Functions of a child's gums
Compared to other parts of the mouth, a baby's gums usually cause the least amount of concern for parents. But their importance cannot be underestimated. It is with the help of the gums that the baby holds the mother's nipple or pacifier. And thanks to the gums (and bones), the child’s teeth stay in place.
The gums have a hard time : in infancy, many functions fall on them, which will later be transferred to the teeth, because it is with the help of the gums that babies chew food. Gums are exposed to food, liquids, bacteria and sharp objects.
The appearance of the gums can provide useful information about how the baby’s intrauterine development occurred, what the child’s current state of health is, and what the baby may expect in the future.
Photopolymer and composite extensions
The method of building up with polymers consists of sequentially building up a tooth at the site of a chip or break with special polymer materials. Such materials, when exposed to radiation from a special dental lamp, immediately harden and become very durable. It is possible to choose the appropriate shade of polymer to match your own tooth enamel color. After the extension is completed, the surface is thoroughly polished.
The composite method involves layer-by-layer building using the material used to make dental fillings. The method is very similar to the previous one, only in this case materials are sometimes used that can harden on their own without exposure to lamps.
The final result of this procedure is always careful polishing of the tooth and giving it not just an aesthetically attractive appearance, but also a suitable shape that will fully correspond to the patient’s natural bite.
White dot on the gum of a child: Bohn's node
Many parents associate the appearance of a white dot on a child’s gum with teething. However, it is not.
The points are similar to a common, harmless phenomenon, which in medical parlance is called Bohn's nodes. About eighty percent of newborns have such gingival (gum) cysts, as they are also called. If they are located on the upper palate, then these are Epstein pearls.
It is not surprising that small white dots on a baby’s gums can be mistaken for teething. But these fluid-filled growths are milia—also known as infantile acne. Both papules and pearls usually gradually disappear on their own as the child grows.
Look at the photo of a white dot on a baby’s gum to get an idea of this phenomenon:
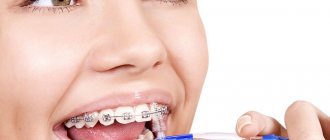
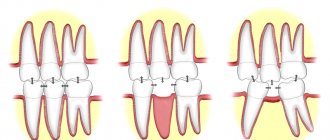
Method 1 - Braces
Today, the most effective way to correct your bite and straighten your teeth is to install braces. They are used in both adolescents and adults. Braces are a very complex orthodontic device that can be fixed in two ways:
- On the outside of the tooth (vestibular braces).
- On the inside of the tooth (lingual braces).
The photograph shows an example of external and internal braces.
Each element of such systems must be manufactured with maximum precision, matching the client’s dental model as closely as possible.
For the manufacture of modern braces, metals such as titanium or nickel-titanium are used, which are highly resistant to corrosion. Hypoallergenic plastics, ceramics, artificial sapphire, combined plastics, polymer alloys, etc. are also used. The main difference between such materials is the degree of visibility of braces to others. There are no significant technical differences.
The main element of such systems are power arcs, which are made from materials that have “shape memory”. Through these arches, the force necessary for crooked teeth to take a physiologically correct position is created. The average time to straighten teeth is 2 years and involves several visits to the dental office to tighten the arches.
Today, there are braces with a self-tightening mechanism (self-ligating), based on the interaction of the structure with the natural efforts of the facial muscles. This allows you to reduce the number of visits to the orthodontist and achieve better results.
Cons of braces
One of the most significant disadvantages of braces is their visibility to others. Because of this, many people who have reached the age of thirty do not decide to correct their bite, so as not to attract undue attention to themselves.
Also worth noting is the labor-intensive care of brace systems. In addition, braces are not recommended for all patients due to not only age-related thinning, but also the threat of premature wear of the enamel.
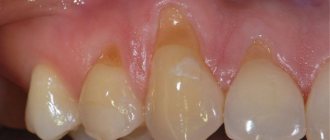
The photo on the left shows damage to the enamel, and the photo on the right shows the development of caries. It should be noted that this problem is primarily caused by insufficient hygiene during wearing and the doctor’s oversight.
Difficulties that arise when correcting a bite with braces
As mentioned above, the process of correcting crooked teeth lasts up to two years. And the older the patient is, the longer this process may take. For example, after thirty years there is a significant decrease in skeletal mobility, including the flexibility of the jaw bones. The situation can even worsen at certain stages of treatment. Then gaps may appear between the teeth, and the teeth may constantly change their position.
What to do after braces?
Many patients mistakenly believe that removing braces is the last step in correcting crooked teeth. But this is not true, because after removing the braces, the force directed to the teeth disappears, which can lead to them returning to their original places over time.
White plaque on a child’s gums: a sign of thrush
White plaque on a baby's gums is the main sign by which parents can diagnose thrush. Fortunately, this is a fairly harmless disease if treated correctly.
Thrush - candidiasis or candida infection - is a fungal infection of the oral mucosa. The fungus that causes it is found throughout the environment. In general, thrush is very common in babies. Although it is rarely detected in the first week of life, it usually does appear in the subsequent weeks.
Distinctive signs of thrush: shapeless white or beige spots that cannot be erased. They usually appear on the inside of the lips and cheeks, on the tongue, which is why they are often confused with traces of milk.
At risk are children suffering from diaper rash and diaper dermatitis caused by a fungal infection.
White plaque on a child’s gums often appears after taking a number of medications from the group of steroids or antibiotics. Since antibiotics are passed through breast milk, some of the drugs may pass to the baby from a mother taking antibiotics.
Women who have a vaginal yeast infection during pregnancy sometimes pass candidiasis to their babies during childbirth.
Transmission of infection also occurs in the opposite direction. If a breastfed baby has thrush, he will infect his mother with it during feeding. Until both mother and child are treated, they will infect each other.
The infection can spread from one child to another through pacifiers, bottles, pacifiers, teething rings and toys that babies put in their mouths. Fortunately, thrush is easily treated with simple antifungal medications.
Literature
- Kois JC. Altering gingival levels: the restorative connection part 1: biological variables. J Esthet Restor Dent. 1994:6(1):3-9. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8240.1994.tb00825.x.
- Kois JC. The restorative-periodontal interface: biological parameters. Periodontol 2000. 1996;11(1):29-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.1996.tb00180.x.
- McLaren EA, Phong TC. Smile analysis and esthetic design: “In the zone.” Inside Dentistry. 2009;5(7):44-48.
- Kokich V. Esthetics and anterior tooth position: an orthodontic perspective. Part I: Crown length. J Esthet Dent. 1993;5(1):19-23.
- Kokich V. Esthetics and anterior tooth position: an orthodontic perspective. Part 2: Vertical position. J Esthet Dent. 1993;5(4):174-178.
- Coslet JG, Vanarsdall R, Weisgold A. Diagnosis and classification of delayed passive eruption of the dentogingival junction in the adult. Alpha Omega. 1997;70(3):24-28.
- Levine RA, McGuire M. The diagnosis and treatment of the gummy smile. Compend Continue Educ Dent. 1997;18(8):757-762, 764.
- Robbins JW. Differential diagnosis and treatment of excessive gingival display. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1999;11(2):265-272.
- Kokich VG. Enhancing restorative, esthetic, and periodontal results with orthodontic treatment. In: Schluger S, Yuodelis R, Page RC, Johnson RH, eds. Periodontal diseases. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lea {amp}amp; Febiger;1990:120.
- Spear FM, Kokich VG, Mathews DP. Interdisciplinary management of anterior dental esthetics. J Am Dent Assoc. 2006;137(2):160-169.
- Dolt A.H. 3rd, Robbins J.W. Altered passive eruption: an etiology of short clinical crowns. Quintessence Int. 1997;28(6):363-372.
- Kois JC. Anterior wear: orthodontic and restorative management. In: Cohen M, eds. Interdisciplinary Treatment Planning, Volume II. Chicago, IL: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc.; 2008:189-210.
- Misch CE. Guidelines for maxillary incisal edge position-a pilot study: the key is the canine. J Prosthodont. 2008;17(2):130-134.
- Lee E.A. Aesthetic crown lengthening: classification, biological rationale, and treatment planning considerations. Pract Proced Aesthet Dent. 2004;16(10):769-778.
- Locker D. Measuring oral health: a conceptual framework. Community Dent Health. 1988;5(1):3-18.
- Spear F. Construction and use of a surgical guide for anterior periodontal surgery. Contemp Esthet Dent. 1999;3(4):12-24.
- Kurtzman GM, Silverstein LH. Esthetic treatment: Soft tissue management and functional mock-ups. Inside Dentistry. 2008;4(6):86-90.
- Allen EP. Surgical crown lengthening for function and esthetics. Dent Clin North Am. 1993;37(2):163-179.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Veneers: pros and cons, removable and non-removable, how they are installed
forum.stomatologija.su
Uneven gums in a child
Many parents, seeing that their child has uneven gums, worry whether the baby will grow crooked teeth. However, irregularly shaped gums are usually caused by an abnormal chin shape - a positional deformity of the chin.
This rare phenomenon is the result of pressure on the chin for a long time during fetal development. For example, a child's growing chin was located for a long time on his shoulder or on the mother's pelvic bone. This defect is similar to head deformities in newborns. The side of your baby's cheek that hasn't been pressed may appear fuller.
The good news is that chin positional deformity usually does not cause any consequences and is temporary. The chin almost always straightens on its own.
What types of teeth are there: irregular shape
- oversized teeth: these are overly large teeth that can interfere with the eruption of neighboring ones, distort the dentition and cause crowding of teeth. Most often, the problem concerns the front teeth (the so-called “bunny smile” occurs), the size of which can be increased up to 6 mm in length relative to the rest in the row. One of the most serious disadvantages of giant teeth is their abnormal appearance, which attracts unnecessary attention and does not meet generally accepted standards of beauty.
- Too small teeth: This is a problem in which the jaw contains teeth with small crowns. The problem often spreads to all the teeth in the mouth. The teeth may be regularly shaped but often grow at large intervals. In addition, due to the too small size, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not meet tightly, as a result of which the patient has problems chewing solid food, since the chewing surfaces of the opposite teeth do not connect,
- teeth in the form of spikes: that is, wide at the base (at the gums) and very narrow in width at the tips, in the form of a spike or cone,
- teeth of any abnormal shape: they have a wide variety of irregular shapes that cannot be structured or described,
- Hutchinson's teeth: teeth that are wider at the base and narrower in thickness at the cutting edge. The problem usually affects the front teeth of the upper or lower jaw. The lower cutting edge also has a small semicircular notch (it is this feature that the scientist characterized as one of the main ones for determining congenital syphilis). On the lower cutting side there is often no enamel and the inner dentin of the tooth is exposed,
- Fournier teeth: similar to Hutchinson teeth, that is, they are shaped like a flat-head screwdriver. But Fournier proved that in the presence of congenital syphilis, there may not be a semicircular notch on the cutting surface of the front teeth,
- Pflueger teeth: the problem affects only the first chewing molars. Outwardly, they resemble an unopened bud - that is, they are greatly underdeveloped in size.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with 8 problems that are hidden behind unpleasant body odor.
Swollen gums in a baby
When a newborn is born, his parents will have to learn how to care for the little one and closely monitor his health. At first, many of them face sleepless nights and colic, and a little later the time comes for new teeth to appear.
If the baby is naughty, the mother should look into the baby’s mouth and look at his gums in anticipation of the first tooth. However, swelling of the gums can be a sign not only of the eruption of baby teeth, but also of certain diseases.
How many canals do human teeth have?
The canals differ from each other in shape and structure, and their number may differ from the number of roots. The number of canals is determined by the dentist using x-rays. However, none of the doctors will give clear rules on their number.
Approximate amount in different types of teeth:
- front incisors - at the top and bottom they have 1-2 canals;
- side – 1-2 pcs.;
- fangs - one at a time;
- 1st premolar – 2 canals at the top, 1 at the bottom;
- 2nd premolar – 1 below and above;
- first molars – 3 each;
- 2nd molar – 3-4 at the top, and 3 at the bottom;
- third molars – number up to 8 pieces.
Several channels can be located in parallel in one root.
Causes
The main and most common cause of gum swelling in infants in the first year of life is the appearance of teeth. Unfortunately, many children have a hard time with the eruption of their baby teeth. They suffer from pain, increased salivation and constant itching. Some babies teething with a high fever and other unpleasant symptoms.
Note that the first signs that the baby will soon erupt a tooth may appear two or even four weeks before it “pecks.”
Most toddlers please their parents with their first teeth at 5-6 months of age , but depending on the individual characteristics of some infants, the first tooth may appear several months earlier, while others acquire their first incisors only by their first birthday.
Mom may notice swelling of the baby’s gums in the following situations:
- The baby developed caries. This disease can affect even the first teeth of a toddler if parents neglect to carefully care for the baby’s oral cavity, lick the pacifier or spoon given to the baby, or allow the child to drink sweet tea or compote at night. Bacteria accumulating on the surface of baby teeth destroy the enamel, and if you do not immediately show the baby to the dentist and do not treat the teeth, the risk of further spread of infection increases, which sometimes ends in tooth loss.
- The baby contracted stomatitis. The disease can be provoked by bacteria, viruses, fungi (they most often affect the gums of children under one year of age) and other causes. In addition to swelling of the gums, stomatitis in an infant is manifested by the appearance of plaque, rashes or spots on the oral mucosa. The baby’s general condition may deteriorate greatly and the temperature often rises.
- The baby damaged his gums with something sharp or hard. As a result of such an injury, the gum mucosa may become inflamed, which will manifest itself as an increase in size, increased bleeding and pain.
- The baby does not have enough vitamin C or other nutrients. This situation can also lead to problems with the gums, making them looser, enlarged and prone to bleeding.
The main differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Both types of teeth have a crown, root and neck.
Inside the crown there is a cavity filled with soft tissue - pulp. Root canals, in which blood vessels and nerve fibers are located, run along the entire length of the roots. The shape of the crown depends on the functional specialization determined by the location of the units in the jaw. The front ones are designed for holding and biting food, while the side ones are needed for chewing. The main differences between temporary and permanent teeth:
- dairy products are smaller in size;
- the ratio of the width and height of the crown of primary teeth is greater;
- the walls of the root canals and the cavity of a baby tooth are thinner than those of a permanent tooth;
- the roots of primary teeth are shorter and wider apart;
- there are small enamel ridges on the necks of baby teeth;
- the enamel layer is thinner than that of permanent ones, milk ones have a more pronounced bluish tint;
- the primary bite consists of 20 teeth, which are divided into incisors, canines and molars (they are also large molars);
- The permanent dentition includes another group - small molars or premolars (total number - 28-32).
What to do
The actions of parents who discover swelling of the gums in their infant will depend on the cause of such changes in the oral cavity. If the baby behaves restlessly, suffers from pain, fever and other unfavorable symptoms, the child should be shown to a pediatric dentist. The doctor will examine the baby’s mouth and determine whether the swelling is due to teething or is a disease that needs to be treated.
During teething
To relieve soreness and itching in the gums of a toddler, parents should purchase special toys for the baby, called teethers. also massage the gums with a clean finger, and if the baby is in severe pain, special preparations with a cooling and anesthetic effect are used, which are produced in the form of a gel.
For caries
If a dentist identifies this disease in an infant, it is important to treat it immediately to prevent further destruction of dental tissue. The treatment method will depend on the stage and severity of the infection. Many children have their teeth silvered or treated with fluoride preparations, and sometimes they have to resort to removing infected tissue and filling them.
For stomatitis
In the treatment of such a disease, they first try to determine its cause, since for herpes stomatitis, antiviral drugs are prescribed, bacterial stomatitis is affected by antimicrobial agents, and for candidal stomatitis, drugs that affect fungi are indicated. Also, a child diagnosed with stomatitis should treat the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions and anti-inflammatory gels.
You will learn a lot of interesting things about the appearance of the first teeth in children from Dr. Komarovsky’s program.
Is it possible to treat teeth crumbling – how can dentists help?
If you detect even minor errors in the structure of your teeth, you should contact your dentist. This doctor will conduct diagnostics to determine the causes of such defects.
- Mineralization. Applications are prescribed for damaged teeth, which are designed to enrich the enamel with fluoride and calcium. The duration and type of such applications are determined by the dentist.
- Coating of crowns with fluoride varnish.
- Using special toothpastes with a high fluoride content.
- Filling. Relevant in the presence of caries, partial splits of teeth due to injury.
- Installation of veneers, artificial crowns. It is used as a last resort measure when the crown is so damaged that it cannot be restored by other methods.
Not pimples, but... teeth!
In some cases, the small white bumps may feel hard to the touch. If you touch them, they will resemble bone. Many mothers are frightened when they notice such a formation in the oral cavity of their baby. They believe that since this bump is not an ordinary pimple, then it is probably a dangerous tumor. However, the white lump may be nothing more than a tooth!
Neonatal teeth
Dental development in the embryo begins at approximately 7 weeks of gestation. By the 13th week, the fetus already has tooth buds in the gums. The baby is born with bare gums, the first teeth begin to cut closer to 6 months.
However, 1–2% of newborns are born with teeth, or they appear in the first weeks of life. A neonatal tooth appears as a small white hard point that will increase in size over time. The gums around such a tooth may be swollen, but usually the appearance of such a “rush” is not accompanied by any inflammation.
The second reason why extraction may be required is excessive fragility and mobility of the tooth due to the unformed root. It crumbles easily, falls out earlier than expected and can get into the baby's respiratory tract. If the neonatal tooth does not cause any discomfort, dentists recommend leaving it.
Baby teeth
Parents wait until the first baby teeth appear around six months. However, a white, dense lump may appear from the gums much earlier - at 4 or even 3 months. What affects such early eruption of milk units:
- heredity;
- living conditions and food;
- metabolic features.
What to do if your two front teeth are large
Before and after photos show how the appearance of your smile and face changes after correction of large incisors. There are several methods that help give a large dental element the required shape. All of these can help make the tooth smaller.
- Contour type plastic surgery. This is a method in which the shape is given by grinding with a special grinding machine.
- Composite restoration (contouring and bonding). After grinding the dental crown, additional composite materials are used. This coating not only improves the shape of the teeth, but also protects the enamel layer.
- Application of veneers. Such onlays can be installed on adjacent teeth so that the front ones do not stand out so much. This is especially true if for some reason turning is impossible. Another option is to install lumineers. These are more elegant plates that do not require much grinding of the teeth, and in some situations the teeth for them do not need to be ground at all.
- There are situations when enlarged teeth are a consequence of a crooked bite. Classic braces help correct this problem. This method is recommended most often in adolescence from 11 to 18 years.
- Implantation. It is used in particularly difficult cases when it is necessary to remove a large tooth. Subsequently, the removed elements are replaced with implants.
Before choosing the appropriate option for a particular case, the dentist will offer to undergo an examination, including an examination and x-ray of the jaws. Experts often recommend leaving dental crowns in their original form, but if it is decided to correct the defect, then it will be necessary to increase hygienic care. Use fluoridated toothpastes, dental floss and even an irrigator. Because the enamel layer will become more at risk of carious destruction.
Strangers in your mouth!
White pimples in a baby's mouth are not always safe. They are often a symptom of oral diseases that require immediate treatment. The most common infections are thrush and stomatitis. These ailments cause a lot of trouble for both the baby and his mother, and if left untreated, they can cause serious harm to the body.
Candidiasis of the oral mucosa
Thrush is an infectious disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida - opportunistic microorganisms that are normally found in the vaginal microflora. The disease is associated with an increase in their number and active reproduction due to the use of antibiotics that kill beneficial bacteria, hormonal fluctuations, decreased immunity, and improper hygiene.
Thrush in newborns and infants is common. Babies become infected with it during the birth canal or during breastfeeding if the mother is sick. It is also easy to catch fungus from dirty nipples, bottles, and toys.
The first symptoms of thrush:
- white thick cheesy coating on the oral mucosa;
- unpleasant, sour breath;
- lethargy, moodiness;
- refusal of food.
Unlike the milky plaque that appears in the baby’s mouth after feeding, the candida film is very difficult to remove without causing pain to the baby. Bleeding ulcers are hidden under the film.
How many wisdom teeth does a person have?
Wisdom tooth or figure eight (third molar). There are 4 of them in total by nature. On the jaw they are located on both sides at the top and bottom. The rudiments are formed by the age of 17, and they fully germinate by the age of 25-30.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Temperature. Teeth? — Julia writes on BabyBlog
The eruption of figure eights is often accompanied by painful and unpleasant sensations in the back of the jaw, and difficulties may also arise when chewing and swallowing.
Many dentists believe that they are involved in grinding food, since in a normal position they can make the chewing function more active, but molars are more susceptible to caries than other molars.
Some dentists believe that it is better to remove third molars, especially if they grow incorrectly, interfere, do not perform their functions and can cause complications.
Dental indications for removal:
- caries that cannot be cured;
- indications from an orthodontist due to crowded teeth, leading to a shift in the main molars;
- injury to soft tissues by the coronal part caused by incorrect position.
The process of removing the figure eight leads to a reduction in pain, preservation of the shape of the face with a certain arrangement of teeth and helps to avoid infection with various infections.
Lipoma and leukoplakia
Lipoma is a benign tumor that is formed from subcutaneous loose connective tissue. Popularly, such a tumor is called a wen.
If the wen in the baby’s mouth is small and single, then it does not pose a danger. The lipoma does not need to be removed by a doctor, and certainly not touched on your own. Trying to squeeze out a wen, it is easy to introduce an infection into the wound. If the lipoma begins to grow and interferes with the baby, it must be removed surgically.
Why do my baby's gums turn white? The cause may be leukoplakia - keratinization of the mucous epithelium. The disease is most often localized on the mucous membrane of the lower lip, in the corner of the mouth, in the depths of the mouth closer to the pharynx, on the tongue and the inside of the cheeks. Reasons for appearance:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- injuries of the oral mucosa;
- lack of vitamin A.
If a baby is diagnosed with leukoplakia, it must be treated immediately. Without proper treatment, the disease can eventually transform into cancer.
What structure do teeth have?
The anatomical and histological type of tooth structure is distinguished, and the structure of the enamel and root is also indicated separately:
- Anatomically, a tooth is divided into three components: root, neck, crown.
Crown – rises above the gum, covered with enamel. According to the type of crown there are: - facial;
- contact;
- lingual.
The root and crown are connected by a neck covered with cement and covered with gum. The root is what attaches the tooth to its socket. It is single-stemmed or with several branches.
occlusion - the place where paired teeth of opposite jaws meet;
- Enamel is a dense tissue that is highly durable and is responsible for protecting the tooth from harmful bacteria; it consists of 94% salts: zinc, magnesium, fluorine and iron. Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids make up the remainder. Enamel also contains a certain amount of liquid elements that participate in physiological processes. The outer shell of enamel is the cuticle. It is used for chewing, as it has a fragile structure, can wear off over time, and therefore requires care. Every tooth is covered with enamel. The basis of bone tissue, located under the enamel, is a complex of minerals that surround the root canal and the entire dental cavity. The smallest channels of dentin tissue help in the processes of nutrient metabolism and transmit nerve impulses.
- Root. Pulp and periodontium:
- Pulp is a cavity inside a tooth (with loose tissue) that has nerve endings and blood vessels.
Participates in providing nutrition and exchange of elements. When removed, these processes slow down or stop altogether. There is a recess in the jaw - the alveolus - this is where the root is placed. It contains mineral tissue and is covered with cement on the outside. The end of the root is the apex, which has blood vessels that nourish the dental tissue. The number of roots varies from 1 to 5.
Periodontium is a connective tissue, a connecting element that can fill the void between the jaw socket and the tooth root. Nutrients enter the dental system through periodontal tissue.
Let the doctor make the diagnosis
A mother needs to have an idea of what diseases her child may develop. However, such knowledge is necessary in order to promptly identify the threat and consult a doctor, and not in order to self-medicate.
Only a doctor can determine why the baby’s gums turn white, whitish spots or white bumps appear. Which specialist is best to contact? Dentists deal with diseases of the oral cavity. If there is a suspicion of infectious diseases, the baby has a fever, then it is better to consult a pediatrician.
Doctors make a diagnosis based on a visual examination. If necessary, the dentist can send for an x-ray to determine whether the growth is a tooth or not. To make an accurate diagnosis, a plaque scraping may be taken.
Is it possible to alleviate the baby’s condition at home or prevent the appearance of white pimples? The famous children's doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky advises carefully caring for your oral cavity. After eating, you need to rinse your baby’s mouth and wipe it with a clean cloth soaked in water. To disinfect, a cleaning cloth can be soaked in a weak soda solution.
If a baby has white spots in the mouth, dense balls or tubercles, Dr. Komarovsky recommends going to the hospital. Only a doctor can determine what caused the pimples and prescribe adequate treatment.
How many roots does a wisdom tooth have?
- The number of roots in eights varies from 2 to 5, the length is 8-10 mm. Their roots are curved and this can cause difficulties during dental intervention.
- Externally, a wisdom tooth is not very different from other molars. Whether they grow or not depends on many factors: jaw size, heredity, etc. The rudiments are formed around 3 years of age.
- Sometimes the eruption process lasts up to 40 years. Tooth growth lasts about 1.5 months. The unpleasant sensations in this case can be explained by the fact that eights do not have the first milk teeth; they have to erupt through dense bone tissue.
- When properly cut, the figure eight lasts a long time.
Diagnosis of microdentia
According to statistics, about 5% of people face the problem of microdentia – abnormally small teeth in an adult. There are several signs that allow you to distinguish microdentia from other dental pathologies.
- teeth of regular shape, but with a significantly reduced crown;
- distances between teeth visible to the naked eye;
- damage mainly to the front teeth;
- wavy or jagged shape of the cutting part of the affected tooth.
In most cases, the presence of microdentia can be determined by visual examination of the patient, but for a more accurate diagnosis, hardware diagnostics are performed. For example, the doctor can measure the overall width of the incisors of both jaws using a special instrument, as well as resort to x-rays.
Isolated
If the patient has one or two small teeth, then we are talking about isolated microdentia. Most often, the front incisors (mainly the lateral incisors) are underdeveloped.
Relative
Relative microdentia is said to occur when the patient has an abnormally enlarged jaw. On such a jaw, even normal-sized crowns can look disproportionately small. Thus, relative microdentia is an overly large gum and small teeth on it.
Generalized
In the most severe cases, when small teeth are located throughout the jaw, the patient is diagnosed with “generalized microdentia.”
At first glance, it seems that small teeth in an adult cause only aesthetic inconvenience, but this is not so. Dentists identify several quite serious problems that microdentia can lead to.
- Distal displacement of teeth, that is, their gradual shift back relative to the optimal position in the jaw.
- The appearance of gaps between the teeth (the so-called diastemas and threes), which lead to disruption of the contact of the lateral surfaces of the teeth. Without support, the ligaments in the dental bed stretch and the tooth becomes unstable.
- Diction disorders, excessive amplification of hissing and whistling sounds in speech.
- Periodontal disease is a disease of the soft tissues of the jaw, caused by accumulations of bacteria in the interdental spaces and an enlarged periodontal pocket due to the high mobility of the tooth.
What to consider when carrying out restoration
Before proceeding with dental restoration, it is necessary to take into account some factors on which the quality of the procedure depends.
First of all, the dentist must pay attention to the suitability of the tissue, and most importantly, the root, for restoration. In other words, check the vitality of the tooth. It is worth noting that modern adhesive systems make it possible to restore almost any roots. However, the canal must be well sealed.
The condition of periodontal tissues also plays an important role. In the presence of certain diseases, restoration is possible only after surgical or conservative treatment, which is often combined with splinting.
An important factor is the patient’s hygiene skills. If not done regularly, the corrected surfaces can lose their shine very quickly. With insufficient care, marginal pigmentation may appear.
Another factor that simply cannot be ignored is the correct choice of materials that will provide sufficient adhesion to dental tissues, which can withstand any chewing loads, and also have excellent aesthetic characteristics.
Stages of aesthetic tooth restoration
The main stages of restoration are:
- Preparing for the procedure. It consists of hygienic cleaning of teeth from tartar and plaque, determining the color of the tooth to be restored and the corresponding shade of the composite material using a special scale.
- If necessary, local anesthesia is administered.
- Drilling out old fillings and installing new ones if it is necessary to replace an old restoration.
- The tooth is isolated from the patient’s wet breath and saliva. For insulation, a latex scarf with holes for teeth is used. This measure is necessary because moisture getting between the tooth and the restoration can lead to various problems, including caries and loss of the structure.
- If the crown of the tooth is severely destroyed (more than half) and the tooth is pulpless, then the restoration must be strengthened with a pin.
- Restoration of the crown part of the tooth with filling material. To make the tooth look natural, a layer-by-layer technique of applying filling material is used. Layers of restoration material of varying transparency and shades are applied to each other, which will subsequently give the restored tooth a natural appearance.
- Finishing of the restored tooth. The final modeling of the tooth shape is carried out using burs, followed by grinding and polishing of the restoration.