supervision of a doctor, you can take systemic drugs, for example, Fluconazole.
Prevention measures
Treating thrush during pregnancy is not an easy task, so you need to try to prevent the fungus from spreading.
To prevent candidiasis, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Wear clothes, and especially underwear, made from natural fabrics that allow air to pass through and prevent the creation of a damp and warm environment.
- Choose the right intimate hygiene products. They should not be aggressive and disturb the natural acidic environment of the vagina (the best option is with a neutral pH level).
- Avoid constipation and dysbiosis by consuming enough fresh fruits, vegetables, and, if necessary, preparations with bifidobacteria. If you find problems with the intestines, consult a doctor immediately.
- If you are prone to fungal infections, regularly carry out tests to determine the pH and, in case of deviations, contact a specialist.
- Maintain immunity: eat a balanced diet, take multivitamins, regularly walk in the fresh air, engage in physical activity (gymnastics, swimming, walking), if there are no contraindications.
Treatment
What can you do
Under no circumstances should an expectant mother self-medicate. Perhaps grandma's recipes will relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, but they will not eliminate the real cause of oral candidiasis. In addition, many traditional medicines are dangerous for the health of mother and baby, since they can only aggravate the condition of the pregnant woman.
During pregnancy, self-medication should be discontinued. Only a specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
For a speedy recovery, the expectant mother needs to follow a number of rules:
- comply with all medical instructions,
- monitor oral hygiene,
- brush your teeth or rinse your mouth with special products after each meal,
- carry out dental sanitation,
- strengthen your immunity.
What does a doctor do
A doctor can determine the presence of thrush in a pregnant woman by appearance. However, it is more important to identify and eliminate the cause of its development.
The treatment regimen for oral candidiasis is developed individually, taking into account the characteristics of women's health, the form and course of the disease, and the duration of pregnancy.
Treatment proceeds in two directions - getting rid of the manifestations of thrush and treating the underlying disease. Medical intervention must be prompt to avoid the spread of the disease and infection of the fetus.
During pregnancy, oral medications are contraindicated. The most commonly prescribed topical medications are:
- antifungal gels,
- ointments,
- creams,
- special disinfectants for rinsing,
- medicinal lollipops.
During pregnancy, with a mild form of candidiasis, a change in diet may be prescribed, in which it is important to include natural yoghurts and acid-containing liquids. These products help restore the natural balance of bacteria, which leads to the suppression of candida pathogenicity.
In more severe cases, antibiotics or antifungal drugs in tablet form may be prescribed in the second half of pregnancy.
The prescription of intravenous infections occurs extremely rarely, only in cases where there is a risk to a woman’s life.
Consequences of candidiasis for mother and child
Thrush is a disease that, in the absence of timely treatment, leads to unpleasant consequences for the expectant mother and baby.
Some women, especially those with a chronic form of the disease, have a question: is it possible to get pregnant with candidiasis? Of course, this is physically possible. But by treating the disease in advance, a woman will avoid many complications.
A fungal infection makes the vagina less elastic, which causes cracks and external and internal tears to form during childbirth.
For this reason, at the end of pregnancy, the gynecologist conducts a thorough examination of the woman in the chair and, having detected signs of microflora disturbance, prescribes treatment.
Thrush complicates the healing process of sutures after childbirth: suppuration and inflammation often occur, requiring antibiotics.
The consequences for the child are more serious. The fungus penetrates the internal organs of the newborn, affecting the eyes, nose, mouth, skin and mucous membranes of the respiratory system. This leads to health problems and, in rare cases, death.
Due to the characteristics of the female body, thrush is a common problem during pregnancy. Natural changes in hormonal levels and decreased immunity in the expectant mother lead to the development of infection.
Treatment is complicated by the fact that many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, so from the first trimester it is worth paying special attention to preventive measures.
Author: Olga Khanova, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Causes
Pregnancy itself can act as a factor in the development of oral candidiasis. This is caused by a number of physiological changes in the female body:
- hormonal imbalance,
- disorders in the gastrointestinal tract,
- decrease in body replacement functions,
- increased emotionality,
- general weakening of the immune system.
Other factors can provoke the development of the disease:
- other infectious diseases,
- oncological diseases,
- diseases of the endocrine system,
- autoimmune diseases,
- low acidity,
- allergy,
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics, antifungal drugs and other drugs,
- smoking.
The fungus begins to multiply when the environment changes. The most favorable conditions are high temperature and humidity.
Thrush in the mouth in adults: symptoms and treatment
Have you been trying to cure FUNGUS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure fungus by taking the product for 147 rubles .
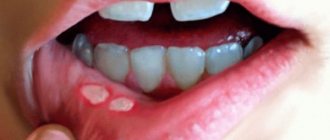
The well-known fungal infectious disease, called thrush, can affect the oral cavity. With this disease, fungal colonies affect the mucous membranes of the mouth, the border of the lips, and the corners around the mouth. As fungi multiply, a cheesy whitish coating appears on the tongue, cheeks, and gums. Oral candidiasis usually appears due to a violation of the microflora in the mouth.
Features of the disease
Our readers successfully use Tinedol to treat nail fungus. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Thrush in the mouth appears if the natural balance of microflora is disturbed due to exposure to aggressive external factors or under the influence of changes in the internal environment of a living organism. Fungal microorganisms live in hard-to-reach places in the oral cavity, namely in cracks in the epithelium, in deep folds, dental cavities or root canals.
How to cure thrush in a woman?
Candida loves warm, moist places with minimal air access, so the fungus is more than comfortable on the vaginal mucosa. To get rid of an unpleasant neighborhood, you need to use the following drugs:
- local action: vaginal suppositories, tablets, creams with econazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole (Clotrimazole, Pimafucort);
- systemic action: tablets, capsules with fluconazole, itraconazole (Nystatin, Fluconazole, Difluzol, Diflucan);
- drugs to strengthen the immune system, probiotics, symbiotics (Wobenzym, Lactovit, Dactiale, Derma-Pro, Vagilak, Viferon).
Figure 3 - Untreated disease spreads quickly
On average, the course of treatment takes from 3 to 6 days. Fungal spores mature within 20 days, so a second course of treatment may be necessary. Some medications (such as Betadine) can be used during menstruation.
In 20% of cases, the treatment prescribed by the doctor does not help. If thrush continues to bother you after a week:
- This is not candidiasis. You will have to retake tests and undergo additional examinations.
- the disease is not caused by Candida albicans, but by another type of fungus that is more difficult to destroy;
- this is a relapse that is possible with diabetes, during antibiotic therapy, or reduced immunity.
If relapses of candidiasis occur more than 4 times a year, the doctor will prescribe preventative treatment.
Figure 4 - Chronic and recurrent candidiasis requires lifestyle changes
Topical medications can cause inconvenience - leaking and staining clothes. So that they are evenly distributed over the surface of the vaginal mucosa and do not cause discomfort, it is best to use them before bed. Suppositories and tablets should be placed approximately in the middle of the vagina. Medicines placed too close will leak out, and if placed too far away they can injure the delicate cervix.
If you have thrush, douching and other methods of “washing there” are prohibited, as this causes an imbalance of the microflora.
Symptoms of thrush during pregnancy: how to identify the disease?
In most cases, the symptoms of candidiasis during pregnancy are no different from those characteristic of a fungal infection, manifestations that overtake women in other periods of life. Among them:
- The earliest symptom of candidiasis can be considered a change in the nature of the discharge. At first, they simply become abundant and have a faint sourish odor, which is similar to whey. This is the earliest stage in the development of candidiasis, which, as a rule, goes unnoticed by a woman. The use of panty liners, as well as excessive sweating during pregnancy, can contribute to the disease. The fungus loves warmth and moisture, and it is these conditions that create “every day”.
- After a certain time, the consistency of the discharge also changes. In the secretion you can observe small white grains, and then whole curdled flakes. It was this specific symptom that gave thrush its name.
- At the same time, an inflammatory process develops in those places where the pathogen invades the epithelium. The surface of the mucous membranes swells, becomes inflamed, and turns red (there may be rashes). Traces of irritation are visible on it, and the nerve endings become more sensitive.
- Severe itching is one of the most striking and unpleasant symptoms of thrush. It intensifies when walking, during contact with water, in a warm room. Sometimes the itching is unbearable, so it can be accompanied by sleep disturbances, irritability, and cause severe discomfort.
- A burning sensation occurs when the areas affected by the infection come into contact with urine.
If you try to treat yourself, using frequent hygiene procedures, douching and washing with antiseptic solutions, then relief occurs only for a short time, and then candidiasis returns again.
The fact is that such methods cannot eliminate fungal colonies, but only affect the intensity of symptoms. As a result, pathogenic microorganisms will continue to multiply, minor bloody discharge may appear, as well as cutting and pulling pain in the lower abdomen.
Attention! Our portal strongly recommends not to self-medicate.
- Leave a message to the doctor using the comment form at the end of the article;
- Call: 8 (800) 505-39-76 (free and anonymous);
- Make an appointment with a dermatologist using this link.
What is thrush and can it harm the baby?
Candida albicans is a microscopic fungus that is responsible for most cases of candidiasis, or thrush. According to some reports, it is present in 80% of people, but in small quantities. In favorable conditions, the Candida fungus begins to actively multiply, causing thrush.
Since its habitat is the intestinal tract, this is where all cases of thrush occur, but the disease can manifest itself in different parts of the body - in the mouth, vagina, on the nipples. In women, vaginal candidiasis is most often observed.
What is the danger of thrush during pregnancy:
- thrush causes unpleasant symptoms, complicating the already difficult situation of a pregnant woman;
- it may return after apparent recovery;
- thrush can provoke the occurrence of more serious inflammatory diseases that require intensive treatment;
- the presence of candidiasis increases the risk of postpartum endometritis;
- fungi make the vaginal walls loose, which increases the likelihood of ruptures during childbirth.
However, thrush does not pose a danger to the baby while he is in the womb. The fetus is reliably protected by the placenta, and candidiasis will not harm it.
There is a small chance that your baby will get thrush while passing through the vagina during birth. The disease in a child manifests itself as white spots in the mouth. This is not dangerous, but thrush can spread through the baby's mouth to the breast during breastfeeding. That is, you and your child can continue to re-infect each other, and then it will be difficult to get rid of the disease.
Why candidiasis is dangerous for pregnant women?
Candidiasis is not a safe infection, especially for a pregnant woman; it can affect the development and gestation of the child, as well as his health in the future, due to infection of the embryo by intrauterine or intrapartum (contact of the child with the vaginal mucosa during birth) route.
- Child infection.
- Spontaneous abortion.
- Attachment of secondary infections.
- Premature birth.
- Changes in pathological processes in the cervix, the occurrence of erosion.
- Lethal outcome for the child.
- Problems with nutrition and development of the child after childbirth.
- Disruption of normal processes in the placenta.
The danger of candidiasis during pregnancy is not only posed to the mother, but can also significantly affect the development and frequent outbreaks of diseases in the child caused by this fungus.