Last update: 01/16/2020
Author of the article: pediatrician Valentina Razheva
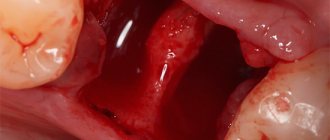
A wound is a damage to the integrity of the skin or mucous membrane (in some cases also muscles, tendons and internal organs), which occurs under the influence of mechanical, thermal or chemical factors. Healing of wounds depends on their area, depth and severity, and can occur both without the formation of cosmetic defects (scars, scars, spots) and with them. In this article we will look at what stages the wound healing process includes, what ointments and creams for wound healing are used in traditional medicine, and what conditions for rapid wound healing must be met.
Types of wounds by method of receipt
To determine how long it will take for a wound to heal, you need to know what the main types of damage are based on how they were received. The healing time of the wounds described below depends on a number of factors, including the degree of tissue damage, its extent, the presence or absence of infection, shock, heavy bleeding, and damage to vital organs.
- Chipped. These wounds are characterized by their small diameter and relatively large depth. Usually accompanied by not too heavy bleeding, due to which the victim may decide that the wound is not dangerous. But make no mistake: puncture wounds can affect muscles, large nerves, blood vessels and internal organs, and if there is a deep wound channel, an anaerobic infection may develop.
- Cut. Such damage is usually caused by sharp flat objects - it can be a knife, a shard of glass, or a blade. They are characterized by smooth edges and fairly severe bleeding, which is caused by damage to capillaries and larger vessels.
- Torn. The edges of such wounds are uneven, areas of skin may peel off, and if they are deep enough, severe bleeding may begin.
- Chopped. Outwardly they are similar to cut ones, but differ from them in greater depth, the presence of uneven edges, bruising and a wide gape. There is a pronounced pain syndrome.
- Bite wounds. They appear as a result of a bite from a domestic or wild animal. Due to the possible presence of microbes on his teeth, there is a high probability of infection of the wound.
- From burns. If the blisters that appear at the site of 2nd degree burns are damaged, a weeping wound may form. If there is a 3-4 degree burn, damage to the deep layers of the skin occurs, resulting in serious, irregularly shaped wounds.
- For bruises. If the injury was caused by a blow with a heavy blunt object, bruised wounds are formed. They have an irregular shape and are characterized by the presence of dead tissue.
- Firearms. They are formed as a result of damage to the skin, muscles and internal organs by bullets, shot, or fragments fired from a firearm. Such wounds have a wound channel, as well as adjacent areas of contusion, concussion and deviation.
- Scalped. A type of laceration characterized by traumatic detachment of the top layer of skin. There is severe bleeding and pain.
Wound healing can occur by primary or secondary intention. In the first case, regeneration occurs relatively quickly, since no cavity is formed between the edges of the separated skin. Secondary intention occurs in cases where there is a large gap, pus appears and there is too much exudate. When a wound heals by secondary intention, granulation tissue is formed.
Phases of skin wound healing
Depending on the depth of the injury, the following classification is distinguished:
- superficial;
- deep;
- penetrating into cavities and internal organs.
Types and phases of wound healing suggest the presence of separate indications and contraindications. A specialist can classify a specific type and prescribe treatment. Superficial injuries are harmless, but those penetrating into cavities pose a threat to internal organs. Each wound requires special attention to ensure effective recovery.
Superficial
This type affects only the epidermis and a thin subcutaneous layer of fatty tissue. It does not pose a danger to internal organs and goes away within a week. Pain is present during healing, but it is mild. Examples: wart, torn mole, splinters on the foot, hands.
Deep
This type damages muscle fibers. This category includes cuts and puncture wounds. With such injuries, movement becomes difficult. It is easier to introduce infection into a deep abrasion, cause suppuration, and healing is more difficult.
Penetrating into cavities and organs
A dangerous type of wound that poses a threat to human life and health. Extensive bleeding - internal and external - may occur. If such an injury occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor. Examples: injuries to the abdominal and thoracic cavities, damaging internal organs:
- liver;
- heart;
- spleen.
Stages of wound healing
The surgeon decides what to apply to wounds for healing. When choosing, he takes into account the healing phase of the wound, the presence or absence of infection and suppuration. It is not recommended to choose remedies on your own (especially for healing open wounds), as this can lead to disastrous consequences.
Let's consider the main stages and stages of wound healing.
Inflammation
At the stage of inflammation, pus may be present in the wound, caused by pathogens entering the cavity. The areas around the wound are usually swollen and tender to the touch. Due to the inflammatory process, toxins can be absorbed into the blood, resulting in an increase in local and general temperature.
At this stage, it is important to ensure good drainage of wound exudate and removal of pus. It is undesirable to use fat-based ointments, as they create a film on the surface of the wound that interferes with the outflow of exudate. Instead, hydrophilic-based ointments and gels are used, which have good osmotic (absorption) abilities. In this case, the products must have an excellent antibacterial effect.
Regeneration and granulation
The regeneration process is characterized by an already formed wound barrier, as well as by the fact that the content of pathogenic microorganisms in the exudate is practically absent. The bottom of the wound is lined with bright red granulation tissue, which easily begins to bleed. The faster it forms, the less time it will take for the wound to heal.
At this time, it is important to provide the wound with reliable protection from damage and the necessary conditions for tissue regeneration. It is also necessary to protect the wound from secondary infection.
During this period, fat-based products are used - ointments that provide protection from damage. Water-based products are used selectively - they are necessary to provide an anti-inflammatory effect.
Epithelization (scarring)
After the bottom of the wound is filled with granulation tissue, the scarring process begins. To speed it up, it is not recommended to use fat-based preparations, as they can lead to unnecessary growth of granulations. Instead, the use of hydrophilic creams, aerosols and gels is allowed.
How to properly bandage
It is recommended to change the bandage on your leg daily; to do this you need to:
- Remove the dressing material. If the bandage sticks to the wound, you should soak the scab with boiled water with the addition of any available antiseptic: furatsilin solution, hydrogen peroxide and others.
- Wash the edges of the wound on the leg with warm boiled water, disinfect with brilliant green or an alcohol solution of calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort. If the surface is contaminated with automotive lubricant mixtures, purified gasoline should be used for hygienic procedures. Treat with gauze balls. Iodine should not be used due to the high risk of burns.
- Inspect the inflamed cavity for the presence of pus and fragments of foreign objects. It is not recommended to remove large, deeply located fragments yourself. It is safer to go to a medical facility to provide qualified assistance.
- If purulent contents have formed on the surface, it is recommended to clean the wound with gauze swabs, blotting each one only once.
- If there is suppuration inside, cleaning should be entrusted to a surgeon in order to eliminate the consequences of inflammation, including blood poisoning and death. Only a doctor who will make a prescription, combining medications for external and internal use, can know how to properly treat a purulent injury.
- After cleansing, cover the wound surface with sterile material and secure with a gauze bandage.
How to speed up wound healing
To speed up the healing of wounds, it is important to provide the victim with timely assistance, because the regeneration process largely depends on the actions that took place in the first minutes after receiving the injury. The first step is to carefully remove foreign bodies (if any) from the wound, clean it of possible dead skin, treat the area around the wound with an alcohol-containing antiseptic, disinfect the surface of the wound with an aqueous antiseptic solution and apply a sterile bandage.
There are many factors that influence the healing time of wounds in one way or another. To activate the body's defenses, it is necessary to ensure a full eight-hour sleep, a diet containing vitamins, macro- and microelements, and quit smoking and drinking alcohol. It is advisable to include fatty fish, nuts, olive oil, dairy products, carrots, and pomegranate juice in the menu.
There are diseases that slow down the healing process and wound healing. These include:
- diabetes;
- anemia;
- oncological diseases and immunodeficiencies;
- hypovitaminosis and general exhaustion of the body;
- some skin diseases (eczema, dermatitis, etc.);
- obesity;
- liver and kidney dysfunction;
- vascular diseases.
Traditional methods for treating and treating open leg injuries
It happens that it is not possible to receive timely medical care. In this case, you can start treating the open wound using traditional recipes.
When choosing how to treat a wound surface, it is recommended to use medicinal plants with a disinfecting effect. These include:
- A water decoction or alcohol tincture of calendula, birch buds, and wormwood.
- Leaves of indoor plants - aloe or Kalanchoe. Remove the thin skin and apply the fleshy side to the wound, securing with a bandage or plaster.
- Bee honey, spread a thin layer on the wound surface, place a sterile napkin on top and bandage it.
- Yarrow greens should be chewed until smooth and applied to a cut or punctured shallow wound.
- Treat the affected area with celandine juice.
The following folk remedies help speed up the treatment of a wounded limb:
- Ointment made according to the recipe of Valentina Seimova. Apply a thin layer of ointment to the injured surface overnight. Do not apply a bandage.
- St. John's wort. Fill a dark glass container ¾ full with dry or fresh flowering herb St. John's wort. Fill to the brim with refined sunflower oil and leave in a warm and dark place for three weeks. Apply the resulting mixture to the wound 3-4 times a day until healing.
- White wormwood, coltsfoot, plantain, calendula. Make lotions on the wound surface using infusion of water.
- Plantain leaves. Apply to the wound with the smooth side, securing with a gauze bandage.
The patient chooses how to treat an open wound on the leg, but it is advisable to consult a doctor before so as not to harm your health. During treatment, it is advisable to provide the diet with vitamins to speed up the healing process. It is recommended to take additional multivitamins.
A laceration is characterized by an irregular shape and uneven edges. Such wounds usually occur after a bite from a dog or wild animal, after deep scratches with various sharp objects. Although severe bleeding from such an injury is uncommon, severe injuries can lead to serious complications. Treatment of a laceration is aimed at stopping the bleeding and applying a bandage. However, the wound must be treated before applying a bandage. We’ll talk about how to properly treat a lacerated wound in this article.
If the wound site is not treated, the bleeding will intensify, blood loss will increase significantly, which may even threaten the life of the victim. In addition, various bacteria are just waiting for the opportunity to penetrate our body, and an open wound is an excellent opportunity for them to achieve their goal. When treating a wound, the likelihood of bacteria entering our body is greatly reduced.
So, the main goals when treating a laceration are:
- Stop bleeding to prevent large blood loss.
- Preventing the penetration of pathogenic bacteria.
- Reduced pain, swelling.
First aid for a laceration:
- First of all, it is necessary to stop the bleeding. To do this, press with slight force on the wound with your hand (do not forget to wash your hands thoroughly with soap before doing this). If the wound is deep, then it is unlikely that you will be able to stop the bleeding with your hands; you will need a tourniquet or any fabric that can be tied as a tourniquet. If the location of the injury is on the arm or leg, then tie a tourniquet above the wound - quite tightly.
- When bleeding has decreased or even stopped completely, the wound should be examined to assess tissue damage, the presence of foreign objects, clothing, etc. We carefully remove clothing, but you should not remove splinters, glass fragments and other sharp objects from the wound yourself, otherwise you may increase the bleeding, which will increase blood loss. A specialist must remove sharp objects from the wound, so it is better not to risk it and entrust this matter to a doctor.
- A very important stage is disinfection. It is necessary to treat the damaged area with an antiseptic to kill all germs. First of all, wash the wound and the areas around it with boiled warm water and soap - this will wash away the dirt and clean the skin around the wound. Then start washing with an antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin solution or a weak solution of manganese. We wash the wound from the top to the bottom. Movements should be careful, without putting too much pressure on the wound site.
- In case of severe pain, we give the victim a painkiller - regular analgin will do.
- Apply ointment. An antibiotic ointment such as bacitracin is best. If you don’t have such a remedy at hand, then you need to lubricate the edges of the wound with iodine or brilliant green, or at least vodka or alcohol (I think there is no need to remind you that we treat the edges of the wound with these products and do not pour them into the wound itself, otherwise the pain will be incredible ). Treatment should be done in the direction away from the wound so that the product does not get inside.
- Apply a gauze bandage. We don’t use cotton wool, because its fibers will stick, and then peeling them off will be very painful. There is no need to apply the bandage too tightly. If blood still oozes through the bandage, then simply wrap additional layers of gauze or bandage.
- Don't forget to take the victim's temperature. If the temperature nevertheless rises, then, obviously, an infection has been introduced. This can be fraught with serious complications. You definitely need to go to the hospital.
- At the emergency room, a specialist will examine the injured area, ask about the circumstances of the injury and the first aid measures provided. If the wound is deep, you will have to apply stitches. Severe cases usually require surgery. At high temperatures, antibiotics are prescribed to fight the infection.
In the absence of complications, treatment of a laceration lasts no more than 8-10 days. This includes a course of medications, dressings, and daily treatment. If complications do arise, then the recovery time is quite difficult to predict - it depends on the patient’s condition and the consequences themselves.
In any case, when you receive a laceration, you shouldn’t leave everything to chance. The victim needs first aid, which consists of stopping the bleeding, treating the wound, and transporting to the emergency room. Now you know how to treat such a wound and can provide first aid to yourself and your loved ones.
Lacerations are formed under the influence of hard, blunt objects acting at an acute angle to the surface of the body. A feature of a laceration is significant detachment, as well as scalping of the skin over a very large area. Moreover, the exfoliated area of skin may lose nutrition and become necrotic. In addition, uneven edges of lacerations slow down the healing process.
A laceration on the leg is quite common. Gardeners and summer residents are most susceptible to the formation of such wounds if they handle gardening tools carelessly, as well as children, fishing enthusiasts, hunters and many others. No one is immune from this trouble.
What to do if a laceration occurs? It should be remembered that all wounds that accidentally form are contaminated bacterially, therefore, in order to prevent additional penetration of bacteria into the wound, when providing first aid, with a cotton swab moistened with an antiseptic solution (alcohol, iodine), remove contamination from the skin surrounding the wound covers. Then the edges of the wound are lubricated with 5% alcohol tincture of iodine, alcohol or a solution of brilliant green and an aseptic bandage is applied. At the same time, you should not remove foreign bodies from the wound and wash it when providing first aid. In addition, in case of extensive injuries to the soft tissues of the lower extremities, as well as in fractures, immobilization is used to prevent even greater damage. In the future, you should go to the hospital to see a surgeon, who will determine further tactics for treating the laceration.
If the laceration is small in size, then it can heal on its own, without the help of a specialist. But if after a few days there is swelling, redness, or increased body temperature around the wound, you should consult a doctor immediately. Features of lacerations, in the form of uneven edges and significant detachment (scalping) of the skin, require careful treatment by a specialist. Deep wounds need to be operated on. They are sutured to speed up healing and prevent the formation of rough scars. This must be done on time to avoid complications. The surgeon dissects the wound and inspects the wound canal, then excises the edges, walls and bottom of the wound, stops the bleeding and sutures the wound. As a result, the wound turns from lacerated and infected into cut and aseptic, which contributes to its rapid healing by primary intention.
Healing of lacerations usually occurs within two weeks. This process depends on many factors. Among them are:
Age of the patient: wounds heal most quickly in children.
Body weight: Cachexia and obesity slow down the healing process.
The presence of secondary infection of the wound, which significantly prolongs and worsens the healing result.
Chronic concomitant diseases (tumors, cardiovascular failure, diabetes mellitus) that slow down the repair process.
Radiation therapy and taking anti-inflammatory drugs in the early stages can slow down the healing process.
It should be remembered that a wound, even the most minor, can lead to the development of sepsis (blood poisoning) and subsequently death. Also, with improper treatment, it is possible to develop a nonspecific purulent infection, as well as anaerobic infection, tetanus, and rabies. Therefore, you should not be surprised why wounds heal poorly. Ultimately, the patient may even lose his leg. Therefore, it would be better to consult a specialist immediately after receiving this injury and not self-medicate.
With an open wound, treatment and the use of antibacterial drugs are required, because if an infection occurs, it can begin to rot. First of all, you need to disinfect the wound and seek help from a medical facility.
Wound healing products
The fastest healing of a wound is possible only if actions are systematically carried out to disinfect the area around it, drying bandages are changed daily, and the damaged area itself is treated with correctly selected preparations. The wound healing agent and its release form should be selected taking into account the stage of healing, as well as the type of wound.
Local preparations for wound healing can come in the form of ointment, gel (jelly) and cream.
- Products containing deproteinized hemoderivat for dairy calves. Such drugs are widely used in Russia and the CIS countries; they are prohibited in the USA, Canada and European countries. They contain components of cell mass and blood serum of dairy calves. These products stimulate the formation of collagen fibers and improve cell nutrition.
- Ointments based on polyethylene oxide. Polyethylene oxide is ethylene oxide with low toxicity. Its action is reduced to removing wound exudate, as well as penetrating deep into the wound and affecting the microorganisms present there. It is reasonable to use polyethylene oxide-based products during the period of removal of wound fluid.
- Ointments and creams based on methyluracil. The most famous drug for wound healing, which contains methyluracil, is Vishnevsky ointment. Typically, such agents are used at the stage of wound regeneration.
- Ointments based on ichthyol. They belong to the group of antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and disinfectants. The effect of these drugs is to draw pus from the wound, which leads to faster healing.
- Antibiotic-based ointments. Antibiotic drugs aimed at combating pathogenic microorganisms, as well as drying the wound.
- Products based on propolis. Propolis has a pronounced antiseptic and analgesic effect. Most often, ointments with it are made on a fat basis, so their use is justified at the granulation stage. In the first stage of healing, it is possible to use an alcohol extract of propolis.
- Ointments based on herbal ingredients. Herbal medicines are widely used for the speedy healing of skin wounds. All herbal products can be divided into several groups according to the nature of the main active ingredient. Thus, there are herbal sorbents (based on polyphenap and aloe), anti-inflammatory (with tea tree essential oil, licorice extract), antibacterial (with chlorophyllipt and essential oils), promoting rapid skin regeneration (with sea buckthorn oil).
- Preparations based on vitamins. The vast majority of vitamin-containing ointments contain vitamins A, C and B5. Retinol acetate (vitamin A) is mainly used for fat-based ointments, so it cannot be used in the first stage of healing, when a crust forms on the wound. Vitamin C is necessary for the formation of collagen, so preparations based on it can be useful for the regeneration and healing of skin wounds. This vitamin is included in many creams and gels for skin regeneration. Dexpanthenol (aka vitamin B5) takes part in the formation of epithelial cells, collagen and elastic fibers. Dexpanthenol also resolves inflammatory foci and improves local blood supply. Available in the form of ointments and creams.
Secondary healing
It can be observed when one of the conditions for the primary one is missing. For example, if the edges of the fabric are not viable. Or they don’t fit closely together. Cachexia (depletion of the body) and a lack of necessary substances in the body can contribute to secondary healing. And this type of tissue restoration is accompanied by suppuration and the appearance of granulations. What it is? Such newly formed glomeruli of blood vessels are called granulation. In fact, this is familiar to every person since childhood, because each of us fell and tore our knees. Everyone remembers that the wounds were then covered with a crust. This is granulation tissue.
In general, types of wound healing and their characteristics are a very interesting topic. Not everyone knows that the tissue repair process occurs in three stages. First, the inflammatory phase of healing takes place (about 7 days), then the granulation phase (7-28 days). The last stage is epithelization. That is, the wound is covered with new, living skin.
Healing wounds from burns
Many people mistakenly believe that burns can be smeared with fatty ointments, sea buckthorn and other oils. Due to the fact that they form a thin film on the surface of the skin, normal heat exchange is disrupted. For better healing of wounds caused by thermal or chemical means, the use of fatty products is allowed only when the wound begins to granulate. At the stage of inflammation and scarring, you need to use creams, sprays and gels on a hydrophilic basis. If suppuration has joined the wound after a burn, the doctor may prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotic and antimicrobial drugs.
Scars
The medical classification knows more than one type of scar. When a wound heals by primary intention, any scar can actually form. It doesn't all depend on how the fabrics are tightened. The type of scar is determined by the prerequisites for the appearance of the wound itself. Let's say a surgical operation. The man transferred it, and the cut made with a scalpel was stitched up. This is primary healing, since the tissues are in close contact and there are no infections. But it will still be called a surgical scar.
Another situation. A man was cutting tomatoes with a sharp knife and accidentally hit his finger with the blade. A domestic accident, one might say. But the type of healing is still the same, primary. However, it will be called an accident scar.
There are also keloid, normotrophic, atrophic and hypertrophic scars. However, they are not relevant to the topic. It is enough just to know about these types of scars.
How to speed up wound healing: folk methods
Traditional medicine can be quite effective, but you should not rely on them entirely. Most often, many of them turn out to be unrecognized by traditional medicine, so before choosing one or another remedy, you should consult a doctor.
- Lilac juice can be used to treat wounds. The leaves are collected, washed and crushed in a blender/meat grinder, after which the juice is squeezed out through cheesecloth. A bandage is soaked in the juice and applied to the wound.
- You can also chop onions to a paste, wrap it in a bandage and apply it to the wound.
- Aloe is an effective remedy for wounds. You need to cut the leaf, wash it and cut it lengthwise. Apply the cut site to the wound and secure with a bandage.
- You can make a remedy from dandelion. You will need to pick the flowers, wash them, place them loosely in a container, pour in sunflower oil and leave for a day. Then keep the container with oil and dandelions in a water bath for 40 minutes and let it sit for another day. After this, strain through cheesecloth and squeeze. The resulting oil ointment is good for wounds.
Treatment
For a shallow cut wound, if the tendon or muscle is slightly damaged, it must be treated with antimicrobial agents and covered with sterile gauze. If the cut is small, you can cover it with a band-aid.
A puncture wound needs to be examined and treated by a physician, as surgery is required in most cases. The treatment required here is as follows: stop the bleeding and treat with antiseptics. If the bleeding does not stop, apply a sterile bandage until the bleeding stops. The patient is given an injection of tetanus serum. In severe cases, oxygen is given to breathe, and if it is necessary to revive the patient, ammonia is given.
For a lacerated wound, you need to treat it with hydrogen peroxide and apply a sterile bandage. To collect damaged skin, you can consult a doctor so that he can do it correctly and provide timely treatment. Before starting treatment of an open wound, it is necessary to find out the reasons for its occurrence, the severity of the damage and the presence of infection.
Only surgeons know how to properly treat an open leg wound. Before you begin treating an open wound on the leg that was caused by a sharp object, you need to correctly determine the cause of the damage and the severity of the cut.
Treatment will be effective if a number of measures are taken:
- Provide first aid
- Treat damage correctly
- Take timely treatment and care.
Proper first aid
First you need to stop the bleeding, so a tourniquet is applied. The edges of the wound should be treated with antiseptics and a sterile bandage applied. Foreign bodies must be removed using tweezers; the edges can be pre-treated with alcohol. If there is a wound and there is deep damage, you should not remove the object yourself; it is better if a doctor provides help and prescribes the correct treatment. To prevent infection of the damage, it is necessary to treat it with antibacterial agents. After completing all the required procedures, apply a sterile bandage.
What antiseptics are used to treat open wounds: furatsilin or chlorhexidine solution. Streptocide powder also has disinfecting properties. A 3% solution of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide and a 2% solution of chloramine are also used. Iodine is not recommended for use; it can cause skin burns. You can use brilliant green as an antiseptic.
Healing ointments can also be used to treat open wounds. Even a small wound, in the presence of infection, can provoke the risk of disease. After proper treatment of the open wound, it is left alone for two days, then healing ointments can be used. The ointment quickly restores damaged tissue and has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Doctors advise treating wounds with ointment after providing primary care. With timely use of the ointment, not only will the wound heal quickly, but scars will disappear.
List of healing ointments:
- Baneocin, recommended for burns and deep wounds.
- Levomekol, a very effective ointment, has an antibacterial effect.
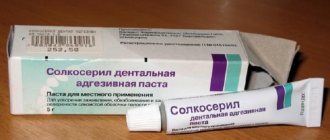
- Solcoseryl not only has a healing effect, but also reduces pain.
- Eplan is an effective remedy for all types of wounds.
To apply healing ointment to an open wound correctly, it is best to apply a thin layer, this is done so that oxygen penetrates. Then the healing of the wound will be accelerated, otherwise, with a thick layer of ointment, rotting may begin.
Subsequently, you can treat the wound with folk remedies, but you must first consult with your doctor so as not to cause the opposite effect. The following herbs and components have healing properties:
- propolis,
- willow bark,
- St. John's wort and plantain leaves.
If the wound is festering, you can use the traditional method: apply a freshly cut aloe leaf, it draws out the pus from the wound. Once the pus disappears, the wound can be lubricated with sea buckthorn oil. Be sure to show the purulent wound to a doctor and consult with your doctor about the use of these remedies. In some cases, only drug treatment will be required. In case of complications, only a doctor can help.
The key to rapid healing of an open wound is timely disinfection of the cut with antiseptics and restoration of muscle tissue. It is better not to self-medicate, but to treat a small open wound and seek help from a doctor. In case of a severe wound, it is necessary to call an ambulance or go to a medical facility, where they will provide effective treatment from the first days.
Probably every person knows what a wound is: everyone has received it at least once in their life. Fortunately, in most cases the matter is limited to minor damage, which, nevertheless, gives a completely clear idea of the subject of our article. Even a person whose occupation is not a surgeon or even a physician must have not only theoretical knowledge of what a wound is, but also practical skills in the initial actions when receiving one. In serious situations, before qualified paramedics arrive, they can save a life - not for you, but for someone who, thanks to competent measures, will survive until the ambulance arrives.
Consumer Reviews
Dasha0708 (spasibovsem.ru)
“I want to share my impressions about La-Cri cream. A couple of days ago I decided to inspect the balcony. I have a terrible allergy to dust, well, naturally, after 5 minutes of being in a huge amount of old trash, I began to itch and sneeze terribly. Usually in these cases, fenkarol and suprastin help me, but I didn’t have it at home. Luckily, my sister came to see me with a small child and left me La-Cri Cream.”
Her baby had rashes and she applied this same cream to them) I immediately began to read the instructions and scope of application. I was very pleased with what I read there) The composition of the cream is almost entirely from natural products. In general, I smeared all my “itches”, red spots and just places where I wanted to scratch. After just a minute of application, the itching began to subside, and after a couple of minutes all the red spots disappeared. I am very pleased with such a quick effect. Now this cream is my first assistant!! I recommend!!!"
Natasha (sponzhik.ru)
“...La-Cri cream for sensitive skin alleviates the symptoms of hypersensitivity and skin inflammation (redness, irritation, itching, rashes and peeling), relieves itching after insect bites and plant burns, effectively nourishes, moisturizes and protects dry and very dry sensitive skin of adults and children from the neonatal period.
FROM MYSELF: The cream is thick and very delicate, beige in color. The smell is sharp, medicinal, and you can smell licorice. I don't find it unpleasant. In terms of action, as I already said, it is very effective and at the same time comfortable. I liked it better than Bepanten, which is too fatty.
I recommend. As far as I understand, it is also suitable for adults. The light texture allows it to be applied to the face, provided, of course, that the smell is not too irritating.”
Sources:
- Molochkova Yulia Vladimirovna, Dermatology. Brief reference book, GEOTAR-Media, 2020.
- Baumann Leslie, Cosmetic Dermatology. Principles and practice, MEDpress-inform, 2020.
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, GEOTAR-Media, 2020.
What is a wound from a medical point of view?
Despite everyone's awareness, let's give these somewhat vague ideas a clearer outline. If we give a more or less scientific definition of what a wound is, then we can say that it is a gaping, visible damage to the skin (often to the deeper tissues of the human body). It is accompanied by a number of symptoms. Common ones include:
- Bleeding of varying severity.
- Obligatory pain sensations.
- Visual observation of the source of blood flow.
Local or private are considered:
- Acute anemia, that is, severe blood loss. It cannot be called a general symptom, since it does not occur with minor damage or quickly taken measures.
- Shock. It also does not accompany all wounds. Accompanies mainly deep and/or extensive damage.
- Infection is typical for individual or improperly treated injuries.
Other, more rare, symptoms may also occur. Any open wound (except perhaps the most minor ones) can lead to extremely unpleasant consequences. Therefore, such injuries require increased attention and constant medical supervision.
Types of injuries by origin
The most extensive classification concerns the mechanism of the wound and the type of object that caused its occurrence.
- Puncture wound. Its entrance hole is small in diameter, but the wound channel is long, although narrow. Typically applied with a sharpener, nail or awl. It is considered the most dangerous due to the high probability of internal damage and the development of infections due to poor oxygen access.
- The cut one, on the contrary, is shallow, with a rather large entrance. Application tool: knife or razor. If large vessels and viscera are not affected, such wounds heal faster than others.
- Chopped is applied with a sharp and heavy object like an ax. The damage is extensive, severe, and often accompanied by bone fractures and fragmentation.
- A laceration caused by an uneven blade sliding across the body with simultaneous pressure is very difficult to treat. May be accompanied by partial loss of cover and underlying tissues.
- have a number of features caused by the type of weapon (shot, bullet, fragment) and the degree of damage. The easiest ones include tangents, in which the bullet does not penetrate inside, but only rips off the surface tissue layer. The most severe are blind, in which the bullet remains inside the body.
Types of wounds based on tissue damage
The upcoming treatment of a wound is fully determined by a number of its characteristics. The first of these is the extent to which the damage has affected the internal membranes lining the peritoneum, the membranes of the brain, any joint or pleura. Here they highlight:
- Penetrating wounds in which the integrity of one of the mentioned membranes is broken.
- Non-penetrating, affecting only the skin and upper muscle layer.
The first type is more dangerous: an open wound of this type takes longer to heal and requires an integrated approach to treatment. The most severe are considered to be penetrating wounds with damage to internal organs - one or more.