Why are tonsils needed?
Doctors call the human tonsils an important part of the immune system. They consist of lymphoid tissue and perform a protective function. When attacked by viruses or bacteria, the tonsils stand in the way of the penetration of microbes, “get to know” them, read information about them and transmit it to other immune organs, which in turn produce antibodies that allow the body to fight the infection.
The tonsils are an important part of the immune system, but only if they fulfill their function. If a person’s immunity is strong, then the tonsils perform their tasks, and the person remains healthy. With weak immunity, it is more difficult for the tonsils to resist the microbes and viruses that have settled on them, so 1-2 days after infection, a sore throat appears in the throat area, as well as other painful and uncomfortable sensations.
If treatment is started immediately, the disease can be mild, without causing serious symptoms or complications. If time is lost, the tonsils become enlarged and swollen. Prolonged or inadequate treatment is fraught with suppuration and the appearance of an abscess on the tonsils.
What is the difference between tonsils and tonsils?
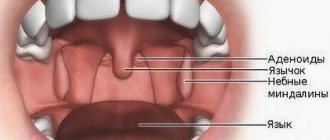
Every baby is born with a concentration of lymphoid tissue in the larynx. This tissue is called tonsils. They called it that for a reason, because of its external design. It looks a lot like an almond. There are 6 pairs of tonsils in the pharynx, but the palatine ones are called tonsils.
Are the tonsils and tonsils the same thing? Yes, it was the doctors who gave a separate name to a pair of tonsils, for their convenience. Translated from Latin, tonsil is a small acorn. The tonsils and tonsils play an important role.
Main functions
Tonsils act as guards in the human body and do not allow harmful bacteria to pass through. As part of the immune system, they are responsible for two tasks:
- Hematopoietic. They participate in the formation of lymphocytes, which remove microbes from the body.
- Protective. Connective tissue is capable of absorbing and making bacteria into their own kind.
Description of the location of the tonsils
Lymphocyte tissue is located in the recesses of the soft palate, on the root of the tongue, on the wall of the nasopharynx and on the mucous membrane of the larynx.
You can get to the palatine tonsil on your own; the rest are visually accessible only to a specialist using special tools. Upon examination, the upper layer of tissue (epithelium) is distinguished.
The organs themselves are covered with several mucous layers that protect them from damage.
If the patient wants to see the organs with his own eyes, it is worth undergoing an examination. Using an endoscope, the doctor will give a complete description, describe the structure and display an image of the organs.
Kinds
There are several types of tonsils. They are distinguished by anatomy, location, and the presence of a pair. Paired tissue clusters:
- palatine (two tonsils 1 and 2), located between the soft palate and the tongue in small pits;
- tubal (5 and 6), located near the canal connecting the throat and middle ear.
Unpaired clusters:
- pharyngeal (3), located near the wall of the pharynx;
- lingual (4), located under the back of the tongue.
Palatal
The structure of the organ is porous. A distinctive feature is the presence of depressions on the tonsils. The entire surface of the organ is covered with lacunae. They are the first to encounter an uninvited infection, catching germs and viruses. There are about 40 such recesses.
During the chronic process, pathogenic microbes hide in the gaps.
In addition to the depressions, the lymphoid tissue is saturated with follicles. In a healthy state, follicles are assigned the function of providing leukocytes and plasma cells to resist infection. During illness, they fight viruses, and in acute conditions they are part of purulent accumulations.
Nasopharyngeal
A collection of tissue in the nasopharynx - adenoids. The location of the pharyngeal tonsils is the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. The nasopharyngeal tonsil is a transverse fold of the mucous membrane. You won't be able to see them, they are not visible. Adenoids consist of mucous membrane, which is covered by ciliated epithelium.
Adenoids are the biggest problem for children. Excessive growth blocks the nasal passages, making breathing difficult and provoking inflammatory processes.
Pipe
A small collection of lymphoid tissue is located in the cavity between the nose and the auditory tube. Despite their small size, the tubal tonsils are responsible for protecting the hearing organs from infections. An enlarged organ blocks the free passage between the nose and ear and can cause inflammation of the middle ear.
lingual
At the base of the tongue there is a lingual growth. The outside is covered with smooth epithelium, but there is roughness and tubercles, it is divided in the middle by a septum, and salivary canals are hidden in the recesses.
Birth defects and tonsil damage
In accumulations of lymphoid tissues there are damage, congenital abnormalities, and neoplasms. Any disease of the organ leads to a deterioration in the general condition. An additional palatine gland is a congenital defect. This deviation is considered safe and no treatment is used.
Damage includes burns and various injuries. Injuries may be local in nature, or may be associated with injuries to neighboring organs. Damage can be caused by foreign objects. The cause of the damage and its elimination are dealt with by the doctor.
Tonsil diseases
The response to the attack of viruses from the lymphoid organs is divided into primary (damage to lymphoid tissue) and secondary (inflammation affects the mouth, nose, throat).
Common diseases include:
- angina;
- tonsillitis:
- adenoids;
- hypertrophy of the glands.
Sore throat is an acute inflammation of the tonsils. The course of the disease is accompanied by high fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. The anatomy of the organ promotes the accumulation of microorganisms in the lacunae. At the site of accumulations, pustules form. The three types of most common sore throats are:
- Catarrhal. Mild degree, with timely assistance, it goes away quickly.
- Follicular. Serious degree of inflammation. If left untreated, complications may occur.
- Lacunarnaya. It is not advisable to treat a sore throat on your own.
Improper treatment leads to a chronic form and can last a long time. Tonsillitis is inflammation that has become chronic. Two forms are observed:
- recurring inflammation (3-4 times a year);
- constant inflammation (low-grade inflammatory process).
A sign of chronic tonsillitis is the presence of plugs in the mouth (on the tonsils). A plug is an accumulation of pus, bacteria, and microbes. It is dangerous to remove them on your own; you should consult a specialist for treatment.
Proliferation of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
Adenoiditis is a consequence of an inflammatory process or long-term chronic inflammation. The anatomy of the location of the tonsils leads to blockage of the passage, making it difficult for a person to breathe through the nose. Inhaling air through the mouth leads to recurring colds. Blockage of the ear canal leads to hearing impairment.
Enlarged palatine tonsils
Enlargement of the tonsils without inflammation is tonsil hypertrophy. A deviation from the norm occurs after illness, due to weakened immunity. Symptoms: snoring, difficulty breathing, swallowing.
With a slight change in rinsing, the tonsils will return to their previous size. A larger increase means serious therapy is required, sometimes surgery has to be used.
There are three stages of organ hypertrophy; the choice of therapy depends on the degree of organ enlargement.
Diseases that provoke the proliferation of pathogenic organisms
There are several such diseases.
Below is a list of the main diseases that cause sore throat:
1. Sore throat.
This disease most often affects children and adolescents. Characteristic symptoms of a sore throat: high body temperature, fever, the patient notices that his tonsils are very swollen, there are signs of intoxication, including thirst and aching joints. A sore throat is accompanied not only by swallowing food, but also by swallowing your own saliva.
tonsils hurt what to do with a sore throat
2. Chronic tonsillitis.
It is caused by frequent infections with tonsillitis, which doctors also call the acute form of tonsillitis. Weak immunity, structural defects of the nasopharynx, growth of adenoids in children, as well as frequent sore throats suffered on the legs without proper treatment are the main causes of chronic tonsillitis. Symptoms: difficulty swallowing, tonsil pain, drowsiness, low fever.
3. Chronic pharyngitis.
This ailment traditionally develops in parallel with other infectious diseases of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract. A characteristic feature of chronic pharyngitis is that the tonsils are inflamed and enlarged, but the patient does not feel a sore throat.
4. Abscess of the tonsils.
It is a complication after a sore throat, most often observed only on one side. Characteristic symptoms are severe sore throat, loss of strength, temperature above 39.5 degrees. In addition to the general symptoms, the patient has a bad smell from his mouth.
Adenoids and tonsils: what is the difference?
“ Adenoids and tonsils in children : what is the difference ?” This question is often asked by parents who come with their child to see an otolaryngologist (ENT doctor).
And it arises because the mother or father, first of all, informs the children’s doctor that they came for an examination with the baby, because “the child has sore adenoids in his nose (throat).”
Is this the correct expression, the definition of a pathogenic phenomenon? Why do experienced pediatricians correct parents and clarify that I cannot get sick from adenoids The child has diseased tonsils, that is, the nasopharyngeal glands. In the throat they are also called tonsils.
So, what is the fundamental difference in these words, the difference between clinical/anthropological and morphological terms? In the most concise and accessible aspect it is explained as follows. Adenoids are a disease. Tonsils (tonsils) are organs (glandular biological plates in the nasopharynx) that are affected by this disease.
And now in more detail about tonsils and adenoids in children.
I. Human anatomy: tonsils
By carefully viewing the schematic image, you can clearly imagine the anatomical definition of the tonsils in humans. To this information you need to add the following:
- The nasopharyngeal tonsils are visually visible and not visible. For example, the almond glands in the nose lie in such a plane that in a healthy state it is impossible to see them (independently). And, the palatine (in normal status) tonsils, located on both sides of the uvula, are barely visible.
In other words, you can only see inflamed nasopharyngeal glands, hypertrophied by painful changes.
The nasal tonsils, already affected by adenoid invasion, “look out” from the nasal anterior locations (closer to the nostrils), from the inside. Like this, as shown in the photograph below.
Or they lie far in the depths, at the posterior exit of the nasal canals (vomers, choanae) into the larynx.
There they can be diagnosed only by endoscopy (instrumental equipment): a thin catheter + a mini LED camera built into it.
- Pharyngeal tonsils (or tonsils), painful, altered by adenoid pathogenic appearance, look like in the attached picture below.
Invaded palatine tonsils in a child are most often seen by parents in cases of tonsillitis.
Important addition! Tonsils, both in the mouth and in the throat sector, are innate organs. In the fetus, during intrauterine development, nasopharyngeal glands from lymphoid epidermal tissue are formed during pregnancy (8-10 weeks).
Provided good health in childhood, minimal respiratory and infectious diseases, the nasopharyngeal tonsils do not bother a person with adenoid growths. Over time, they decrease so much that they are neither visible nor perceptible.
- The physiological characteristics of the tonsils include their protective functionality. Nasopharyngeal, oblong layers, consisting of a porous, diffuse lymphoid structure, are part of the unified immune system of human anatomy. Why, specifically to it, and not to another system? Because these tonsillar organs produce a genetic immune, protective basis - leukocyte macrophages, lymphocyte cells that destroy foreign, harmful viral pathologies.
Removal of tonsils, nasal adenoids (generally from the body) in the developing childhood period is an undesirable decision. The child is deprived of a natural primary barrier, protection from pathogenic microflora that enters the body through the oral and nasal cavity.
Tonsils are important, like all visceral organs. They need to be treated promptly, just like the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys or stomach.
II. Medical clinical etiology: what are adenoids
"Tonsilla pharyngea", which means "Adenoids" in Latin. From the ancient Greek language: - “ἀ δήν” is “gland”, “εἶδος”, translated as “species”. Medical pathomicrobiology interprets the terms as adenoid growths, purulent neoplasms in the form of ulcers, pasty loosening of lymphoid/glandular tissue.
In general, massive damage to the nasopharyngeal organs (tonsils, tonsils) with a similar pathogenic picture is called adenoid vegetation (or other similar terms) adenoidoplasia, adenoidopathogenesis.
Articles on the topic Breathing exercises for children according to Buteyko
Invaded palatine tonsils in a child are most often seen by parents in cases of tonsillitis. If white, purulent plugs are scattered on the outer planes, this is follicular tonsillitis. But, diseases of the tonsils with a sore throat-like infection indicate that this is a manifestation of adenoid excessive invasion (see photo above)
Nasal adenoids, in the primary format, are initially not only visible (runny nose, copious mucus discharge from the nose), but also audible.
This means that the following has happened: a pathologically hypertrophied, enlarged nasal tonsil (on both sides or one side) causes difficulty breathing through the nose. Children are forced to breathe through a constantly open mouth (oral syndrome).
Due to a long-term similar, unnatural position, the child’s face acquires a specific type - “adenoid face”.
Children have a nasal voice, unclear pronunciation, and noisy snoring. In addition to such obvious pathological symptoms, adenoid disease destroys the health of the child as a whole. Especially if adenoid pathology, the disease is not treated, it is started, brought to severe stages and degrees of anamnesis.
III. Epilogue as "Post Poskriptum"
About how adenoids have a detrimental effect on other organic systems of children, which cause them diseases of visceral, vital organs (heart, kidneys, pancreatic pathogenesis, liver dysfunctions) - articles on our website tell about this in a very interesting and informative way - https:// adenoidy.com .
It is difficult for parents who do not have special medical education to penetrate and understand complex medical terminology (as on other sites on social networks). Here, on these pages, about adenoids and tonsils in children, it is written very simply, clearly, without avoiding special terminology.
Moreover, adults need to know about the most common childhood diseases, such as adenoiditis (sick tonsil adenoids) in children. Knowledge will help the closest people of a sick child to successfully cope with this terrible disaster.
Articles on the topic Tonsils and adenoids
Source: https://adenoidy.com/adenoidy/adenoidy-i-mindaliny-v-chem-raznitsa.html
Inflammation of the tonsils without pain
People often go to the doctor with the following complaint: their throat does not hurt, but their tonsils are swollen. This symptom is accompanied by malaise, soreness or tingling, but there is no pain. The main reasons for this condition include:
tonsillitis during the recovery stage - plaque and pain have already passed, but redness of the mucous membrane still remains;
chronic tonsillitis - it is accompanied by constant redness of the mucous membrane, but there is no pain;
a mild form of pharyngitis or laryngitis, which is characterized by only mild soreness;
respiratory infections, which are accompanied by a red throat and hyperthermia;
thermal damage to the mucous membrane;
consumption of food dyes.
If such a problem occurs, it is recommended to consult an otolaryngologist. Only a doctor can determine the cause of such a symptom and prescribe treatment if necessary. Therapeutic measures include taking antipyretic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs. If an infectious disease is diagnosed, the doctor must prescribe antibacterial agents.
Most often, the following medications are prescribed to treat a sore throat:
Inflammation of the glands with painful sensations
If the tonsils hurt, this may be evidence of an acute form of tonsillitis and pharyngitis. If your tonsils hurt, this indicates the onset of influenza or acute respiratory viral diseases. This is the body’s reaction to the penetration of pathogenic microflora.
The tonsils are a barrier that limits the access of pathogens, viruses and fungi to the organs of the respiratory system. If the immune system is weakened, pain symptoms appear a few days after the penetration of bacteria or viruses.
Most often, a condition where the tonsils are painful and swollen is observed with sore throat. The severity of the inflammatory process varies. With catarrhal tonsillitis, a burning sensation, soreness, pain when swallowing, and hyperthermia at the subfebrile level appear. At the same time, the tonsils hurt greatly, and plaque appears on them.
With follicular angina, the body temperature rises to febrile levels, and signs of intoxication of the body appear. At the same time, the tonsils hurt greatly, they also become swollen and loose.
With the development of lacunar angina, the symptoms are similar to the follicular form. In this case, the tonsils are greatly enlarged in size, inflamed, their surface is covered with a yellow or white coating.
To cure such a disease, the doctor must determine the type of pathogen. Treatment consists of taking medications and using traditional methods. An integrated approach will help the body overcome the disease faster.
Most often, the treatment regimen includes:
- Taking antibacterial drugs. These medications are prescribed for bacterial infections. Most often, the doctor prescribes drugs that are part of the penicillin group.
- Taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs. Such drugs are used for viral diseases. They prescribe Cycloferon, Viferon, Immunal, Bronchomunal.
- Gargling. Antiseptic drugs, furatsilin, Rotokan, saline solution, hydrogen peroxide and decoctions of medicinal plants are used.
- Spray irrigation. Such medications will help reduce the severity of swelling, reduce pain and inflammation. Ingalipt, Chlorphyllipt, Hexoral, Cameton, Tantum-Verde, Vicks, Angilex are often used.
- Lollipops or lozenges that have antiseptic and analgesic properties - Strepsils, Lisobakt, Faringosept, Septolete.
tonsils hurt, inflammation of the tonsils
How to preserve the function of the tonsils?
Making this organ function properly is not that difficult. First of all, it is necessary to refuse to remove it for preventive purposes, even if the doctor advises it. An exception here may be tumors of the tonsils, their mechanical damage, as well as their enlargement to such an extent that they will interfere with swallowing and breathing through the mouth.
In addition, it is very important to always be fully treated for tonsillitis and tonsillitis. To do this, it is necessary to carry out complex therapy, one of the components of which must be antibacterial drugs. You need to take them for at least 7-10 days in dosages recommended by a specialist.
If sore throats develop and plaque forms on the surface of the tonsils, you should never try to remove it yourself. Even one slight wrong movement can severely damage the lymphoid tissue, resulting in permanent loss of tonsil function.
Other causes of inflammation and enlargement of the tonsils
Swelling and inflammation of the tonsils can occur not only as a result of the penetration of harmful microflora.
The most likely reasons are the following:
• allergic reaction of the body to any irritant; • reaction to bad habits, such as smoking; • laryngeal injury;
• dry indoor air; • toxic burn of the larynx; • various neoplasms in the larynx.
A characteristic difference between these ailments is the patient’s normal body temperature. In some situations, the right decision would be not to interfere with the inflammation process and allow the body to cope with the inflammation on its own. In other cases, immediate treatment measures should be taken. Only a specialist can determine the exact cause of enlarged tonsils.
Click here - all materials about tonsils (tonsils)
All site materials about tonsils (tonsils)
Differences between tonsils and tonsils
Both terms are used quite often. But are there any differences? As it turns out, there are none. The tonsils and tonsils are the same organ.
Why are they called that? One word can have different origins and stylistic connotations depending on the geographical location of its appearance. This situation has not spared medicine either.
Tonsils is a term that comes from the Latin language. Tonsils is a designation for an organ that appears in ancient Greek medicine. There is an opinion that tonsils are a popular designation for an organ, and tonsils are a purely medical definition among workers in this field.
Like any organ, the tonsils have their own structure and structure. It is customary to subdivide them:
- to paired tonsils;
- unpaired tonsils.
The structure of the paired tonsils implies the presence of two identical parts. This type consists of palatine tonsils and tubal tonsils. Unpaired tonsils do not have a second identical part. This type is divided into pharyngeal and lingual tonsils.
In addition to its structure, this organ has certain tasks that it performs in the body. One of the most important is the development of special protective immune cells. And it is on these tasks that the structure of the tonsils depends. Thus, the pharyngeal tonsil is a collection of several balls that have a special epithelium in the form of “eyelashes”.
In turn, the lingual consists of two parts, separated by a groove. Tubular, the smallest, is a cluster of nodules responsible for protecting the hearing aid.
Swollen tonsils in children and adults: treatment features
Only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment and give other recommendations on how to treat tonsils, having first established an accurate diagnosis. Treatment for a sore throat is usually done at home. The main goal of therapy is to eliminate inflammation, swelling and discomfort in the throat, as well as reduce high fever.
Patients experiencing severe swelling and sore throat should remember that in some cases urgent medical attention is necessary.
swollen tonsils
In such dangerous situations you need to consult a doctor:
• with severe swelling of the throat and intense pain that prevents swallowing food and water; • when the body temperature is above 40 degrees, the patient is in a feverish state and has slurred speech;
• in case of impaired breathing with throat wheezing, unusual secretion of saliva; • with severe swelling of the throat, turning into swelling of the lower jaw, neck and face;
• if nausea and vomiting develop along with swelling of the throat; • for painful lymph nodes in the neck, their sudden enlargement, as well as sudden congestion and pain in the ears
In such situations, a delay in seeing a doctor increases the risk of developing unpredictable consequences and dangerous complications.
Which doctor can help a patient?
For a preliminary diagnosis, you should first contact a therapist who can determine the nature of the ailment, exclude or confirm the allergic component and, if necessary, prescribe laboratory tests. A preliminary diagnosis - tonsillitis, tonsillitis or pharyngitis - in most cases is a referral for further treatment to an otolaryngologist (ENT doctor).
Causes of diseases and their symptoms
Inflammation of the tonsils can occur for many reasons. Knowing them, you can predict the development of the disease and take proper precautions.
The main causes of disease of the tonsils (glands):
- contact with infected people;
- hypothermia – sudden changes in temperature, prolonged exposure to the cold;
- inflammation of the mucous tissue of the oral or nasal cavity due to harmful climate conditions or work environment;
- caries;
- frequently consumed junk food;
- sinusitis;
- lack of vitamins or other necessary elements in the body;
- weakened immunity during and after illness;
- genetic predisposition to diseases of the tonsils.
Signs of development of tonsil disease:
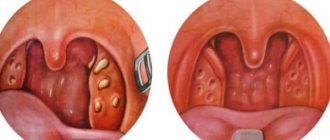
- change in the shape of the tonsils - their size increases, the pink tint changes to a bright red color;
- yellow coating possible;
- the appearance of ulcers on the tonsils that have a bad odor;
- sore throat due to large innervation (the presence of a large number of nerve endings in the tonsils) and when eating;
- change in state - previously having hardness, they turn into loose, soft;
- the appearance of scars between the tonsils and the sky;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
Common symptoms include weakness, sore throat and headache, aching bones throughout the body, and fever.
General rules for treating enlarged tonsils
treatment of tonsils
In medical practice, there are several general rules for treating an inflamed and painful throat:
1. The patient must remain in bed.
2. At high body temperature, which often accompanies swollen tonsils, you must take antipyretic drugs.
3. Several times a day you should try to disinfect the oral cavity. To do this, you should gargle and rinse your mouth, and also lubricate the affected tonsils with special solutions.
4. Try to drink a lot. Drinking plenty of fluids helps remove pathogenic plaque from inflamed tonsils and remove it from the body naturally.
You can relieve a sore throat if you prevent its irritation by following simple nutritional rules. All hard and tough foods should be removed from the diet. Also exclude salty and sour foods.
How are tonsils different from tonsils?
Every mother knows that children's bodies are often exposed to diseases, especially children often suffer from sore throat, which can cause many complications. Let's figure out how to treat inflamed tonsils for children and adults, whether there is a need to remove them, and why our body needs them in general.
Tonsils and tonsils - what's the difference?
I would like to initially clarify one point. All parents should understand the terms: tonsils and tonsils (we will learn from this material what the difference is, and whether there is one at all). They are actually the same thing.
From a medical point of view, the correct name is palatine tonsils, but tonsils are more familiar to the people. Do not faint when the doctor gives your baby an unfamiliar diagnosis - tonsillitis.
So that these words do not cause fear, you need to understand what they mean.
- The tonsils are an important organ of the immune system, located in the throat, between the palatine arches, closer to the root of the tongue. The tonsils consist of lymphoid tissue.
- Doctors call tonsillitis inflammation of the tonsils. The disease can be either acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis is familiar to parents in everyday life as a sore throat.
- In fact, the tonsils are the protectors of the entire body. It is this organ of the immune system that acts as a barrier to harmful microorganisms. The lymphoid tissue that makes up the tonsils is capable of producing special antibodies that take part in the fight against pathogenic microbes. It turns out that the main element of the immune system in children is the palatine tonsils, which protect the baby from the penetration of viruses, infections and bacteria.
Why does the body need tonsils?
Accumulations of lymphoid tissue located between the nasal and oral cavities are primarily necessary to protect the child’s body from all kinds of viruses and bacteria. When the baby inhales, in addition to air, it also captures pathogens of various infections, and the tonsils (photos will be presented in this article) stop and neutralize them.
In addition to its protective function, the palatine tonsils are involved in the regulation of hematopoiesis, forming lymphocytes (immune system cells) that participate in the formation of antibodies.
Causes of inflammation of the tonsils
The tonsils are able to protect our body only with a normally functioning immune system. Weakened immunity significantly reduces the ability of the tonsils to retain and neutralize viruses. What happens in this case? Microbes simply settle and accumulate on the surface of the tonsils, as a result of which they become inflamed.
In this state, they not only do not provide protection for the body, but, on the contrary, pose a threat. The most common disease of the tonsils is tonsillitis; in its acute form, sore throat. Each of us knows how difficult this disease is to bear: high fever, terrible sore throat.
In fact, the symptoms of a sore throat are not as terrible as the complications that appear after the disease. No medical specialist can compile a complete list of possible dangers, since it is updated every year. Inflammation of the tonsils in some cases can lead to damage to the heart, joints, kidneys and other organs.
To date, doctors have identified over 100 diseases directly related to tonsillitis. The results of recent studies have shown that angina can even lead to impaired reproductive function.
Therefore, inflammation of the tonsils is a rather serious and dangerous disease, and even if for some reason it could not be avoided, it is necessary to promptly and competently begin treatment.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils
When the palatine tonsils become enlarged, there is less space in the oropharynx, making breathing difficult and food moving worse. But this is not the worst thing. If the adenoids and tonsils (tonsils) are simultaneously inflamed, then the baby’s speech also suffers.
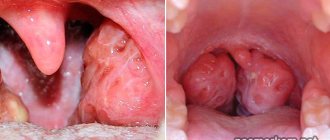
Each mother will be able to independently determine the condition of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx. With inflammation, uneven rounded formations of a pale pink or yellowish color will be visible from behind the lateral arches.
What do tonsils look like in normal condition? Outside of an exacerbation, there is no plaque on them and white dots filled with pus; there is no swelling or redness. When you press on the palatine tonsil, a soft consistency is noted.
Based on all these signs, the condition of the tonsils is determined.
If the tonsils have enlarged to such a state that they practically close together, then the child will have to be switched to semi-liquid foods. If necessary, this diet is followed until complete recovery.
On the one hand, tonsils and tonsils (we already know what the difference is) protect our body from attacks by viruses and bacteria right at the entrance; on the other hand, they become a serious threat when they fail to cope with their tasks. With poor immunity or hypothermia, an exacerbation begins, and the infection that accumulates in the tonsils leads to inflammation, accompanied by high fever and sore throat.
Why are enlarged tonsils dangerous?
Inflamed palatine tonsils become a source of infection for the entire body, a so-called powder keg, when it explodes, which will lead not only to tonsillitis, but also to a number of other inflammations (most often otitis media).
Since the enlarged tonsils are not able to perform their main function (protective), the infection easily enters the ear through the Eustachian tube.
In addition, chronic tonsillitis (inflamed tonsils) is often accompanied by rhinitis, sinusitis or sinusitis.
Enlarged tonsils lead to decreased immunity, therefore, frequent colds and general weakness of the baby are “just around the corner.” The child looks tired, he does not have enough strength for long-term physical and emotional stress, some even begin to lag behind the school curriculum.
Degrees of tonsil enlargement
Otolaryngologists classify the tonsils (photos of normal and inflamed conditions are presented in this material) according to the degree of their enlargement. This makes it much easier to diagnose the baby’s condition and choose the necessary treatment tactics.
So, ENT doctors distinguish three degrees of enlargement of the palatine tonsils:
- The tonsil occupies a third of the space between the anterior edge of the palatine arch and the vomer.
- The amygdala takes up 2/3 of the space.
- The entire space is occupied by a hypertrophied gland.
Problems related to tonsils
As mentioned earlier, the protectors of our body (tonsils) can become inflamed, but in addition to this, they cause other troubles to the child’s body:
- Some children are born with defects in the development of the tonsils, for example, the presence of an additional palatine lobe. As a rule, in such situations no special treatment is prescribed.
- Hyperplasia or proliferation of tonsil tissue. Observed in childhood, if the child does not experience any discomfort, intervention is not necessary.
- Various injuries. Most often, a burn occurs when swallowing a boiling liquid or chemical substance. Such tonsil injuries must be treated exclusively in hospital and as quickly as possible.
- Fish bones can get stuck in the tonsils. In this case, you will need the help of a specialist to remove the foreign body.
- Tumors on the tonsils are extremely rare; they can only be gotten rid of through surgery.
Treatment of tonsils
Children aged 3 to 10 years are most susceptible to inflammation of the tonsils. Some children suffer from sore throat periodically, while others simply do not have time to rest from the illness. Treatment tactics will be individual for each case.
When you have a sore throat, the first thing you need to do is bed rest. In addition, during the disease several therapeutic measures are prescribed: general and local therapy, drinking plenty of fluids, taking antihistamines, and immunostrengthening therapy. It is strictly forbidden to touch purulent tonsils, even to get rid of purulent exudate.
Many mothers with a sore throat force their child to gargle with an antibacterial solution in the hope that in this way they will get rid of plaque on the tonsils. However, the benefits of this procedure remain in doubt. In fact, the solution does not reach the surface of the tonsils.
Direct contact of the inflamed tonsils with the solution is observed while drinking. That is why patients with sore throat recommend drinking tea with lemon, warm milk with honey, soda and butter several times a day.
Now it’s worth paying a little attention to antibiotics. Without them, it will not be possible to cure a sore throat (what the tonsils look like during the disease can be seen in the photo), moreover, the likelihood that the disease will become chronic increases.
Since bacteria quickly adapt to antibiotics, the range of drugs is expanded every year. Therefore, it is not surprising that your child’s pediatrician prescribed not penicillin, but a stronger modern medicine.
Only a specialist should decide which antibiotic is right for your child, taking into account the history of allergies, atopic dermatitis or bronchial asthma.
Treatment with traditional medicine
I would like to talk about the most effective methods of combating inflamed tonsils, which are mainly used to treat children.
- A decoction of chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, pine buds, violet, horsetail and string. All herbs are mixed and poured with boiling water, infused for 2-3 hours. The prepared decoction is used to gargle.
- Honey and red pepper are good for sore throat. Place the necessary ingredients on the compress paper, light a wax candle from below and wait until the honey melts. Then remove the red pepper pod and take 2 tablespoons before meals.
- For tonsillitis, an infusion with Kalanchoe is effective. It is used for gargling.
We hope this article will help young parents understand terms such as tonsils and tonsils, and they will also understand the difference between sore throat and tonsillitis.
Source: https://glivec.su/2018/05/20/chem-mindaliny-otlichajutsja-ot-gland/
Folk remedies for treating enlarged tonsils
Home therapy can help in cases of mild inflammation of the tonsils. The most effective are gargling with soda or herbal infusions. You can brew calendula, cornflower, black elderberry flowers, chamomile and other medicinal herbs. You can also prepare a mixture of honey, a few drops of lemon juice and 1 teaspoon of chopped ginger to rinse enlarged tonsils.
Inhalations of the upper respiratory tract help well. They reduce pain and soreness, and also disinfect the oral cavity. Inhalations can be done with medicinal plants, essential oils, onions and garlic.
Inhalations for the treatment of swollen tonsils
In parallel with taking medications, inhalations can be used. After using them, recovery occurs much faster. This procedure can be carried out only in the absence of elevated body temperature.
For inhalation the following are used:
- peppermint oil;
- tea tree oil;
- fir oil;
- jacket potatoes;
- a decoction of sage, chamomile, St. John's wort;
- Zvezdochka ointment.
You can reduce the severity of inflammation by inhaling with onion juice. It is mixed with saline, heated and the vapor is inhaled. Using a nebulizer is also effective. The device is filled with special preparations that have an antiseptic effect - Lorde, Dekasan. For purulent sore throat, inhalation is not performed.
Compresses for the treatment of swollen tonsils
compresses for the treatment of tonsils Compresses
are effective in treating inflamed tonsils. To perform this procedure you will need:
- Grate a head of cabbage. Fold the gauze in several layers and place the resulting pulp on top of the gauze. Place it on your throat and wrap it with a terry towel on top. After two hours, you can remove the compress.
- A paste of sea salt and water is spread on a towel. Apply the compress to your throat for an hour.
- You can prepare a concentrated chamomile decoction. Half a glass of chamomile inflorescences is poured with two glasses of boiling water. The broth should be infused for about half an hour and should be warm before the procedure. Then you need to strain the broth, moisten a terry towel in it and wrap it around your throat for an hour.
- Rub the neck and chest area with fir oil. This remedy is used only in the absence of an allergic reaction.
Gargles for the treatment of swollen tonsils
tonsils hurt, what to do, gargling
To prepare an effective gargle, you will need:
- Mix a teaspoon of salt in a glass of hot water.
- Dilute a tablespoon of hydrogen peroxide in half a glass of hot water.
- Prepare a decoction of calendula, sage and chamomile. Use a tablespoon of dry raw material per glass of water.
- You can prepare an infusion of garlic. To do this, you need to chop a few cloves of garlic and pour a glass of warm water. After two hours, you can strain and use for rinsing.
- Mix freshly squeezed lemon juice with honey.
- Pour boiled and chopped beets with water in equal parts.
- Mix about 20 drops of propolis tincture in a glass of water.
- To prepare the rinse, you can pour boiling water over a mixture of dry leaves of plantain, wormwood and calendula.
- You can dilute several crystals of potassium permanganate in water. You should get a slightly pink solution.
- Pour two tablespoons of yarrow into a glass of boiling water. After an hour, you can strain and use.
- Pour two tablespoons of St. John's wort into a glass of vodka or alcohol. Let it steep for 14 days. After this, the product can be used.
- Dilute three to four drops of basil oil in a glass of warm water.
- Pour 2 tablespoons of walnut leaves into two glasses of water. After an hour you can use it.
- Pour a liter of boiling water over a mixture of herbs - lemon balm, fireweed, mint, chestnut flowers. All components need to be taken one tablespoon at a time.
Warming to treat swollen tonsils
If there is no hyperthermia, warming up using the following devices is effective:
- Ural Federal District. This is heating using ultraviolet rays. After the procedure, blood microcirculation improves, epithelium regenerates, and the inflammatory process decreases.
- Quartzization. The antiseptic effect occurs through exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- UHF therapy. The procedure involves exposing the body to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Under the influence of this procedure, blood and lymph circulation are stimulated, and the severity of inflammation is reduced.
- Phototherapy. The procedure involves using monochromatic light waves that penetrate deeply into the tissue. The result is a reduction in swelling, improved well-being, and an increase in natural protective functions.
- Salt warmers. The result is vasodilation and rapid regeneration of damaged mucosa.
Warming the throat and tonsils
The listed procedures are carried out in a clinic.
Consequences of swollen tonsils and tonsils
In chronic tonsillitis, the most common consequences are rheumatic pathologies:
development of rheumatic carditis;
damage to the membranes of the joints - polyarthritis of the rheumatoid type;
damage to nerve fibers and cells – rheumochorea;
inflammation of the epidermis of the rheumatic type.
Such lesions develop due to the influence of pathogenic microflora on heart tissue, as well as as an autoimmune reaction of the body to streptococcus. The cells of the body are similar in structure to staphylococcus cells. It is because of this that the immune system perceives its own cells as foreign and begins the process of destroying them.
Other dangerous complications of tonsillitis include:
laryngeal abscess, which is characterized by the accumulation of pus in the cavity of the lacunae;
otitis media, which is characterized by inflammation in the middle ear;
inflammation of the membranes of the brain when infection penetrates into the cranial cavity;
sepsis, which is characterized by the introduction of an infectious process into the blood.
These complications develop only in advanced forms of angina, in the absence of timely and correctly prescribed therapy. With frequent chronic tonsillitis, the risk of developing glomerulonephritis increases, which is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the kidneys and severe disorders in their functions.
Tonsils, tonsils, adenoids: what are they, what is the difference
The terms tonsils and tonsils are often compared; what is the difference and does it exist at all? This is what we will talk about.
Anatomy and physiology of the organ
Tonsils are a specific lymphoid accumulation that is oval in shape and localized in the pharynx. The location of clusters and the role they play are interconnected. This is a kind of barrier for microorganisms that enter the respiratory tract from the external environment. They also take part in the body's immune response.
There is a certain classification of tonsils:
- paired (palatal, tubal);
- unpaired (pharyngeal, lingual).
Sometimes when talking about tonsils, you hear the word “tonsils” - this is misleading, because some people think that these are synonymous concepts, while others think that they are completely different.
Tonsils and tonsils are the same thing. It’s just that most often the palatal lymphoid accumulations, which are quite clearly visible, are called tonsils.
Translated from Latin, the word tonsils means “small acorn.” Because of the visual similarity, the term has spread.
It is considered colloquial and is used in everyday life. Medical terminology accepts the word tonsils.
The totality of this lymphoid tissue is represented by a porous structure. The tonsils have lacunae, each with up to 20 pieces. These grooves play a very important role because they enable the immune system to recognize foreign microorganisms.
The surface of the tonsils is covered with follicles, which fill the oval organ from the inside. Thanks to them, protective immune cells are produced - lymphocyte cells. The role of macrophages and plasma cells is also great, because they also overcome infection.
All tonsils, depending on the functions performed, have characteristic structural features:
- the pharyngeal tonsil consists of several balls of mucous membrane with ciliated epithelium;
- the lingual tonsil consists of 2 halves due to the median groove;
- tubal tonsils are the smallest, they are based on diffuse lymphoid tissue and lymphoid nodules, the functions of which are aimed at protecting the auditory organ.
All these glands are covered on the outside with a mucous membrane. There is a capsule. Innervation is at a high level, and therefore inflammatory processes are accompanied by pain.
Hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil
The terms tonsils and adenoids are often used. There is a connection between them. What's the difference? In order to understand these terms, you need to study the pharyngeal gland.
In addition to the palatine tonsils, as already mentioned, there is also such a lymphoid formation as the pharyngeal tonsil. It will not be possible to see it well in the mouth, because it is located above the back wall of the pharynx, where the roof of the nasopharynx is.
Under the influence of certain factors, this amygdala can enlarge, and a state of hypertrophy develops. In medicine, it is usually called adenoids, and the inflammatory process is called adenoiditis.
During normal functioning, the adenoids enter the lymphatic pharyngeal ring. Immediately after birth, a person does not yet have adenoid follicles.
After three years, the body develops a powerful protective system, the essence of which lies in the lymphatic follicles. They are the ones who can stop the spread of microorganisms and maintain health.
Thanks to immune cells - lymphocytes, the defense system can recognize a foreign organism and destroy it.
In children 15 years of age, some tonsils may shrink or disappear altogether. This is exactly what concerns the adenoids. But in adults, there is no longer lymphoid tissue at the site of the adenoids. Therefore, for a long time it was believed that adenoiditis is a childhood disease that almost never occurs in adults.
Such misconceptions arose due to the fact that it is almost impossible to see adenoid growths due to the anatomy of the nasopharynx of an adult. Only with the help of medical equipment and modern diagnostics has it become possible to identify this defect.
The leading role here is played by examination using an endoscope, the flexible tube and optical component of which helps to see the adenoids in adulthood.
There are many factors for the appearance of adenoids; they often arise due to inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx.
Adenoid growths in childhood predict the return of the problem in the future. After all, after their removal, the situation may repeat again due to a surgical error or hereditary predisposition. Further treatment will depend on the degree of proliferation and, accordingly, the size of the adenoids.
Adenoid vegetations
It is customary to distinguish 3 degrees of adenoid vegetations:
- At the first, a slight increase in size is achieved, at which the upper part of the lumen from the nasal passages is closed. Since discomfort or inconvenience is not detected, diagnosing the disease is not an easy task. A small clue is snoring at night. It occurs due to prolonged monotonous position of the body, in which the adenoids block the openings of the passages and, as a result, prevent normal air circulation. Therapy at this stage is conservative.
- The second degree is characterized by such an enlargement of the tonsils when 1/2 of the nasal passages are blocked. Such changes often lead to asthma attacks. Breathing through the nose becomes difficult at any time of the day or night. This is especially dangerous in autumn and winter. During these periods, a person begins to breathe through his mouth. The infection has every chance of easily entering the body and spreading successfully. Quite often, surgical intervention is a reliable method of treatment.
- The third degree of adenoid vegetations is a rare phenomenon, especially in older people. It completely stops the air flow. Due to such changes, the auditory tube is not filled with air, and as a result, the pressure in the middle ear does not normalize. Such gross disturbances in the normal functioning of the tympanic cavity lead to hearing problems and the development of otitis media of the middle ear. Permanent infectious diseases of the respiratory system are often found to be concomitant. There is only one way out of this situation - surgical intervention followed by removal of the adenoids.
In the treatment of this disease, it is important to remember that a surgeon should be contacted if it is impossible to treat with medication, if complications arise. Although adenotomy is a minimally invasive operation, it is still necessary to avoid exposure to negative factors during rehabilitation. For a quick recovery, you need to stick to a diet, get more rest and limit physical activity.
The key to a healthy body is a strong immune system and timely overcoming of diseases. Avoid causing respiratory diseases and chronic inflammation. Their elimination and further prevention can ensure the health and good mood of everyone. Get treatment and be healthy!
Source: https://pneumonija.com/oropharynx/v-chem-raznitsa-mezhdu-mindalinami-i-glandami.html
When is surgery necessary?
In most cases, problems with the tonsils are treatable, and patients soon forget about the pain and sore throat. However, if the inflammatory process is protracted or chronic, the disease greatly exhausts the patient and causes complications, then doctors recommend removing the tonsils.
This recommendation is explained by the following: the tonsils, as a defense against the oncoming infection, have ceased to perform their function, therefore regular inflammatory processes in the larynx help the source of infection to invade other organs. In any case, surgical intervention must be agreed upon with the patient. In this case, all indications and contraindications, the patient’s age and possible complications are taken into account.
Recommendations for therapeutic measures
It is worth treating the tonsils immediately after the first symptoms appear. This is due to the fact that it is inflammation of the tonsils that affects the spread of infection throughout the body. Organs at risk include kidneys, ears, cardiovascular system, and even joints.
We suggest you read: Why is there a bitter taste in the throat?
There are 7 main types of treatment for tonsils:
- vacuum type washing;
- use of laser tools;
- coagulation;
- drug treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- cryodestruction;
- treatment with folk remedies.