What it is
Officially, painful cracks on the tongue and along the edge of the tongue are called glossalgia. This is a fairly common neurosomatic disease.
Most common symptoms:
- dryness in the tongue area;
- itching and burning;
- swelling;
- soreness.
The insidiousness of glossalgia is that it does not go away on its own; without appropriate treatment it is impossible to get rid of a crack in the tongue.
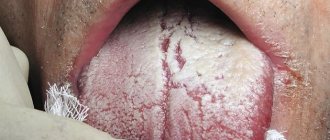
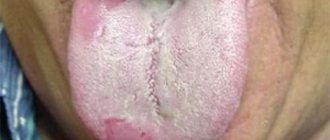
At an early stage of the disease, the doctor may not notice pronounced cracks in the tongue, since they are microscopic and mainly manifest themselves as burning and pain. If you do not respond to this symptom in a timely manner, over time a crack may form at the tip or in the middle of the tongue, longitudinally, as well as cracks under the tongue and on the sides. In this case, the doctor also notes swelling and swelling of the tongue, atrophy of the salivary glands and filiform papillae on the surface of the tongue. The sooner you start treatment, the easier it is to get rid of glossalgia, so if you have cracks in your tongue, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why does the tongue sting: the reason
Why there is a burning sensation in the mouth, why the tongue stings - the reason for the occurrence of such symptoms is associated with the following conditions and diseases in the oral cavity...
- Dryness of the oral mucosa (xerostomia) –
the symptoms of dry mouth and burning tongue are inextricably linked.
Insufficient hydration of the mucous membrane with saliva causes the appearance of numerous small cracks in the mucous membrane (including the tongue), lips, which may be accompanied by a “tongue stinging” sensation or burning sensation. The tingling sensation will be especially pronounced if you consume drinks or foods containing acids. Dryness is caused, as a rule, by a decrease in the volume of saliva secreted by the salivary glands, and less often by the habit of breathing through the mouth (especially against the background of constant nasal congestion). In some cases, it may be caused by dehydration or Sjögren's disease. Treatment of xerostomia is very complex, and for successful treatment it is very important to determine the cause of dry mouth.
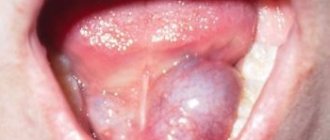
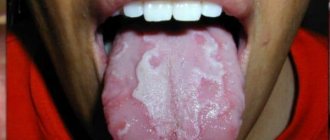
- Oral candidiasis (Fig. 2-4) – with candidiasis, fungal infection of the oral mucosa occurs, the tongue is especially often affected by the fungus. Candida fungus is present in the oral cavity of completely healthy people. Only by reducing the body's defenses and the barrier function of the mucous membrane does Candida acquire pathogenic properties.
A decrease in the body's immunity and local immunity of the oral cavity can occur due to the use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, the presence of malignant tumors, radiation and chemotherapy, blood diseases, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, dysbacteriosis, vitamin deficiency, diabetes mellitus.Symptoms: There are several forms of candidiasis, and symptoms can vary greatly depending on the form. Mainly on the mucous membrane of the tongue/cheeks, you may notice white spots or an abundant white cheesy coating. In some cases (with atrophic candidiasis), there is no plaque, but the mucous membrane is bright red. Patients may feel the tip of their tongue sting or have a burning sensation.
Treatment of fungal infection of the oral cavity must be carried out against the background of sanitation of the oral cavity from caries, treatment of chronic inflammation of the tonsils (if any).
- Poor-quality removable dentures – if you have a pinching sensation on the tip of your tongue and you have removable dentures, then you can immediately suspect several possible causes.
Firstly, tingling and burning of the tongue may occur due to an allergic reaction to excess monomer in acrylic plastic, which happens if the dental technician has violated the ratio of the ingredients of the plastic. Secondly, the reason may be that the prosthesis base is too large, resulting in too little space for the tongue and limiting its mobility. Thirdly, in patients who have been using dentures for a long time, the quality of oral hygiene noticeably deteriorates, which leads to the parallel development of denture stomatitis (this can be either a fungal or bacterial infection).
- An allergic reaction can be a contact allergy to the materials of a removable denture in contact with the tongue (plastic, metal base of a clasp denture), or to the metal of artificial dental crowns.
The symptom when the tip of the tongue is red and stings is in some cases just a consequence of an allergy. If you stop wearing a removable denture for a while and start taking antiallergic medications, then a decrease in the severity of tingling/burning symptoms indicates the allergic nature of these symptoms (24stoma.ru). An allergic reaction to a prosthesis in 99% of cases is also associated with poor-quality manufacturing of the prosthesis from plastic (excess monomer).
- Hard dental deposits (Fig. 5, 6) - in many people with insufficient hygiene, you can see entire conglomerates of tartar on the inner surface of the lower teeth. Tartar consists of billions of pathogenic microorganisms that produce toxins and pathogens.
Constant contact of the tongue with the infected surface of dental plaque can lead to chronic, subtle inflammation of the mucous membrane (especially at the tip of the tongue), which can cause symptoms such as stinging of the tongue, burning of the tip of the tongue. If there are deposits, you need to have ultrasonic cleaning of the deposits done by a periodontist. - Tongue diseases – there are a great variety of various diseases of the tongue, but mainly in patients there are two diseases in which tingling and burning of the tongue are most common:
1) Desquamative glossitis: this disease is also called “geographic tongue”. This is due to the fact that in this disease, red foci are found on the tongue (the death of the epithelium of the tongue has occurred in these areas). Over time, the lesions may become covered again by epithelium, but appear in other places on the tongue, i.e. the drawing changes all the time and resembles a geographical map (Fig. 7-9).2) Folded tongue: this disease is characterized by the presence of large folds on the tongue, usually located symmetrically. The largest is the longitudinal fold; numerous transverse ones extend from it. The presence of folds predisposes to the development of inflammation of the tongue mucosa, candidiasis, and sensitivity to various irritants (Fig. 10-12).
Treatment of tongue diseases is complex: complete sanitation of the oral cavity and inflammatory throat diseases, it is possible to conduct a microbiological study, based on the results of which medications (antibacterial or antifungal, etc.) are prescribed.
- Leukoplakia of the oral mucosa (Fig. 13, 14) - this disease is characterized by impaired desquamation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane, as a result of which white plaques can form on the surface of the oral mucosa (including the tongue). With leukoplakia, one of the symptoms may be a burning sensation. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic. It usually occurs in smokers. Refers to precancers, i.e. If left untreated, it can transform into cancer. Treatment consists of complete cessation of smoking, sanitation of the oral cavity, treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases of the throat, and the use of keratolytic drugs.
- Herpetic infection (Fig. 15) - most patients are faced with a herpetic form of stomatitis, in which numerous blisters first form in the oral cavity, and then erosions, the appearance of which in turn can cause tingling or burning. Herpetic blisters and erosions can occur on any part of the oral mucosa, including the tip of the tongue.
- Teeth grinding is a condition commonly called bruxism.
It is expressed in the fact that a person unconsciously clenches his teeth tightly at night, which is expressed in their grinding against each other. Many patients do not know that they have bruxism, because... at this time they are sleeping. Usually, the diagnosis is made by relatives who can hear the grinding noise at night. With bruxism, teeth marks can usually be seen on the tongue (Fig. 16). Often, in addition to fingerprints, there may be a burning sensation or tingling sensation on the tongue.
- Lichen planus (Fig. 17, 18) is a chronic disease in which either foci of hyperkeratosis (they look like white spots, which may resemble leukoplakia or candidiasis), or erosions and ulcers may appear on the oral mucosa. Pinching and burning are characteristic of erosive-ulcerative forms. The disease is treated by an immunologist.
Congenital fissures
It happens that a patient has cracks in the tongue since birth or childhood, which practically do not cause him any concern. Such cracks are usually transverse and are caused by the development and formation of the tongue.
Some patients have a so-called folded tongue, a congenital feature of tongue development. It is usually considered normal and does not require any treatment. The exception is red cracks in the tongue, which form at the bottom of the folds and cause pain to the patient. This happens with insufficient oral hygiene, so those with a folded tongue must carefully clean not only their teeth and gums, but also their tongue from plaque. If the owner of a folded tongue has developed cracks, treatment should be prescribed by a competent doctor, taking into account the design features of the patient’s tongue. To prevent the formation of folds in the depths, more attention should be paid to the sanitation of the oral cavity.
Treatment of cracked tongue
If there are no complaints and the discomfort is only an aesthetic defect, no special treatment is required, the underlying disease should be treated.
In some cases, the reasons for the formation of cracks are so serious, for example, gastric or duodenal ulcers, that patients simply do not care about such an insignificant defect. And all efforts and means are aimed at combating the underlying pathology. And as soon as the acute stage has been stopped, the cracks that appear disappear by themselves. If there are complaints of pain and any discomfort, then in addition to specific treatment, local treatment is prescribed:
| METHOD OF EXPOSURE | REASON FOR PRESCRIPTION, END RESULT |
| Sanitation of the oral cavity. Training in local oral hygiene, with the selection of hygiene products and items |
|
| Elimination of irritants: hot, sour, salty, sweet, spicy |
|
| Use of local medications (decoctions, infusions, antiseptics) |
|
| Use of anesthetics |
|
| Application of keratoplasty |
|
| Treatment of concomitant diseases |
|
At first glance, tongue defects are purely cosmetic in nature, and often simply do not cause discomfort. But the human body is a perfect system, and any negative manifestation has a basis. The most important task of the doctor and the patient is to notice it in time and take all necessary measures.
Author:
Melnikova Svetlana Georgievna, dermatologist
How do they look
Small cracks in the tongue can be completely invisible to the naked eye; only an experienced doctor can examine them using special instruments. The larger ones are clearly visible to the naked eye; they resemble longitudinal or transverse grooves on the tongue. Deep cracks look like crevices; sometimes the tongue appears to be cracked or split into two parts. If you notice such a problem, consult a doctor, even if nothing is bothering you at the moment. If an infection gets into the crack, the course of the disease may be complicated by the inflammatory process.
Reasons for appearance
Reasons for education:
- lack of nutrients, iron and vitamin PP in the patient’s body;
- anemia;
- lack of B vitamins;
- allergic reaction to toothpaste or medications;
- chronic fatigue and constant nervous tension;
- mechanical damage to the tongue (nervous biting, chewing);
- disruption of capillary blood flow in the tongue;
- the patient has diseases such as gastritis, enterocolitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis;
- wearing uncomfortable dentures.
The main reason why the tongue is cracked is mechanical injuries due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the patient’s body. In this case, it is enough to bite your tongue while chewing food so that a painful crack forms at its tip.
Another fairly common reason why a patient’s tongue is cracked is a malfunction in the patient’s central nervous system, which is caused by chronic fatigue, frequent stress, and lack of sleep. This is a reason to suspect a problem with the hypothalamus.
It happens that patients are perplexed: why there are cracks on the tongue, there seems to be no visible reason for their appearance. In this case, the answer to the question of why cracks appear can only be given by an experienced doctor, after a thorough diagnosis. It is necessary to do a detailed blood test to determine which microelements and vitamins are missing in the patient’s body. Quite often, correction of the nutritional system helps get rid of the disease.
Many people are probably interested in the question of what cracks mean. After all, the tongue, as is known, signals the presence of many diseases and pathological conditions of the human body. Cracks in the tongue are a sign of a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body. Quite often, cracks are caused by worms, as they deplete the human body, causing anemia and iron deficiency. They also indicate a diseased liver, since with this disease the human body does not receive many microelements important for health.
Cracks in the tongue on the side can be a sign of thyroid disease; in this case, it swells and is injured at the edges by the patient’s teeth.
By crack location
Based on the location of cracks, one can judge the following pathological conditions of the body:
- a longitudinal crack in the tongue in the center of this organ is a characteristic sign of glossitis or a disorder of the immune system;
- a tongue riddled with cracks is observed in diseases of the digestive or endocrine systems;
- characteristic symptoms on the tip of the tongue occur in patients with stomatitis, as well as in people under constant stress; in addition, such damage occurs as a result of mechanical impact;
- defects on the lateral surfaces of the tongue are a consequence of blood diseases, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the digestive and endocrine systems.
Of course, this method of determining the cause of the pathological condition of an organ cannot be considered accurate without a thorough examination and examination by a specialist.
Treatment
The main question that worries patients with glossalgia is how to cure cracks in the tongue. In fact, everything is not so difficult. The treatment method depends on the cause of glossalgia.
- First, it is necessary to eliminate the dental causes of tongue cracks - correct an incorrect bite, replace defective fillings, and adjust the prosthesis. Next, the patient should be carefully examined by a therapist, neurologist, and, if necessary, by an endocrinologist and gastroenterologist. And only after this should treatment for glossalgia be prescribed.
- Typically, treatment for fissures consists of drug therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment with medications is to improve blood circulation in the tissues of the oral cavity, as well as to improve general cerebral circulation. For this purpose, drugs such as trental, cavinton, nicotinic acid, and vitamin C are prescribed.
- The tone of the autonomic nervous system should also be improved; for this purpose, sedatives are prescribed - tincture of valerian, motherwort, persen.
- Additionally, the doctor may prescribe procedures such as hirudotherapy or electrical neurostimulation using a TENS device. A good effect is achieved by using electrophoresis, as well as iontophoresis of novocaine.
- If the tongue is severely painful, the doctor may prescribe local painkillers - lidocaine, dicaine.
- If the patient has cracks in the tongue, plaque and burning, it is necessary to adjust the diet. During treatment, you should completely exclude from the diet foods that irritate the surface of the tongue - such as sour juices, vegetables, pickles and marinades. You should not consume large amounts of spices, especially pepper and salt. It is advisable to quit smoking.
- After each meal, be sure to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with salted water or a decoction of medicinal herbs. Oak bark, sage, propolis, and honey have a healing effect.
Types of spots on a child's tongue
In a healthy child, the mucous membrane in the mouth has a slight pink tint without rashes or blotches. Increased body temperature or infection causes the color to change to a more intense red or burgundy due to the rush of blood. Therefore, pediatricians always try to examine the mouth of a young patient to identify a possible problem at an early stage.
Experts divide conventionally dark or white spots on a child’s tongue into several groups:
- Unevenly exfoliated epithelium, in which “islands” of food plaque accumulate on the surface.
- Intensive proliferation of mucosal cells in some areas of the tongue, resembling a compaction.
- Spots with clearly defined boundaries, distinguished by color.
In the first and second cases, the appearance of a defect is the result of a mechanical injury. The baby often bites his tongue when excited, pulls objects with sharp or uneven edges into his mouth, and scratches the delicate surface of the organ with internal braces.
Another common way to get a spot or small growth is by eating too hot or sour foods, which damage the microscopic papillae.
A response occurs:
- epithelial cells die from acids and fly off, sticking to each other;
- uncontrolled tissue growth occurs at the burn site.
In case of injury (cut or crack), recovery is quick and does not require special monitoring. Sometimes parents are alarmed by a brown spot on a child’s tongue: this is how a bruise appears after a bite or burn.
After a few days, the ability to sense tastes and temperature returns. To speed things up, you can treat the baby’s entire oral cavity with antiseptics and herbal decoctions allowed in childhood: chamomile, sage, calendula. Sea buckthorn oil has good regenerating properties. They lubricate the affected areas after any meal.
If increased formation of thickenings is observed, it is imperative to find the cause of this failure.
It is often associated with constant rubbing from braces or biting the tip. This is a unique type of callus that requires consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. In most cases, after removing metal structures and getting rid of a bad habit, the surface of the tongue is leveled within a few weeks without additional procedures or surgeries.