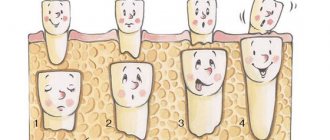
Reasons why teeth grow second row
Teething pathology can be caused by the following factors:
- chronic diseases, various infections;
- problems arising during the development of milk units, which subsequently has a negative impact on the formation of root incisors or molars;
- genetic predisposition;
- unbalanced diet;
- deficiency in the body of vitamins and minerals necessary for the proper formation of teeth;
- incorrect location of the primordia.
Teething order
First, the child’s incisors are cut, their number should be 8, then fangs grow - 4 pieces, the last to appear are 8 molars. As for the time when teeth should begin to emerge, this is a very individual process. For some, milk begins to grow at 5–8 months, while for others only after a year. But the cutting order is the same for everyone, it looks like this:
- 6–12 months - lower central incisors;
- 8–14 months - upper central incisors;
- 9–15 months upper lateral incisors;
- 10–16 months lower lateral incisors;
- 16–24 months upper and lower canines;
- 2–5 years upper and lower second molars.
An acceptable deviation is considered to be 2–3 from the norm.
In the video, Dr. Komarovsky explains the sequence of teething:
Symptoms
During the period when a child’s primary incisors appear and they are replaced by root units, parents should regularly examine the baby’s oral cavity. If you are alarmed by any manifestations, you must make an appointment with a pediatric dentist.
| Symptomatic manifestations | |
| Name | Description |
| Painful sensations | They are most often experienced when pressing on the mucous membrane or while eating. The soft tissue around the incisor may become inflamed. |
| Swelling of the gums | Pathological processes - tissue reaction, which manifests itself in the form of swelling. |
| Physical weakness, fever (up to 38-39 degrees) | During the inflammatory process, the temperature often rises and weakness in the muscle tissue is felt. |
| The baby tooth is loose but does not fall out | The symptom indicates a lack of solid food or pathology in the development of the jaw system. |
| Excessive salivation | When the nasopharynx is swollen, the nose becomes clogged, and as a result of breathing through the mouth, the mucous membrane dries out. Excessive salivation is a protective function of the body, preventing the penetration of germs and infections through the oral cavity. |
| Development of rhinitis | This process develops against the background of swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. |
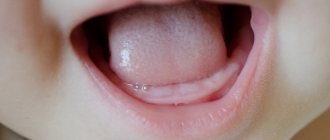
| No interdental gaps | From about 4 years of age, children develop large gaps between their teeth. If such a sign is not observed, then, most likely, a narrowing of the rows is developing. This leads to the growth of a second row of teeth. |
In children
The pattern of baby teeth must be different from that of an adult, because if the same person first treats baby teeth and then permanent ones with the same location, difficulties will arise in filling out a dental card. To eliminate all ambiguities, numbering is carried out according to the same principles, but completely different designations are assigned to the rows.
How to count children's teeth? The top right row is correctly designated as the fifth ten. That is, the first incisor on it has number 51 and so on. The upper left row is designated by the number 6, the lower left - 7, and the lower right - 8. If the dentist counts using this system, then when you hear that a child has caries on the 73rd, you do not need to imagine a mouth full of teeth.
In this case we will talk about the lower left canine. Once children have permanent teeth, their numbering is no different from the adult pattern.
Growth of baby teeth in the second row
Hyperdontia (supernumerary tooth) in the picture
The rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the womb, so their pathologies are associated with a lack of space in the jaw for all the incisors. Among the most common reasons that provoke improper growth of baby teeth:
- unbalanced diet of a woman during pregnancy;
- deficiency of calcium, fluorine (essential microelements necessary for the formation of bone tissue);
- lack of solid food;
- uncontrolled use of a pacifier;
- heredity.
It also happens that molars and molars come in second row. This phenomenon is explained by the following factors:
- underdevelopment of the jaw, due to which there is not enough space to accommodate a full set of teeth;
- hyperdontia (superset of teeth).
Purpose of teeth
The jaw of each person consists of certain segments with their own functions. They depend on the location of the dental unit and its size. The front incisors, of which there are 2 pairs on each jaw, are used for biting off food.
They are located in the center and are visible even with the most modest smile. After them, fangs are located on the jaw. There are only 4 of them in the mouth, and they are designed to hold food and help in biting it off. Next are the premolars, 2 on each side of the jaw, and molars, 3 on each side. They are designed for chewing and grinding food. The third molar is considered to be a wisdom tooth, and since many people have them growing into adulthood, and some have not grown at all lately, the dental record will indicate the presence of only two molars.
Consequences
Even one molar that grows behind a baby tooth causes a lot of trouble. Ignoring the problem and lack of treatment leads to the following consequences:
- the child’s diction is impaired;
- the process of chewing food occurs poorly, the food is not crushed to the desired consistency;
- additional load on other teeth provokes displacement of healthy units, this provokes intense curvature of the bite;
- diastemas and trema (gaps) form between the chewing teeth and the front permanent teeth;
- the roots of healthy incisors and molars become bent.
Basic principle of numbering
The count always starts from the central incisors and goes in both directions, regardless of how dentists count teeth. Unit numbers are assigned according to their arrangement in this order, and in some systems according to function. Each jaw has 2 rows of teeth directed to the left and right of the central incisors. Each row has 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars and 3 molars, their numbers are assigned accordingly.
How do dentists count teeth by numbers? Thus, the first central incisor of each row has the number 1. The second incisor is 2, the canine is 3, the premolars are 4 and 5, respectively, and the molars are 6, 7 and 8. The last eighth is the wisdom tooth.
Treatment
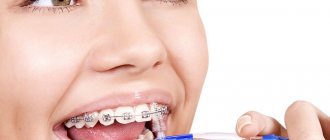
After the removal of supernumerary or baby teeth, braces are used to correct the anomaly.
Double dentition is not only a cosmetic defect, but also causes physical pain and discomfort to the child, so the problem must be solved together with specialists.
The dentist, having studied the nature and nature of the pathology, selects a suitable treatment method. In this case, the following are taken into account: the characteristics of the body, x-rays, test results, and symptoms. What to do:
- To correct the bite and free up space for the growth of the molar, the baby tooth is removed. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. The operation should be performed immediately after the tip of the molar appears. Most often, the dentition straightens spontaneously without installing a brace system.
- to eliminate jaw underdevelopment . The main tool used is braces (removable, non-removable), which fix the correct position of the teeth as they grow. The only drawback of the method is poor quality care of the structure due to its age. As an alternative, you can use Invisalign - a transparent elastic mouthguard that is almost invisible in the child's mouth. It is removed before eating or performing hygiene procedures. The only negative is the high cost of the design.
- The treatment of overcrowding involves several stages: removal of baby teeth and fixation of molars with a bracket system that corrects the bite. If extra teeth appear in a baby under 6 months of age, they are removed immediately.
Those teeth that are located outside the dentition are subject to removal. The exception is the canine; its natural replacement occurs at 11-13 years of age. If the canine is removed early, it can lead to severe malocclusion.
The following remedies are used to eliminate symptoms:
- ointments/gels for external use (Kamistad, Kalgel, etc.) – provide an instant but short-term analgesic effect;
- antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc.);
- the homeopathic drug Dentokind is recommended for use during the period of teeth change;
- rinsing with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and other plants that have an antiseptic effect - the procedure is indicated for children over 2 years old.
Possible complications
Chronic osteomyelitis of the lower jaw
As a result of incorrect or untimely treatment of hyperdontia, the situation may become more complicated. The most common options are: malocclusion and the development of speech defects.
Ignoring the problem of the growth of double dentition leads to chronic osteomyelitis of the jaw against the background of the inflammatory process of dentin, as well as to the death of the rudiments of molars and their abnormal growth.
In addition, the child receives psychological trauma caused by the aesthetic factor and the negative attitude of others.
What are the dangers of installing a bridge on one implant?
For those planning to install a bridge on different supports (one is an implant, the other is a living tooth), it is important to consider that they have different levels of fixation in the bone:
- the artificial root is firmly held in the jaw due to sufficient implantation depth and complete osseointegration, therefore it will take on the main load;
- a natural tooth is “springy”, since it has physiological (natural) micromobility.
These differences in use will create a shock-absorbing effect when distributing the load, which will destabilize the structure, and as a result will lead to loosening of the supports and failure of the product itself. Therefore, this option for installing a bridge is impractical.
Both supports are at risk. A loose artificial root creates conditions for the development of an inflammatory process in bone structures, which will lead to its rejection. A natural tooth as a support will quickly deteriorate due to increased load, preliminary grinding and depulpation. Which is why it will have to be removed.
Preventive measures
Solid foods will help the process of changing baby teeth to molars.
You can reduce the risk of dental anomalies (growth in two rows) by following the following recommendations:
- If you identify any problem in the oral cavity (including if a tooth has come out crooked or second row), you need to contact your dentist in a timely manner.
- The child's diet should include solid foods. This will help baby teeth fall out on time.
- If there are no upper respiratory tract disorders, then it is necessary to teach children to breathe through their nose. If nasopharyngeal diseases are detected, it is recommended not to delay treatment.
- From an early age, the baby should be involved in hygiene procedures to avoid the development of caries.
- It is necessary to wean the baby from putting everything in his mouth, especially sucking a finger or any objects.
- Do not let the child touch the growing incisor with his hands or constantly lick it with his tongue.
No matter how serious the problem may seem, it can be corrected quite easily if you contact a specialist in a timely manner.
Causes of pathology
There are three main reasons for the anomaly.
Violation of the order of shedding and eruption
The anomaly is usually observed up to 14 years of age. The second row of teeth comes in as a result of the fact that the milk teeth did not have time to fall out. In this case, the permanent teeth can be greatly displaced behind the primary incisors, molars, and canines. This situation naturally leads to malocclusion with all the ensuing consequences: facial asymmetry, digestive disorders, difficulties with chewing food, problems with diction.
Underdevelopment of the jaw system
Teeth in two rows appear due to the slow rate of jaw growth as a result of a hereditary factor, demineralization of bones, the presence of bad functional habits in childhood and infancy, and vitamin deficiency. The permanent ones are growing at a fast pace. But the formation of free space for them occurs much more slowly. The result is crowding of the smile elements - they do not have the opportunity to arrange themselves in an even and complete row.
The chance of getting a correct bite increases significantly if you contact an orthodontist as early as possible. With a fully formed jaw, correcting the defect will take a long time and diligently, no less than two years. For these purposes, children over 12 years of age are most often prescribed braces.
Supernumerary elements of a smile
This is the appearance of additional, “extra” units of the series. This phenomenon is called hyperdontia. It is quite rare - only 2% of people suffer from this pathology. In this case, one or several supernumerary teeth may be observed, most often we are talking about incisors, less often – about molars and canines.