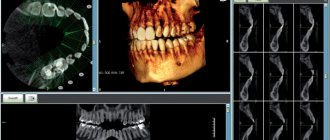
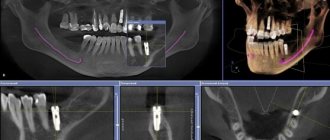
What is a 3D dental image?
A 3D image of a tooth is the result of a computed tomography scan. It belongs to the group of innovative inventions, but has already become popular. Using this form of diagnosis, the dentist receives a three-dimensional image of the jaw with a detailed display of all the details. Thanks to this, the doctor can examine the patient’s teeth from a convenient angle at any time.
An analogue of 3D diagnostics is an orthopantomogram (OPTG) - a panoramic image of the jaw. However, unlike a three-dimensional model, it is a display of teeth in a two-dimensional plane. The main disadvantage of the method is that the image has significant distortions, and the dentist may incorrectly interpret the OPTG.
3D photographs do not have this drawback. On the contrary, even when forming a tooth section based on a three-dimensional model, the doctor receives an accurate image that completely imitates the real “situation.” The 3D model allows you to assess the condition of teeth, gums, bone tissue, and see existing problems.
Thanks to the introduction of this method, dentists were able to significantly increase the effectiveness of their work. The risk of affecting healthy areas or not completely eliminating tumors, on the contrary, has significantly decreased.
What X-ray equipment is needed?
A 3D X-ray of the jaw is performed using a computed tomograph. This is modern digital equipment that provides high-quality diagnostics with minimal radiation exposure to the patient. To obtain an accurate image, ultra-sensitive detectors are connected to the tomograph.
To transfer the received data to a computer and create a three-dimensional model, special software is needed.
Based on the complexity of the disease and the required accuracy of the image, a multilayer study is done. As a result, the doctor receives up to 10 projections of the human jaw.
Where can I take a photo of a tooth?
Computed tomography is becoming an increasingly common procedure offered by dentistry in Moscow. However, unlike a digital orthopantomogram, it can so far only be found in large clinics offering a wide range of services. You can always find out where to take a 3D photograph of a tooth in Moscow from the specialist who referred you for this study. The price for a computed tomography scan of the jaw, or 3D dental image, in Moscow varies from clinic to clinic and starts from approximately 2,500 rubles.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Ekaterina Gasparova
Indications for this type of examination
A 3D image for dental examination is used in the diagnosis of complex injuries and diseases of the jaw. Indications for prescribing computed tomography include:
- incorrect position of the tooth in the gum;
- neoplasms in the maxillary sinuses or jaw;
- extensive inflammatory process;
- malocclusion;
- disorders of motor functions of the mandibular joint;
- difficulties with implantation and prosthetics;
- fractures of the lower jaw;
- diagnosis of caries complications;
- planning orthopedic treatment and evaluating its results;
- planning cephalometric changes;
- diagnosis of periodontitis.
Are there any contraindications
Although the effectiveness of 3D diagnostics has been repeatedly proven in practice, it is not prescribed to everyone. Like any procedure, it has its limitations and contraindications.
Women during pregnancy will be denied a dental CT scan. The method is considered especially dangerous for the fetus in the first months after conception. Ionizing radiation can provoke the development of intrauterine pathologies and prevent the correct formation of the internal organs of the embryo. For those who are breastfeeding, a computed tomography scan is prescribed on the condition that the mother stops feeding milk for a day, replacing it with formula.
3D x-rays can be prescribed either without a contrast agent, which is injected into the soft tissues of the oral cavity, or with its use. In the second case, the doctor must make sure that the patient does not have an allergic reaction to the components of the drug. The procedure with the introduction of contrast is also contraindicated for patients suffering from diabetes, renal failure, iodine intolerance, and thyroid diseases.
Carrying out a tomography requires absolute stillness. Therefore, the procedure is prescribed to hyperactive people and those who suffer from neuroses or are mentally unstable, only if they take sedatives. The same circumstance forces dentists to rarely use this method of radiography for children. This is especially true for children under school age.
If there is at least one contraindication to dental computed tomography, the dentist must prescribe another diagnostic method.
How is a CT scan performed?
A CT scan takes from 14 to 24 seconds.
A CT scan takes from 14 to 24 seconds, depending on the scope of the study, the frequency of acquisition and settings. During this time, the device manages to take up to 200 pictures in different projections.
Important! Before diagnosis, you must remove all jewelry and accessories.
The procedure itself is performed as follows:
- The patient's neck and chest are protected with a lead apron.
- The subject rests his forehead against the fixing support, clamps the bite block with his mouth so that the teeth fall into special holes, and grabs the handles with his hands.
- Having taken the correct position, you must wait until the device finishes working.
The examination is carried out by a radiologist. Before the procedure, he pre-consults the patient about the necessary actions.
Within a few minutes, the received data is processed, and a three-dimensional model of the jaws is built. If desired, the examinee may ask to record the results on removable media.
How to prepare for a 3D photo
There are no restrictions imposed on the patient to take a 3D photograph of the teeth. Exceptions include groups of people suffering from neuroses, hyperactivity and related diseases. Before the procedure, they are advised to take sedatives prescribed by the attending physician.
In the computed tomography room, the patient must remove all metal elements located in the head area. This applies to hoops, hairpins, earrings and other items. During the examination, they may distort the image.
In order to protect the patient from radiation, a protective apron is first put on him. It has a special lead layer.
A mandatory preparatory step is fixing the patient in one position. This is done to ensure that accidental movement does not reduce the clarity of the image or distort it. You need to grab the special handles with your hands and rest your head against the support. A plate is placed in the mouth, which should be clamped with the teeth.
Computer X-ray of teeth: indications
Among the indications for computed tomography of the jaw, or, as it is also called, 3D dental imaging, are anomalies in the structure of the jaw, the temporomandibular joint, the presence of impacted (not erupted or not fully erupted) and dystopic (rotated in the wrong direction or grown in the wrong direction) in its place) teeth; complex fractures of the jaws, damage to the dentition; preparation for maxillofacial operations. CT is also significantly superior to orthopantomography in preparing and performing implantation, in diagnosing inflammation in the area of tooth roots, determining the number of roots and root canals of a tooth, diagnosing cracks in the roots and detecting tumors at the initial stage; when assessing the severity of periodontal and periodontal disease. When planning a sinus lift or bone grafting, you will also have to take a 3D photo of your teeth. If bone tissue is clearly visible on a regular x-ray, then CT also allows you to see soft tissues, blood vessels, canals and changes in the mucous membrane. It is believed that a 3D image of teeth is more informative than one panoramic image and a set of targeted images of all teeth together.
How does the procedure work?
After the patient has put on a protective apron and taken a seat at the machine, the medical staff begins the procedure. At the top of the tomograph there is an X-ray tube with a receiver. Once launched, it begins to move around the head. The duration of the procedure is 20-30 seconds. During this time, the computer receives several dozen projections of the jaw, made from different angles. Next, the program processes the available data and models a 3D image. The patient can receive the result within 10-15 minutes. For convenience, it is recorded on digital media. Other doctors can study the examination results from it. In addition, information in this format will be stored longer, which will allow you to track the dynamics of pathology in the oral cavity and evaluate the effect of treatment.
Precautionary measures
Despite the fact that computer modeling of the jaw is safer for people than classical x-ray diagnostics, during the procedure the patient still receives a dose of radiation. Therefore, it is important to wear a protective apron before starting the examination. If the doctor does not provide it for any reason, you should refuse the scanning session and have the tomography performed at another medical center.
Orthopantomogram (panoramic photograph of teeth)
An orthopantomogram is a panoramic x-ray of both jaws and adjacent areas (temporomandibular joint and maxillary sinuses). Also, along with an orthopantomogram, computed tomography of the jaw is common, which allows you to obtain the same image, but in a three-dimensional format.
An X-ray of the jaw is an integral procedure preceding any dental treatment. It allows you to obtain accurate data on the location of teeth and tooth germs, the presence of damage, tartar, caries, the condition of the bone tissue of the jaw, as well as the joint and maxillary sinuses. This ensures the accuracy of the diagnosis and helps to select the appropriate treatment regimen.
There are many indications for taking a panoramic photograph:
- malocclusion;
- the presence of impacted (unerupted) and dystopic (improperly located in the gum) teeth;
- an inflammatory process involving several adjacent teeth;
- pathological neoplasms in the bone tissue of the jaw (osteoma, odontoma, etc.);
- fractures of the lower jaw;
- disturbances in the normal functioning of the mandibular joint;
- osteomyelitis of the lower jaw;
- atrophy of bone tissue with incomplete dentition (a photograph of the jaw helps to develop a prosthetic scheme);
- ameloblastoma;
- cystic formations in the jaw and maxillary sinuses.
For the same indications, a three-dimensional photograph is also prescribed, which helps to visualize the jaw and dentition even more fully.
In addition, a panoramic image that captures the maxillary sinuses can be used in the diagnosis of ENT diseases .
What does an orthopantomogram look like?
How does the procedure work?
There are two varieties of this procedure: using film (analog) and digital. In the first case, the image is developed on film, just like a standard x-ray. This is a relatively simple and inexpensive method of examination, but it has significant disadvantages.
- the image on the film may be distorted due to the presence of earrings, piercings, prostheses, random movements of the patient during the examination, and even the superimposition of the image of the hard palate on the maxillary sinus;
- A film image fades over time and loses sharpness, so turning to X-rays after a few years is no longer useful.
A digital orthopantomogram is characterized by a higher quality of the resulting images, which can be printed or saved on electronic media at the request of the patient. In addition, the digital orthopantomography procedure is carried out much faster - literally in a few seconds, and the image appears faster and easier.
Before the procedure, the patient must remove all metal objects and jewelry - piercings, earrings, and, if possible, dentures. Then he is put on a protective lead collar to cover the neck and thyroid gland area, and the same apron to protect the torso. The patient then stands inside the device and bites on a small plate connected to it.
What does the procedure look like?
The upper part of the device, containing the radiation source - the X-ray tube and its successor - the film, begins to move around the patient's head, taking a picture. The duration of the entire procedure does not exceed 30 seconds. All this time it is necessary to remain motionless so that the picture is clear and not blurred. The finished image is recorded on a medium or given to the patient in 10-15 minutes.
The radiation dose received during digital orthopantomography is small - 10-40 μSv (microsievert), while the permissible radiation exposure during the year is 1000 μSv. In addition, the patient is protected during the examination by a lead apron, which reduces radiation exposure to a minimum. If all protective measures are followed, this procedure does not pose any harm to the body.
Precautions during examination
A panoramic photograph of teeth is a safe procedure that can be performed even on young children. Moreover, it is children who need it in the first place - for complete visualization of the dentition and the prevention of problems with bite and development of permanent teeth.
The only restriction exists for pregnant women in the first and last trimester. At this time, it is undesirable to expose the body to any radiation exposure. However, there are no contraindications for the second trimester. For pregnant women, such an examination will also be useful in preventing dental problems caused by calcium leaching, a common occurrence during pregnancy.
Interpretation of examination results
Orthopantomography is performed by a radiologist, who also interprets the results. However, the patient is also not given basic knowledge of what can be seen in the image.
The dentition in the finished image looks like a “smile” with the corners raised up. If they are lowered down, this indicates low image quality and possible distortion.
The right side of the jaw in the picture is on the left, the left is on the right. Sometimes, for convenience, the parties sign with the letters L (left) or R (right).
The doctor reads the picture.
In the picture you can see:
- the location of the roots of the teeth, as well as root canals and the rudiments of teeth that have not yet erupted. Assessing the location of dental follicles and the possible direction of their eruption is extremely important in orthodontics - with timely examination, bite defects and possible problems with the development of third molars (“wisdom teeth”) can be identified;
- fillings and crowns. Modern fillings are made from special X-ray contrast agents, which helps during examination to evaluate their location, condition, quality of filling cavities, and so on;
- tissue defects, both bone and, partially, soft. The image clearly shows cracks, jaw fractures, and pathological neoplasms in bone tissue. At the same time, it allows you to see granulomas, cysts, areas of inflammation;
- maxillary sinuses (sinuses), nasal passages and septum. The image clearly shows the size and outline of the nasal sinuses, as well as the curvature of the nasal septum, which can be the cause of various ENT diseases. The cavities in the picture have a dark tint, and the bone partitions have a light tint; the contrast is high enough to notice any changes in the normal shape;
- temporomandibular joints. An orthopantomogram allows you to assess their condition and identify signs of incipient arthritis. Such signs are asymmetry of the joints and their irregular shape.
What does the photo look like?
The data obtained during the survey takes the form of multiple projections. To create a three-dimensional model, a computer program assembles them into a separate whole. If further diagnostics take place in an office equipped with computer equipment, the doctor opens the image in electronic form from a digital media. The latter is given to the patient after the tomography. To get a more complete picture of the problem, the dentist can rotate the model, finding the area of interest, and also display the corresponding projection of the teeth on the screen. You can enlarge small elements, create slices, take the necessary measurements and other operations online.
The doctor may request a printed photograph of a three-dimensional model of the jaw. In this case, the patient is given an image in the format 8x5 or 5x5 cm. Up to a dozen main projections and sections are imprinted on them. This option is considered less convenient for diagnostics and is used mainly in offices that are not equipped with computer equipment.
What You Can Find
3D dental X-ray provides the opportunity to obtain the following information:
- visualization of the condition of teeth and gums in a three-dimensional model;
- the presence and size of foci of pathologies;
- the effectiveness of treatment or surgery;
- location, nature and size of neoplasms, cysts and other tumors;
- determination of the main parameters of the jaw and its geometry;
- graphic recording of the location of nerves;
- counting the amount of bone tissue.
Indications for the study
There are certain indications for performing three-dimensional computed radiography:
- Diagnosis of anomalies in the development of the dental system.
- Assessment of the position of impacted (unerupted) and dystopic (improperly positioned) teeth.
Impacted wisdom teeth
- Diagnosis of traumatic injuries - the patient’s well-being after an injury does not at all mean that everything is fine with him. Often severe damage is not visible to the naked eye and makes itself felt a little later. Computed tomography allows you to see and eliminate all the consequences of an injury in a timely manner, without waiting for serious consequences.
- Planning surgical interventions in the maxillofacial area, including preparation for implantation and sinus lifting - before the operation, it is important to identify in advance all possible factors that could complicate the procedure.
- Planning orthodontic treatment – Before installing braces, it is important to make sure that the teeth and bone tissue can withstand the load. It is especially important to take a 3D x-ray for teenagers before installing braces, as this will allow you to find out the location of the rudiments of wisdom teeth and predict the direction of their growth. If it turns out that their eruption can negatively affect the condition of the dentition, they will have to be removed.
- Suspicion of inflammatory processes in the jaw.
- Diagnosis of neoplasms.
- Computer modeling for the manufacture of some orthodontic structures.
- Identifying the consequences of improper endodontic treatment - sometimes treatment of pulpitis can result in serious consequences. In some cases, the dentist fails to fully process and fill the root canals, which subsequently leads to complications. Due to the fact that the tooth is sealed, it is very difficult to find out about the development of deviations at an early stage - symptoms arise already with pronounced changes.
Root canal filling
- Quality control of the treatment performed - often a computed tomography scan is prescribed after completion of treatment. For example, after a complex tooth extraction, this is necessary to ensure that there are no bone or tooth fragments.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
If we compare the creation of a panoramic image of teeth and a 3D model, the latter operation has more advantages for the patient:
- The duration of the procedure is less than a minute;
- all actions are absolutely painless;
- the radiation dose received by the body during the procedure is only 0.02 mSv (similar data is shown by the use of a mobile phone);
- the results of the examination are known after 10 minutes;
- diagnostics provide complete information about the condition of teeth without the need to undergo additional procedures.
In turn, the dentist receives from working with a tomograph the opportunity to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment, reducing the risk of error. You can re-examine the model on the computer at any time.
However, this method also has several disadvantages. The main one is the high cost of the procedure. The diagnosis has a number of contraindications, which prevents it from being prescribed to all patients without exception.
Harm of 3D dental diagnostics
The low radiation parameters received by the patient when undergoing dental computed tomography make this method the safest among those available in our time. On average, in the 15-20 seconds that the procedure lasts, a person receives about 0.02 mSv. The same parameters apply to using a microwave or mobile phone.
According to the regulations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the maximum annual radiation dose for humans is 5 mSv. Thus, creating a 3D image for diagnostics and dental treatment does not harm the body and does not cause anatomical pathologies.
The safety of computed tomography theoretically makes it possible to use it to diagnose children. However, there are other contradictions here that do not allow a child under school age to take a picture. They are associated with excessive mobility of children.
Methodology
Three-dimensional computed radiography is a simple and quick procedure. The patient will not feel any pain or discomfort during the study. You need to go into the cabin and place your chin on a special stand that fixes your head in the correct position.
You should remain completely still during the scanning process.
The entire process takes place under the supervision of a specialist who will answer any questions and explain the procedure. The results will be ready immediately after the procedure is completed - they will be saved on the clinic’s computer. If desired, they can be transferred to a disk or flash card.