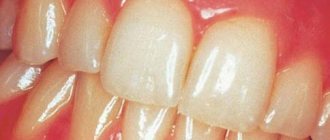
Folded tongue: photos and symptoms
Usually the anomaly is detected in early childhood, but it also occurs in adults, since sometimes this problem does not bother the patient in any way, and the person is not even aware of its presence. The signs of the disease are as follows:
- Macroglossia, or enlargement of the tongue, which can affect a person's speech and chewing function. Usually the patient keeps his teeth in an open position.
- Folds and grooves appear on the surface, which are covered with papillae.
- The tongue is significantly thickened.
- The back and tip of the tongue are smoothed, the filiform papillae have atrophied.
- Increased sensitivity (especially in people who have undergone infectious diseases and surgical operations).
- Regular tingling and pinching sensation.
- Lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Smell from the mouth.
The folds, in turn, are different: transverse, deep longitudinal (and not very deep), fringed. Usually the main longitudinal fold (it is the largest and deepest) runs from the tip along its midline. The remaining folds lead exactly to it.
Sometimes this pathology accompanies desquamative glossitis (geographic tongue) - this is inflammation, as a result of which some areas of the organ become several shades lighter or acquire a gray tint. In general, the picture of the organ resembles a map, which is why it got its name.
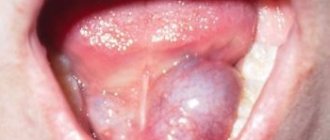
Symptoms of papillomatosis on the tongue
To independently determine the presence of condyloma on the lingual surface, you need to remember several characterizing signs of this formation:
- The growth is always attached to the mucous membrane with the help of a thin stalk or is based on a wide sole, which visually looks like an elevation above the general surface.
- The color of the process is almost identical to the mucous membrane. This is explained by the fact that the wart itself is formed from cells of the superficial layer of the tongue.
- Papilloma is always soft to the touch and resembles the inflorescence of a cauliflower head.
- Multiple papillae may form, the dimensions of which do not exceed 2 mm.
For the most part, such growths are benign formations and extremely rarely degenerate into a life-threatening tumor. However, if such a process on the tongue begins to change its color from pink to darker with a purple tint, bleeds, hurts and periodically becomes inflamed, then this may indicate that irreversible changes have occurred in the wart cells. To prevent the development of this process, it is necessary to promptly treat this pathology.
Possible causes of pathology
The exact causes of the anomaly are unknown. But there are a number of factors that can provoke the appearance of pathology:
- chronic diseases of the liver, stomach, duodenum;
- skin diseases;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- bone marrow diseases;
- acute infections;
- violation of the mucous membrane of the tongue and its trophic function;
- lack of vitamins and essential microelements in the body;
- collagenosis;
- human reaction to vaccination;
- hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, lactation).
Oral health
In front of me is an organ of a layered type, as it consists of membranes: mucous and muscular. The organ belongs to the initial section of the gastrointestinal tract, because its mucous membrane is of the skin type: MPNE. This organ is the tongue. The tongue section passed through the leaf-shaped papillae. Cross section. Leaf-shaped papillae are outgrowths of the STP of the tongue, from which the secondary ST papillae arise. In the thickness of the epithelium covering the papillae there are taste buds, consisting of flattened cells resembling orange slices. The STP CO contains numerous blood vessels. The basis of the tongue is the muscle layer. The muscles run in three mutually perpendicular directions. Below the muscles lie layers of the RVNST, which contain: blood vessels, bundles of nerve fibers, islands of adipose tissue, end sections of the protein and mucous membranes of the lingual salivary glands.
· NO MUSCULAR PLATE AND SUBMUCOSA!!!
· IN THIS PREPARATION YOU WILL NOT FIND THE SO-CALLED LOWER SURFACE OF THE TONGUE, BECAUSE THE LEAF-LIKE PAPILIA ARE LOCATED ON THE SIDE SURFACE OF THE TONGUE AND THE CUT OF THE LOWER. IT DOESN'T GO AGAIN!!!
Amygdala
In front of me is an organ of a layered type, as it consists of membranes: mucous and submucosal. The organ belongs to the initial section of the gastrointestinal tract, as it has a mucous membrane of the skin type (multilayered squamous non-keratinizing epithelium, in this organ it is infiltrated with lymphocytes). This is the amygdala. It is a collection of several folds of the oral mucosa. In the lamina propria of the tonsil, there are numerous lymphoid follicles, which represent the B-zone. The center is the reactive zone, large immature B lymphocytes, the mantle zone is mature B lymphocytes. Interfollicular connective tissue is infiltrated by T lymphocytes and represents the T-zone. The submucosa of the tonsil is its capsule and performs a protective function (limiting the source of inflammation).
· FIND A LONGITUDINAL SECTION OF A NERVE
Esophagus
In front of me is an organ of a layered type, as it consists of membranes: mucous, submucosal, muscular, adventitial. The organ belongs to the initial section of the gastrointestinal tract, so it has a skin-type membrane: MPNE. This organ is the esophagus. Its CO forms longitudinal folds, due to which the lumen of the organ (esophagus) is uneven. The organ was cut transversely. (Next we look at how the cut went):
– the cut was made in the upper part of the esophagus, since the MO consists of PPMT
- the cut was made in the lower part of the esophagus, since the esophagus consists of gastric esophagus.
Submucous membrane of the esophagus - RVNST. It has many blood vessels. MP SO is poorly expressed - single bundles of SMCs. The mucous membrane of the esophagus is the RVNST, which contains many blood vessels and the end sections of the esophagus’s own glands (mucous). The ducts of these glands open onto the surface of the epithelium, and in the section they enter the subcolon, muscle and propria layers. The muscular lining of the esophagus - 2 layers, consisting of their PPMT/SMC: internal circular and external longitudinal (in humans and vice versa in dogs) Be sure to ask the teacher whose esophagus you are looking at!
M/d muscle layers are layers of RVNST containing intramural ganglia (Auerbach's nerve plexus). The adventitial membrane is the RVNST, which without sharp boundaries passes into the surrounding connective tissue.
· RVNST IN JSC IS NEEDED FOR FIXATION
· IF YOU ARE CONFUSED IN MO WITH CUT, K.P. THE CROSS SECTION OF MMC IS COLORED BRIGHTER THAN LONGITUDINAL
Transition of the esophagus into the stomach
This preparation is a section of the digestive tube in the area of the transition of the esophagus to the stomach. Proof of this is the different structure of the shells.
-esophageal epithelium MPNO is replaced by OCE of the stomach
-the relief of the esophagus is smooth (since the cut is longitudinal - there are no folds!), and the relief of the stomach is uneven, numerous pits are visible
-the lamina propria of the esophageal mucus may contain the cardiac glands of the esophagus (may not be present on the specimen), and the lamina propria of the gastric mucosa contains the cardiac glands of the stomach (mucous)
-MP CO of the esophagus consists of 1 layer of SMC, and in the stomach there are 3 of them
- the submucosa of the esophagus contains its own glands of the esophagus (complex alveolar-tubular) and their ducts; these glands enter the subcolon of the stomach, but quickly disappear
-MO of the esophagus – 2 layers of SMC, stomach – 3 layers of SMC (as in the esophagus, mb Auerbachian nerve plexus)
Source: cyberpedia.su
Treatment of folded (scrotal) tongue
The anomaly usually does not bother its owners, however, sometimes they complain about its appearance: cracks.
A folded (scrotal) tongue requires especially careful care. Because food residues may be trapped in the folds. Because of this, bad breath occurs, as well as accompanying unpleasant symptoms: burning and inflammation.
In addition, the grooves may bother people who have suffered acute infections or surgical interventions. The reasons in this case are also clear: the overall tissue reaction in the body decreases, and the sensitivity of the surface of the folded tongue increases significantly. Therefore, it reacts painfully to chemical irritants and drugs.
If the patient does not properly care for the diseased organ, then the inflammatory processes can drag on, and this is a very favorable place for the development of fungal infections.
The dentist treats this pathology. It is he who will select oral care.
Sometimes a folded tongue requires surgery. This happens in cases where the organ is too enlarged and interferes with the patient. The operation involves excision of part of it.
So, in general, drugs are used to eliminate related problems:
- Fungal and bacterial diseases: anti-inflammatory, antifungal drugs, immunocorrectors, antiseptic treatment.
- Candidiasis: clotrimazole cream, shading with aniline dyes, 10% sodium borate solution in glycerin.
- Painful sensations: antiseptic rinses, mouth baths with citral solution, application of medications with anesthesin.
The structure of human language and diseases
Of all the known human organs, the tongue is an accurate determinant of certain diseases. Of course, all the signs are conditional; a person will need a detailed examination to determine the presence or absence of the disease. But it is still worth noting that each part reacts to pathological processes from a different angle.
- The back part of it may indicate a blood disease or a variety of infectious diseases. A noticeable coating will appear on the surface of the organ.
- Poor oral hygiene. A normal tongue should appear pink in color and should be within normal size. It must have a reliable humidity indicator.
- Any plaque present on its surface may indicate the presence of problems in the human body. Therefore, it is worth getting rid of it as soon as possible, regardless of how you are going to solve the problem. In the end, you will be able to improve the condition of the oral cavity and the formation of dental plaque.
Why does plaque appear on the tongue?
Today, the main problem with the appearance of plaque on it is problems with the gastrointestinal tract . That is, there is an inflammatory process in it . The mucous membrane of the tongue consists of many papillae with taste buds. Thus, they can become inflamed at any time.
- A large, enlarged, swollen and white tongue indicates that a person has chronic gastritis with a high level of acidity. It could also be enteritis or frequent constipation.
- If there is a coating on the tongue, this may indicate that the patient is experiencing a serious process in the body. This could be a stomach or duodenal ulcer.
- After a heavy meal, even if the person is healthy. Then the plaque may appear in the morning and disappear during the day. But in the event that plaque is constantly present on the organ, this is the main reason for visiting and consulting a doctor.
In ancient times, people were able to determine the presence of a particular disease by language. Even today, using the knowledge of this plan, it is possible to easily determine the presence or absence of various types of diseases. The front part of the organ can symbolize the condition of the heart and liver. The condition of the gastrointestinal tract will be indicated by the condition of the lower part of the tongue.
The sides of the tongue indicate the condition of a person’s kidneys. That is, if you have knowledge, you can always identify the problem at certain stages of the disease.
Diagnosis of diseases by tongue color
The appearance of plaque , as well as a change in the color of the tongue, may indicate the condition of the body as a whole. The middle part is the gastrointestinal tract. White plaque in this area will indicate gastritis, ulcers and other stomach problems.
The dry appearance of the organ can cause dehydration, as well as the presence of an intestinal infection. In addition, it may be a manifestation of an acute abdomen - peritonitis, appendicitis or internal bleeding in the patient. If there are disturbances in the area of bile secretion, dryness may be accompanied by a bitter taste in the morning. Problems with the thyroid gland and metabolic disorders can be a sign of dry tongue.
In addition, white manifestations may appear on it, which are subsequently removed. White spots will indicate the onset of an infectious disease, these include influenza and parainfluenza. It is worth paying attention to signs of dysbiosis, thrush and stomatitis. If the ulcers become gray in color, this may be the result of injury to the tongue, as well as antibiotic treatment.
It is worth regularly studying your language and paying attention to if it changes a little in your body.
The structure of a healthy organ
The presence of a healthy organ is indicated by a pink tint of the tongue with a central fold over the entire surface. A healthy tongue is soft to the touch and does not cause discomfort. At the same time, it is easy for them to move when talking and eating. The taste data are well expressed and can be distinguished. For a healthy person, a minimal amount of white plaque is a normal condition. Its quantity may vary, but it should be minimal. But the presence of a thin white coating indicates that the pathology is insignificant, but is developing rapidly.
The following diseases can lead to the formation of plaque
- caries;
- gingivitis;
- pathological processes in the gums;
- Oral candidiasis.
The first reason for the appearance of defects in the structure of the tongue may be problems with the gastrointestinal tract, food allergies and lack of vitamins. It can also be the formation of white or yellow plaque. Lumps that occur on the tongue should be examined by a specialist in this field.
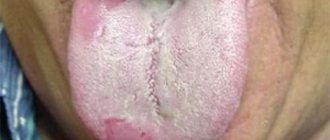
Cracked tongue
The tongue is one of the organs that cannot have a smooth surface. Cracks in the tongue can occur in chronic diseases and persistent mental disorders. A variety of cracks may indicate the following problems.
- dysfunction of a part of the brain;
- the occurrence of an allergic reaction;
- somatic problems in the body.
If cracks are found in the tongue, you will need to consult a doctor, as there is a possibility of pathological processes. If the cracks are in the middle, there is a possibility that there are problems with the spine. Curved cracks may indicate that there are problems in the lower back and cervical region.
Wounds and ulcers on the tongue
Ulcers, wounds, and plaque are not a rare occurrence on the tongue and can occur for various reasons. These may include injury to the tongue, thermal effects on the tongue, problems in the dental area and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In some cases, Crohn's disease may manifest itself.
These ulcers can range from small to large in size. Their presence in small quantities can cause discomfort.
One of the main problems that can cause ulcers on the tongue is syphilis. Treatment must be quick and professional. In this case, there will be several ulcers that will quickly spread over the surface of the tongue. In the case of syphilis, the surface of the tongue will be shiny, hard and red. But such an ulcer is not painful.
Quite often, warts form at the root of the tongue or on the sides. This indicates that the person has HIV. If flat ulcers form at the end of the tongue, along the sides and along the lines, this indicates that the person has the initial stage of tuberculosis.
Features of care
If you have this pathology, you do not need to self-medicate; careful care and supervision by a specialist are required. In general, you should take care of your oral cavity as follows:
- general oral hygiene;
- rinsing;
- if the patient uses removable dentures, they should also be thoroughly cleaned after eating;
- it is necessary to avoid spicy, salty food, it should not be too hot or cold;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- You need to brush your teeth with a special paste;
- the toothbrush should be made of synthetic materials: this will help avoid damage;
- regular visits to the dentist.
Such careful care will help neutralize the oral cavity from bacteria, which will prevent their proliferation and the occurrence of associated infections.
Article Expert:
Treatment of pathology
Before starting treatment, you should consult your pediatrician or therapist. He will collect information about existing diseases, give directions for a blood test, tongue scraping and saliva testing for bacteria. This is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
It is necessary to give up smoking and alcoholic beverages. In addition, it is important to rationalize your diet: exclude hot, spicy, salty and any other foods that provoke discomfort and inflammation of the tongue.
Drug treatment
After eliminating extraneous factors, you can begin treatment with drugs:
- antiseptic solutions;
- antimicrobial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiallergic;
- cooling and healing-accelerating gels, ointments and compresses;
- antifungal;
- immunostimulants;
- vitamins;
- painkillers.
Laser evaporation
During the operation, the grooves are sutured, and then the folds and remaining grooves are evaporated with a laser. After the operation, the tongue becomes smooth. The operation is contraindicated before 5 years of age. Ideally, after 18 years of age, because in adolescence, all the muscles of the body grow rapidly and all efforts can be nullified.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Treatment during these periods consists of using herbal gargles. If after restoration of hormonal levels the changes do not disappear, systemic treatment is prescribed.