November 11, 2020 Last revised: September 12, 2020 Dental diseases
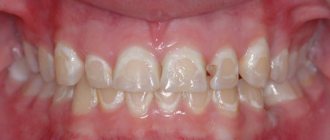
If you notice dull, dark areas on the surface of one or more teeth, take the situation seriously. At the initial stage, enamel erosion can be painless; every tenth patient does not complain at all about increased tooth sensitivity even when the disease is actively progressing. However, without promptly seeking help from a dentist, you can wait until there is no trace left of the enamel on the teeth, and the damage reaches the dentin tissue.
How to distinguish enamel erosion from caries?
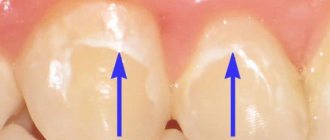
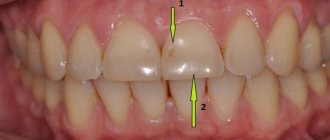
- Localization of the lesion. Often, stains form on the front surface of the teeth. In most cases, non-carious lesions are symmetrical, that is, they affect two teeth of the same name at once. The first to be affected are the upper incisors, canines and premolars.
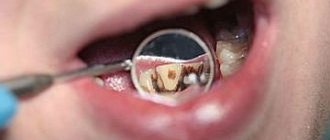
- Spot shape. The defect has an oval or round shape. This is easy to determine if you completely dry the teeth from saliva. In the initial stages, erosion will immediately manifest itself in the form of an area that has lost its luster. The boundaries of the stain will become clearly visible if you lubricate the tooth with the usual 5% tincture of iodine.
- Surface texture. A carious tooth is always rough to the touch. An erosive spot, on the contrary, is smooth.
The incisors and molars located on the lower jaw are least susceptible to erosion.
In addition to external defects, enamel erosion has another symptom that is simply impossible to ignore - increased tooth sensitivity. A dark spot will not only ruin your smile, but will also torment you with aching pain every time you want to brush your teeth, drink something hot or cold, or go outside in frosty weather.
The tooth may not hurt - this is indirect evidence that the process is in a stabilized stage, when dental tissues are not worn out so quickly. But if the slightest irritation is painful, then erosion has entered the active stage. During this period, the enamel is destroyed especially rapidly.
Diagnostics
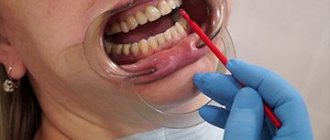
In the process of carrying out diagnostic measures, a specialist must collect the most complete anamnesis to make an accurate clinical diagnosis, since erosion is often mistaken for carious manifestations or a wedge-shaped anomaly.
The success of treatment is directly determined by the quality of diagnosis, which includes the following manipulations:
- the use of iodine - at the stage of formation of the disease, an effective method for identifying it is staining problem areas with iodine. It will give the defect a more pronounced color;
- The distinctive feature of the disease is considered to be the shape and location of the lesions , as well as their smoother surface in comparison with the rest of the tooth.
Do not underestimate the advisability of holding consultations with specialized specialists - endocrinologist, gastroenterologist .
Having identified deviations in the activity of vital systems of the functioning of the body as a whole, it is easier to understand the nature of the formation of pathology and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Development of the disease
Depending on the area of eroded areas, doctors divide 3 stages of disease development.
1st degree. This is the initial stage, at which erosion has only touched the surface layers of the enamel. But now the disease can be diagnosed. The lack of natural shine in some areas of the tooth is the first sign.
2nd degree. Dentists call this clinical picture a situation of moderate severity. Pathological destructive processes have already affected the entire thickness of the enamel and, perhaps, managed to reach the tissues bordering the dentin - the so-called enamel-dentin junctions.
3rd degree. The protective layer of enamel is destroyed, erosion has managed to affect the dentin. You cannot delay any longer, otherwise the tooth will be completely destroyed and only prosthetics can save it.
The course of erosive disease in each patient is individual. On average, erosion takes about 10-15 years to reach dentin from its initial stage.
Stages
If you do not go to the clinic in a timely manner, the initial stages of the disease may simply not be noticed, since the symptoms are practically not expressed.
At the same time, doctors still take into account the process of formation of the anomaly to classify the stages of the disease:
- initial - atypical fragments are single in nature and affect a very thin surface layer, as a result of which they are very difficult to detect on their own;
- medium - destructive processes grow into the deeper layers of the hard tissue of the organ and the patient begins to react acutely to hot and cold temperatures;
- deep stage of progression - the surface is almost 100% destroyed, deep damage to dentin has begun.
If we consider the pathology from the point of view of the degree of damaging effects on the tooth, we can distinguish the following phases of the disease:
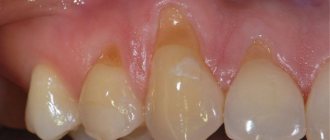
- active – develops quickly, symptoms are pronounced. Erosion is localized by multiple focal manifestations, is accompanied by pain and quickly changes color pigment, making the surface dark and dull;
- phase of relative stability - proceeds more calmly, there are no external signs. It is a consequence of the formation of tertiary dentin, which relieves pain and performs a protective function.
Erosion of tooth enamel and its causes
Oddly enough, doctors still don’t know for sure why the enamel suddenly loses its strength and the process of destruction begins. The etiology of the disease is being carefully studied, practitioners are trying to establish cause-and-effect relationships, and so far they have voiced three main circumstances that could serve as a trigger for erosive processes.
Chemical
It is known that tooth enamel is affected by acid, which we consume along with foods and drinks that have a strong sour taste. The protective layer of the tooth literally softens, but only for a short time. Saliva gradually restores the natural acid balance and everything returns to normal. But, if the amount of acidic food in the daily diet goes off scale, the acid level does not have time to return to normal and then the risk of developing erosion increases several times. Vegetarians and lovers of strict diets, in which fruits make up the lion's share of the diet, cannot ignore this circumstance.
If apples, citrus fruits and juices, sweet soda, pickled and soaked vegetables make up 60% of your daily food intake, then you can be identified as at risk
Mechanical
Harmless daily hygiene procedures can contribute to the occurrence of erosion. It is better to give up the habit of brushing your teeth with a hard toothbrush with synthetic bristles forever - this is fraught with mechanical damage not only to the upper layers of enamel, but also to the soft tissue of the gums. You shouldn’t get too carried away with tooth powders and whitening pastes either - if the reminalizing effect of saliva is weakened, the likelihood of noticing erosive stains on your teeth over time is too high.
Endocrine
Erosion of tooth enamel may be a symptom of underlying thyroid problems. Thus, hyperfunction of the endocrine gland (thyrotoxicosis) causes increased salivation and causes some changes in the composition of saliva. This circumstance often affects the condition of tooth enamel.
40-50% of patients suffering from erosion of tooth enamel were diagnosed with concomitant diseases, one way or another associated with abnormalities in the endocrine system
Consequences of refusing therapy
Do not underestimate the problem and delay treatment. At first glance, a harmless situation can transform into serious consequences.
It could be:
- rapid wear of dental units , and, as a result, their premature destruction;
- darkening of the coronal part of organs;
- hypersensitivity , manifested not only by intolerance to cold, hot and sour, but also by acute pain even with minimal contact with the tongue and lips;
- frontal units acquire an almost transparent, unaesthetic appearance , their strength and structural content are impaired.
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion
To prescribe effective treatment, it is first necessary to determine the level of mineralization of the teeth. Unfortunately, there are no instrumental or laboratory methods for such research yet. Therefore, doctors make diagnoses based on the data contained in the anamnesis and general clinical symptoms.
Treatment of erosion does not happen in one visit to the dentist's office. This is a long process that includes a whole range of activities:
- removal of dark pigment;
- reminalizing therapy (saturation of dental tissues with fluoride and calcium);
- filling (if there is severe damage to the enamel on the face, the dentist will advise covering the tooth with a crown).
The longest stage is the application of preparations containing fluoride and calcium. Depending on the depth and area of destruction, solving the problem may take 10-15 sessions. You should strictly follow the schedule for visiting the dental office - if the dental tissues do not receive the required dose of minerals, proper adhesion to the filling material will not occur and then all efforts will be in vain - therapy will have to start all over again.
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion in the active stage, which is accompanied by severe painful sensitivity, requires additional physiotherapeutic procedures. So, the doctor may also prescribe electrophoresis. In this case, the course of treatment will most likely be continued.
Erosion of tooth enamel: drug treatment
The following drugs are most often used to reminalize a tooth.
- Calcium glycerophosphate. Its task is to replenish calcium deficiency within a month (the average duration of a standard course of treatment with the drug). To do this, you need to take 1.5 g per day, dividing the daily dose in equal parts into three doses.
- Calcium gluconate. Saturates hard dental tissues with calcium and has an anti-inflammatory effect. To do this, an application of a 10% solution of the drug is applied to the tooth surface, previously dried from saliva and cleaned. The duration of one session is a quarter of an hour. During this time, the tampon with the solution is changed three times. For prevention, 5 sessions will be enough, but if you have to deal with an advanced clinical picture, then the number of procedures can reach 30.
- Sodium fluoride. Promotes active restoration of bone tissue. The procedure is as follows: the tooth surface is thoroughly cleaned and dried, then a sterile cotton pad soaked in a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied, after 3-4 minutes the application is removed and the mouth is thoroughly rinsed with water.
- Fluoride varnish. Disinfects and has an analgesic effect. Before applying the medicinal substance to the eroded area of the tooth, it is treated as in the two previous cases. Then, using a brush, a viscous liquid with a distinct pine smell is applied in a thin layer to the erosion site. After 2 days the procedure must be repeated.
As a concomitant therapy, the doctor may prescribe vitamin complexes. Avoiding acidic foods and citrus fruits, as well as maintaining good oral hygiene, is strictly necessary.
General overview
Erosion of tooth enamel is a lesion of the outer surface of an organ that is of non-carious origin.
The primary symptoms are quite sparse - single convex fragments of the relief, and a reaction to temperature changes.
And only against the backdrop of progression of the pathology, the patient can independently observe more serious manifestations that force him not to delay a visit to a specialist - pigmentation, pain of varying degrees of intensity, which is difficult to relieve with analgesics.
How to prevent the development of the disease?
The most common myth about tooth enamel erosion says something like this: this disease is most often diagnosed in middle-aged and older people. In reality, the situation is somewhat different. Official statistics indicate 40 cases per 100,000 people. Moreover, young people (and even children!) risk no less than older people.
In some ways, young people are even more susceptible to erosion than their parents. Because with age, the latter accumulate more and more minerals in their teeth, which means they become less sensitive to the effects of external harmful factors. This phenomenon has been proven and has a medical term - mineralization. At the same time, the harmful environmental background, the massive consumption of sweet carbonated drinks, fresh juices, and juices are the reason that every year the number of cases of enamel erosion in the age group from 18 to 25 is growing rapidly. That is why everyone needs to arm themselves with basic knowledge about preventive measures.
Prevention of enamel erosion
- It is necessary to limit the amount of consumption of acidic foods and drinks. The less acid that gets into your mouth, the stronger your enamel will be.
- If you do decide to drink juice or soda, use a straw. You should not keep the liquid in your mouth for a long time; swallow as quickly as possible.
- Try to acquire a new habit: end each meal with a product that neutralizes the effect of acid. This could be half a glass of milk, a piece of cheese or any other of your favorite fermented milk products. Those who are not ready to consume milk so often can purchase special lollipops at the pharmacy.
- Chew chewing gum (without sugar!) - it stimulates salivation. The more saliva, the faster the natural acid balance will be restored.
- Brushing your teeth twice a day (after breakfast, and in the evening, as soon as the last piece of dinner is eaten) is a good habit. But there is a catch: if you ate acidic food for dinner, then it is better to postpone traditional teeth brushing for half an hour or an hour.
- There is no need to be overzealous when brushing your teeth. Do not press the brush too hard, otherwise it will easily damage the top layer of enamel. And one more thing: you should start the procedure from the inside of the dentition, gradually and smoothly moving on to cleansing the outside.
- It is better to throw away a hard toothbrush with hard synthetic bristles immediately. To keep the enamel strong, you need to get a brush with soft natural bristles or medium-hard bristles.
- Choose your toothpaste carefully. You should not constantly buy tubes labeled “whitening” - their chemical composition may be too aggressive towards the enamel. Pastes with various kinds of abrasive particles (granules, etc.) scratch the tooth - it is also better to avoid them. But what is worth paying attention to is fluoride-containing toothpastes, which promote tooth mineralization, and therefore make the enamel stronger.
Diagnosis of damage to hard dental tissues
At the stage of diagnosis, the doctor collects an anamnesis, examines the lesions, and, if necessary, makes a differential diagnosis.
The patient may complain of:
- dental hypersensitivity;
- aesthetic discomfort when talking or smiling;
- problems with the pronunciation of sounds “s”, “z”.
It is important to distinguish erosion from a wedge-shaped defect, in which the lesion extends along the neck of the tooth, and superficial caries, which is expressed by a rough lesion of the enamel.