Why do my gums hurt? The main causes and diseases in which pain is expressed
The reasons for this condition, when the gums hurt and ache, can be different:
- dental diseases;
- injuries and damage to soft tissues, foreign objects;
- psychosomatic diseases.
Often the cause of sore gums is improper or insufficient oral care. As a result, inflammatory processes occur, which, with the addition of secondary problems or the ingress of pathogenic bacteria, manifest themselves in the following dental diseases:
- Stomatitis.
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Periodontitis and Periodontitis.
The cause may also be a large amount of tartar, a cyst, an abscess, or a fistula.
| Major dental diseases | Causes, manifestations | What other symptoms besides pain? |
| Stomatitis | An inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa due to a violation of its integrity and the entry of bacteria and viruses. It can be caused by trauma, burns, during the installation of prostheses, or in the presence of streptoderma, scleroderma. | Ulcers, blisters, erosions on the oral mucosa. Redness of the gums. Swelling around the affected areas. |
| Gingivitis | Pathological inflammatory process in soft tissues without violating its integrity. It occurs as a result of malocclusion pathology, trauma, immunodeficiency, metabolic disorders, and a large amount of dental plaque. | Bleeding, redness, swelling, unpleasant odor from the mouth. |
| Periodontal disease | The disease is characterized by a deep inflammatory process in the periodontal tissue. Often the damaging factors are bacteria and viruses. Without treatment, teeth may fall out. Causes: chronic diseases of teeth and gums, gastrointestinal tract diseases, heart diseases. | Bleeding, inflammation, redness of the gums. Loose teeth. |
| Periodontitis and Periodontitis | Periodontitis is an inflammation of the gum tissue that, if left untreated, becomes more complicated and develops into periodontitis. Diseases of the roots of teeth and the connective tissue around them. Reason: caries and penetration of bacteria into the open root canal, bruise in the root area or tissue damage, errors during dental treatment. | Increased body temperature. Swelling around the affected tooth, its mobility. Bruise and swelling on the cheek. Bad breath. Abscess. |
The appearance of pain in the gums is sometimes caused by secondary causes:
- Diseases of the blood and endocrine system.
- AIDS, HIV, tuberculosis.
- Diabetes.
- Pregnancy.
- Benign or malignant neoplasms.
- Long-term use of certain medications.
Pain after treatment or tooth extraction
After dental procedures with rupture of tissue integrity, severe pain in the gums may occur, which is a completely natural process. This is a normal reaction of the body to external intervention and usually goes away within a few hours or 2-3 days, depending on what procedure was performed:
- removal of a tooth;
- treatment;
- installation of prostheses, implants;
- cutting off the “hood” when wisdom teeth grow.
If the pain does not go away within the period agreed with the dentist, then there is a possibility that pathological processes are occurring in the oral cavity at the site of the procedure that require additional treatment.
Types of painful sensations
So, we found out that in addition to damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane, including as a result of poor-quality dental treatment, the cause of throbbing pain can be one of the diseases described above. In addition, specialists take into account the nature and intensity of painful sensations, which largely depend on the location of the tooth. In some situations, patients experience constant pain, while in other cases the symptom manifests itself in short-term attacks. Below we discuss in detail the most common reasons why patients complain of pulsation in the gums.
Discomfort under the filling
If your gums begin to ache and pulsate under a recently filled tooth, then first you need to consider the type of filling. So, for example, temporary filling is often carried out with the aim of killing the pulp. In this case, a devitalizing agent is added, which gradually destroys the neurovascular bundle. Therefore, the patient may experience pain under the gum for the first few days as the pulp gradually dies. However, if the symptom persists for a longer time, you should definitely see a doctor.
If you feel discomfort under a permanent filling, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If a patient has a permanent filling installed, under which pulsation has appeared, in any case you will have to contact the dentist, and most likely you will need to take an x-ray of the problem tooth. There are quite a few potential causes of pain here: from banal caries to periodontitis.
Pulsation under the crown
Why might pulsation appear under the crown? Most often, this is due to poor quality treatment of the nerve or penetration of infection beyond the apex of the tooth during mechanical cleaning of the root canal before prosthetics. In such a situation, the only way out is to urgently contact your doctor to eliminate the consequences of the errors. If you do not respond to the problem in time, you may be left without a tooth altogether.
If the tooth under the crown is bothering you, this indicates a problem.
Pain in the area of the extracted tooth
However, most of the patients' questions are related to what to do if throbbing pain appears after tooth extraction. Obviously, extraction, especially when it comes to wisdom teeth, inevitably causes postoperative pain, since this is a rather complex and serious procedure. Injury to soft tissues occurs, and it takes time for them to fully heal and restore. Here you need to be extremely careful, since it is one thing when it comes to the natural reaction of the body, and quite another when it comes to complications. One of these is alveolitis - suppuration of the socket due to the loss of a blood clot, which serves as protection against infection entering the wound.
The photo shows inflammation of the socket after tooth extraction
The gums pulsate, but do not hurt
When pulsation occurs in the gums, but a person does not experience any significant pain, most often this indicates the development of apical periodontitis - suppuration causes the feeling that a pulse is clearly visible somewhere inside the jaw. This phenomenon is associated with the process of releasing space for purulent exudate1.
Inflammatory processes in the periodontal tissues cause itching and pulsation
At rest, the patient does not experience pain, but discomfort may appear when pressing on the tooth while chewing food or hygienic cleaning. This symptom is characteristic of inflammatory processes spreading in the tissues surrounding the tooth, namely in the periodontal tissues. Also, pulsation without visible pain may appear in the first stages of the formation of a hilar cyst.
Reasons why teeth ache
Aching, throbbing pain in the teeth or gums, which develops into acute or subsides, may be the cause of:
- development of an allergic reaction;
- the appearance of microcracks;
- eruption of wisdom teeth;
- inflammatory process under a crown, pin or filling.
- sinusitis;
- angina pectoris;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- improper growth of teeth.
Aching pain is sometimes periodic and occurs for psychological reasons, more often in suspicious people.
Treatment
If you experience any pain in the mouth, discomfort in the gums, even if it is short-term, or when your teeth are aching, you need to contact a dentist to find out the true cause and for the correct treatment.
Relief of pain in gums and teeth
Sometimes toothache is intolerable, and there is no opportunity to visit a doctor at this time. Therefore, the question arises: what to do if your teeth and gums ache, how to treat it? Pain is relieved with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics in the form of tablets, gels, ointments, and rinses.
| Pills | Rinse, sprays | Gels, ointments |
| Xefocam, Ketanov, Ketorolac | Furacilin | Metrogil Denta |
| Nurofen | Miramistin | Paradontax |
| Nimesil | Chlorhexidine | Holisal |
| Aspirin | Hydrogen peroxide | Asepta |
| Spasmalgon | Forest balm | Periodonticide |
| No-shpa | Chlorophyllipt | Argosulfan |
| Paracetamol | Tantum Verde | Nise |
| Diclofenac | Stomatophyte | Dentol |
| Analgin, Baralgin | Listerine | Kamistad |
Treatment of the cause of aching pain in the gums
It is possible to cure aching pain in the gums and teeth only if the cause is completely eliminated, so you need to consult a dentist.
- In case of tartar, carry out a cleaning procedure.
- For stomatitis, rinse with an antiseptic and treat mouth ulcers.
- For gingivitis, correct the bite, take a course of anti-inflammatory pills and vitamins, and normalize metabolism.
- For periodontal disease, depending on the stage, undergo a course of drug treatment or surgical intervention.
- For periodontitis, in most cases a complex of methods is used: surgery, drug treatment and physiotherapy.
- When wisdom teeth erupt, use gels or cut off the “hood”, and in case of abnormal growth, remove it.
In other cases, a diagnosis of the patient’s health as a whole is carried out in order to determine the cause and eliminate it.
Treatment of gums at home
At home, gum treatment is carried out only in mild cases, in case of gum damage (trauma, scratch), stomatitis or teething. For this purpose, special means are used: tablets, ointments, rinses:
- Rotokan.
- Malavit.
- Solcoseryl.
- Mexidol Dent Fito.
Traditional methods of relieving pain
To treat pain in the gums, traditional methods are used:
- Rinse with soda or in combination with iodine. 1 tsp. soda and 5 drops. iodine for 1 tbsp. warm water 3-4 times a day.
- 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. 1 tbsp. l. dilute in 1 tbsp. water, rinse 2-3 times a day.
- Dental phytocomplex or herbal collection, which is brewed in 0.5 liters of water 2 tbsp. l.
- A decoction of oak bark, sage, chamomile or calendula. Pour 1 tbsp into a container with 0.5 liters of hot water. l. one of the herbs and boil for 5-7 minutes. Then cool, filter and rinse the mouth with a warm solution 3-4 times a day.
- Alcohol tincture of propolis 5 drops. per 200 ml of warm boiled water. The rinsing procedure is performed 3–5 times a day.
- Solution with tea tree oil 5 drops. for 250 ml of water.
- Calamus root 2 tbsp. spoons are boiled in 0.5 liters of water, then infused for 60 minutes, filtered and used as an antiseptic solution for gums.
Prevention of gum disease
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from gum pain, but by following general recommendations, you can reduce the risk of dental diseases.
- Clean the mouth 2-3 times a day with a toothbrush and quality toothpaste, floss and mouthwash.
- Do not consume low-quality foods and drinks, avoid smoking and alcohol.
- Take vitamins.
- Eating not only soft food, but also gnawing hard food (carrots, apples).
To prevent the occurrence of diseases, visit the dentist once every six months.
Aching pain in the gums - main causes, treatment
Aching pain in the gums is a problem that occurs in our oral cavity much more often than caries. Sometimes these two pathological processes are closely related. But very often, soreness in the gums is the cause of an independent disease. A reasonable question immediately arises: what do such unpleasant sensations threaten us with, besides discomfort?
Can they signal serious pathologies or is it just a minor functional disorder of our masticatory apparatus that will go away over time on its own, without intervention on our part? Let's look at this problem in more detail. This will help us better understand the causes of pain in the gums.
Why does a healthy tooth hurt?
Is the tooth intact, but does it hurt when you press it? The appearance of the oral cavity does not indicate its health. There may be no visible damage, but numerous pathological processes may occur in the tooth root and surrounding tissues.
If the whole tooth hurts when pressed, you should consult a dentist, as there may be serious damage to the root or root zone. Lack of timely treatment can lead to serious and irreversible consequences.
If seemingly healthy tooth when pressed, it could be the following pathologies:
- Inflammation of the gums (periodontal disease). Initially, the disease does not cause pain and is manifested only by bleeding gums. Over time, the inflammation progresses and is characterized by the tooth aching when pressed.
- Mechanical damage (cracks in enamel). Due to minor mechanical damage to the enamel, dentin is exposed and sensitivity worsens. Thus, severe pain may occur when pressing on the tooth while drinking cold or hot drinks, sour foods, etc.
- Damage to adjacent teeth can cause pain in healthy teeth. All this is explained by the structural features of the nervous system that innervates the oral cavity.
- If the gum under the tooth hurts when pressed, then most likely it is hidden caries. The disease is dangerous because it does not manifest itself visually. Caries can develop on the back surface of the crown or deep within the root system.
- Hidden pathologies. This should include a cyst and injury. These diseases may not be noticeable during external examination, but as they progress, they can cause pain in the gum above the tooth when pressed.
- Inflammation of the facial nerve. Sometimes the cause of discomfort may not be a dental disease. Inflammation of the facial nerve can spread to its branches, which are responsible for innervation of the upper and lower jaw. As a result, the gums and teeth hurt when pressed.
- Cold. Often patients with ARVI complain that pain appears when pressing on the tooth. This is due to the fact that against the background of the disease there is an exacerbation of pathological processes that previously existed, but did not bring any concern.
Why do my gums hurt?
The vast majority of discomfort in our gums is caused by dental diseases, in particular:
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- stomatitis;
- periodontal disease.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a pathological inflammatory process that occurs in the gums and is accompanied by swelling, redness, and bleeding. The disease is a consequence of infections, injuries, malocclusion, metabolic disorders, and vitamin deficiency. Sometimes it acts as a concomitant symptom of other diseases of the oral cavity (periodontitis, periodontal disease).
In addition to gum pain, signs of gingivitis include:
- ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- odor from the mouth;
- increased pain in the tooth when pressing, biting, or eating.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathology can take catarrhal-necrotic forms and lead to complete loss of teeth.
Periodontitis
A lump on the gum hurts when pressed - a common symptom with which patients with periodontitis turn to the dentist. This pathology refers to inflammation of the root membrane (periodontal tissue), which is the connective tissue surrounding the tooth root. The disease is characterized by acute pain in the affected area, aggravated by touching the affected area, as well as swelling of the gums, mobility of the affected tooth, increased temperature, and swelling of the cheek.
If the gums are swollen and painful due to periodontitis, and a person puts off a visit to the dentist in every possible way, then over time the disease can cause serious complications. These include perimaxillary abscess, osteomyelitis, phlegmon, and jaw cyst.
Pathology develops as a result of complications of carious processes that spread to adjacent tooth tissues and cause decay of nerve fibers and damage to the ligamentous apparatus.
Stomatitis
Inflammation affecting the oral mucosa is called stomatitis. Depending on its type, the patient develops erosions, ulcerations, blisters, and catarrhs in the affected areas. This disease is also characterized by redness and swelling that form around pathological foci. All this together leads to the fact that a person’s gums hurt, and the pain has varying intensity.
Stomatitis acts as an independent disease or as a concomitant process with other diseases. The reasons for its manifestations are:
- streptoderma;
- scleroderma;
- immunodeficiency states of the body;
- mechanical injuries;
- dentures;
- burn of mucous membranes;
- some medications;
- poor oral hygiene;
- diabetes;
- various infections.
Treatment of stomatitis in most cases is conservative and boils down to identifying the allergen and treating the underlying disease. When pathological factors are eliminated, stomatitis manifestations usually go away on their own.
Periodontal disease
With aching pain in the gums, the cause is often periodontal disease, that is, a destructive dystrophic process, as a result of which the flow of nutrients to the jaw bone tissue is disrupted. The consequence of the pathology is a disruption of the normal blood supply to the gums, which causes a weakening of the ligamentous apparatus and bone tissue of the tooth.
The main cause of periodontal disease is the activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Diseases of the digestive system, as well as cardiovascular and endocrine problems may have an indirect role in the manifestation of this pathology. The disease has a long-term course and is accompanied by pain, increased bleeding of the gums, inflammation, and bad breath. Lack of treatment can result in tooth loss.
Other reasons
In addition to all the problems described above, the reasons why gums hurt are:
- facial injuries;
- damage caused by a crown or filling;
- wisdom tooth growth;
- developmental anomalies of the jaw apparatus;
- increased sensitivity of the oral cavity;
- pregnancy.
How to quickly get rid of toothache
The majority of patients experience mild toothache that is not complicated by other symptoms. If this happened in the evening or on the weekend, then the question arises - what to drink to prevent pain? You can take the painkiller Nurofen or Ketorol (you can even Paracetamol - it is less effective, but has a weaker effect on the liver than others), and visit a doctor as planned.
To relieve pain, you can also resort to traditional medicine. What methods of traditional treatment have become widespread? Usually these are rinses with solutions of soda and salt, decoctions of sage, chamomile and oak bark. You can apply a cold compress, a piece of salted lard or propolis to the problem area. Or you can drop camphor oil onto a piece of cotton wool and apply it to the tooth.
When you need to see a dentist urgently
- very severe pain: the patient is not helped by painkillers,
- swelling of the cheek: a sign of an abscess - accumulation of pus in the soft tissues, may be accompanied by fever,
- the lower jaw hurts for a long time and severely: if the discomfort radiates to the left arm, accompanied by heartburn for several days, then we can talk about heart problems.
To summarize: how to recognize a disease by the nature of the pain
| Nature of pain | Possible disease/problem |
| Monotonous, occurs when chewing, getting food on the tooth, reaction to sour/sweet, cold/hot | Caries, caries under a filling. Or poor-quality treatment when filling canals |
| Acute, which intensifies closer to sleep, does not go away at all or subsides very slowly after no pressure is applied to the tooth | Pulpitis. You urgently need to see a dentist! |
| Monotonous, red and bleeding gums | Gingivitis, periodontitis. You need to visit a periodontist and start with professional hygienic cleaning |
| Occurs after eating, for example if you eat fibrous meat | Food stuck between teeth - improve hygiene. But visit a doctor - there is a problem with your gums! |
| Sharp or severe pain when clenching teeth, tooth mobility | Root apex fracture. You need to see a doctor - there is a risk of tissue necrosis, nerve death |
| Pain from sour and sweet, hot and cold | Increased sensitivity of enamel. Lack of vitamins and unbalanced diet |
| Monotonous pain and swelling of tissues, face | Cyst or granuloma, chronic or acute periodontitis. See a doctor urgently! |
Prevention of oral diseases
To ensure that a happy smile is not overshadowed by problems and pain, you need to follow simple preventive rules. The main thing is to take care of your health - maintain oral hygiene and eat right. It is advisable to eat food rich in vitamins and minerals - this way they are fully absorbed. Visits to the dentist should occur at least twice a year - and this is only for routine examination. If something is sick, then you should not delay visiting a doctor. After all, it is easier to cure the initial stage of the disease than its advanced form.
Category Miscellaneous Published by kosmetik-dent
Diagnosis for pain in the gums
If the gums under the tooth hurt, the best solution would be an immediate visit to the dentist or periodontist. These specialists will carry out a set of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, which include:
- X-ray examination.
- Tartar removal.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Restoration of mucous membranes.
- Correction of prostheses.
- Curettage.
The range of diagnostic and treatment procedures can be adjusted by the attending physician, taking into account the specifics of a particular pathological process.
What does pulsation in the gums indicate?
Pulsating sensations in the gum against the background of its swelling and pain are a clear signal of the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane associated with injury to soft tissues and the penetration of infection into them (the strength and frequency of attacks are important in diagnosis).
In addition, the symptom may be a consequence of various pathological processes. The most frequently diagnosed are:
- progressive caries short-term attacks of pulsating pain are possible with carious destruction of the middle and deep stages, most often provoked by external irritants - such as a reaction to cold/hot, sweet/salty.
- acute pulpitis is a complication of caries associated with the penetration of harmful microorganisms deep into the dental tissues: upon reaching the pulp, they provoke a serious inflammatory process, accompanied by severe painful sensations, which usually intensify at night.
- periodontitis is a consequence of untreated pulpitis (or, alternatively, the result of poor-quality treatment of dental canals), accompanied by the formation of a purulent abscess at the root of the tooth.
Other factors can also provoke pulsating pain in the gum tissues; only a specialist can determine the real cause of the problem, therefore, if you feel pulsation in the gums, do not delay your visit to the dentist!
Help with gum pain
Many diseases that cause pain in the gums tend to last a long time. It is this feature that poses the main danger to our health. We understand perfectly well that such manifestations do not threaten us with immediate death. Therefore, many of us have become accustomed to pain localized in the oral cavity. And to the excited question from our loved ones, “what’s wrong with you?”, we, as always, give a relaxed answer: “It’s okay, my gums just hurt again.”
However, when there is pain in the gums, what to do is the question that every patient asks. It should be noted that by ignoring such manifestations, we unwittingly turn our mouth into a source of permanent infection. In fact, into a biological bomb that can “explode” at any moment. And the results of such an “explosion” can be very disastrous, resulting in the total loss of all our teeth.
It is very easy to avoid such a catastrophe. It is enough to visit the dental office and carry out a number of simple procedures, which, with the modern level of medicine, will be absolutely painless:
- Periodontitis is treated by surgical release of exudate followed by physical therapy, warm rinses, and antibiotics.
- In case of periodontal disease, priority is given to surgical methods - targeted tissue regeneration, the use of grafting materials and membranes.
- To get rid of gingivitis, it is advisable to use professional mouth cleaning and systemic use of antibacterial drugs.
If you have pain in your gums, before visiting a specialist, you can rinse your mouth with various solutions that help relieve inflammation and alleviate the patient’s condition. These include chlorhexidine, furatsilin, baking soda solution (a teaspoon per glass of warm water). Good health to you and take care of yourself!
If you have a toothache, then life becomes hateful
How to distinguish toothache from pain caused by inflammation of the gums, especially since the gum pain is often very intense, affecting the entire jaw? In order to independently differentiate a painful condition and choose ways to neutralize pain, you need to know for what reasons pain in the gums may occur.
My gums hurt, what are the causes of the pain?
Gingivitis is the main cause that occurs in 90% of clinical cases of gum inflammation. Gingivitis is a precursor to another gum problem, periodontitis. The disease has its own causes, among which the most common is poor or irregular care of teeth and the oral cavity in general. Often, bacterial plaque that accumulates in hard-to-reach mucous parts of the gums becomes tartar after three days, and the tartar can no longer be cleaned with a toothbrush. Gingivitis can also be caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy and puberty. In addition, uncontrolled use of certain medications can cause hyperplasia of the gum tissue. Among the causes of gingivitis may be vitamin deficiency (vitamin C - scurvy), herpes. Symptoms of gingivitis are typical - bleeding, swelling of the gums, which are slightly behind the teeth. There is practically no pain at the beginning of the process, however, gingivitis of herpetic etiology is often accompanied by gum sensitivity, erosiveness and pain. Periodontitis. This is a chronic inflammatory process that affects everything that surrounds the tooth, it is no coincidence that the name of the disease has Greek roots: παρα - about, around, ὀδούς - means tooth. The cause of periodontitis has a natural explanation - bacteria that constantly enter the oral cavity and live there, multiplying and destroying everything that is around. The cause of periodontitis is irregular or complete lack of dental care, caries, and a weakened immune system. The symptoms are very characteristic - the gums begin to become inflamed, swollen, and slightly lag behind the teeth. Then you feel that your gums hurt when exposed to cold or very hot substances (food and water). Cyst. This phenomenon is dangerous because it is asymptomatic; at first the gums become slightly inflamed, but do not hurt. Many people either do not pay attention to this sign or try to correct the situation with the help of medicated toothpastes. The symptom subsides, but the process simply “hides” deeper to such an extent that a dense small nodule is formed at the site of the primary inflammation - a granuloma, and then a cavity filled with bacteria and their waste products, that is, a cyst. The cyst grows and begins to damage the root tissue. A cyst is rarely accompanied by acute pain; cystic formations are characterized by an increase in body temperature and periodic weak, aching pain in the gums. The cause of cystogranuloma is most often infection of the gums, less often – trauma and a general infectious disease. Stomatitis, its various types - catarrhal, ulcerative, aphthous. This is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, which rarely occurs as an independent disease. Most often, stomatitis accompanies candidiasis, scarlet fever and other serious diseases. Stomatitis is a common name that combines glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) and gingivitis (inflammation of the gums). The symptoms of stomatitis are identical to those of periodontal disease and gingivitis, the difference is a white coating on the mucous membranes or tongue, and with ulcerative stomatitis - erosive tissue damage. A chip that may be the result of a blow or injury. Part of the tooth may break off when chewing hard food - nuts, bones. Recently, chipping is a consequence of caries, which destroys not only the tooth, but also the gum. Often, vitamin deficiency, especially calcium deficiency in the body, leads to the fact that some of the teeth begin to crumble in the literal sense of the word. When a chipped tooth comes into contact with other teeth, it involuntarily begins to damage the gums; an infection can get into the wounds, which means an inflammatory process can begin. Gum pain often occurs after the removal of a diseased tooth. These painful sensations are completely natural and transient. If your gums hurt for five days, you should contact your dentist to find out the real cause of the discomfort. Prosthetics. It happens that dentures and implants are chosen poorly and injure the gums. Even if the pain is not acute and tolerable, you should not wait for the inflammatory process in the gums. You need to see a doctor again to have the prosthesis adjusted.
What can you do on your own if your gums hurt?
If you have recently had dentures, then most likely you need to see a doctor again to troubleshoot the dentures and adjust them so that your gums are not injured or hurt.
If your gums hurt after using a certain toothpaste that you decided to try for the first time, you just need to change it to a more familiar or medicinal one designed to prevent periodontal disease (Lakalut, Parodontax).
If your gums hurt and are swollen, this may indicate the formation of gumboil, the pain becomes extensive, spreading along the jaw, you should immediately contact a dental clinic. Any delay is fraught with acute inflammation of the periosteum up to phlegmon (purulent inflammation spreading throughout the body, sometimes to the neck and below).
If your gums hurt very badly, and there is no opportunity to visit a doctor in the next 24 hours, you can take an anesthetic drug - ketanov, analgin, paracetamol. You can also rinse your mouth with Chlorhexidine solution.
If the cause of pain in your gums is a chipped tooth, then you need to schedule a visit to the doctor as soon as possible to restore not only the health of your gums, but also the beauty of your smile.
What not to do when your gums hurt:
Do not heat the gums or use hot rinses; You cannot open an abscess (flux) yourself; You cannot endure pain for more than three days (after tooth extraction - a maximum of five days); You cannot try to fit dentures on your own.
How to treat if your gums hurt?
Obviously, the best thing you can do is visit a dentist as soon as possible. It is the doctor who will be able to choose the right toothpaste, a remedy to relieve the first manifestations of gum inflammation. While the process has not developed to a pathological stage, it can be neutralized by regular brushing of teeth using specialized products and rinses.
If the inflammation is in the development stage, the doctor will determine the root cause, and, possibly, clean the infected canals, remove plaque and stones, put in a new filling, sharpen the prosthesis, in a word, eliminate areas of injury and infection.
If pain in the gums indicates an acute phase of inflammation, surgical treatment is also possible.
If your gums hurt, you need to understand that this symptom is not only unpleasant, but also alarming, which indicates that an infectious process has begun and can affect not only the oral cavity, but also other vital organs, such as the heart. According to statistics, about 15% of pathologies of the cardiovascular system are associated with poor condition of teeth, which are a source of bacterial infection that penetrates into the heart muscle through the bloodstream. Therefore, if there is the slightest sign of gum inflammation and gum pain, you should immediately visit a doctor to prevent the disease at an early stage.
Treatment No comments
TOP 10 reasons why a tooth may hurt
Sometimes a person who is faced with toothache is perplexed - why does this happen, because the teeth are apparently completely healthy? In this case, you should not put off going to the dentist. It is the doctor who will be able to determine what caused the pain - it could be due to increased sensitivity, or due to caries under an old filling, or due to many other factors. Conventionally, they can be divided into several types: caused by bacteria (caries, pulpitis, gum disease, etc.), mechanical damage or provoked by general diseases of the body.
Let's look at the 10 most common causes of toothache:
Reason 1. Caries and its consequences
These diseases are caused by bacterial microflora, which destroys teeth both from the inside (pulpitis) and from the outside (caries). But first things first.
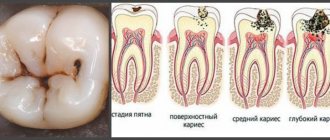
Caries occurs in almost every person. Appears as dark spots on the enamel. Interestingly, the initial stage of caries appears not as dark, but as white spots. In these places, the pathogenic process has just begun, and the waste products of bacteria little by little destroy the minerals that make tooth enamel hard. Gradually, the microbes penetrate deeper and the lesion becomes larger in size. The disease can spread to neighboring elements. If caries has reached the dentin, the process accelerates, because this layer is softer and more porous. If caries is not treated in time, the infection will penetrate into the pulp - i.e. the process of inflammation of the nervous and vascular tissue will begin. Pulpitis can be cured without “killing” the nerve, but not always. Typically, the inflamed contents of the pulp and root canals are cleaned out, disinfected and filled.
Painful sensations during caries and pulpitis are of a different nature. If caries causes mild pain, accompanied by a reaction to hot and cold drinks, food and air. The pain with pulpitis is often very strong and sudden (you can get sick at night, so much so that you “climb the wall”). The damaged element is painful when pressed and tapped. Unpleasant sensations can radiate to the nose, cheeks, temples (if the upper tooth is affected) and to the neck, ear (if the inflammation is in the lower row).
With caries, the pain subsides if the irritant is removed. For example, we ate something sweet, it got on our tooth, and it hurt. With pulpitis, the pain will last for a very long time.
Pain syndrome also occurs as a result of neglected or poorly treated caries, or rather even pulpitis - for example, with gumboil (periostitis), with periodontitis or even cysts. With gumboil, an additional purulent blister appears on the gum; with periodontitis, pain is often absent, but swelling of the mucous membranes and even parts of the face occurs. The insidiousness of cysts and granulomas is that, again, there may be no pain, but they appear as the tumors grow.
Reason 2. A new tooth grows and pericoronitis occurs
Pain during teething can occur in both children and adults. It is not uncommon for people at 70 and 80 years old to have “eights” - wisdom teeth. They are the ones that cause a lot of problems and are often painful.
Mostly the sensations are pulling and aching in nature. The head and neighboring elements may hurt. Their growth is often complicated by insufficient space on the jaw, so teething is accompanied by painful inflammation of the gums (called pericoronitis). Also, “sages” can grow incorrectly and damage the roots of “sevens”. In these cases, the “eight” must be “sacrificed” and removed.
Reason 3. Gum inflammation
Diseases such as periodontitis and periodontal disease affect the gums. There is pain and bleeding of the gums, pain when clenching the jaws and chewing food. Many patients are often confused and do not understand what exactly hurts – the gums or the tooth. At the same time, these pathologies lead to the fact that the roots of the teeth are exposed, which causes their increased sensitivity. If the infection is advanced or rapid, it can penetrate into the dental pulp through the apexes of the roots - this can result in the loss of one tooth, several, or even all of them in a row.
Reason 4. ARVI, sinusitis, sinusitis
Sinusitis and sinusitis are bacterial or viral inflammations of the mucous membranes of the nasal sinuses. Because Since the paranasal sinuses are located in close proximity to the upper jaw, their diseases can be reflected in the pain of those teeth that are in close proximity to the nasal sinuses. Often the lower dentition also reacts, for example, with sore throat and pharyngitis, since with these pathologies soreness of the lymph nodes often occurs.
Reason 5. Injuries, root fracture, cracks and chips
Chipped fillings, cracks in the enamel, and a fractured root tip can be caused by injuries due to bruises or chewing/biting very hard foods. Here, the pain from the injury itself may be joined by soreness due to inflammation (when the infection enters the pulp through microcracks). The sensations can be very different - strong, weak, sharp and dull. For a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an x-ray or an orthopantomogram (OPTG).
Reason 6. Whitening procedures and pastes with abrasive particles
In pursuit of a Hollywood smile, some patients notice that they have increased tooth sensitivity (hyperesthesia). This means that, along with the removed bacterial plaque, the mineralization of the hard tooth covering - enamel - is disrupted. In this case, all teeth may suffer at once, but most often the front teeth suffer from sharp and sudden “shots” - after all, they are located in the visible zone of the smile and during whitening they are given special attention.
Reason 7. Hard toothbrush and strong pressure while brushing
Everyone knows that you need to brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes. But not everyone knows how to choose the right toothbrush with the required hardness and how hard you can press on the tooth surface. Meanwhile, this is very important for oral health. Brushing too harshly can damage the enamel, rewarding a person with aching toothache and increased sensitivity to hot/cold.
Reason 8. Hypothermia and inflammation of the facial nerves
Fun winter games and walks are undoubtedly good for health and maintaining immunity. But a long stay in 20-degree frost, wind, or being outside without a hat can cause a very unpleasant disease - inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. This pathology almost always entails aching pain in the teeth.
Reason 9. General diseases of the body
The modern world sets a fast pace of life, but this is not suitable for every person. Therefore, various neurological conditions, stress and chronic fatigue arise. With such pathologies, the brain can receive and send incorrect signals to the nerve endings. They, in turn, can manifest themselves as a dull toothache that bothers a person for a long time. All these conditions are treated not by a dentist, but by a neurologist or psychotherapist.
Cervical chondrosis can appear due to being at the computer when a person’s head is turned to one side for a long time. In this case, there is an incorrect position of the spine, which contributes to the compression of blood vessels and nerves. The latter condition may cause pain in the lower jaw, lower molars and premolars.
Also dangerous are stomach diseases, frequent heartburn - when stomach acid refluxes into the oral cavity. Enamel is destroyed by acids, dentin is exposed - sensitivity and pain increase.
Reason 10. Lack or improper intake of vitamins, dietary disorders
People with weak enamel (as well as children and the elderly) should avoid products with vinegar and citric acid, and vitamin C should be taken only with meals. Why? Because acids destroy enamel and cause hyperesthesia - this causes pain. The best source of vitamin C can be rosehip decoction - it is not sour, but it contains several times more useful vitamin than lemons.
Poor nutrition negatively affects the mineralization of enamel and the condition of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. And, again, beneficial substances are washed out of the enamel, it becomes fragile and sensitive to irritants. The diet of a healthy person should include greens, fresh vegetables, berries, nuts, eggs, legumes and cottage cheese (not low-fat! - calcium is almost not absorbed from it).
Interesting fact! Acute imaginary toothache is not an invention of overly sensitive people. This condition may appear at the site of the tooth after its removal and last 1-2 weeks. Experts explain phantom soreness as a feature of the restoration of nerve endings in the gums.
Causes of pain in the gums when pressing
If the gum under the tooth hurts even with slight pressure, this is a reason to immediately consult a specialist. Such pain often varies in intensity: from relatively weak to severe. It is important not only to diagnose the cause of its occurrence, but also to begin timely treatment - this way you can avoid the development of serious complications.
In fact, there are many reasons for soreness in the gums, but dentists have identified several of the most common:
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum margin, often accompanied by redness of the mucous membrane, swelling and bleeding. This pathology occurs due to the accumulation of a large amount of microbial plaque (often from poor oral hygiene and irregular teeth brushing). Less commonly, gingivitis develops after incorrect orthodontic treatment.
- Periodontitis – the cause of acute pain in this pathology is an abscess formed at the root of a tooth affected by caries. A cavity with purulent contents, attached to the apex of the root, also appears with pulpitis. Soon a fistula forms on the purulent sac, through which its contents flow out. This disease is distinguished by the spontaneous occurrence of painful sensations and a gradual deterioration in general well-being. At the same time, the patient always feels which tooth is bothering him, and even feels its “elevation” above the others.
- Periodontitis is a disease that develops due to untreated gingivitis. With this pathology, all the necks of the teeth open, pus begins to ooze from the gums, and the teeth become shaky and mobile. Typically, periodontitis affects the entire oral cavity, but in some areas of the gums the symptoms are more pronounced.
It is necessary to treat gum diseases quickly , otherwise the pathology develops into periostitis, which is accompanied by a deterioration in the general health of a person, a sharp increase in his body temperature, swelling and swelling of the gums and cheeks, as well as the instability of all teeth. In addition, during prolonged inflammatory processes, toxins are released in the gums, which provoke the development of sepsis and blood poisoning.
Gingivitis and periodontitis
In addition to inflammatory infectious processes, gums can also become very sore from poor quality treatment by a dentist. Usually, pain in the area of the treated tooth is considered normal for 1-2 weeks, but if the pain continues for a long period of time and does not decrease, then this is a sign of unsuccessful treatment.
After filling diseased teeth (namely, improperly filling the canals with material), pain in the gums often occurs - bacteria develop in the voids of the canal, which provoke an infectious process.
In some cases, the dentist leaves the edges of the filling uneven, which also causes pain in the gum, damaging it. Increased natural sensitivity of the gums and teeth can also cause pain. Attacks in such cases are caused by even slight pressure on the gums or exposure to external irritants.
But such pain goes away quickly enough and does not require special treatment. It is better to use toothpastes for sensitive teeth and rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile and oak bark.
Treatment with a dentist should not be postponed - the disease will not only not disappear over time, but will also lead to the development of serious consequences. Doctors treat even the most “advanced” gingivitis and periodontitis, trying to preserve the naturalness of dental tissues as much as possible.
Injury to the gums near the teeth also causes pain - the habit of gnawing something or cracking nuts often leads to microcracks in the tooth enamel. Usually such chips are left unattended and “announce” themselves with sudden pain. Injured teeth must be treated, otherwise the damage reaches the dental pulp, provoking an inflammatory process.
Less popular causes of pain
Periodontitis
- loosening of teeth;
- severe pain in the affected area;
- the appearance of swelling of the lips or cheeks.
A fistula appears at the site of the disease, from which pus is discharged. If periodontitis occurred a long time ago, there is a possibility that the disease has become chronic. In this case, it can only be discovered by chance, for example, when visiting a dentist. The latent form of periodontitis is characterized by minor manifestations of discomfort and mild pain.
When the gums near a tooth are very sore, this may be a sign of gingivitis. As the disease develops, the gum tissue does not lose its integrity. Signs of gingivitis may include the following:
- temperature increase;
- swelling of the lower or upper gums;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- the appearance of hard dental deposits;
- severe discomfort that occurs when brushing your teeth.
In most patients, the disease proceeds unnoticed. Often, a disease can be recognized only when it has already entered the chronic stage, in which the body’s defenses are not able to independently overcome intoxication. The main factors that cause gingivitis are:
- hormonal imbalances;
- traumatization of soft tissues by sharp edges of teeth or broken fillings;
- formation of tartar due to irregular oral care.
Periodontitis
In some cases, if the gums near the tooth hurt and become inflamed, this may be a manifestation of periodontitis. This condition is a complication of other inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane. Manifestations of periodontitis are: exposure of the neck of the tooth, the appearance of purulent discharge from the gum pockets and loosening of the teeth.
The infection affects the mucous membrane and bones of the jaw. This type of disease is characterized by very severe pain inside the jaw, swelling of the tissues around the tooth, and an increase in the depth of the gum pockets. The main cause of periodontitis is considered to be poor oral hygiene. In addition, the occurrence of periodontitis may indicate a decrease in the level of immunity. Against the background of a weakening of the body’s protective functions, conditions arise that contribute to the appearance of periodontitis, namely:
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, menopause or taking hormonal contraceptives;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- consequences of chronic diseases (gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the hematopoietic system).
When a tooth becomes inflamed under the denture, a sharp throbbing pain appears, which radiates to the ear or temple area. This occurs as a result of improper preparation of the tooth for a crown. The appearance of pain and inflammation can be caused by significantly exceeding the period of use of the crown. After five years of use, the prosthesis needs to be replaced.
After installing a filling, treatment complications often arise when a tooth hurts or the gums hurt. This is due to insufficiently thorough sanitation of the canals, which leads to the occurrence of periodontal abscess. Inaccurate polishing of the surface of the filling can cause it to be indented when closing the teeth and chewing food.
Constant trauma to the gingival margin contributes to the appearance of pain in the gums. Irritation and redness of the mucous membrane is observed due to exposure to medications or dental instruments during dental treatment. Depulping a tooth does not always go smoothly. Pain can occur if the quality of root canal treatment is poor, or if the root is not completely removed.
Medicines suppress pathogenic bacteria, relieve swelling and redness of soft tissues, and promote rapid wound healing. Usually the doctor prescribes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Furacilin, and treating the gums with Cholisal, Asepta or Metrogyl Denta gel. Paradontax toothpaste copes well with inflammation.
They are:
- inside the tooth;
- and in the soft tissues that support the crown and root.
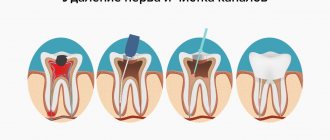
After nerve removal
Let's start with the reaction apparatus inside the mineral formation. There is a chamber inside the pulp in the canals of the masticatory units. It houses the neurovascular bundle, a response apparatus designed by cunning nature. Dental caries is a direct path that allows bacteria to penetrate into the pulp.
Treatment:
- The dentist either cleans out the resulting cavity destroyed by bacteria nearby. Yes, precisely by bacteria, because caries is the process of damage to hard tissues by bacteria.
- Or it is introduced into the canal and removes the nerve when inflammation has started in the pulp chamber, and pulpitis has begun, and the tooth has unbearably ached.
Problems inside the canals may occur after treatment. Reasons: introduction of sealant into the cavity above the channel (exit beyond the channels); filling the material not to the end of the cavity (with voids); introduction of infection inside; tissue burns caused by treatment agents during treatment.
The process of filling tooth canals
But after removing the sensitive apparatus, existing problems (destructions) in hard tissues will not make themselves felt at first. They will appear after the bacteria move to the root apex area. Living microorganisms irritate the soft structures that fix the root, causing inflammation there, and therefore swelling.
When the nerves in the canals are removed, meaning the apparatus for responding to the problem, the masticatory element does not respond to the problem. A tooth hurts if there is a nerve in it, and only when destruction of hard tissue occurs in the vicinity of the pulp or bacteria have entered the sensitivity chamber and caused irritation. Inflammation has begun in the pulp chamber, causing pulpitis.
- reaction to cold, hot food;
- twitching inside the tooth;
- the intensity of sensations, even if they do not last long.
And when the gums become inflamed and their tissues swell, they will only react to hot things. An unpleasant sensation will occur in the form of pain in the root zone. And due to the swelling of the soft structures that hold the tooth, it feels like the gums hurt when pressed.
An inflamed gum will make itself felt even in a calm state by twitching, and the tooth can hurt in different ways. Everything will depend on the cause and localization of the response process. After all, sometimes inflammation at the top of the tooth in the structures holding the root makes itself felt as pain in the tooth. That is, the reason is not in the chewing element, that is, not inside it, but in irritation of the structures holding the root, when an inflammatory reaction began there. But it feels like pain in a tooth.
For gum pain, dentists usually recommend:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nimesil, paracetamol, aspirin);
- rinsing with solutions (furacilin, manganese, salt, soda);
- rinsing with herbal decoctions (oak bark, chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, calendula).
However, for most diseases, eliminating pain does not solve the problem. After all, the disease does not go away anywhere. Despite the good regeneration of the oral cavity, advanced diseases of the teeth and gums cause great harm to our health and financial well-being. Take care of your dental health in a timely manner!
Because we can't knock and touch
Getting used to and adjusting the prosthesis to the jaw at the beginning of wearing causes pain. To eliminate discomfort, the doctor helps to fit the prosthesis.
We suggest you read: A white spot on the oral mucosa hurts
The appearance of pain after a few years is associated with atrophy of the jaw bones. In such a situation, the doctor replaces the prosthesis.
Against the backdrop of weakening protective functions, dental diseases develop rapidly.
The impetus is insufficient oral care and lack of timely treatment (elimination of a dental problem before pregnancy).
For painful gum conditions:
- Hygienic cleaning. Plaque is removed from the teeth and gums, fillings and teeth are polished (which causes microdamage to the gums), and the oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic.
- Recommendations for further antiseptic treatment at home.
- In difficult cases, surgical methods are used to eliminate the problem.
- To stop the development of periodontal disease - physiotherapy and massages.
When treating medium-sized caries:
- External and x-ray examination of the diseased tooth.
- Removal of carious tissues and antiseptic treatment.
- Installation and correction of fillings.
When flux forms:
- Examination of a diseased tooth by a doctor.
- Carrying out an X-ray examination.
- Opening the abscess and removing exudate. Cleaning the canals and carrying out antiseptic treatment. The use of surgical methods in case of failure of conservative therapy (gum incision, tooth extraction).
- Installation of a filling or crown.
- Observation by a dentist to prevent relapse of the disease.
When treating advanced caries and pulpitis:
- External and x-ray examination of the affected area.
- Cleaning the gums and teeth from affected tissue. Antibacterial treatment. Tooth filling.
- Crown installation and correction.
Thus, painful sensations in the tooth and gums indicate a number of diseases: from simple ones that do not require treatment to dangerous ones, such as oncology. If your teeth ache, your gums are swollen and bleeding, and your health has worsened, you should visit a dentist. The doctor will identify the cause of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Swelling around the affected tooth, its mobility. Bruise and swelling on the cheek.
Bad breath. Abscess.
It is very easy to avoid such a catastrophe. It is enough to visit the dental office and carry out a number of simple procedures, which, with the modern level of medicine, will be absolutely painless:
- Periodontitis is treated by surgical release of exudate followed by physical therapy, warm rinses, and antibiotics.
- In case of periodontal disease, priority is given to surgical methods - targeted tissue regeneration, the use of grafting materials and membranes.
- To get rid of gingivitis, it is advisable to use professional mouth cleaning and systemic use of antibacterial drugs.
- Consequences of dental canal filling.
- The appearance of a cyst.
- Stomatitis.
- Consequences of prosthetics.
- Pregnancy period.
- Irregular brushing of teeth;
- poor oral care;
- the presence of large deposits of tartar;
- weak immunity;
- the appearance of bumps and growths.
How to eliminate pain
Of course, only a dentist can help eliminate both the cause of the pain and the painful sensations themselves. But, before visiting him, you can try to relieve the attacks on your own. To do this you need to know a few tips:
- you can take painkiller tablets (“Paracetamol” or “Analgin”);
- thoroughly brush your teeth, freeing the inflamed tooth cavity from food particles and plaque;
- rinse the entire oral cavity with a solution of baking soda, potassium permanganate or furatsilin.
It is strictly forbidden to apply warm compresses to the sore spot or warm the cheek, as well as take antibiotics or any anti-inflammatory drugs on your own. You cannot put an analgesic into the cavity of a diseased tooth - this can not only cause an infection, but also cause a severe burn to the mucous membrane.
The chosen treatment strategy depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms. At the onset of the disease, therapy may consist of refilling the dental canals. By removing the source of inflammation, the dentist achieves stable remission of the affected tooth and complete restoration of damaged tissue. But an advanced stage of pathology or an area of damage that is too large is treated with surgery and removal of the diseased tooth.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies also effectively help relieve pain and eliminate both acute and chronic inflammatory processes: decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage or oak bark), a solution of baking soda or sea salt with the addition of a few drops of iodine can be used to rinse the mouth.
When gum pain is caused by disease, professional teeth cleaning, especially between teeth, is recommended. This procedure is carried out by a dentist and removes all accumulated deposits, as well as tartar.
Treatment of gums at home
There are situations when the gums hurt very much, but there is no way to consult a specialist.
The pain can be relieved at home. Salt water helps relieve pain . It is necessary to rinse your mouth after every meal.
Hydrogen peroxide, which is stirred in warm water in one to one proportions, has the same effect. The resulting solution kills all harmful microbes, relieving inflammation and pain.
A bag of ordinary black tea relieves pain quite well . It contains a large amount of tannins that relieve tissue swelling. Astringents can even stop gum bleeding. After brewing, the black tea bag must be cooled and applied to the sore spot.
Many people use baking soda to relieve pain. It perfectly destroys all harmful bacteria that are in the mouth. But you need to be careful and not keep soda in your mouth for too long, otherwise you can burn the mucous membrane.
You can use medicinal herbs for rinsing, such as chamomile, propolis, valerian, sage, oak bark.
A variety of antiseptic drugs , such as betadine, periodontocide, and caposol, relieve pain and eliminate inflammation well They wash out and destroy pathogens.
However, it is worth remembering that in some cases, self-medication is very dangerous due to the possibility of developing pulpitis, periodontitis or abscess. And these cases require urgent medical intervention.