Why does biting happen?
As a rule, the tongue is not seriously damaged and causes only mild discomfort to the person. But in some cases, the damage is accompanied by the appearance of blood, pain, significant wounds (this happens due to sports injuries, a fall, a blow, etc.).
We will look at what to do if there is bleeding from the tongue, how to heal the wound and avoid complications.
Often a person unknowingly bites the soft tissue of the mucous membrane, after which he becomes aware of the problem through the salty taste of blood in the mouth, vibration at the bite site, burning and pain. A number of observations and studies made it possible to form a group of factors that most often lead to damage to the mucosa.
The cause of tongue bite may be congenital malocclusion, a defect in the structure of the jaw, or pathology of dental development.
- Thoughtfulness . While thinking about important projects or everyday worries, daydreaming, or concentrating on studying material, we automatically chew our lips and the inside of our cheeks, and sometimes, out of zeal, we can bite our tongue.
- This often happens during chewing , when a person quickly and thoroughly chews food, while being distracted by his thoughts, TV, newspaper or interlocutor. While eating, try not to talk with your mouth full to avoid damaging soft tissues. Also, you should not eat in a hurry, throwing large pieces into your mouth.
- Sometimes there are dental reasons for such situations. This may be a congenital malocclusion, a defect in the structure of the jaw, a pathology in the development of teeth (chaotic arrangement, unnatural direction of growth, etc.).
Very often nowadays people bite soft tissues due to improperly manufactured or installed dentures and implants.
- Separately, it is worth highlighting anesthesia in the group. After performing dental, plastic and other manipulations in the area, local anesthesia wears off for 2-4 hours, during which the patient can eat and communicate. A person practically does not feel the numb parts, so he can literally “chew” the soft mucous membrane and tongue. Unfortunately, in this case, he learns about the problem only a few hours later, when the anesthesia stops working and the first painful sensations appear.
- Habit . This reason is also quite common and is related to the first point about thoughtfulness. For some people, the desire to chew and bite the mucous membranes, lips (and then, by chance, the tongue) arises in any situation: fear, panic, concentration, decision-making, excitement, fascination, surprise, etc.
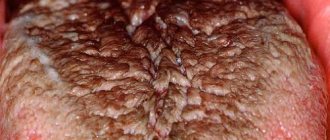
Crack in the middle of the tongue
The formation of a pronounced stripe exactly in the middle of the tongue can be a sign of 2 types of glossitis:
- A folded tongue, which is a congenital feature and is observed in a person from birth. The syndrome is also called scrotal tongue. The surface in this case is covered with grooves, which are located symmetrically relative to each other. One of them is clearly in the center. Scrotal syndrome does not cause discomfort or other painful manifestations.
- Diamond tongue is considered a chronic disease. This is characterized by the appearance of a red, diamond-shaped area near the root of the tongue. Since the disease is chronic, symptoms may disappear or reappear. No pain is observed. The surface within the boundaries of the diamond-shaped area is smooth or bumpy.
A crack in the middle of the tongue is formed due to a weakening of the body's immune system. At the same time, increased dryness is observed in the mouth, which provokes the formation of furrows.
When medical intervention may be needed
Sometimes a small wound after a bite can heal on its own, and a person will forget about it within a few hours. But in other cases, when there is a fall, a dislocated jaw, a bruise or blow to the area, the tongue and other soft tissues of the mouth can be severely damaged, which may even require the help of specialists.
If your tongue is seriously damaged, you should consult a specialist.
Let's look at the main symptoms of complications after biting:
- the muscle is very swollen and swollen at the site of the bite;
- a brightly colored hematoma has formed in the area, which causes discomfort during eating and communicating;
- in the morning you can see blood on the tongue, the reasons for which are a strong bite depth, for example, when the tooth has completely passed through the soft tissue, or poor blood clotting, which is why the wound continues to bleed after a long time;
- a long and deep wound with jagged edges has formed, from which blood oozes during chewing, communication and muscle tension;
- initially there was no noticeable discomfort, but gradually the situation began to worsen, the tongue became swollen, sore and numb, taste and temperature receptors were impaired;
- the wound began to fester and darken, become inflamed and increase in volume, which may indicate infection;
- plaque, characteristic rashes and ulcers (stomatitis), other dermatitis and inflamed areas appeared on the tongue, which also indicates that pathological microflora has entered the wound.
When should you see a doctor?
- The swelling and wound do not disappear within 4 days.
- On days 2 and 3, the wound begins to increase in volume and spread to healthy areas.
- Pain, burning sensation and discomfort persist for more than 3 days while eating food and liquid, or communicating.
- The hematoma at the site of the bite did not resolve within 3-4 days.
- We noticed suppuration and discoloration of the area, plaque formation, pimples and ulcers, and furrows on the tongue.
- The integrity of the muscle has been seriously compromised (bitten through, part of the tongue bitten off, jaw or lips not closing properly).
Try to get an appointment with a therapist, otolaryngologist or dentist as soon as possible.
Bleeding tongue: causes, description of symptoms, treatment and dental consultations
The tongue reflects the condition of the internal organs (especially the digestive system), so any cracks or plaque could be signs of serious health problems. But most often the tongue bleeds for completely harmless reasons, that is, due to mechanical injury.
Questions of physiology
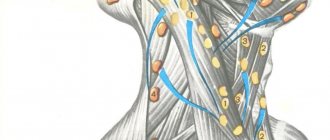
The tongue is an organ consisting of striated muscle tissue, externally covered with a mucous membrane.
It relates to the digestive system, participates in the process of grinding food, preparing products entering the oral cavity for the further process of digestion.
The spade-shaped body of the tongue helps to mix food, crushed into small fragments and moistened with saliva.
The tongue contains many taste buds, which determine the sensation of taste.
At the tip there is an area responsible for recognizing sweet taste, on the sides of the front of the tongue the salty taste is determined, and on the lower part - sour. The root zone is responsible for the perception of bitterness.
The tongue is the most mobile organ of the speech apparatus, so it ensures the reproduction of a huge number of words and individual sounds.
Causes of bleeding
Why does my tongue bleed? The most common cause is trauma, which can be thermal (burn), mechanical (cut, bite), chemical (irritation) or physical in origin.
The taste of blood in the mouth may appear when eating quickly, after talking, or when chewing.
Injury can be caused by sharp protrusions of dentures or the edges of decayed teeth, fragments of food (bones), cutlery (fork, knife), during dental procedures (preparing the dentition for the installation of crowns).
Mechanical damage
If your tongue is bleeding, the cause is most likely mechanical damage. As a rule, this is an injury caused by negligence during eating, talking or dental procedures.
Physical injuries are mainly caused by a maxillofacial blow or an accident. Thermal damage occurs when burned with steam, drinking too hot drinks, the cause may be fire, radiation, or an electrical appliance.
Chemical damage occurs when aggressive chemicals come into contact with the mucous membrane.
Pathological condition
If your tongue bleeds, this may be one of the symptoms of glossitis.
Inflammation is caused by viral or bacterial microflora; it can be an independent pathology or accompany some systemic diseases.
For example, stomatitis is often caused by the entry or activation of the herpes virus into the body. Mechanical injuries contribute to the development of the disease; smokers and people who abuse alcohol are at risk.
If the tongue bleeds, common causes of this condition are concomitant pathologies: liver diseases (carcinoma, cirrhosis, hepatitis), chronic renal failure, chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, intestinal inflammation, peptic ulcer. This symptom is characteristic of intoxication with salts of heavy metals, helminthiases, and vitamin deficiencies.
The first sign of the disease is a feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity. Then salivation increases, swelling occurs, the tongue becomes bright red, taste sensations become dull, and eating becomes painful and difficult.
Often the patient's speech becomes slurred due to swelling. If left untreated, mushroom-shaped growths may form on the tongue.
If the disease is caused by an infection, then symptoms of inflammation are characteristic: local fever, swelling, general deterioration of well-being.
Diagnosis and treatment
If your tongue hurts or bleeds, you should consult a doctor. The specific clinical picture allows a diagnosis to be made during a routine dental examination. To clarify, bacteriological, biochemical, histological, cytological or serological diagnostic methods are used. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will make a diagnosis. Glossitis can be:
- deep, localized in the area of the floor of the oral cavity;
- diamond-shaped, usually developing against the background of chronic diseases;
- folded - congenital anomaly;
- desquamative (“geographical language”);
- Gunter's, which is a symptom of folic acid or vitamin B12 deficiency;
- interstitial, accompanying syphilis in the third period.
If your tongue bleeds, what should you do? To make eating easier, you should give preference to pureed soft dishes and soups.
During the day, as well as before and after meals, rinsing with a weak antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine, furatsilin) is recommended. In cases of severe pain, applications with antiseptics are used.
Plaque is removed with a swab soaked in proteolytic enzymes. The skin regeneration process is accelerated by local products with vitamin A.
In rare cases, surgery may be required. Strong anti-inflammatory, antifungal agents and antibacterial drugs are prescribed according to indications. Hormonal medications (hydrocortisone, prednisolone) in the form of ointments for topical use are used in short courses for difficulty breathing.
Possible complications
In advanced forms of the disease (if the tongue constantly bleeds, removal of plaque is accompanied by severe pain, there are purulent ulcers), an abscess may form.
At the same time, salivation increases significantly, the tongue greatly increases in size, acute throbbing pain occurs, and speech is impaired. A serious complication is the development of phlegmon.
Suppuration becomes pronounced, speech and breathing become difficult, the patient refuses to eat, and possible attacks of suffocation. Symptoms of general intoxication of the body become pronounced.
Cracks in the tongue
The tongue cracks and bleeds for other reasons.
Cracks can appear due to a lack of vitamins (especially vitamin A and group B), anemia, diseases of the blood and digestive system (ulcers, colitis, gastritis), hormonal imbalances, damage to the body by parasites, allergic reactions.
The cracks may not bleed, and symptoms include swelling, discomfort when chewing food, burning, dry mouth and loss of taste. Blood may appear when cracks are damaged.
Treatment of cracked tongue
If the tongue bleeds in the morning, then first of all mechanical factors and an allergic reaction to oral care products should be excluded. It is necessary to adjust dentures and fillings, correct the bite, change toothpaste or brush (replace with a softer one). Treatment usually includes rinsing with disinfectants and sanitation of the mouth.
First, you should contact a dentist, who, if necessary, will refer the patient to a therapist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists. Complex vitamin supplements, pharmaceuticals, and physical therapy are often prescribed. If there is a concomitant disease that can cause the tongue to bleed, then treatment must be started.
It is important to adjust your diet. Usually it is recommended to exclude smoked, spicy and salty foods, and give up bad habits. As part of drug therapy, painkillers (Lidocaine, Novocaine), disinfectants (potassium permanganate, soda, furatsilin solution) and normalization of blood supply (Trental, Capoten), and electrophoresis are used.
Modern medicine offers hirudotherapy among the methods of treating cracks in the tongue that cause bleeding. Leeches are placed directly on the tongue and lips, sometimes on the palate. Many years of experience in using this method of therapy have shown excellent results, but not every patient will decide on a specific procedure.
First aid for a serious bite
If there is no medical worker near you, and there is no opportunity to go to the hospital (the incident happened in the forest, on the beach, in the countryside, etc.), then you should provide first aid to the victim.
Of course, we are talking about serious bites, accompanied by bleeding and disruption of tissue integrity. If the bite is minor, it is enough to rinse your mouth with cool water or alcohol to disinfect the area and refrain from eating for the first few hours.
So, what should be the first aid for a bite?
Ice should be applied to the wound site to stop bleeding.
- Stop the bleeding. Many people have no idea how to stop bleeding from the tongue at home. To do this, the patient rinses his mouth with cold water and applies a piece of ice or an ice bottle to the injury site to numb the pain and stop the bleeding. If possible, apply a cotton swab soaked in peroxide or chlorhexidine to the bite site. It is important not to overdo it here, because chemical solutions can damage the enamel and get into the esophagus.
- Now let's move on to pain relief. To reduce discomfort, keep the ice on the bite site longer. If possible, apply a solution of lidocaine or novocaine, lubricate with baby gel, and take an oral drug that acts as an analgesic.
- In the oral cavity of every person there is a pathogenic microflora, which, if it enters an open wound, can cause suppuration, infection, and further inflammation. You can disinfect the wound with a solution of methylene blue (not iodine or brilliant green), chlorhexidine, or, in the absence of such, an alcoholic drink (vodka, cognac, low-alcohol drink, etc.).
- After disinfection, isolate the area, try not to speak, and refuse food for several hours. From the liquid you can drink water, compote and tea. From now on, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Current treatments
The bleeding of an injured tongue increases due to the content of blood vessels. This is caused by the structure of the organ; the tongue consists of muscle tissue, which requires blood flow. Stopping bleeding is easy, you should use these tips:
- To prevent infection, which may lead to consequences, it is worth rinsing your mouth with an antiseptic and hydrogen peroxide.
- You can speed up the process of blood clotting and slow down blood flow using ice packs. You can wrap a napkin or a paper towel in a few ice cubes and apply it to a specific area.
- If the bleeding is not severe, you need to take a piece of gauze, fold it several times and press on the swollen area to reduce the flow of blood.
- If suddenly the advice does not help, then you need to call an ambulance or go to the clinic yourself. Stitches will be required.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?
An examination of the affected organ by a qualified specialist can help stop the bleeding and determine the cause of its occurrence. Speaking about oral ulcers, we can say that there is definitely no threat to the human body from a small amount of blood. If such a situation arises, it is sufficient to treat the areas with antiseptics.
And injuries characterized by wounds or cuts require surgery. In such a situation, catgut sutures are applied and the organ is disinfected. Suspecting the presence of a foreign body inside a puncture or cut, the wound is examined with a probe.
If there is heavy bleeding, it is difficult for the doctor to apply stitches. In this situation, he resorts to ligation of the artery.
How to heal a wound after biting
After you have stopped the bleeding, numbed the area and disinfected the area, you should promote the speedy healing of the wound. The faster it heals on its own, the lower the chance of going to the doctor with complications.
So, what should be the actions after providing first aid?
To heal the wound, you should rinse your mouth with a pharmaceutical mouthwash, as well as herbal decoctions.
- When you get home, you should thoroughly and carefully brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with a pharmaceutical mouthwash. These manipulations should be performed after every snack, sleep, and also at night.
- Additionally, several times a day we rinse our mouths with a decoction of oak bark, sage, calendula, St. John's wort, chamomile and other herbal infusions.
- Also treat the area with a disinfectant solution (furacillin, trachysan, chlorhexidine) a couple of times a day. Antiseptic sprays and lozenges are also suitable.
- Creates a competent menu. First of all, avoid drinks and foods that are too hot or cold. Thermal irritation of the mucous membrane interferes with spontaneous healing. Cold drinks can be used only in case of severe pain for pain relief in the absence of more effective anesthetics.
- The menu should be filled with vitamins that promote active healing (group C, B, etc.). Lean on raw vegetables, fruits, herbs and meat products.
- Contact your doctor. Many people ask what to do if a child bites his tongue until it bleeds.
Here, try not to get carried away with cold liquids and chemicals, but as soon as possible get an appointment with a pediatrician for competent medical care.
How to stop bleeding on the tongue due to injury?
- Structure and functions of language
- Injuries on the tongue
- How to stop bleeding on your tongue
Tongue injuries are a very common occurrence. And they are often accompanied by bleeding. Let's talk about how to stop bleeding on the tongue.
Structure and functions of language
The tongue is an outgrowth of the floor of the oral cavity. It is found only in vertebrates. The shape and position of this organ are very variable and depend on the functions that it performs at one time or another. When the tongue is at rest, it is spade-shaped and fills the oral cavity. The tip touches the back surface of the teeth.
The human tongue is composed of striated muscle tissue. This organ is covered with a mucous membrane. Anatomically, the organ is divided into the root of the tongue and the body of the tongue. The upper surface of the tongue is called the dorsum. The tongue has two grooves: terminal and longitudinal, and under it there is a frenulum - a fold of the oral mucosa.
The human tongue plays an important role in the process of chewing, speech, taste and salivation. This organ is also very important in the process of sucking milk by an infant.
The lips grab the nipple, the soft palate closes the pharynx, and the tongue acts as a piston. So, it moves back, creating negative pressure. When the jaw is raised, the milk is swallowed.
Therefore, the child’s tongue is quite large and occupies the entire oral cavity.
The tongue is the main organ of taste. Taste buds are located throughout its surface. The tip of the organ is responsible for sweet, the side edges of the front part are for salty, the side edges of the back part are for sour, and the root is for bitter. Through the pores, food enters the taste buds, chemical irritations become nerve impulses that transmit information to the nervous system.
Interestingly, in animals this organ performs many more functions. In dogs, for example, it is a means of thermoregulation. In hot weather, they stick it out of their mouths and breathe actively.
This is the only part of their body that can actively evaporate moisture, namely saliva. Excess heat also disappears with evaporation. And cats use this organ as a tool for hygiene procedures: with its help they lick themselves and their cubs.
Also, the cat's tongue has special tubercles - they make it possible to separate the meat from the skeleton.
Injuries on the tongue
Organ injuries are divided into mechanical, chemical and physical. Bleeding most often occurs due to mechanical damage.
This can be biting the tongue while eating or talking, preparing teeth for crowns using a probe, bur or disc, filling teeth, damage from dentures, blows to the face (mainly on the jaw), wounds with a bone, knife or fork.
The result of mechanical trauma is a mechanical ulcer or, in more severe cases, superficial erosion. Treatment of such a wound depends on its size. Minor injuries are treated with an antiseptic. Until complete healing, you need to carefully monitor oral hygiene: rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours with special products.
For deep wounds, stitches are applied. Self-medication is unacceptable here, but first aid is very necessary: stop the bleeding, ensure the cleanliness of the mouth, and rest the tongue.
How to stop bleeding on your tongue
To stop bleeding from your tongue, follow these rules:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry them with a towel. You can use antiseptic and rubber gloves. Achieve maximum sterility. This is necessary to prevent germs and infection from entering the tongue. Inflammation in this organ is very unpleasant, painful and difficult to treat. If infected, you will not be able to speak, eat or even drink normally for a long time.
- Take the appropriate position. Sit down and tilt your head forward to prevent blood from flowing down your throat, interfering with your breathing and ability to speak. But be prepared for blood to start leaking from your mouth: prepare a container or lean over the sink.
- Remove anything from your mouth that could interfere with you or cause additional damage to the wound. This could be chewing gum, tobacco, piercings, dental braces, etc. Try not to talk so as not to strain your tongue again.
- Stop the bleeding by covering the wound. Take a sterile material that you can press to the wound (gauze, clean napkin, cotton pad, etc.). Apply the material to the wound and apply light pressure. You need to hold it for at least 15 minutes until the bleeding stops completely. Change material if necessary. Do not check the wound for the first 15 minutes. Only when you notice that there is less blood on the material, look at the wound. Determine the approximate time during which the bleeding should stop. Add another five minutes to it - just in case. Wait this time, make sure the bleeding has stopped, and remove the material from the wound.
- Rinse your mouth with cold water - this will wash away any remaining blood, slow down bleeding and moisturize the oral cavity. Then rinse your mouth with an antiseptic - it will destroy all possible bacteria.
- If you notice irritation or feel pain, apply a piece of ice. You can take any painkiller according to the instructions.
In the first days after an organ injury, do not engage in heavy work or physical exercise - this may provoke new bleeding.
If you have a swollen tongue, broken teeth, or a blow to the head or jaw, see your dentist.
Traditional methods will help cope with severe pain on the organ due to injuries. Bedstraw is very useful, promoting wound healing. Add a tablespoon of herb to a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 30 minutes, filter and rinse your mouth with this decoction.
Sage infusion will also help - its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect is useful. So, 2 tbsp. l. immerse in 1/2 liter of boiled water, let stand for half an hour, rinse your mouth with the infusion 10 times a day. The benefits of St. John's wort and crushed burdock roots are also known.
Of course, the best way to avoid pain and bleeding on the organ is prevention. However, much to our chagrin, the tongue is a very delicate organ that is susceptible to many injuries.
Even teeth or spicy food pose a danger to him. Therefore, we can only urge everyone to be careful and careful with the language.
And of course, do not forget about basic self-help skills, for example, stopping bleeding from your tongue on your own.
Source: https://abrikosov-sons.ru/krov/kak-ostanovit-krov-na-yazyke
Prohibited actions after biting
Faced with such a rare case as a strong bite, many people panic and begin to use all the means at hand. Let's look at what you shouldn't do immediately after tongue damage:
It is forbidden to apply antibiotics, burning ointments, iodine and other agents that can cause a burn to the wound.
- drink herbal infusions hot or chilled in the refrigerator;
- use alcohol tinctures with vodka (they can burn the mucous membrane and increase pain);
- apply iodine, brilliant green, alcohol and other burning ointments to the wound, which will again cause a burn on the delicate surface and can aggravate the situation;
- press on the wound with your fingers, teeth, press your tongue to the roof of your mouth, etc.;
- introduce infection into the mouth through dirty hands and nails, unwashed foods and objects (pen cap, pencil, cork, etc.);
- sprinkle antibiotics on the affected area or take them orally without a doctor's prescription.
Compliance with the above recommendations will help to heal the defect quickly and without consequences.
[tube] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n-EWc05XT2o ">