Factors preceding the onset of the disease
The main cause of candidiasis of the oral cavity and tongue is a weakening of the human immune system. The following circumstances may precede this:
- systematic use of alcohol and narcotic substances, as well as smoking tobacco products;
- deviation of the functioning of the mucous glands of the body from the norm due to undergoing a course of treatment with drugs that include an antibiotic;
- lack of sufficient amounts of vitamins, which may be associated with age-related changes, congenital pathologies, changes in seasons, as well as poor diet;
- the presence of developmental disorders of the tongue or larynx;
- the appearance of cracks and ulcers on the outside or inside of the oral cavity;
- In women, candida often begins to progress during pregnancy, as well as the lactation period, since some of the beneficial substances are used to support the life of the child.
In addition to weakened immunity, candidiasis in the tongue can be caused by such features of people's daily activities as:
- failure to comply with basic rules aimed at maintaining oral hygiene;
- lack of preventive measures associated with visits to the dental office, and, as a result, unsatisfactory condition of the teeth;
- improper care of products intended for straightening the bite, as well as for replenishing the required number of teeth (dentures, braces);
- direct contact with the salivary glands of an infected person (kissing, using a toothbrush, eating food from the same container).
Eliminating the spread of candida in children is quite simple. With timely detection of tongue candidiasis, treatment of an adult will also proceed without significant complications.
Description of the pathology
Candidiasis occurs as a result of the proliferation of yeast fungi of the genus Candida. They are constantly present on human skin and mucous membranes. But normally their number is small and is regulated by the protective mechanisms of the immune system. With its weakening, the spread of microorganisms begins.
Adults are rarely affected by candidiasis. At risk are newborns (5% of patients), infants (10% of cases) and the elderly (10%).
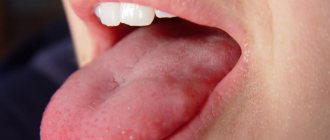
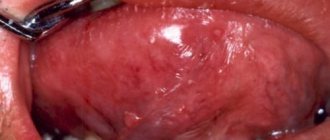
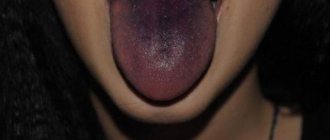
The main symptom is a white coating on the mucous membrane.
Important! The disease is characterized by the appearance of a white, cheesy coating on the oral mucosa. Outwardly, it looks like curdled milk, which is why candidiasis is often called thrush.
Initially, plaque forms in the corners of the lips. As the disease progresses, it spreads throughout the entire oral cavity, including the gums and tongue. Curd deposits can be easily removed with a cotton swab or toothbrush. Beneath them a reddened, ulcerated surface is found. Itching, burning, swelling, discomfort when chewing and talking are also noted.
Symptoms that appear with candidiasis
Each stage of infection development can be determined by its corresponding symptoms:
- At the first stage of candida activation, the disease may look like a manifestation of a common cold. This stage is characterized by slight swelling and redness in the tongue and cheeks. A weakening of taste buds may occur. There is no significant increase in body temperature or manifestation of pronounced symptoms.
- After the fungus, having broken down the tissue, strengthens itself in the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, it begins to reproduce. Thrush on the tongue acquires characteristic symptoms, that is, the formation of small scattered whitish grains. Painful sensations appear in the mouth. In this form, plaques are easily removed without leaving any cracks underneath.
- As it progresses, candida forms a continuous growth on the tongue, consisting of individual pinpoint protrusions. Body temperature can rise to thirty-nine degrees. Bleeding ulcers form under a milky coating covered with a shiny mucous film. The tongue increases in size, which leads to difficulty eating and impaired speech functions.
If candidiasis that affects the surface of the tongue is not treated in time, it can lead to death not only for a child, but also for an adult. This is due to the fact that when the infection spreads, there is difficulty breathing. In addition, the body temperature rises to extreme levels, which leads to gradual intoxication of the body.
Danger of pathology
If left untreated for a long period of time, thrush on the tongue can lead to serious complications. They pose the greatest danger to children, since they cannot inform their parents about the discomfort they experience. Over time, their thin cheesy coating becomes a thick layer of fat covering the inflamed surface and bleeding ulcers. Ignoring the disease can lead to:
- Fungal cheilitis;
- Glossitis;
- I get stuck in the corners of my mouth;
- Mycotic stomatitis.
Fungal cheilitis
Glossitis
Seizures in the corners of the mouth
Mycotic stomatitis
In the final stages, thrush of the tongue causes the formation of such an amount of white plaque that it closes the larynx. Because of this, any consumption of food or drink causes serious discomfort to a person. The surface of the tongue is covered with numerous cracks, from which blood is released. The lymph nodes may become inflamed and enlarged. Diaper dermatitis, erosion of the esophagus and inflammation around the sphincter are often associated with thrush.
Lack of timely treatment of tongue candidiasis significantly increases the risk of genital thrush.
Spread of fungal infection in children's bodies
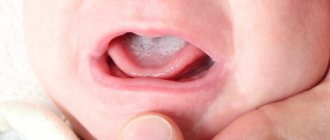
In children, the disease progresses somewhat differently than in adult men and women. Candidiasis may appear on the surface of a child’s tongue due to:
- congenital pathologies transmitted by inheritance;
- staying in hospital for a long time;
- birth in early pregnancy;
- excess sugar in the milk produced by the female body, or in a special formula;
- unformed immune system.
This may also happen because a nursing woman has an unbalanced diet and, as a result, a lack of vitamins is passed on to the child .
The main areas that are affected at the beginning of the progression of candida in a child’s body are the inner sides of the cheeks and lips.
The disease develops in several stages:
- The first signs appear (slight redness of the throat, low temperature). The baby may appear completely normal.
- The appearance of white scattered formations in the cheek area. The child begins to behave restlessly, refuses to eat, and sleeps poorly.
- The growths increase in size and the appearance of new spores, which look like a single white mass covered with a matte film. The tongue begins to be damaged, accompanied by swelling and pain. Rashes may appear in the lip area.
- The peak of the spread of yeast fungus, which is accompanied by:
- constantly high body temperature;
- the presence of bleeding cracks in the oral cavity under plaque, which darkens and acquires a yellowish tint;
- the formation of cracking swellings in the corners of the lips;
- complete refusal to eat and continuous crying.
It is very important to diagnose and begin to treat candidiasis of the tongue in a child in the first stages of its development, otherwise the disease becomes chronic.
Symptoms of fungus on the tongue and forms of the disease
Fungus on the tongue, the symptoms of which depend on the form of the disease and the degree of spread, are classified as acute and chronic.
Symptoms of fungus on the root of the tongue in acute form, in turn, are divided into:
- pseudomembranous candidiasis;
- atrophic thrush.
- white fungus on the root of the tongue, which is diagnosed as chronic, can take the form of:
- hyperplastic;
- atrophic.
Forms can transform one into another or arise independently, under the influence of provoking factors.
Fungus on the tongue, the symptoms (photo) of which occur in an adult, begin with a small coating in the form of white grains on the surface of the cheeks on the inside and slight redness.
As the disease progresses, the area of plaque increases, and it itself transforms into plaques covered with a film resembling milk.
Later, Candida plaques may appear on the gums, palate, tonsils, and also spread to the skin around the lips.
It is very easy to remove plaque from the mucous membrane at first, although during the activity of the fungus, a small wound (ulcer) forms under the plaques.
This means that the fungus penetrates deeper into the cavity.
Characteristic signs of fungus on the tongue are:
- burning and itching in the mouth;
- discomfort when swallowing food, saliva;
- irritation that occurs when the membranes of the oral cavity come into contact with hot, spicy and sour foods;
- feeling of a “coma” in the throat;
- possible increase in temperature;
- formation of microcracks in the corners of the lips;
- the appearance of a jam, a whitish coating on the lips;
Carrying out diagnostics if you suspect activation of candida
Before you begin to treat candidiasis that forms on the tongue, you must undergo a procedure related to determining the type and stage of the disease. You should not self-medicate, as this can lead to irreparable consequences.
The presence of infection is detected through a thorough examination of the mucous membranes, as well as taking various tests:
- In laboratory conditions, plaque and mucus are scraped from all affected areas. Next, the substance is sent for research to determine the degree of health deviation from the norm.
- It is mandatory to donate blood, as this will determine the amount of sugar in the body. This is done in order to find out the true cause of fungal overgrowth, which may be excess sugar or diabetes.
When thrush of the tongue occurs, treatment is prescribed only after the results of an examination by highly specialized specialists (gynecologist and mycologist for women, endocrinologist for men) are received.
To avoid experiencing all the symptoms of candida infection in the future, you should take care of your health and follow preventive measures.
Features of thrush in the mouth
Thrush of the tongue is extremely rare in people as a separate disease. Most often, it occurs against the background of other pathologies. In most cases, it is possible to diagnose abnormalities during a trip to the dentist, caused by an acute inflammatory process of the cheeks and gums. When signs of this pathology appear, the specialist conducts an advanced diagnosis, allowing you to quickly identify the type of fungal pathogen. During the examination, it is possible to easily determine the form of the disease:
- Pseudomembranous - the surface of the tongue softens, the papillae fill with blood. A white coating quickly grows on it, causing serious discomfort when eating food.
- Hyperplastic - numerous papules and plaques appear on the tongue, causing its surface to become inflamed. Most often, this type of thrush also affects the cheeks.
- Acute atrophic – occurs due to prolonged lack of treatment. It is characterized by redness, swelling, and inflammation of the tongue, on which a white coating appears.
- Chronic atrophic - while eating food, a person experiences burning and pain, he is tormented by constant discomfort and a whitish coating on the surface of the cheeks.
Methods of treating and eliminating symptoms of the disease
Tongue candidiasis can be treated in several ways:
- Use of antiseptic and antimycotic drugs . The main goal of this method is to prevent the development of fungus and gradually eliminate its activity. These preparations are intended for rinsing and lubricating the affected areas. Used in the early stages.
- Ingestion of medications . It is used when the disease process is prolonged and has pronounced symptoms. The main drugs are intraconazole, fluconazole and ketoconazole. It is recommended to use together with vitamin complexes.
- Traditional medicine , such as decoction of calendula, juniper, celandine (used for rinsing). Ointments made from sea buckthorn or St. John's wort oil work well. It is recommended to drink raspberry or carrot juice, kombucha tincture.
If candidiasis is detected in the area of the tongue in an infant, treatment occurs in a gentle manner, under the close supervision of a competent specialist.
Causes
Candidiasis of the tongue develops when the composition of saliva and microflora of the oral cavity changes. This is facilitated by:
- Prolonged or uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
- Acute respiratory diseases: influenza, acute respiratory infections, ARVI, tonsillitis.
- Poor quality dentures: mismatch of bite, allergenic materials.
- Excess carbohydrates in the daily diet.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins B and C.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Weakened immunity due to AIDS, tuberculosis, HIV.
- Smoking, alcohol and drug abuse.
- Chemotherapy.
- Pathologies of bite and tongue.
- Systemic diseases: atrophic gastritis, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The main causative agent is Candida fungus.
Important! Candida fungi are able to survive even in the most unfavorable conditions. They are not affected by extremely high or low temperatures or X-ray radiation. They can also remain viable for up to 2 hours outside their usual environment: on clothing and household items.
Infection with candidiasis occurs through contact and household contact. The carrier transmits the fungus through a kiss, using the same utensils and hygiene products. A newborn can become infected during childbirth, when passing through the mother's birth canal.
Diseases of the mouth area associated with candidiasis
A fungal infection of the oral cavity is sometimes accompanied by accompanying symptoms. Thrush on the tongue in adults often occurs with associated diseases , which cause a lot of inconvenience:
- swelling and bleeding of the gums, as well as the presence of dental plaque. Pain syndrome occurs even with a slight load on the teeth;
- the formation of small watery blisters on the outside of the lips, causing unpleasant sensations (itching, tightness, tingling). When these formations appear, it is necessary to immediately scrape them and begin to treat them, since they can subsequently cause serious complications (damage to the nervous system, severe pain in the head and abdomen);
- cracks and crust formation on the corners of the lips (popularly called jams). They have a white coating that is easy to remove. The presence of seizures does not always indicate candidiasis of the oral cavity and tongue in a man, since they can appear as a result of fulfilling work obligations associated with the presence of contaminants.
When the first signs of fungal spread appear, you should contact specialists who diagnose such diseases.
Seizures on the corners of the lips
Treatment of fungus on the tongue
How to treat a fungus on the tongue of an adult can only be determined by a specialist - a dentist, a periodontist; less often, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist or a mycologist is necessary.
Self-medication can provoke the course of the process in an acute form, with its subsequent transition to a chronic form.
Drug therapy
Fungus on the tongue, which is treated with local and systemic drugs, is quite difficult to eliminate. The treatment will be long and complex.
To understand how to treat fungus on the tongue, you need to know what drugs can “kill” pathogenic microorganisms.
These include antimiotics. They are divided into two groups:
- Polyene antibiotics - perfectly reduce the amount of white plaque in the mouth, heal erosive formations in a short time. Drugs such as Levorin and Nystatin are recommended to be absorbed slowly in order to prolong their stay on the mucous membrane and enhance the effect.
- Imidazoles - they are taken over a longer course, from 1 to 3 weeks, depending on the severity of the disease. This group of antimiotics includes the following drugs: Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Econazole.
As an additional treatment for fungus on the tongue, antimicrobial agents are prescribed that can stop the spread of fungi and their growth:
- Diflucan;
- Fluconazole;
- Nizoral;
- Decamine caramel.
To get rid of fungus on the tongue, as an additional therapy to the main treatment, the following help:
- vitamins that create an acid-reducing environment on the mucous membranes - B6, B2, PP, C;
- antiallergic drugs - Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Fenkalor, Pipolfen;
- calcium gluconate – as a general tonic;
- iron preparations (Conferon, Ferroplex);
- products that help produce gamma globulins and leukocytes to fight fungi - Methyluracil, Pentoxyl.
Sanitation of the oral cavity and local treatment
White coating on the tongue can be removed using topical agents:
- aniline dyes – fucorcin solution, methylene blue;
- based on iodine - Lugol's solution, Yodicirin;
- bactericidal action - Lysozyme, Lizak.
Hygiene procedures performed for the oral cavity several times a day are also important.
This will help quickly get rid of plaque on the tongue, soothe inflammation, and heal wounds.
To do this, after eating and, always, at night, use solutions with:
- baking soda;
- brown;
- boric acid;
- Iodinol.
Prevention to prevent the development of candidiasis
You can avoid damage to the oral cavity by fungal growths only by observing the following rules:
- keeping the oral cavity clean;
- avoiding frequent use of alcohol and tobacco;
- abstaining from contact with an infected person;
- proper care of jaw dentures and braces;
- other procedures aimed at maintaining normal immunity (taking vitamins, visiting the dental office, sports activities).
If the scraping still gives a positive result, you need to start treatment as quickly as possible.
To prevent yeast fungus from manifesting itself as a serious disease, it is necessary to adhere to sanitary standards and a healthy lifestyle. It is strictly forbidden to make a diagnosis from a photo, as improper treatment can lead to death.
Prevention
People rarely think about preventing candidiasis until the disease first strikes them.
Although tongue thrush is a disease that is quite easy to prevent, it is very difficult to cure.
To prevent the growth of fungal spores in the mouth, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Follow the rules for wearing dentures. You should not leave them in your mouth overnight. In the morning, before putting on, the dentures are thoroughly washed with a brush and then dried thoroughly. If the denture rubs or presses, you should immediately fix the problem by contacting your dentist.
- Stop smoking.
- Treat anemia in a timely manner, control blood sugar levels, and compensate for vitamin B 12 deficiency.
- When taking medications that dry out the mucous membrane, you should often take sips of water to restore fluid balance.
- Do not come into contact with sick people.
- Treat inflammation in a timely manner: seizures, stomatitis, gum damage, herpes on the lips.
Mild forms of tongue candidiasis, with consistent and timely treatment, resolve within 1-2 weeks. The main way to protect the body from this disease is to maintain hygiene and maintain immunity.
Diagnostics
In order for the treatment of thrush on the tongue to be as successful as possible, it is necessary to conduct an extensive diagnostic examination. Any qualified doctor can handle this. First of all, he will conduct a visual examination of the tongue, after which he will send the patient for a series of studies. They will take a biochemical and mycotic blood test and an oral smear. Based on this, a bacteriological culture will be performed to determine the type of pathogen.
To alleviate their condition at this stage, patients are advised to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid unauthorized prescription of medications;
- Ensure proper oral hygiene;
- Follow a special diet that will stop the fermentation process;
- Play sports, which will reduce stress on the nervous system.
Candidiasis
Cervical cancer
Diabetes
HIV
Thrush
2088 27 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Candidiasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Candidiasis is an infectious disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It is caused by the active proliferation of fungus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genital and internal organs and on the skin.
All representatives of the genus Candida belong to opportunistic microorganisms, that is, they are constantly present in the normal microflora. But with a decrease in immunity, changes in hormonal levels and for a number of other reasons, these fungi can begin to actively colonize the mucous membranes and skin.
The most common members of the genus are Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. In 90-95% of cases of urogenital candidiasis, C. albicans is the dominant pathogen.
The first contact with fungi of the genus Candida occurs during the passage of the child through the birth canal. However, the medical literature describes cases of detection of these microorganisms in amniotic fluid, which indicates the possibility of a vertical (transplacental) transmission route. Transmission of the fungus of the genus Candida also occurs through breastfeeding, skin contact between the child and the mother, and through household and food routes.
These microorganisms produce endotoxins and enzymes that cause cell death and tissue necrosis, which enhances the adhesive (attachment to cells of the mucous membranes or skin) ability of the fungus and ensures penetration into tissue.
Overproduction of these and a number of other substances determines the pathogenicity of representatives of the Candida family.
Causes of candidiasis
- Exogenous (external) factors facilitating the penetration of fungi into the body:
- occupational hazards leading to frequent skin damage;
- prolonged exposure to a warm and humid environment;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes.
- Factors leading to a decrease in the body's resistance:
- presence of chronic diseases;
- long-term use of drugs that disrupt the natural microflora;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress, disturbances in sleep and rest patterns.
Risk factors for developing candidiasis
- Metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis), diseases of the immune system (HIV infection), endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, etc.).
- Long-term use of certain drugs: hormonal contraceptives, systemic glucocorticosteroids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, cytostatics.
- Long stay or living in an area with high humidity and temperature, comfortable for the circulation of fungal spores in the environment.
Classification of the disease
Based on the localization of the process, the following are distinguished:
- Urogenital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa.
- Superficial candidiasis.
- Interdigital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of periungual ridges and nails.
- Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Urogenital candidiasis (UGC)
– a widespread disease: according to medical statistics, about 75% of women of reproductive age have registered symptoms of UGC at least once.
There are acute and chronic forms of urogenital candidiasis, candidiasis of the vulva, vagina and other urogenital localizations.
In some cases, when diagnosing, a clarification is used: complicated or uncomplicated UGC, which reflects the number of exacerbations per year and the severity of the disease. Symptoms of female urogenital candidiasis
- The appearance of white-yellow cheesy or creamy discharge from the genital tract. The intensity of discharge may increase before menstruation, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels.
- Unpleasant sensations, itching in the genital area, often aggravated by sexual intercourse or urination.
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, the presence of damage to the skin of the genital organs (cracks, microtraumas).
- In the chronic course of UGC, dryness of the mucous membranes of the genital tract develops.
Symptoms of male urogenital candidiasis
- Redness, swelling, discomfort in the genital area.
- Whitish discharge of a cheesy structure from the genital tract.
- Pain and burning during sexual intercourse and urination.
Superficial candidiasis
can be erythematous (the main symptom is reddened areas of the skin with a weeping surface) and vesicular (the formation of papules, vesicles and pustules in the affected area - inflammatory elements located in the superficial layers of the skin). The lesion begins with large folds of skin, gradually spreading to other areas of the body. In the depths of the folds, weeping occurs (separation of serous exudate through the smallest defects of the epidermis), a violation of the integrity of the skin contributes to the addition of a secondary infection.
Interdigital candidiasis
localized in the space between the fingers. In this case, redness of the skin is noted, followed by the appearance of bubbles in transparent contents. The disease spreads quickly in close groups (in kindergartens, schools, etc.).
Oral mucosal candidiasis (OCOR)
Oral candidiasis causes discomfort, especially when eating - burning, pain, dryness. Depending on the location of the process, several forms of oral candidiasis are distinguished.
Often, CSOPR and the gastrointestinal tract accompanies immunodeficiency conditions: HIV infection, acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or congenital immunodeficiency (for example, with T-lymphocyte pathology). In the presence of these diseases, candidiasis occurs with the most severe symptoms, is difficult to treat, and is aggressive in nature.
The most common manifestation of CSOPR is candidal stomatitis, which mainly affects infants and adults with weakened immune systems.
With this pathology, the oral mucosa turns red, swells, and whitish films with a cheesy consistency appear on it. In the initial stages of the disease, plaque is easily removed. As the disease progresses, the films become denser, are difficult to separate, and when removed, the bleeding mucous membrane is exposed.
With candidal stomatitis, the tongue may be affected, which is manifested by redness of the back of the tongue, the appearance of plaque and desquamation of the epithelium. These symptoms are accompanied by severe pain in the affected area when talking, eating, and palpating the tongue.
Smokers, more often than other types of CSOPR, develop chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, accompanied by the formation of white, merging plaques that rise above the surface of the hyperemic mucosa.
With this pathology, the consistency of saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foaming; there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, a gray or white coating on the mucous membrane. In 10-40% of cases, this clinical form of candidiasis becomes malignant (i.e., becomes malignant).
Older people most often develop a chronic atrophic form of oral candidiasis. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. The lesion is often localized under dentures, which causes pain.
Candidal cheilitis and candidiasis of the corners of the mouth mainly occur in children and the elderly. The lesion is usually bilateral, with the formation of red, painful cracks in the corners of the mouth, covered with an easily removable white coating or scales. With a long course of the disease, a bacterial infection may occur.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
The diagnostic search algorithm for candidiasis of any localization includes taking material from the affected area, followed by microscopy and culture to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
In order to diagnose conditions that lead to a decrease in immunity, a general blood test is used;
Rinse and diet for candidiasis
It is imperative to rinse the mouth with alkaline liquids to reduce the amount of plaque, remove fungal microorganisms, relieve inflammation, and heal ulcers.
Procedures must be done every three hours
, and also necessarily after a meal, before going to bed. This must be done diligently for 14 days; even if the condition improves, you should not stop your actions.
If you have candidiasis, you should definitely rinse your mouth with alkaline liquids.
Naturally, oral thrush cannot be avoided without a special diet.
. Eliminate all yeast foods to avoid microflora activation. When eating spicy and salty foods, the already inflamed mucous membrane is irritated, resulting in severe pain.
It is worth switching to food with a more liquid and puree-like consistency at a warm temperature. You need to completely exclude spices, spices, sweets, and fast food from your diet.
As you get better, you should gradually introduce new foods to the menu. For three months it is worth eliminating foods that cause such diseases.
Symptoms and common diagnostic methods
Given the widespread prevalence of the disease, it is necessary to know what it looks like, its symptoms and consult a specialist in time. If you delay treatment, the tongue fungus will develop into a chronic form and then it will be more difficult to get rid of the disease.
Signs of a bacterial infection
The onset of fungal development looks like the rapid appearance of white dots in the mouth. Most often they form on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, cheeks and tongue. The bacterial lesion appears as small flakes located on the tongue and cheeks. After a little time, they increase in size, become covered with a white film, and redness begins around them. The lesion then spreads to the throat and lips.
Fungus on the tongue Fungus on the tongue
The white coating is initially easily removed mechanically, but then the fungus penetrates deeper and deeper into the oral mucosa, and painful wounds appear. The infection spreads quickly. Soon even the area under the tongue becomes covered with cheesy ulcers. The body reacts to inflammation with fever and weakness.
Curdled coating on the tongue
As the infection develops, there are symptoms that you need to pay attention to: unpleasant itching in the mouth, pain when swallowing, white coating on the tongue and gums. The appearance of these sensations signals a failure in the immune system and the emergence of pathogenic microflora. It is necessary to undergo an examination and quickly select the necessary treatment, which will completely destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
Diagnosis and methods for determining candidiasis
Unfortunately, most often a visit to a medical facility occurs in an advanced stage, when the yeast parasite has entered the patient’s body. Therefore, a specialist visually determines the symptoms of candidiasis and makes a diagnosis. To correctly determine the type of fungus, a scraping is made from the tongue. Additionally, the following may be prescribed: smears from the pharyngeal mucosa, as well as examinations of the stomach and esophagus.
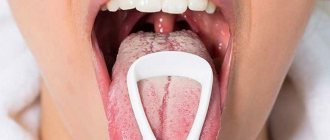
Tongue scraping for candidiasis
A smear from the surface of the tongue is a fairly informative analysis, since it can be used to determine the amount of certain pathogens in the oral cavity. Also, based on the results, you can understand how healthy the patient’s digestive system is. Depending on the specific flora on the tongue, it will be clear which microflora predominates in the gastrointestinal tract, since all pathogens enter through the mouth. You should not be surprised if, in the presence of stomach diseases, scrapings from the surface of the tongue are prescribed, because this analysis can really tell a lot. At the first signs of fungal infection of the oral cavity, a microflora examination may be prescribed.
In what situations is this analysis most often done: glossitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, human immunodeficiency virus, severe somatic pathologies and various conditions associated with a decline in immunity. You need to take the test either in the morning on an empty stomach or 2 hours after eating or drinking. Otherwise, the results will not be informative. You should also not rinse your mouth or brush your teeth beforehand. Upon contact with cleaning agents, many microorganisms are destroyed. Most often, scrapings from the tongue are taken to recognize signs of Candida fungi. Thanks to scraping, it is possible to identify the smallest threads of pseudomycelium of fungi of the genus Candida.
The fact is that oral candidiasis can masquerade as many other diseases. For example, stomatitis, cheilitis, gingivitis and glossitis are often confused with thrush. Most often, newborn children suffer from fungal infections, since their body microflora and immunity in general are just beginning to form, which means that diseases will occur frequently until the child grows up and his body gets stronger. If, after analysis, threads of pseudomycelium or budding cells are clearly visible under a microscope, then candidiasis can be diagnosed with 100% confidence. In such a situation, conventional antiseptics will not help; you need to use only local or systemic antifungal medications, depending on the prevalence and severity of the disease.
Why does thrush occur in the mouth?
Since the child’s body is highly susceptible to various pathologies, the main reason for the appearance of fungus in the mouth is insufficient hygiene of the mother’s breasts during breastfeeding. If the child is on artificial formula, then the result of the appearance of fungus is the lack of proper sterilization of nipples and bottles. Important factors influencing susceptibility to infectious and fungal diseases: poor immunity due to prematurity of the child, dysbiosis (violation of the integrity of the intestinal microflora) due to the use of antibacterial agents, vitamin deficiencies or the passage of the fetus through the infected birth canal of the mother.
To collect the scraping, just do a couple of simple manipulations. Using a special spatula or a regular cotton swab, the laboratory technician makes several light movements along the surface of the tongue so that the contents of the saliva are accurately caught on the sampling material. After collection, the resulting material is sent to a special metal container to be sent for laboratory research. Mothers do not need to worry about their baby; the smear will not cause any discomfort to the newborn. The earlier the sampling is carried out, the faster the cause of the disease will be identified, and the faster the child will recover.
What other tests may require scraping from the surface of the tongue?
A smear from the surface of the mouth can be carried out not only to identify pathogens, but also to determine bile acids. To carry out the analysis, you need to use the diagnostic method of color thin layer chromatography. In order for the diagnostic result to be reliable, the study must be carried out on an empty stomach in the morning before breakfast without prior drinking or taking medications. After collection (the procedure is simple and the same as described above), the collected material is placed in a special test tube and filled with ethyl alcohol. Next, the sampling material is tightly sealed and left for several hours specifically so that all the substances dissolve well among themselves.
This is followed by an evaporation procedure using a water bath exactly until the volume of the liquid decreases by half. Then a chromatographic plate is required, it needs to be heated in a dryer for an hour, then a drop of the test substance is applied to the plate, which is sent to the dryer, and then it is cooled and developed. Then you can examine the result; if there are individual spots, then bile acids are present in large quantities.
lekhar.ru
Treatment in adults
Therapy should be local and internal: the latter involves a general strengthening of the immune system and the use of antifungal drugs, which are also used externally. Additionally, oral rinses are introduced into the local therapy regimen, changing the pH of the microflora. It is possible that it will be necessary to influence concomitant diseases and prevent bacterial infections that can develop against the background of candidiasis. The general therapeutic regimen includes:
- local and external antimycotics;
- immunostimulants;
- calcium gluconate;
- B vitamins;
- sources of iron.
polyene antibiotics;
Local therapy
Candidiasis of the tongue and several other dental diseases at most stages, except the last one, with the formation of plaques and the addition of a bacterial infection, can be treated through the use of external agents. They suppress the activity of the fungus and prevent the penetration of microorganisms into tissues. For this purpose, you can use both antifungal ointments (lips, skin around) and rinsing solutions. Doctors advise: