General information
Dental pathology is not a serious disorder, but in the absence of proper treatment it can provoke some complications. The main reason for its development is considered to be the loss of teeth without subsequent implantation or prosthetics. According to research, more than 30% of patients who have had at least one tooth removed do not think about the implantation procedure.
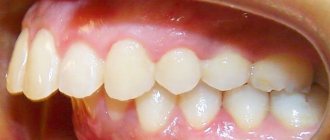
This is how the phenomenon manifests itself when a tooth is lost
This is due to the fact that with such a minimal loss, the process of chewing food is not disrupted, so a person does not rush to the dentist. It is noted that 2-3 months after the removal of one or more units, a gradual displacement of healthy teeth begins. If a person does not visit a specialist for a year to install implants, the procedure will be quite problematic.
When one tooth is removed, the pathology develops quite slowly. If the number increases, rapid displacement of healthy teeth begins, elongation of the alveolar processes and other disorders:
- dysfunction of the muscles of the lower jaw;
- advancement of the upper or lower dentition;
- changes in the structure of the alveolar processes;
- exposure of the root of healthy units located directly next to the void;
- formation of a gum pocket around healthy teeth;
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular apparatus;
- narrowing of the periodontal fissure;
- changes in collagen fibers;
- dystrophic processes in the pulp;
- disturbance in the structure of the periodontium.
As a rule, several months or even years after the removal of one or several units, prosthetics and implantation become very complicated. It is for this reason that experts strongly recommend making a replacement no later than 10-14 days after extraction.
General overview
The Popov-Godon phenomenon is a complication after tooth loss, manifested by severe deformation of both dentitions.
The main manifestation of the phenomenon is that the teeth located opposite the defect move vertically, filling the void formed due to edentulism. Sometimes the protrusion is so significant that they reach the mucous membrane of the gums in the place of missing teeth.
The teeth located next to the defect also change their location; can rotate around an axis, tilt in any direction (vertically, distally, mesially, in the lingual and vestibular directions, or in the form of a combination of several movements). Pathological restructuring begins from the defect and then spreads to the entire row.
The severity of deformities depends on many factors - the number of lost units, the extent and location of the defect, the condition of intact teeth, the type of occlusion, the time that has passed since the loss of teeth, the patient’s health and age. Popov-Godon syndrome develops much faster in children than in adults.
The jaw arch is a single whole, working in harmony with the other elements of the dentofacial apparatus. Its deformation leads to traumatic articulation, diseases of the dental support system, and TMJ dysfunction. In addition, the uncorrected Popov-Godon phenomenon seriously complicates prosthetics.
When the pathology is severe, protruding teeth put pressure on the alveolar ridge, leading to chronic injury, which can malignize (become malignant). It is possible to block the lower jaw, leading to overload and disruption of the TMJ with pain.
Obviously, the cause of secondary deformations is the adaptation of the dentofacial apparatus to changed working conditions, the restructuring of the periodontium due to the lack of chewing load.
But the details of this process are still unclear. There are different theories explaining the deformation of rows during prolonged edentia. Theory of articulatory (author Godon) and relative physiological (Katz and Schroeder) balance, hypotheses of Kalvelis, Kurlandsky and others. But each of them has its critics.
The primary cause of malocclusion is, of course, tooth loss. It can be caused by vitamin deficiency, diseases of the oral tissues (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), surgery, or injury.
Symptoms and classification
Depending on the nature of the displacement with the Popov-Godon symptom, experts identify several options for the development of the pathology: vertical protrusion of the lower or upper jaw, displacement of the lower or upper teeth, inclination of the teeth or the entire row inward, or a combined disorder. The last type is the displacement of teeth in different directions and to varying degrees.
There is also another classification from V. A Ponomareva. It involves dividing pathology into two forms:
- The first is characterized by tooth displacement and simultaneous lengthening of the alveolar process. The difference is the absence of a gum pocket. The root is also not exposed, there are no dystrophic changes in the pulp. This form is considered mild and it is possible to get rid of clinical manifestations quite quickly.
- The second is accompanied not only by displacement of teeth, but also by the development of an inflammatory process, exposure of the root, and signs of dystrophic changes in the pulp. It is worth noting that with this type, the alveolar process may lengthen or not, depending on the characteristics of the individual patient and the time over which the pathology develops. Treatment in this case is complicated and requires an integrated approach aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and correcting the dentition.
As a rule, the pathology is accompanied by malocclusion, a decrease or increase in the distance between the teeth, and their deviation forward or backward. There are signs of gum inflammation, tooth root exposure and changes in the pulp. The last symptom appears later than the others and is considered the main one in Popov-Godon syndrome.
Classification
V.A. Ponomareva identified two possible paths for the development of pathology:
- It is not the tooth itself that moves, but the area of the gum on which it is located. This area is called the alveolar process, which noticeably increases, protruding the bony organ. But periodontal pockets do not form and the root is not exposed.
- The root emerges and becomes exposed. The shift is accompanied by necrosis of surrounding tissues.
There are three degrees of pathology:
- I – moving forward, the root is practically not exposed, there are no pulpal dystrophic changes.
- II – protrusion reaches a third of the length of the tooth, the root is exposed, and pulpal dystrophic changes appear.
- III – the alveolar process lengthens, root cement is exposed, accompanied by inflammatory processes and modification of the jaw arch.
In choosing a treatment technology, the degree of development of the pathology plays a decisive role.
The definition of pathology is based on a number of signs. The main ones are:
- tooth loss;
- modification of the series;
- no decrease in the height of the chewing surface;
- reducing the distance from the surface of the displaced element to the gum in the lumen of the opposite jaw.
The pathology has secondary symptoms:
- increasing the size of the alveolar process;
- possible necrosis of periodontal tissues;
- the process has no effect on other elements.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the pathology, a specialist examines the oral cavity and assesses the condition of the lower and upper jaw. To accurately determine the shape, it uses the classification of the Popov-Godon phenomenon. It is with its help that the doctor will be able to more accurately determine the stage of development of the disease.
An important point is differential diagnosis, which helps to separate pathology from partial edentia, which has similar clinical manifestations. For this purpose, the specialist compares the ratio of the dentition to each other in a state of physiological rest. It is also necessary to determine the distance between the teeth in the anterior and lateral projections.
What is the Popov-Godon phenomenon?
The Popov-Godon phenomenon is a dentofacial pathology, expressed in abnormal dental shifts provoked by tooth extraction and failure to timely prosthetize the defect (loss of an element of the dentition).
The syndrome was initially recorded in 1880 by V. O. Popov. Then, in 1904, Hodon also noticed a modification of the dentition due to the loss of some links.
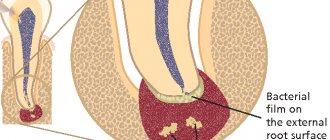
Often, teeth without opposing counterparts move quite noticeably and almost come into contact with the mucous membrane of the alveolar process of the opposite side. The work of the muscles of the lower jaw is immediately blocked.
The Popov-Godon phenomenon in the photo:
The results of the analyzes indicate that such a syndrome rearranges the alveolar bones in dental units left without opposite analogues: the periodontal gap narrows, the routes of collagen fibers change. At the same time, certain dystrophic transformations occur in the pulp.
Such situations happen repeatedly and complicate the process of prosthetics, and therefore orthodontic devices have been created that are designed based on the category of removable or fixed dentures. Through them, teeth devoid of antagonists are allowed into occlusion, along with the synchronous separation of other links.
If there is a noticeable movement of the dental unit, the pulp is removed from it and trimmed within the occlusion curve. Significant exposure of cement provokes its extraction.
If it is necessary to wear the plates 18 hours a day, treatment will last at least six months and depends on the complexity of each individual case. If the effect of orthodontic treatment is less positive, prosthetics are performed.
About 30% of the population, having removed a tooth, often do not even think about restoring it, explaining this by disagreement with damaging neighboring links.
Physiologists, thanks to research, have found that when a tooth is lost, a person does not lose the ability to chew food well. But the body does not tolerate emptiness, and the neighboring teeth, moving, try to hide the gap, causing gaps to appear between themselves.
An even more serious situation is where the dental analogue from the opposite area grows towards the void, interferes with proper chewing and increases the functional load, which contributes to the modification of the bite.
Visual video about dental deformation:
Clinical picture
After extraction, a natural compensatory reaction of the body develops. It leads to quite unpleasant consequences - deformation of the dental arch, impaired chewing function, changes in bite and pathologies of the temporomandibular joint associated with overload of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus.
The more teeth are lost, the faster the accompanying disorders develop:
- change in occlusion and inclination of the dentition;
- the formation of a gum pocket and exposure of the roots of the teeth located adjacent to the socket of the missing unit;
- narrowing of the periodontal space;
- pulp dystrophy and changes in periodontal structure.
All these violations in the future significantly complicate the work of doctors if the patient nevertheless decides to install an implant or prosthesis.
Development mechanism
If a denture or implant is not installed, the adjacent teeth gradually move towards the missing unit. In addition, on the opposite jaw, its antagonist begins to “lengthen,” as it were.
The reason for this phenomenon is changes in the periodontium - the so-called adaptive restructuring caused by the loss of the usual functional load. It entails metabolic and microcirculation disorders in periodontal tissues.
At the beginning of the process, tissue hypertrophy occurs, and in the later stages, tissue atrophy occurs, accompanied by partial periodontal resorption.
This is interesting: Aesthetic braces: types and effectiveness of treatment with braces
Symptoms
The removal of a tooth or several teeth causes a compensatory reaction on the part of the body, which is expressed in deformation of the dental arch and the jaw itself. Neighboring teeth begin to shift towards the missing one. As a result, the spaces between the remaining teeth increase. Not only the dentition in which the tooth is missing is deformed, but also the dentition of the opposite jaw. With the Popov-Godon phenomenon (syndrome), a significant displacement of the tooth in the opposite jaw occurs. The tooth seems to “grow” from the dental arch and creates a “lock” when the jaws move. This disrupts the chewing function and often disrupts the bite. Often, along with the tooth, the jaw bone is also deformed, which creates additional problems during treatment. In some advanced cases, this can lead to problems with the temporomandibular joint due to overload of the ligaments and articular surfaces.
Simultaneously with tooth displacement, an increase in the alveolar process (dentoalveolar elongation) may occur, which leads to the formation of a gum pocket and exposure of the tooth root. Dentoalveolar elongation occurs due to changes in the structure of the periodontium due to the loss of the usual functional load (adaptive restructuring), in which there is a disruption of metabolic processes and microcirculation in the periodontium, an increase in the size of the alveolar process and the volume of bone tissue. At the beginning of the process of adaptive restructuring of the periodontium, an increase in the volume of tissues formed occurs, while the tooth moves beyond the occlusal plane, and in a later period the atrophic process with the phenomena of periodontal resorption (“atrophy from inactivity”) predominates.
Diagnostics
It is based on a visual examination of the oral cavity using a classification of the phenomenon and a detailed study of radiographic data.
In addition, the dentist makes a differential diagnosis of the Popov-Godon phenomenon with partial edentia by assessing occlusion in a state of physiological rest.
To determine the pathology, a specialist examines the oral cavity and assesses the condition of the lower and upper jaw. To accurately determine the shape, it uses the classification of the Popov-Godon phenomenon. It is with its help that the doctor will be able to more accurately determine the stage of development of the disease.
An important point is differential diagnosis, which helps to separate pathology from partial edentia, which has similar clinical manifestations. For this purpose, the specialist compares the ratio of the dentition to each other in a state of physiological rest. It is also necessary to determine the distance between the teeth in the anterior and lateral projections.
The first parameter is considered the most important, since only when a displacement is detected in the central region can we talk about the development of a pathological process. If clinical manifestations are present, but there are no changes in this area, edentia of varying degrees of severity is most often suspected.
An additional method is an X-ray examination and study of the resulting images. After establishing an accurate diagnosis and the extent of the lesion, the specialist determines a treatment regimen that is individual in each case.
Signs
- Partial edentia.
- Deformation of the occlusal curve.
Supra- or infraocclusal position of the teeth, in which the maxillary elements fall below the occlusal curve, and the mandibular elements move above it. The distance between the chewing surface of the displaced units and the alveolar ridge of the opposite jaw decreases until it completely disappears (the teeth touch the soft tissues). - Increase in the volume of the alveolar process.
- The appearance of gum pockets, periodontal resorption (in the 2nd form of the syndrome).
- Blocking LF movements.
At the same time, the occlusal height is maintained, and the remaining teeth remain intact (normal). In the 1st form of the syndrome, the patient does not complain of discomfort or pain.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis consists of isolating the Popov-Godon phenomenon from other pathologies that may be mistaken for it.
With the syndrome, teeth that do not meet the opposition of antagonists cross the occlusal plane and invade the “foreign” space , while in other pathologies there is no crossing of the occlusal plane.
This is interesting: How long to wear retainers after braces: types, installation, analogues
The P-G phenomenon is sometimes mistakenly mistaken for a decrease in occlusal height due to tooth abrasion, distal displacement of the MF, or the general absence of antagonists in all teeth.
To establish the true picture, the models installed in the occluder are studied, paying main attention to the position of the occlusal plane, the distance between the defective teeth and the soft tissues of the opposite jaw.
It is important that the models are set in centric relation and the normal height of the lower third of the face is maintained.
Treatment options
To eliminate the symptoms of the pathology and prevent its further progression, specialists use several methods of therapy. The following are considered the most popular:
- grinding;
- disocclusion;
- hardware-surgical treatment;
- surgical intervention.
Grinding is used to treat patients over 35 years of age at the initial and middle stages of the disease. Most often it is used in the second form of pathology when the teeth are displaced by no more than half of their own height.
After examining the patient's x-rays, the specialist determines the degree of grinding. The procedure is simple and involves grinding down teeth. If it only removes a small area, after the manipulation the patient undergoes treatment to restore tooth enamel. In cases where the procedure exposes dentin, covering with a crown no later than 2 days after the procedure is considered a prerequisite.
Typically, such treatment does not require much time, and if immediately after it all teeth are restored and implants are placed in the place where it is necessary, the risk of relapse is significantly reduced.
Disocclusion technique
This method brings results only when treating patients no older than 40 years old who suffer from the first form of pathology. It consists of a mechanical effect on crooked teeth using a special device. It is made of special high-strength materials. The first stage of therapy is the introduction of the structure into the oral cavity and comfortable placement.
The device should correct the patient’s bite, straighten the teeth and prevent further progression of the disease. The time required to achieve maximum effect varies depending on the extent of the lesion and the age of the patient. It was noted that in patients under 30 years of age, the alignment process occurs much faster.
In severe cases of protrusion, the design will not help to completely straighten the teeth and correct the bite. In this case, the specialist resorts to the second stage of treatment: covering the upper part of the teeth with a special plastic that quickly hardens. It allows you to separate the teeth and maintain a distance of no more than 2 mm between them. Thanks to this, the bite is corrected, the upper and lower dentition is aligned. This technique is used until the defect is completely eliminated.
After eliminating the violation, the specialist strongly recommends that the patient fill the voids in the oral cavity by introducing implants or dentures. If this is not done, the pathology will begin to develop again and repeated treatment will be longer and more difficult.
Hardware-surgical therapy
A similar technique is used in cases where disocclusion did not bring results, and the gums around each displaced tooth became inflamed. This therapy is especially relevant when the root is exposed and dystrophic changes in the pulp.
The essence of the method is to install special prostheses in the places where the prostheses were extended, which gradually correct the violation. The time it takes for the structure to remain is strictly individual and depends on the degree of dental disease. In medicine, this technique is called compactosteotomy.
Installation of the device requires local anesthesia and special attention in the area of the upper palate. It is in this part that the prosthesis often damages the mucous membranes. After the implementation of the structure, careful care of the oral cavity is required, since the doctor places sutures that need to be processed.
https://youtu.be/Aw8LUcQi0-8
Surgical intervention
The technique is indicated for patients with the second form of the pathological condition, as well as with rapid progression of the disease, the presence of symptoms of gum inflammation, exposure of the tooth root and malocclusion. The procedure is to extract all units that deviate. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Before it is carried out, a complete examination of the patient is carried out. The following are considered mandatory steps: laboratory blood test with determination of platelet count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, as well as glucose level, electrocardiogram, x-ray of the skull with special attention to the jaw. After receiving all the results, the specialist determines the drug that will be used to relieve pain.
Preventive actions
The most effective prevention of the Popov-Godon phenomenon is to avoid situations that lead to tooth loss.
The main preventive measures include:
If it was not possible to avoid tooth loss, it is necessary to replace them as quickly as possible with bridges, removable dentures or implants with a crown.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Do you have a similar dental deformation?
Why undergo diagnostics on the issue of dentoalveolar deformities, incl. Popov-Godon phenomenon and treatment in our center is beneficial for you? The German Implantology Center is one of the best clinics for dentistry, orthodontics, prosthetics and dental implantology in Moscow and Russia. We confidently occupy the FIRST
place in the ranking of clinics since 2020. The treatment plan drawn up in consultation will be the most accurate and 100% responsive to the current situation of possible health problems of your dental system.
The highest level of service, the most advanced technologies:
- the most modern computed tomography and diagnostic technologies, including for various dentofacial deformities
- the most advanced atraumatic technologies for the treatment of teeth and gum inflammation,
- Precise orthodontics and the world's best bite correction systems
- the best implantation
- high-quality open and closed sinus lift operations
- the most beautiful orthopedics
- And - more than 10 years of successful experience in using Nobel, Straumann, Ankylos, XiVE, Astra Tech implants in medical practice
All this is GUARANTEED
you the optimal individual solution to your problem of the dental system and malocclusion. Contact us, we will be happy to help you! Click the red button “Yes, I want a consultation on the problem of the Popov-Godon phenomenon!”, fill out the contact information, and our managers will contact you to discuss a convenient appointment time for you.
Reviews
Have you ever encountered this pathology? If you have experience in treating the Popov-Godon phenomenon, share it in your reviews. Your experience will help other people make the right decision.
Source: zubovv.ru
Hodon's phenomenon is a deformation of the dentition, manifested in the form of pathological movements of teeth, as a result of non-prosthetic replacement of lost teeth. Sometimes, instead of the term “Hodon phenomenon,” the synonym “Popov-Godon phenomenon” is used.
The photo shows that there are no lateral teeth on the lower jaw, and the upper molar has dropped into the vacant space. This is a good illustration of the Hodon phenomenon.
It is about the possibility of such complications that arise after tooth extraction, if timely prosthetics of the dentition defect is not performed, that dentists warn their patients. A missing tooth or several teeth is called a dentition defect.
Classification of manifestations according to Ponomareva
Based on research materials on the symptoms of Popov-Godon syndrome, V. A. Ponomareva identified two forms of the phenomenon.
One stands out in that, in addition to the displacement of the dental unit, a noticeable increase in the alveolar process is formed, although the tooth root is not exposed and a gingival pocket is not formed.
The second form involves dental displacement, accompanied by necrosis of periodontal matter and exposure of root cement. It includes two subgroups.
In the first, an increase in the alveolar process is noted if periodontal resorption is insignificant. In the other subgroup, a similar phenomenon is not observed; resorption of periodontal tissues is located at a level of at least half the size of the root.
Classification
According to the classification of V. A. Ponomareva, there are 2 stages of the Popov-Godon phenomenon:
- The first is characterized by dentoalveolar elongation (an increase in the height of the alveolar ridge). In this case, there are no gum pockets and the root parts are not exposed. Periodontal resorption does not exceed 1⁄4.
- In the 2nd form, the roots are exposed, periodontal resorption is at least half the height. But the dentoalveolar elongation is not increased compared to the first form.
In general, the division of the phenomenon into the 1st and 2nd forms is arbitrary, since in essence they represent the early and late stages of one process.
Treatment methods for dentoveolar elongation
Partial adentia, aggravated by the curvature of the dental units, is eliminated one by one: first the curvature is corrected, then regenerated.
The syndrome can be treated using different methods, based on the type, stage and severity of abnormal curvatures:
- grinding method;
- sequential disocclusion method;
- hardware-surgical;
- surgical method.
Grinding
The most commonly used method for eliminating Popov-Godon syndrome is the grinding method. It is suitable for patients over 35 years of age with a displacement of no more than 1/2 of the tooth height. Intended for use in the second type of syndrome and ineffective use of disocclusion technique.
When calculating the degree of abrasion, it is first necessary to analyze diagnostic models or lateral extraoral radiographs and teleradiographs.
Having determined the occlusal plane, a dental shift is established to determine the volume of tissue removed along the occlusal surface. On x-rays, the location of the line indicates the need for pulp removal.
When the displacement is small, you can simply grind the fabric down to the enamel. Upon completion, it is recommended to undergo a fluoride varnish therapeutic course. If it is advisable to remove the dentin layer, the tooth must be covered with a crown.
When vertical extension has developed as a result of the disintegration of its antagonist, both the destroyed element and the opposite analogue are covered with crowns. The required height for the new crown is formed and the blockage of the lower jaw in the sagittal direction is eliminated.
Jaw prosthetics. Video: