Microabrasion – gentle polishing of enamel to remove plaque and prevent caries
Every day, the enamel of our teeth is affected by a huge number of external factors.
Excessive consumption of sweets, coffee and tea, smoking - all this leads to gradual demineralization of the protective layer of teeth and, as a result, a change in its color. It is important to understand that this is not only an aesthetic problem. Under bacterial plaque, hard tissues are quickly destroyed, which in the absence of regular hygiene inevitably leads to the onset of carious processes. The situation can be corrected in the early stages using a microabrasion procedure. Microabrasion
is a gentle polishing of teeth to remove pigmented areas and prevent the development of caries. Most often, such changes include white spots, which cause aesthetic discomfort to patients.
Read more about what it is and when the technique is used further in this material.
Contraindications
The procedure is not recommended under certain conditions:
- tetracycline staining;
- moderate enamel underdevelopment;
- age-related staining;
- severely thinned enamel, cracks and erosive defects;
- wedge-shaped defects;
- exposed necks of teeth;
- severe form of fluorosis;
- pathologies of oral tissues;
- pulpless teeth.
Microabrasion is contraindicated for women during pregnancy and lactation. In addition, the procedure is not performed on baby teeth.
The essence of the microabrasion method
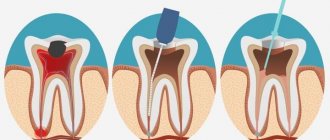
This is a modern method that involves gentle grinding and polishing of teeth, when the doctor carefully removes the thinnest layer of enamel using a special mixture of abrasive particles. The thickness of the removed layer usually does not exceed 25-70 microns, which makes it possible to prevent excessive thinning of the enamel and, accordingly, the development of hyperesthesia, that is, its high sensitivity. In particularly difficult cases, up to 200 µm1 is removed. You can see how your teeth look before and after the procedure in the photo below.
The photo shows teeth before and after the microabrasion procedure
Such therapy is used in dentistry in cases where the patient has heavily soiled and pigmented areas on the teeth that cannot be removed using the classic method of professional cleaning. In addition, this is one of the methods for preventing the further development of carious processes if the medical history is still in the initial stages of its development. The method is effective in situations where caries has not yet had time to destroy the upper protective layer of teeth and its internal tissues, that is, it is at the stage of demineralization.
How does the procedure work?
Previously, eliminating cosmetic smile defects was possible only through the use of composite materials and the installation of crowns. Modern technologies make it possible to get rid of uneven staining of teeth without boron preparation; one of these technologies is microabrasion, or micro-abrasive treatment. The essence of the method is to grind off a microscopically thin layer of enamel, followed by polishing. Thus, this is not a therapeutic event, but a cosmetic one.
Due to the fact that the impact is only on the upper layers of enamel - the thickness of the removed layer is usually no more than 0.2 mm - this procedure does not lead to serious irreversible consequences. Microabrasive treatment minimally changes the contours of the enamel surface and is a more conservative method than tooth restoration with composite materials.
Microabrasive treatment does not require anesthesia, as it is painless. Before the procedure, the doctor decides on the need for professional hygiene. The dentist then determines the patient's natural enamel shade using the standard Vita scale and creates a treatment plan. The patient's eyes are protected with glasses.
Algorithm for the procedure:
- isolation of the working field using a rubber dam. Performed to protect the mucous membrane;
- applying an abrasive mixture to the surface of the tooth being treated and rubbing it in using slowly rotating attachments - cups. For microabrasion, the drug Opalustre is used, which contains microparticles of silicon carbide and 6.6% hydrochloric acid;
- rinsing off If the result is positive, move on to the next stage, if not, repeat the previous one;
- polishing the tooth surface with fine fluoride paste to achieve an optimal aesthetic result;
- registration of color changes.
As a rule, one visit to the clinic is enough to eliminate enamel discoloration. The best results are achieved by a combination of microabrasion and clinical bleaching.
In what cases is it prescribed and when is the use of the technique contraindicated?
As mentioned above, the main indication for the procedure is the presence of pigmented areas of enamel that are not amenable to standard methods of removing contaminants. Thus, experts in the field of dentistry identify a number of other phenomena and conditions for which the procedure may be prescribed:
- hypoplasia - spotted form,
- the first stage of caries development,
- the presence of foci of demineralization,
- rough surface layer of teeth, including after orthodontic treatment.
The photo shows hypoplasia of tooth enamel.
However, the procedure is not performed if the patient is diagnosed with the following pathological conditions: tetracycline teeth, severe thinning of the enamel, the presence of erosive lesions and cracks on it, fluorosis, underdevelopment of the protective layer, wedge-shaped defects. Microabrasive treatment is also not prescribed to patients with mental disorders, diseases of the oral tissues, or individual intolerance to the components of the drugs used. The procedure is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, for temporary teeth and after their depulpation, as well as for poor oral hygiene.
Microabrasion of tooth enamel - restoring the aesthetics of a smile
Last update: 01/28/2020
At any age, a person can face such a problem as discoloration of tooth enamel. There are several reasons for this phenomenon, but one of the most common is fluorosis.
Uneven coloring of the enamel disrupts the aesthetics of a smile and causes certain psychological discomfort during communication. One of the methods for restoring aesthetics in case of discoloration is microabrasion.
We'll talk about what this method is and what indications there are for microabrasion of tooth enamel.
Fluorosis as the main indication for microabrasion
Dental fluorosis is a chronic disease that affects tooth enamel due to excessive accumulation of fluoride in the human body.
The main cause of the development of the disease is long-term use of water and toothpaste with a high content of fluoride compounds. With fluorosis, enamel discoloration occurs, which manifests itself in the form of spots.
The problem mainly affects children at the stage of formation of permanent teeth.
This problem especially concerns residents of endemic areas. In Russia, these are the Leningrad region, the Republic of Mordovia, the Nizhny Novgorod region, the Urals, and Western Siberia. In these regions, the concentration of fluoride in ordinary water exceeds sanitary standards (>1.5 μg/l).
This also includes natural springs and artesian wells. In addition, in many cities, water is fluoridated for prevention.
The danger of fluorides is that they accumulate not only in teeth, but also in bones, and if accumulated in excess, they can even lead to bone cancer - osteosarcoma.
The disease occurs in 3 stages:
- mild form of the lesion - small chalky spots and stripes on the surface of individual teeth;
- moderate damage - pigmented spots of yellow or brown color are added, covering several teeth;
- severe form - almost the entire tooth is covered with brown spots, while the crown of the tooth is deformed, the enamel is erased or chipped.
Enamel microabrasion is used only for mild or moderate fluorosis (spotted and chalky-mottled forms). But the indication for the procedure is not only fluorosis.
Other indications for enamel microabrasion
- Spotted and streaked form of hypoplasia, in which white and yellow spots appear;
- focal demineralization of enamel during initial caries;
- unevenness on the enamel surface, for example, after removing the braces;
- dense pigmented coating, including Priestley's black coating.
Contraindications
The procedure is not recommended under certain conditions:
- tetracycline staining;
- moderate enamel underdevelopment;
- age-related staining;
- severely thinned enamel, cracks and erosive defects;
- wedge-shaped defects;
- exposed necks of teeth;
- severe form of fluorosis;
- pathologies of oral tissues;
- pulpless teeth.
Microabrasion is contraindicated for women during pregnancy and lactation. In addition, the procedure is not performed on baby teeth.
How does the procedure work?
Previously, eliminating cosmetic smile defects was possible only through the use of composite materials and the installation of crowns.
Modern technologies make it possible to get rid of uneven staining of teeth without boron preparation; one of these technologies is microabrasion, or micro-abrasive treatment.
The essence of the method is to grind off a microscopically thin layer of enamel, followed by polishing. Thus, this is not a therapeutic event, but a cosmetic one.
Due to the fact that the impact is only on the upper layers of enamel - the thickness of the removed layer is usually no more than 0.2 mm - this procedure does not lead to serious irreversible consequences. Microabrasive treatment minimally changes the contours of the enamel surface and is a more conservative method than tooth restoration with composite materials.
Microabrasive treatment does not require anesthesia, as it is painless. Before the procedure, the doctor decides on the need for professional hygiene. The dentist then determines the patient's natural enamel shade using the standard Vita scale and creates a treatment plan. The patient's eyes are protected with glasses.
Algorithm for the procedure:
- isolation of the working field using a rubber dam. Performed to protect the mucous membrane;
- applying an abrasive mixture to the surface of the tooth being treated and rubbing it in using slowly rotating attachments - cups. For microabrasion, the drug Opalustre is used, which contains microparticles of silicon carbide and 6.6% hydrochloric acid;
- rinsing off If the result is positive, move on to the next stage, if not, repeat the previous one;
- polishing the tooth surface with fine fluoride paste to achieve an optimal aesthetic result;
- registration of color changes.
As a rule, one visit to the clinic is enough to eliminate enamel discoloration. The best results are achieved by a combination of microabrasion and clinical bleaching.
Efficiency and safety
Microabrasion allows you to get rid of enamel discoloration. As a result, not only the appearance of the tooth improves, but its further destruction is stopped. In addition, micro-abrasive treatment allows you to avoid tooth grinding and restoration using expensive composites. After the procedure, age spots do not return.
Efficiency depends on the degree of damage: microabrasion helps either completely eliminate surface stains on the enamel or mask discolored areas. Provides a natural glossy shine to the enamel surface. The result is noticeable immediately after the procedure.
The main complication after the procedure is increased tooth sensitivity. To eliminate it, it is recommended to use special toothpastes and rinses for sensitive teeth, for example, low-abrasive ASEPTA Sensitive toothpaste.
Additionally, it is necessary to use remotherapy products as an opportunity to mineralize damaged areas, for example, ASEPTA Plus Remineralization.
This professional toothpaste restores weakened and damaged enamel, saturates it with essential macro- and microelements.
Clinical researches
ASEPTA products are clinically proven effective. For example, repeated laboratory tests have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%.
Clinical studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66% after just 4 weeks.
Consumer Reviews
Anna about ASEPTA Sensitive toothpaste (proberry.ru)
“Summer has begun. We are constantly leaving somewhere. Then to the village. Then we are going on a trip to the south. For our family of three, we have to take several toothpastes, for our daughter, our own, for my husband and me.
There are a lot of bags, so the less space the toothpaste takes up, the better. Osepta toothpaste has taken its place in our cosmetic bag. If I was in a store and saw it in a small tube, I would definitely take it.
I’m also very pleased that the paste has healing and preventive properties. And even on vacation we will take care of our teeth.”
Ekaterina Kosheleva about ASEPTA Remineralization toothpaste (market.yandex.ru)
“I have suffered from increased sensitivity of teeth for as long as I can remember. Previously, I tried to cope with this with the help of folk remedies, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and the like. It is easy to guess that this gave a temporary and weak effect.
But when the pharmacist at the pharmacy recommended this remineralizing paste, bright times came for me) I’ll note right away that you shouldn’t expect an immediate miracle - I noticed obvious improvements after 2 weeks of cleansing.
My teeth no longer react with wild pain to hot food, now I can even treat myself to mulled wine without the prospect of my jaw cramping. Good pasta.
I will add that this paste from Asepta not only reduces hypersensitivity, but also helps strengthen teeth and gums and reduce hypersensitivity, increases the resistance of teeth to the formation of caries.”
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING”, researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky
First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof.
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof.
Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO, researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky.
First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky
St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist.
Source: https://asepta.ru/spravochnik/zubi/mikroabraziya-emali-zubov-vozvrashchenie-estetiki-ulybki/
What are the pros and cons?
The technique has quite a few advantages, among which specialists and patients often highlight the lack of need for any preparation. In addition, the procedure is completely painless and does not cause any discomfort. If microabrasion is used to prevent further tissue demineralization, then after its successful implementation it is possible to avoid large-scale tooth preparation for its further restoration. In general, the technique saves in cases where other options for removing plaque and pigmentation do not help.
“They performed microabrasion on me. I found white spots on my front teeth, the doctor said this is how caries begins. After the examination, the dentist suggested grinding off a thin layer to ensure that the lesions were removed. I agreed. There was no pain at all during the procedure. Only then did sensitivity to cold and hot appear. Personally, everything went away for me literally in 3-4 days.”
Evgenia S.S., Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Among the disadvantages, one can highlight a fairly impressive list of restrictions on the use of the method. In addition, after the procedure, almost all patients experience increased sensitivity of the enamel layer - hyperesthesia goes away on its own within a few days, but for this you need to strictly follow the instructions of your doctor.
Indications for microabrasion
Indications for microabrasion are pigmented contamination of the enamel layer, which cannot be eliminated during normal hygienic measures.
In addition, the procedure is advisable if the patient has:
- spotted form of hypoplasia;
- initial stages of dental caries;
- foci of enamel demineralization;
- irregularities on the surface of the enamel layer (including those that arose when removing the bracket system).
Step-by-step description of the process
To begin, the patient must sit comfortably in the dental chair. Despite the fact that the procedure is completely painless and does not require prior administration of anesthesia, it is important to create a psychologically comfortable environment for the person so that he can relax and allow the doctor to work in peace. Once the patient is ready, a special composition will be applied to his teeth, which includes hydrochloric acid, carborundum and silicon abrasive gel. The product is applied to the enamel using a special rubber nozzle. The paste is left for a while to soften the enamel layer a little. Afterwards it is removed using special rubber cups.
So, enamel microabrasion involves the following steps:
- First, the specialist isolates the treatment area from the mucous membrane and neighboring healthy teeth. For this, a special gel can be used, for example, “Axil” or rubber dam,
- then the dental retractor is fixed,
- an abrasive mass is applied to the surface of the enamel,
- the product is gently rubbed into the dental tissues, usually using special rotating rubber cups,
- excess mixture is removed,
- Remo-gel is applied to the affected area, stimulating the processes of restoration of damaged enamel and replenishing the lack of minerals in dental tissues,
- remineralization – carried out if there are appropriate indications,
- At the final stage, the doctor evaluates the result of treatment, advises the patient, and gives him a reminder about further dental and oral care.
The photo shows the application of the gel to teeth during microabrasion.
If there is such a need, the procedure is repeated.
The duration of the rehabilitation course directly depends on the degree of contamination of the teeth and the depth of the spread of carious processes.
Clinical example of microabrasion in fluorosis
Microabrasion
A - young patient with fluorosis on the upper central incisors; B and C - treating stains with Prema paste using a grooved rubber head. To protect the patient, glasses and rubber dams are used; D — application of Prema paste with a hand tool; D — after microabrasion, the stain on the left incisor was completely removed; E - the treated enamel surface is polished with prophylactic paste; F - fluoride is applied to the treated surface; Z—result of treatment.
The figure above shows the treatment of fluorosis of the upper central incisors in a young patient using microabrasion. The teeth are isolated using a rubber dam. This helps protect the gums from the effects of the acid contained in the Prema paste. To protect the eyes from splashing paste, the patient wears glasses. The defect area is treated with Prema paste using a corrugated rubber head (B and C) and a lowering tip (10 times) at low speeds of the drill (as when fixing pins), applying moderate pressure. This reduces the chance of over-grinding the enamel and prevents the paste from spattering.
For the treatment of small, localized white or light brown idiopathic spots, Prema paste can also be applied using hand instruments (D). At the same time, the paste is periodically washed off to see if the defect is still preserved. Care must be taken not to sand off too much enamel. To do this, use a mirror to periodically inspect the cutting edge to assess the thickness of the ground layer. The procedure is continued until the stain is eliminated or as long as this is considered possible (D). The treated areas are then polished with a fluoride-containing prophylactic paste to restore the surface shine (E). Then, to accelerate the remineralization process, local application of fluoride (F) is carried out. The treatment results are presented in Figure H.
Efficiency and safety of the procedure
Microabrasive treatment makes it possible to completely remove pigmented stains on the surface of teeth, as well as stop carious processes at the very beginning of their development. Thus, this is not only a solution to an aesthetic problem, but also a prevention of further rapid destruction of dental tissue under the influence of pathogenic bacteria. According to statistics, the effectiveness of the procedure is 50%2. This means that the success of treatment largely depends on the age of the patient and the depth of the lesion. Enamel is easier to process and recovers faster if the patient is young enough. Over the years, dental tissues become less amenable to this type of therapy, but it still makes it possible to avoid severe grinding and installation of an artificial crown.
Teeth may become sensitive
The most common complication of microabrasion is increased sensitivity of the enamel. To reduce the severity of the symptom, the patient must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations after the procedure. To alleviate the condition and speed up the recovery process, experts recommend rinsing with a 10% calcium gluconate solution. You can buy it at any pharmacy, but before using it, it is better to consult a doctor. The first time after microabrasion, you should use hygiene products for sensitive teeth and try to avoid consuming sour and spicy foods. Also make sure that the food is not too hot or cold.
It is important that the doctor has a high level of professionalism and relevant experience. Mistakes made by a specialist during the procedure can provoke the appearance of erosive areas on the enamel and injured areas on the gums. To eliminate such complications, the patient will have to treat the affected areas with antiseptic agents, drugs with wound healing and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Greenwall L. Whitening techniques, 2003.
- According to WHO.
Contraindications to microabrasion
Microabrasion, just like other medical procedures, has a number of contraindications. For example, the use of this method of combating discolorations of tooth enamel is not recommended for persons who have previously been diagnosed with the following pathologies:
- dentinogenesis imperfecta;
- cracks on the surface of the enamel layer;
- allergic reaction to components present in the abrasive gel and other drugs used during the procedure;
- periodontal diseases;
- pathological exposure of the necks of teeth;
- enamel erosion;
- amelogenesis imperfecta;
- moderate enamel hypoplasia;
- psychical deviations;
- fluorosis occurring in a destructive or erosive form;
- presence of wedge-shaped defects;
- excessive thinning of the enamel layer.
In addition, contraindications to microabrasion are:
- age-related change in the shade of the enamel layer;
- the presence of so-called “tetracycline teeth”;
- change in the shade of pulpless or baby teeth;
- carrying out orthodontic treatment;
- lactation and pregnancy;
- poor oral hygiene.