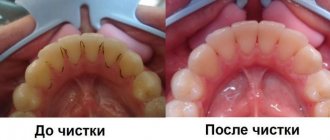
Action of Chlorhexidine
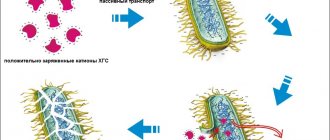
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic, successfully used in the treatment of various diseases, including gynecological ones. It is active against the following number of microorganisms: treponema, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gonococcus, cytomegalovirus, herpes virus, bacteroides, Trichomonas vaginalis.
After treatment, a small amount of the product remains on the skin, which ensures a long-lasting antibacterial effect. The antimicrobial effect is maintained even with pus, blood and other physiological fluids, but the effectiveness decreases slightly.
Viruses (with the exception of herpes), as well as fungi, show resistance to the drug. Chlorhexidine does not have a systemic effect; when applied topically, it does not penetrate the bloodstream.
Pros and cons of chlorhexidine mouthwash
Chlorhexidine is a popular agent used for oral antiseptic treatment. Dentists often prescribe this drug in their own practices. This purpose is determined by certain advantages of the described antiseptic solution:
- Has a significant effect on pathogenic microflora.
- Characterized by a wide range of antimicrobial action.
- The drug is affordable - its cost ranges around 15 rubles. per bottle.
- The aseptic effect lasts for several hours after the rinsing procedure;
- Chlorhexidine can be used by women during pregnancy and breastfeeding (with caution).
- A solution of this drug can be used in relation to children, but the drug should be of lower concentration.
However, uncontrolled rinsing with Chlorhexidine in childhood is undesirable and can lead to some negative consequences. For this reason, the drug can be prescribed to children only by the attending physician, subject to absolute indications. Also, the dentist will indicate the required concentration of the antiseptic composition and the duration of therapy.
Despite all the positive aspects of the Chlorhexidine solution, it has a certain number of disadvantages, the main of which are:
- Chlorhexidine has a rather bitter taste, which can sometimes make rinsing difficult for some patients. There is a particularly negative attitude towards treating the oral cavity with such a product in children.
- An antiseptic solution for the most part does not have the required therapeutic effect in the case of a viral infection, with the exception of herpes.
- If Chlorhexidine is prescribed in a course and rinsing is not a one-time procedure, then hard dental tissues become grayish in color. Also, a similar effect is observed with excessively frequent use of an antiseptic solution.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with The sky is yellow and your throat hurts
Often, after stopping rinsing with this composition, the enamel color is quickly restored to its original color.
Composition and release form of the drug
In gynecology, different versions of Chlorhexidine are used:
- aqueous solution (0.02 - 20%);
- vaginal suppositories;
- gels for vaginal use.
For douching with Chlorhexidine, predominantly weakly concentrated aqueous solutions of up to 0.2% are used. More concentrated solutions are used to treat ulcers, burns and sutures after surgery.
Pharmacies usually have solutions of Chlorhexidine bigluconate 0.05%. This option is perfect for vaginal douching and treatment of the genitals. The auxiliary substance for this product is simple purified water, with which you can dilute the drug in a bath to the desired concentration.
Interaction with other drugs
Due to incompatibility, Chlorhexidine should not be used simultaneously with the following medications and substances:
- iodine;
- phosphates;
- chlorides;
- borates;
- detergents with an anionic group: sulfonic acid, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, saponins;
- any alkali;
- antiseptic solutions for douching;
- soap.
Using soap before douching with Chlorhexidine is not recommended.
Indications for use in gynecology
Chlorhexidine has proven itself in use for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of a bacterial nature and fungi, as well as diseases that are transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse:
- thrush (candidiasis);
- nonspecific cervicitis, vaginitis and vulvovaginitis;
- chlamydia;
- herpes.
It can also be used to prevent infections, treat sutures, as a means for intimate hygiene, and to eliminate unpleasant odors in cases of thrush.
Chlorhexidine is used to prevent sexually transmitted infections. Despite the relative safety of the product, douching should not be used excessively. Too frequent injection of the solution into the vagina can harm the microflora, which will contribute to the development of a new problem - dysbiosis.
How to rinse your mouth correctly?
It should be remembered that after a tooth is removed, a dense blood clot forms on top of the bone tissue. Forming a kind of “cushion”, it prevents contact of the hole from which the tooth was pulled out with the contents of the oral cavity, food debris, pathogenic bacteria and microbes. Such a blood clot is not tightly attached at first, so rinsing too vigorously can cause it to fall out of the wound. This, in turn, will cause an inflammatory process (alveolitis): along with constant aching pain, the gums will swell, and bad breath will appear.
So, from all of the above, we can draw the following conclusion: for the first time after tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth, this can lead to negative consequences. It is enough to make antiseptic baths by taking liquid into your mouth and, after holding it for several minutes, spitting it out.
How to do douching at home?
The Chlorhexidine package is shaped like a rubber bulb, so it can be used for douching. But it will be more convenient to use the usual rubber bulb to insert the required amount of solution into the vagina and not pour in too much.
To carry out one procedure, a dosage of 10-15 ml of Chlorhexidine solution will be sufficient. The procedure must be carried out while in a supine position. After injecting the product inside, you need to raise your legs slightly, bending your knees, to avoid the antiseptic leaking out too quickly. It is recommended to remain in this position for 5-10 minutes. After this time has expired, you can get up.
It is also worth considering that the remaining solution may leak out of the vagina, so it is worth attaching a sanitary pad to your underwear.
So, how to do douching correctly? Instructions for use are divided into the following steps:
- Disinfect the syringe.
- Prepare a solution of 0.05%. If the solution is more concentrated, then it should be diluted with water.
- Pour into a syringe.
- Lie in the bathtub or on the bed, placing a medical blanket under you.
- Immerse the nozzle of the douche into the vagina 5-7 centimeters and pour the product inside.
- Raise your legs with your knees bent and lie there for 3-5 minutes.
- Lower your feet and let the substance flow out.
- Attach a sanitary pad to your underwear, as the product will gradually come out.
- Avoid urinating for the next couple of hours.
Do not heat the solution. Due to an increase in the temperature of the antiseptic, it can change the chemical properties of the drug and negate the pharmacological ones.
How to use
Considering the different forms of microorganisms that chlorhexidine should affect, the concentration and treatment mechanism are selected by the dentist individually, depending on the overall picture of the disease. Examples of treatment can be viewed in the table below:
| Disease | Concentration of chlorhexidine solution | Reception scheme | Duration of therapy |
| For stomatitis | 0.05% | Apply after complete cleansing of the oral cavity. Rinse your mouth with the solution for 30-60 seconds without stopping, 2 times a day. | Up to 10 days |
| For gingivitis | 0.05% | Rinse twice a day immediately after brushing your teeth and using dental floss. | Up to 10-12 days |
| For gum inflammation | 0.05% | First, the patient rinses the mouth with chamomile decoction or iodine-saline solution. Then, treat the mouth with 1 tbsp. l. chlorhexidine. It is forbidden to eat food within 2 hours after the treatment procedure. To treat infants, the affected areas are moistened with a cotton pad soaked in chlorhexidine. | Up to 10 days |
| After tooth extraction | 0.05% | Treatment is carried out 1 hour after brushing your teeth, 2-3 times a day. The solution is poured into the mouth and held for 1-2 minutes, while the head is slightly tilted from side to side. Head movements should not be too sharp to avoid injury to the protective blood clot. It is forbidden to eat food within 1 hour after treatment. | The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor individually. |
| For toothache | 0.05% | Rinsing is carried out 3-5 times a day, holding the solution for 1-2 minutes. | 7 days |
| For periodontal disease | 0.05% | It is used at the time of removing plaque in the form of baths. The product must be in contact with the pockets of periodontal tissue and remain in effect for 2-3 minutes. | 5-7 days |
| For preventive purposes | 0.05% | Caress the oral cavity for 20 seconds, 2 times a day | 5 days |
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Thrush in a child’s groin: how to treat it, causes, what it looks like (photo)
Restrictions on use
Not all women can douche with Chlorhexidine, as allergic reactions may occur. To prevent unwanted consequences, it is recommended to conduct a test. To do this, apply a small amount of the drug to the middle third of the forearm. If after 10-15 minutes no reactions occur on the skin, then the product is suitable for the procedure.
If redness, swelling or itching appears on the skin, the drug should not be used under any circumstances. It is best to contact a gynecologist who can choose a different remedy to treat the problem.
It is strictly forbidden to use the solution with soap or iodine. When douching with Chlorhexidine, there is a high risk of damaging the vaginal microflora, since the drug destroys all bacteria - both harmful and beneficial. To restore the microflora after douching, you need to use probiotics.
Chlorhexidine rinses after tooth extraction
We should also talk about rinsing after tooth extraction. It may not always be required. If this operation was easy, treatment with chlorhexidine can be carried out once, a few hours after removal, and not as a rinse, but with a cotton swab soaked in the drug. The gums are treated in the same way after the loss of a baby tooth. You need to rinse your mouth if the following situations arise:
- complex tooth extraction with dissection of the gums;
- tooth extraction due to an inflammatory process at the root of the tooth;
- the presence of significant carious cavities in adjacent teeth;
- blood clot damage.
Contraindications to the use of the drug
Chlorhexidine is considered a fairly strong drug, and there are many contraindications for its use, including:
- age under 18 years;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- allergies and hypersensitivity to components;
- viral skin diseases.
As an alternative, you can douche with a decoction of chamomile, use phytosuppositories with pumpkin oil, propolis or sea buckthorn. You can also use vaginal suppositories with Chlorhexidine.
Can children rinse their mouths with Chlorhexidine?
Tooth extraction may also be required in childhood. Typically, this measure is required when baby teeth are loose, but in case of severe carious lesions, molars may also need to be removed. Preventive treatment with antiseptics in childhood is especially necessary. This is due to several factors:
- insufficient activity of the immune system to suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- poor hand hygiene and non-compliance with sanitary standards;
- increased sensitivity of the gums and soft tissues surrounding the tooth to the effects of pathogenic bacteria and inflammatory processes.
Can children rinse their mouths with Chlorhexidine?
If necessary, Chlorhexidine can be used in childhood, but the rules of use will differ from the preventive treatment of adult patients. For children, it is recommended to dilute the drug with boiled water in a ratio of 2:1 (2 parts Chlorhexidine - 1 part water). You should rinse your mouth strictly under adult supervision and only if the child knows how to spit out the product and does not swallow it.
The number of procedures is also slightly reduced. The maximum permissible number of rinses in childhood is 2 times a day. The course of prevention depends on the age of the child. Approximate norms are presented in the table below, but they may vary depending on the condition of the oral cavity, the complexity of removal and other individual characteristics of the child.
Treatment of a child with the drug is allowed
Table. The duration of the course of use depends on the age of the child.
Douching with Chlorhexidine during pregnancy
Frequently asked question: Is it possible to douche during pregnancy? Pregnancy is a contraindication for douching
.
Main reasons:
- High risk of fetal infection. This can happen in the last weeks, because the cervix opens slightly during these periods and the plug comes out. If the pressure is too strong, fluid may enter the cervix.
- Imbalance of vaginal microflora.
Is it worth douching with Chlorhexidine for sanitation before childbirth? Douching is not recommended; only washing is recommended. If your doctor prescribes douching during pregnancy, you should consult another doctor.
Chlorhexidine suppositories can be used 2-3 per day during pregnancy. Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the drug. If side effects occur (itching, burning, redness), you should stop using the drug. Chlorhexidine can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. No self-medication!
Possible contraindications and side effects
"Chlorhexidine" has practically no contraindications, with the exception of various groups of dermatitis. The manufacturer warns about possible intolerance to the drug and allergic reactions to the components of the solution, but practice shows that allergies to the drug are very rare - less than 1% of patients.
Contraindications and side effects
Side effects during use are rare. Patients may experience increased dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tingling, burning and itching. These phenomena are of moderate intensity and do not require discontinuation of the drug or cessation of treatment.
Important! Most patients tolerate Chlorhexidine well, but in very rare cases, adverse reactions may occur. Extremely rarely, intolerance can manifest itself as a pinpoint, pale pink rash on the surface of the tongue, gums and inner surface of the cheeks. If this symptom appears, you should consult a doctor.
"Chlorhexidine" is sold in all pharmacies
Chlorhexidine analogs
There are several possible substitutes and analogues of Chlorhexidine, which also contain chlorhexidine digluconate as the active ingredient:
- Amident;
- Hexicon;
- Citeal.
There are also drugs with a different active substance, but with a similar effect:
- Vagotil (active ingredient - polycresulene).
- Miramistin (active ingredient - benzyldimethyl ammonium chloride monohydrate).
Read
Also:
- Depantol suppositories in gynecology: why and how to use?
- How to tighten your breasts at home
- Douching ASD 2: antiseptic and stimulant in gynecology
- How to properly perform vaginal douching?
Recommendations for use
To rinse the mouth, it is recommended to use an undiluted 0.05% aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine. Main rules for use:
- rinse in the morning and before bed after eating and brushing your teeth;
- use this product for no more than 14 days, for preventive purposes - less than 10 days;
- do not dilute the prepared solution with water;
- rinse your mouth for at least 1 minute (time sufficient to fix the drug on the oral mucosa and teeth).
Read also: What to give your child for toothache
Chlorhexidine is intended for external use only (treatment of affected tissues of the mucous membrane, skin, medical instruments, disinfection of surgeon's hands and dentures). To avoid the drug entering the body, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the drug is inaccessible to children.
To heal the hole after tooth extraction
Chlorhexidine (0.05%) in the form of a bath is regularly used in the first 3 days after tooth extraction. Frequency of use: 30 seconds at least 3 times a day. After the specified period, rinsing is indicated (exactly the same solution is used as in the bath) - one minute only 3 times a day.
During the process of tooth extraction, the doctor treats most of the oral cavity with an antiseptic - a drug containing Chlorhexidine. This reduces the risk of tissue infection and bacterial growth in the wound area.
If, after tooth extraction, negative consequences appear in the form of alveolitis or an empty socket, you should immediately contact the surgeon who performed the operation or the attending physician. He will carefully examine your mouth, treat the wound and prescribe the necessary medications. Chlorhexidine in this case is not a panacea.
To relieve gum inflammation
Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) is a common problem that can be solved very simply if you visit a doctor in a timely manner and prescribe therapy.
Pharmacies offer many ointments and antibiotics that can cope with inflammation, but home methods (in particular, rinsing with Chlorhexidine) can have a good effect as an additional remedy in the fight against microbes and damage to the tissues and mucous membranes of the mouth. If the gums bleed and swell, we can talk about their inflammation caused by various diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.). Bacterial plaque and hard deposits on teeth are the main cause of gum disease. Chlorhexidine, as a remedy for inflammation, is effective only after professional removal of tartar and plaque; it will not be able to cope with deposits.
For oral diseases
The drug is widely used in the presence of the following pathologies and diseases of the oral cavity:
- Stomatitis. The solution destroys pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Treatment should not exceed 10 days.
- Gingivitis and periodontitis. Bacterial plaque, which causes loose teeth and bleeding gums, cannot be removed with Chlorhexidine. However, its use is mandatory during the plaque removal procedure itself and after its completion (in the form of regular rinses). The duration of treatment is about two weeks.
- Inflammation of the hood over the wisdom tooth due to emerging problems with eruption.
- Irritation of the wound opening after tooth extraction due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into it.
- Infections in the throat area.
Video
Chlorhexidine. Instructions for use.
HIV infection is one of the most dangerous diseases of humanity. Finding ways to prevent or treat this disease still remains one of the most pressing issues in modern medicine. Recently, a myth has appeared that Miramistin is very helpful against HIV. This is a new antiseptic product made in Russia. In different sources, we found different opinions about whether this remedy helps in the treatment and prevention of HIV or not. Let's figure out how the product can help treat the infection and whether it can compete with chlorhexidine.
How to use chlorhexidine to prevent sexually transmitted diseases
Prevention after casual relationships helps prevent infection with STDs and the development of complications.
In this case, it is recommended to use medications that have antibacterial, antiviral and antiseptic effects.
Oral administration of drugs is possible only after consultation with a doctor, who is recommended to be contacted immediately after unprotected or questionable sexual contact.
When is prevention necessary?
To prevent STIs, it is recommended to avoid questionable sexual intercourse and regularly use a condom. If you have had unprotected sexual intercourse, you should immediately take preventive measures and consult a venereologist.
A barrier contraceptive does not provide a 100% guarantee, therefore, if an STD is suspected, it is necessary to carry out emergency prevention and contact a specialized clinic for diagnosis and drug prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. The reason for contacting a venereologist may be the appearance of the following symptoms:
- rashes on the genitals;
- redness, swelling of the genitals;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies during sex and when urinating;
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area;
- non-physiological discharge from the vagina or urethra (yellow, gray, green with a foul odor).
In addition, the patient may experience increased fatigue, muscle weakness, and body aches. Body temperature may rise to subfebrile or critical levels.
Prevention for men
Prevention of STDs after casual sex includes a set of measures to minimize the risk of infection within 2 hours after sex. To do this, a man needs:
- Immediately after sex, empty your urinary reservoir - urine has antiseptic properties. Due to the physiological characteristics of the structure of the genitourinary system, by urinating it is possible to cleanse the urethra and mucous membranes of the penis from pathogenic microorganisms.
- Wash your hands under running water and soap, take a shower and clean the groin and buttock area, penis with antibacterial soap.
- Treat the groin and penis with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, and potassium permanganate solution.
- Douche the urethra with antiseptic agents: insert the tip of the bottle or syringe into the urethra and pour in a few milliliters of solution.
- After treating the genitals, refrain from urinating for 3-4 hours.
- Wear clean underwear made from natural materials.
Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases for women
Prevention of STDs after casual sex for women involves step-by-step adherence to the following recommendations:
- Immediately after intimacy, empty your bladder. This will help clear the urethra of viruses and bacteria that may have entered during sex.
- Wash your hands with soap.
- Take a shower, paying special attention to the groin area and genitals. During hygiene procedures, it is recommended to use antibacterial, laundry or tar soap, which have a disinfecting effect.
- After a shower, treat the external genitalia with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
- Douche the vagina with antiseptic agents. To do this, you need to lie on your back, raising your pelvis, and pour about 50 ml of the solution into the vagina. Wait 2-3 minutes and stand up to allow the liquid to pour out.
- After douching, insert Betadine, Chlorhexidine or Hexicon suppositories into the vagina.
- After the procedures, put on clean underwear and avoid urinating for 2-3 hours.
Emergency prevention after casual sex is effective only within 2 hours after casual sexual contact.
List of drugs and their features
After emergency measures to prevent sexually transmitted diseases, it is recommended to use medications with antibacterial, antiviral and disinfectant effects.
Drug prevention of casual relationships with oral medications is effective within 48 hours after sexual intercourse. For this purpose it is recommended:
- Penicillin antibiotics (Ticarcillin, Penicillin, Oxacillin) for intravenous and intramuscular administration at a high risk of syphilis infection. The drugs are prescribed once in a dosage of 2.4 million units.
- Cephalosporins are antibiotics for emergency prevention of gonorrhea and syphilis. Ceftriaxone, Cefixime and other drugs of this group are prescribed once in a volume of 400 mg.
- Macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin) are recommended to prevent infection with Treponema pallidum, gonococci, and chlamydia. Daily dosage is 1000 mg with a single or double dose.
- Aminoglycosides (Spectinomycin, Gentamicin) are used once in a volume of 2 g of the active substance to prevent gonorrhea.
- Nitroimidazole derivatives (Metronidazole) are effective against STDs caused by protozoa. For trichomoniasis, it is prescribed in a single dosage of 2 g, which corresponds to 8 tablets.
The combined action drugs Oletetrin and Safocid are prescribed to prevent STDs of unknown etiology.
Safocid contains 4 tablets: one each of Azithromycin, Fluconazole and 2 tablets of Secnidazole, which are taken immediately. The drug is active against the pathogens of gonococcus, chlamydia, trichomoniasis and candidiasis.
Safocid can be replaced with a tablet of Azithromycin and Fluconazole, 2 tablets of Tinidazole.
Olethetrin is a combined medication with an antibacterial effect and has a bacteriostatic effect. Contains oletethrin and tetracycline. The active ingredients are active against the pathogens of gonococcus, syphilis, and chlamydia. A single dosage of 2 g is prescribed.
Drug prevention after casual sexual intercourse in women should include the use of intravaginal suppositories with antiseptic properties:
- Hexicon (Chlorhexidine) - suppositories with the active substance chlorhexidine. Used in the first 2 hours after sex to prevent chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, syphilis, candidiasis and herpes. The suppository is inserted once deep into the vagina after douching.
- Betadine is an antiseptic and disinfectant with iodine. The drug is active against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa. Prescribed once after emergency measures to prevent STIs. Not recommended for hypersensitivity to iodine and pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Pimafucin is a derivative of natamycin. Belongs to the group of polyene antibiotics that are active against Trichomonas and fungi. Does not affect viruses and bacteria.
Prevention of diseases of viral etiology (human papillomavirus, genital herpes) involves oral administration of antiviral drugs: Kagocel, Famciclovir, Arbidol.
To maintain immunity and prevent viral infections, it is also possible to use rectal suppositories with interferon (Viferon, Genferon), which are prescribed in a course of up to 10 days with a single administration of 500 thousand or 1 million units at night before bedtime. The use of drugs with interferon can strengthen the body's defenses and increase resistance to STIs.
How often is it necessary to prevent sexually transmitted diseases?
Prevention of STDs includes the constant use of barrier contraceptives (condoms), which minimize the risk of infection. To prevent sexually transmitted diseases, you can also use spermicides, which not only suppress sperm activity, but also have a slight antimicrobial effect.
Drug prevention of STIs is a last resort method of disease prevention. This method cannot be used regularly as an alternative to a condom. Frequent use of local antimicrobial drugs disrupts the microflora of the genital organs, which leads to dysbacteriosis and a decrease in local immunity. This together increases the risk of infection.
Conclusion
Prevention of STIs after casual sex includes emergency measures in the form of hygiene procedures, genital irrigation and douching, which are effective only within 2 hours after sex. Drug prevention of STDs is carried out within 2 days and includes taking antibacterial drugs, as well as the use of rectal antiviral drugs and vaginal suppositories.
Sources
One of the most important places in the world is occupied by sexually transmitted diseases, namely venereal diseases.
To talk about any prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, we need to find out which diseases are included in their group. And what microorganisms cause them.
Source: https://ginekologiya-urologiya.ru/preparaty/kak-ispolzovat-hlorgeksidin-dlya-profilaktiki-venerologicheskih-zabolevanij
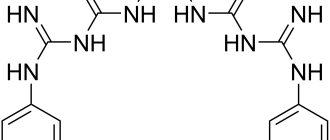
Difference between Chlorhexidine Bigluconate and Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine and Chlorhexidine Bigluconate are the same drug with different dosages. Chlorhexidine has 20% of the main substance and should be diluted for medicinal purposes, when Chlorhexidine Bigluconate is available in dosages of 0.05%-1% - as a rule, it should not be diluted.
DETAILS: Rowatinex - instructions for use, price, reviews, capsule analogues
Chlorhexidine Bigluconate is a solution, and Chlorhexidine is a pure, concentrated drug that should be diluted for medicinal purposes and is a component of many antiseptic medications.