What diseases cannot be treated for teeth?
Teeth cannot be treated during ARVI. The body is weakened by microbes and infections. The risk of infection of open wounds, which increases during dental and surgical procedures, is already very high. Anesthetics and painkillers have a negative effect on a weakened body. It will also be uncomfortable for the patient to sit for a long time with his mouth open when he has a runny nose. You can also infect your doctor.
An extremely undesirable procedure for ARVI is tooth extraction. An open wound is the best place for pathogenic microorganisms.
Important: This is additional stress for a person, which can aggravate the course of the disease.
But ARVI is not an absolute contraindication to dental treatment. If the situation is urgent and there is a risk of developing flux or purulent inflammation, it is better to consult a doctor. In other situations, it is better to treat the cold first.
Cold on the lips
If herpes has worsened, oral treatment should be carried out only in emergency cases. Treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, tooth extraction are strict contraindications for diseases.
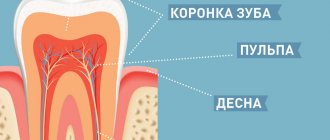
Treatment involves certain mechanical intervention. The herpes virus easily enters the bloodstream and causes herpetic stomatitis, and ulcers will appear in the oral cavity. The most dangerous phase for infection is the rupture of the bubbles.
The appearance of acute herpes indicates weak immunity. Low immunity has a bad effect on the condition of teeth. If relapses of herpes are frequent, you need to contact an immunologist and do not forget about preventive visits to the dentist.
Interesting: 90% of the planet's inhabitants are infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1.
When is anesthesia needed?
Theoretically, it is not always possible to give an injection before treatment. If the carious cavity has just appeared, and the drilling is superficial and short-lived, then often this does not cause discomfort. But if serious treatment is required, and even more so with the removal of a nerve and filling of canals, then it is impossible to do without pain relief.
Among patients, there is a separate category of people who believe that pain relief is an undesirable procedure that requires unnecessary costs and causes harm to the body.
The latest generation of drugs are radically different from their predecessors: they are quickly eliminated from the body and do not have a negative effect on it. At the same time, pain during manipulation can cause an increase in the patient’s blood pressure and an acceleration of the heart rate, which should not be allowed.
As a rule, the need for anesthesia is directly proportional to the fear of dentists: the more the patient is afraid, the lower his pain threshold. This is easily explained from a physiological point of view: adrenaline, released during fear, increases painful sensations several times.
Treatment during pregnancy
Dental problems are a common problem among pregnant women due to hormonal changes. We must try not to bring the condition of the oral cavity to the point of requiring serious treatment. Vitamins prescribed by doctors in the early stages of pregnancy will help with this.
A pregnant woman should see a dentist if the following symptoms appear:
- Bleeding gums when brushing teeth and eating.
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
- Toothaches, periodic or constant.
These are signs of incipient inflammation and should be treated, especially during pregnancy. If you start, you will have to do much more painful manipulations. Without anesthesia. Pregnant women are allowed to have fillings. They are not dangerous to the health of the unborn baby.
During pregnancy you can treat:
- Caries at an early stage.
- Periodontitis, pulpitis.
- Periostitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Gingivitis.
- Stomatitis.
Important: It is better to avoid dental intervention in the first and third trimesters. In the first, the formation of the child’s organs and systems occurs, in the third, the excitability of the uterus increases. Any irritants can cause miscarriage or premature birth. The second trimester is the safest for dental treatment. But first you should consult with your obstetrician-gynecologist.
The following procedures should not be performed during pregnancy:
- Whitening and strengthening.
- Removing stones.
- Correction of teeth or bite position.
- Removal of wisdom teeth.
Is it possible to use anesthesia for a pregnant woman during dental treatment? It is possible if the doctor prefers local anesthetics. They are hypoallergenic and the body tolerates them well. They do not penetrate the placental barrier and do not harm the fetus. Anesthesia with a high content of adrenaline should not be used. Lidocaine lowers blood pressure, causes seizures and other side effects. Stopangin causes fetal pathologies and provokes post-maturity. Sodium fluoride disrupts the functioning of the heart and negatively affects the health of the unborn child. Surgery is performed only for urgent indications.
Recommendations for dental treatment during pregnancy:
- For pulpitis or periodontitis, it is better to start treatment as early as possible.
- In the second half of pregnancy, you need to undergo a routine dental examination.
- In the third trimester, teeth should be treated carefully. Stressful situations should not be allowed.
- Before visiting the dentist, you must inform the doctor about your situation.
Complicated caries, periodontitis, pulpitis, stomatitis can negatively affect the development of the fetus:
- Provoke premature birth.
- Low body weight.
- The infection spreads and affects the soft tissues of the fetus, which can lead to miscarriage.
General anesthesia in dentistry - consequences and complications
The inability to restore adequate breathing if it suddenly stops is the leading cause of death during general anesthesia. This may occur due to intolerance to anesthesia drugs or their incorrect dosage. Therefore, it is very important that the clinic has all the necessary resuscitation equipment, and that the anesthesia itself is performed by an experienced anesthesiologist-resuscitator. But problems can be associated not only with poor clinic equipment and poor quality of anesthesia, but also with a lack of proper control over the patient’s condition during general anesthesia, which can cause another unpleasant complication of anesthesia - intraanesthetic awakening, when a person wakes up during surgery. In various cases, he may experience pain, hear sounds, and also remember events that happen to him. Intraanesthetic restoration of consciousness is a complication of anesthesia that does not pose an immediate threat to human life, but can cause psychological problems, including mental disorders.
Against this background, a relatively harmless complication of anesthesia can be considered a violation of cognitive functions, which experts often associate specifically with general anesthesia. It is known that anesthesia destroys brain cells, although this process is not fatal. In some cases, for about three days from the moment of recovery from the state of anesthesia, the patient may also experience nausea, vomiting, and headache. Increased excitability, insomnia, and inexplicable panic are likely. Possible complications also include medical errors.
Raising the topic of general anesthesia, it is impossible not to take into account the fact that many patients are afraid of allergies to certain pharmacological agents. If there are still concerns and the patient is prone to various allergic reactions, then doctors may recommend taking allergy tests for specific components of the future anesthesia. By the way, not a single test with a negative result can give a 100% guarantee that an allergic reaction will not occur during anesthesia. Such testing can also be dangerous: if the allergen contained in the drug is incompatible with the body, then even with a small dose, anaphylactic shock may occur. The extremely low probability of complications during anesthesia suggests that conducting a dangerous allergy test in this case does not make sense.
Other conditions in which dental treatment is dangerous
You should delay visiting the dentist if chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, or mental illnesses worsen. Sometimes with scarlet fever, tuberculosis, syphilis and various fungal infections, the oral mucosa is affected. In such cases, the tooth should not be removed. A tooth cannot be pulled out even after a recent heart attack.
It is better not to go for dental treatment under anesthesia if you have recently consumed alcohol. The specialist will not guarantee painless treatment. Even with strong anesthetics.
It is also not recommended to treat teeth for women during their menstrual periods. The sensitivity threshold increases, and the risk of complications increases.
Indications and contraindications
We list the main cases when experts really recommend using this method of anesthesia:
- if you are allergic to local anesthesia, when it is impossible to choose a suitable medicine with less effect on the body;
- low pain threshold, at which a person feels too much pain and simple anesthetics do not work on him;
- in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system in combination with the patient’s fear;
- requires extensive intervention;
- increased gag reflex;
- in the treatment of serious diseases in advanced form;
- removing “eights”, especially if they have not erupted;
- extraction of units with complex root systems;
- in the process of prosthetics, if necessary, grinding of teeth;
- for performing maxillofacial surgical procedures;
- when implanting more than one rod per session;
- in cases of treatment of pathological diseases of hard tissues;
- when deleting several units at once.
Read also: Perforation in a tooth
But it also has its contraindications when it is advisable to choose some alternative:
- for heart rhythm disturbances and other serious heart diseases;
- if the patient is under the influence of drugs or alcohol;
- while taking a course of hormonal medications;
- with exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- impaired renal or liver function;
- recent infectious disease;
- if in the last six months a person has had a heart attack or stroke;
- some problems with the endocrine system;
- in case of an allergic reaction to the components of the anesthetic.
Tooth extraction under anesthesia
Anesthesia in dentistry is performed for the treatment of both adult patients and children for the purpose of therapeutic, surgical (tooth extraction, implantation, etc.) dental care.
The essence of sedation is that while the drug is administered the patient is asleep, after the drug is stopped, its effect ends in about 4 minutes. The drug is administered for medical sedation using a special syringe dispenser. To minimize the dose and eliminate negative consequences, conduction anesthesia is performed in parallel.
The anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s condition visually and through a special patient monitor, which records pulse, respiratory rate, blood oxygen saturation level, body temperature, and, if necessary, blood pressure and ECG. To ensure the safety of the activities being carried out, the rooms are equipped with a medical suction device, a defibrillator, an anesthesia-respiratory apparatus, and oxygen is also supplied.