November 25, 2019
Not everyone knows what a tooth abscess is. Almost anyone can be susceptible to this dangerous and unpleasant disease. But you need to be able to distinguish it from others in order to consult a doctor in time and carry out treatment. It is even better to know what risk factors lead to the development of pathology and what absolutely cannot be done so as not to complicate its course. The editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal will tell you how to cure a tooth abscess and then avoid serious health consequences.
What is a tooth abscess
What is a tooth abscess? This is an acute inflammation characterized by the accumulation of pus in a limited area of the alveolar process of the jaw. The development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by pathogenic microorganisms: under their influence, within a short time after the onset of the disease, a painful compaction appears on the oral mucosa (most often on the gum, next to the diseased tooth), inside which there is pus. And such a seal or lump cannot be opened or squeezed out on your own, because... this can lead to the penetration of pus into the deeper layers of tissue and its spread with blood and lymph to neighboring organs.
Causes
The main cause of an abscess is the entry of bacteria into the pulp, which further provokes a pathological process. This can happen after tooth extraction, but also under the influence of a number of factors:
- Infections, acute respiratory viral infections or tonsillitis, especially if the diseases have severely weakened the immune system.
- Neglected condition of the oral cavity, the presence of diseases (periodontitis, cysts, caries).
- Dislocation, fracture or blow to the jaw.
- Dentin chip or enamel injury.
- Boils on the face or mucous membrane.
- Infection following an injection during a dental procedure.
The development of a purulent complication is often preceded by a violation of the integrity of the natural protection of the tooth. An abscess and its symptoms appear after inflammation. The longer the process takes place, the brighter the intoxication of the body becomes.
Types of pathology
Doctors distinguish several types of pathology - periapical, gingival and periodontal abscess.
The first type - periapical - affects the tooth pulp, and if it is not cured in time, the tooth will have to be depulped or completely removed. This form of pathology often occurs on primary molars and becomes one of the most common causes of their premature removal1 (along with apical periodontitis).
The second type - gingival - affects the soft tissues of the oral cavity, but if it is advanced, it can also affect the periodontal ligaments, as well as penetrate the periosteum and cause gumboil. The third type predominantly affects the root, which leads to loosening and pathological mobility of the tooth.
Gingival appearance affects soft tissue
A purulent abscess is dangerous because if it is not treated, the contents of the neoplasm can spread throughout the body, causing general intoxication, damage to the jaw bone, liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, hearing and respiratory organs, and even the brain. A patient who does not seek help in a timely manner risks losing teeth and developing meningitis, but the most dangerous situation is the development of sepsis and death.
Other forms and stages
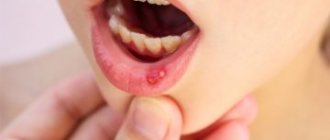
Accumulation of pus
An abscess can occur in two stages - chronic and acute. In rare cases, the disease may disappear without the intervention of specialists, in other words, the abscess is opened and pus is released into the oral cavity. However, the disease can also become chronic with all the ensuing consequences.
Purulent tooth abscess
Purulent is an acute stage. It may be asymptomatic, but swelling near the problematic tooth will appear in any case. Headaches and enlarged lymph nodes are possible. Over time, the pain will become throbbing, and the swelling on the gum will become the size of a walnut.
Chronic abscess
On palpation, moderate pain occurs, the general condition of the body does not change. Despite the fact that the abscess can open on its own, the infection will not go away, but will only become chronic. Eventually you will have to face complications.
Gums become swollen
Abscess after tooth extraction
Situations often occur when diseased teeth have to be removed. At the time of manipulation, anesthesia relieves pain, but there will be a hole that bleeds and brings discomfort.
In order for it to last fully, a person must follow simple rules. If the wound does not heal for a long time, bleeds, purulent plaque and bad breath appear, you should seek help from the hospital as soon as possible.
An abscess occurs because an infection enters an open wound. Another reason for this condition is the unsterile instruments used by the dental surgeon.
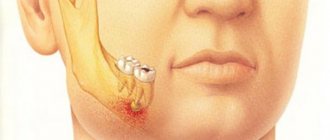
Root abscess
In medicine, a tooth root abscess is called periapical. The main and most common cause of its occurrence is deep caries due to non-compliance with the rules of personal oral hygiene.
The inflammatory process is caused by microbes that enter the bloodstream. The danger lies in the fact that the infection can quickly spread along with the bloodstream throughout the body.
Disease at the very root
You don’t have to wait long for symptoms - the body temperature rises, the condition becomes weakened, the gum tissue swells, and severe pain bothers you.
Wisdom tooth abscess
Such a tooth grows into soft tissues that are constantly supplied with blood. Sometimes, to remove it, it is necessary to split the tooth into multiple fragments, as a result of which the injured area increases.
After tooth extraction, the body temperature may rise, and the tissue around the hole begins to redden and swell. Compared to other holes, this one takes a long time to heal. If relief does not occur after a few days, and the swelling continues to increase, it means that an infection has occurred. In this case, you should consult a doctor.
Baby tooth abscess
The disease can affect not only adults, but also children
The condition is dangerous because under the baby tooth there are the beginnings of a permanent one. From the roots of a baby tooth, an infection can reach them, causing them to die.
Unlike adults, the infection will move deep into the skull quickly. From the source of inflammation, toxins can penetrate into the blood, and allergies or asthma will begin to develop.
Interesting! The dentist decides what to do, treat or remove a baby tooth.
Frequent abscesses indicate that the infection was not fully treated and it became chronic. The problem can spread deep into the jaw bone and further to neighboring teeth, thus, more and more new foci of suppuration will be disturbed.
Prerequisites for the development of the disease
The most common reason leading to the disease is the presence of dental problems and oral infections in the patient: caries, pulpitis, gingivitis, cysts and granulomas, herpes and stomatitis. The development of pathology is often provoked by weak immunity, previous influenza, tonsillitis, and pyoderma. The presence of other diseases in a person - HIV, AIDS, oncology, diabetes, hypothyroidism, obesity.
Pathology often occurs against the background of untreated caries
A purulent formation can develop against the background of injuries to the maxillofacial apparatus or due to mistakes made by the dentist at one of the stages of treatment of caries or pulpitis (for example, due to leaky filling of root canals, poor asepsis).
The gingival form of pathology most often occurs against the background of mucosal injuries. It also happens that a person simply scratched his gum with a fish bone or injured it while brushing his teeth, and bacteria entered the wound, which led to a serious inflammatory process.
You will be interested to know that there is not only a tooth abscess. In clinical practice, cases of abscesses occurring in the soft tissues of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles and internal organs are known. There is also a throat abscess. Read about this disease in a separate article on the website.
Mechanism of development of the disorder
A tooth abscess develops as a result of an infection in the body.
It can occur due to improper treatment of diseases of the teeth, gums or oral cavity, as well as due to weak immunity. Conductors of infection into the body are lymphatic and venous vessels, as well as intermuscular and interfascial tissue. Inflammation spreads along them by breaking through and melting surrounding tissues.
The development of a dental abscess depends on the level of pathogenicity of the microflora and the immunobiological characteristics of the body.
Depending on these signs, the disease can progress in different ways:
- very active, with dangerous violations of a general and local nature;
- with moderate activity or lethargy;
- developing slowly and lasting for quite a long time, without having significant clinical manifestations, in this case the abscess takes on a chronic form.
What are the symptoms of a tooth abscess?
The symptoms of the disease are quite clear. It is easy for any person, even without being very attentive, to understand that something is wrong with him, especially when the pathology has just begun to develop and is in an acute stage.
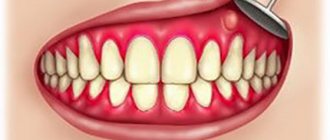
First of all, there is an acute pain in the tooth, which intensifies from pressing, biting, and chewing food. Pain also occurs as a response to eating cold or hot food. The pathology is always accompanied by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, swelling of the face. At a later stage of the disease, pus may be released from the gums. This is accompanied by the appearance of a putrid odor when breathing, a taste of iron or bitterness in the mouth, loss of appetite, increased body temperature, general weakness and enlarged lymph nodes.
Acute pain in a tooth can be a symptom of pathology
“Once in my life I encountered such a phenomenon as a tooth abscess. I didn’t know what it was. The fact is that at first there was severe pain, but because... I took good pills and it went away easily. After about a week, she practically went away altogether, and nothing bothered her. And one fine day, by the way, this happened only three months after that situation, I began to have terrible pain, but only in the face area, I could not understand where exactly it hurt. There was a chill. My husband called an ambulance and they took me to surgery. It turned out that it was an abscess, and when the first signs of pain subsided, I thought that there was nothing wrong, but in fact, as the doctors said, the disease had become chronic, the destruction of the root and nerve of the tooth began, and then inflammation of the bone tissue. It’s good that all the medical services reacted with lightning speed in my case, otherwise I don’t know how it would have ended. Naturally, the tooth had to be removed.”
When the disease is advanced, a breakthrough of purulent contents from the resulting cavity may occur, which can blur the clinical picture, because the patient feels relief, the pain goes away, the swelling subsides. However, you shouldn’t relax, because... the disease can lead to the formation of fistulas and damage to all surrounding tissues by purulent exudate, as well as recur.
There is no point in delaying treatment, but many patients are concerned about what measures will have to be taken to get rid of the problem. Read on and find out what stages the treatment process will consist of.
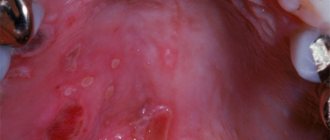
Oral abscess
Oral abscess
is an acute inflammatory disease of the oral cavity, which is characterized by focal accumulation of pus in the tissues.
With an abscess of the oral cavity, limited compaction and swelling of the mucous membrane is observed, painful to the touch, which is accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being and an increase in body temperature.
An oral abscess is diagnosed by a dentist during an examination based on an assessment of the condition of the tissues. Treatment of an oral abscess includes surgery - opening the abscess, as well as anti-inflammatory drug therapy.
K12.2
Cellulitis and abscess of the mouth area
An oral abscess is a local purulent inflammation of the tissues of the gums, tongue, palate or cheek.
This disease is one of the most common problems in surgical dentistry and manifests itself regardless of the age and gender of the patient.
Most often, an oral abscess occurs as a result of complicated dental pathology, but its development is also possible due to a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane or in general infectious diseases.
In the absence of timely and correct treatment, an oral abscess can develop into a chronic form and also cause severe complications such as phlegmon and sepsis. Therefore, self-medication for oral abscess is strictly prohibited. To prevent consequences, it is necessary to immediately consult a specialist at the first symptoms of the disease.
Oral abscess
Most often, an oral abscess occurs as a complication of dental pathologies, for example, periodontitis or advanced periodontal disease. These diseases are characterized by the destruction of periodontal joints and the formation of so-called periodontal pockets, in which intensive proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms occurs, causing an inflammatory process.
An oral abscess can form as a result of infection in the wound when the integrity of the mucous membrane is violated, for example, with a syringe needle during anesthesia or in case of mechanical trauma.
The cause that provokes the development of pathology can be boils in the facial area, streptococcal and staphylococcal sore throats.
It has been noticed that oral abscesses often occur against the background of influenza or other common infectious diseases that weaken the immune system.
In most cases, an oral abscess is caused by an infection involving more than 3-5 microorganisms. The most common etiological agents are staphylococci, streptococci and gram-negative anaerobic flora (Eikenella corrodens, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Enterobacteriaceae spp., etc.).
Depending on the location, there are several types of oral abscesses:
- A gum abscess
appears near a specific tooth. This is the most common type of abscess. In the absence of proper treatment, it can develop into diffuse inflammation or into a chronic form, which is characterized by periodic exacerbations, leakage of pus from the formed fistula, foul odor from the mouth and intoxication of the body. - An abscess in the floor of the mouth
is located under the tongue and causes severe pain during talking and eating. If spontaneous opening occurs, the leakage of pus can cause secondary foci of inflammation in the pharynx and neck. - Palate abscess
most often occurs due to periodontitis of the teeth of the upper jaw. It threatens the spread of infection to adjacent tissues of the palate and peritonsillar region, as well as the development of osteomyelitis of the palatine plate. - An abscess of the cheek,
depending on the depth of the lesion, can be localized both internally, on the side of the mucous membrane, and on the outer surface of the cheek. An abscess in this location is extremely dangerous due to possible spread to nearby facial tissues. - A tongue abscess
is characterized by swelling of the tongue, difficulty eating, speaking, and even breathing. This type of abscess is the most dangerous; when the first symptoms develop, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
The formation of an oral abscess usually occurs quite quickly. At first, pain may appear that resembles the symptoms of periodontitis - the pain is localized in the area of a specific tooth and intensifies when biting.
Soon after this, a painful and dense swelling appears at the site of development of the pathological process.
Externally, it is a rounded formation on the gum, which in some cases can reach the size of a walnut.
An abscess of the tongue develops rapidly - rapidly increasing pain appears in the thickness of the organ, it quickly increases in volume; the patient experiences difficulty chewing and swallowing, and in severe cases, suffocation occurs. When inflammation is localized under the mucous membrane of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, as well as closer to the surface of the skin (face or submandibular region), upon examination, redness and swelling can be observed at the site of the infection.
Any abscess of the oral cavity, as a rule, occurs against the background of deterioration in general health, increased body temperature, sleep disturbances and appetite. The progression of the pathology can lead to a breakthrough of the abscess.
The release of pus brings significant relief to the patient: pain decreases, swelling subsides, temperature decreases, and overall well-being improves, but this should not be a reason for reassurance due to the possible development of complications.
The inflammatory process can continue, become chronic and spread to nearby tissues. An oral abscess can lead to many serious consequences, such as the loss of one or more teeth, the development of phlegmon and sepsis. In order to avoid complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, who will prescribe the correct treatment.
An oral abscess is diagnosed by a specialist based on a visual assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane during a dental examination.
It is completely unacceptable to wait for the spontaneous opening of an oral abscess or to independently use antibacterial agents.
To relieve symptoms before contacting a doctor, you can use painkillers and rinse your mouth with warm antiseptic solutions.
Oral abscess is treated exclusively through surgery. In order to eliminate the source of infection and prevent the spread of the inflammatory process, the dental surgeon performs an opening of the abscess, drainage and antiseptic treatment of the cavity. Sutures are usually not required after this operation, since the size of the incision is small.
After removal of the pus, as a rule, the patient feels better, the pain subsides, the swelling subsides, and the normal contours of the face are restored, but if the oral abscess has developed significantly, the final recovery may be somewhat delayed.
In the postoperative period, antibiotics, antihistamines, immunostimulants and vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed. In some cases, physiotherapeutic procedures, such as fluctuarization or UHF therapy, are used for a speedy cure. It is also recommended to avoid solid foods and eat a nutritious diet after surgery.
In general, the success of treatment of oral abscesses depends on the timeliness of contacting a doctor and the general condition of the patient’s body. It is very important to start treatment as early as possible - in this case the prognosis is usually favorable. If surgery is performed on time and there are no complications, the oral abscess will completely heal within 1–2 weeks.
To prevent oral abscess, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene, avoid injuries to the mucous membrane, and, in the presence of periodontal diseases, promptly treat them.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology/oral-abscess
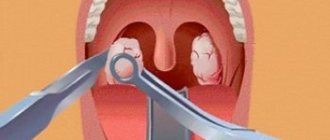
Stage No. 1: surgical opening of the abscess
Do not try to treat an abscess at home. This should only be done by a professional - a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon. To begin with, the specialist will open the abscess using a scalpel or laser equipment - the procedure will be carried out under anesthesia, so you will not feel pain. Next, the doctor will treat and aseptically treat the affected tissues with saline solution, medications and ointments. If necessary, drainage or tamponing may be installed to evacuate pus for several days.
The photo shows an operation to remove pus
You need to know that the acute form of the pathology is often accompanied, like gumboil, by severe swelling of the face and soft tissues of the oral cavity. And here it is impossible to do without emergency help from a surgeon, because a formation with purulent contents can burst at any moment. At the same time, it is quite difficult to predict in which direction this will happen: a breakthrough is possible both in the oral cavity and in the direction of vital organs - the sinuses, ears, and others.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing the disease will not be difficult, since its manifestations are clearly visible externally.
By external signs you can determine the stage of development of the infection:
- Formation (initial stage). The skin swells, turns red, and hurts when touched.
- Second stage. The formation begins to turn yellow and becomes soft to the touch. Pain appears and body temperature rises.
As a rule, with an abscess, the patient's lymph nodes become enlarged, but they are painless when touched.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following tests are recommended:
- General blood test - with an abscess shows nonspecific signs of inflammation (staphylococci and streptococci in large quantities).
- Bacterial culture - pus is taken for analysis.
Important! At the first signs of an abscess (redness, pain, fever), do not self-medicate. It is prohibited to open the inflamed area yourself. This is fraught with unforeseen consequences (blood poisoning, purulent melting of the walls of a blood vessel), even death.
Stage No. 3: elimination of painful sensations
Remember that painkillers (without the remaining stages of treatment) will not help cure an abscess, and relief from taking these medications should not be a reason to postpone a visit to the dentist.
Doctors prescribe tablets and syrups after removing the abscess, i.e. during the rehabilitation period after surgery. They should be taken as needed. Nurofen, Ibuprofen, and Ketanov do the best job.
After surgical treatment, specialists prescribe medications
Stage No. 4: taking antibiotics
In the presence of a purulent abscess, antibiotic therapy cannot be avoided. After surgery, your doctor will prescribe medication to help stop the infection from spreading. As a rule, the course of taking antibiotics is designed for 7-10 days, and it cannot be interrupted even if you feel better (if the procedure went without complications, the patient usually feels significant relief on day 4-5). On average, the full rehabilitation period after surgery is 10 days.
Do you suspect that you have a tooth abscess or any other purulent inflammation (cyst, fistula, osteomyelitis, gumboil)? Do not warm up the painful area under any circumstances, because this will further spread the infection.
Treatment methods
Currently, two main methods of treating abscesses are used: the use of potent medications and surgery. Often these methods are used together. In the early stages of the development of pathology, taking medications is enough to eliminate it, but in most situations more drastic measures are necessary.
Opening the capsule containing purulent masses localized in the soft tissue area is carried out using local anesthesia. After the intended incision site is numbed, the tissue is cut, purulent masses and dead skin are removed. After this, antiseptic treatment is performed and drainage is installed. If the pathology in question is present in the area of internal organs, a more serious operation is required, which is performed under general anesthesia.
How to treat an abscess at an early stage of development? In this case, the patient must undergo a course of antibacterial drugs. Before prescribing a course of treatment, the patient must undergo a full diagnostic examination, which will reveal the severity of the disease and the type of pathogen. If there is hypersensitivity to antibiotic medications from the penicillin group, chloramphenicol is prescribed. In addition, in certain situations, drugs from a number of macrolides can be used to achieve the desired result. This category of medicines includes Azithromycin, Clarithromycin and Erythromycin.
Antimicrobial drugs are often used during abscess treatment. Complex therapy includes medications that normalize vitamin balance, metabolism and the state of the immune system. It is on strengthening the protective functions of the body that the main emphasis of complex therapy is placed.
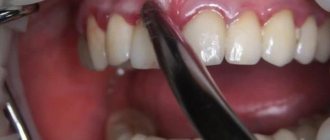
Stage No. 5: antibacterial wound treatment at home
Antiseptic rinses will help stop the inflammatory process, prevent the development of complications after surgery, and will also promote rapid regeneration of damaged tissues. Your doctor will tell you what means to rinse your mouth with. Among the recommended antiseptics are “Chlorhexidine” and “Miramistin”, soda-saline solution, decoctions of chamomile flowers or oak bark. It is important to use them not only during daily oral hygiene, but also after meals.
Rinsing with antiseptic drugs will help stop the inflammatory process
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
- Andreeva V.A., Bintsarovskaya G.V., Valeeva Z.R., Timchuk Ya.I. Analysis of the causes of premature removal of primary molars in children. Reports of the Belarusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics, 2020.
Expert “In order to never encounter this disease, it is necessary to undergo timely preventive examinations at the dentist and perform sanitation of the oral cavity, as well as maintain your immunity at a sufficiently high level.” Implant surgeon, ch.l.h. Vedeneeva Alla Sergeevna
Consulting specialist
Ozhegina Natalya Mikhailovna
Doctor rating: 9.3 out of 10 (4) Specialization: Dentist-therapist, hygienist Experience: 10 years
Comments
At a dental appointment, a doctor diagnosed my eldest son with a tooth abscess. He said that it couldn’t be saved and had to be removed. My question is, will it be possible to do implantation after this? He is still quite a young man, only 25 years old, so I wouldn’t want to wear a prosthesis.
Oleg Vyacheslavovich (11.29.2019 at 16:42) Reply to comment
- Dear Oleg Vyacheslavovich, it is not possible to install an implant immediately after removal, because removal of a tooth with an abscess falls under the definition of “complex removal,” and implantation requires careful preparation and the exclusion of even the slightest contraindications. However, 4-6 months after the socket of the extracted tooth has healed (all this time you can wear a removable immediate prosthesis “butterfly”), your son will be able to undergo a classic two-stage implantation. The main thing is not to delay this procedure and remember that already a year after extraction, the jaw bone tissue in this place can significantly atrophy, which will require preliminary surgery to build it up.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (08.12.2019 at 09:12) Reply to comment
If, as a result of improper treatment, an abscess of the lower large tooth begins, what is done in this case? Is there any other way to save this tooth or will it all have to be removed?
Elesey (12/10/2019 at 07:31 pm) Reply to comment
If you endure the pain and there is no abscess, then can the abscess go away on its own? Or do you just need to go to the dentist and carry out long-term treatment with antibiotics?
Anna (12/10/2019 at 08:49 pm) Reply to comment
Tell me, what should be the first action if a person begins to develop an abscess in one of his teeth? Also, a lot of pus had accumulated under the gum and the right side of the cheek was very swollen.
Dmitreva Daria (12/11/2019 at 00:16) Reply to comment
Please tell me, can a tooth abscess occur in a preschool child? How is such a tooth treated and can it be saved? Because the tooth itself is a molar.
Nella S (12/11/2019 at 01:15) Reply to comment
Or the abscess of the same tooth may recur if all treatment is completed. Did you open it up, clean it, install drainage? And what prevention exists for such cases?
Andrey (12/11/2019 at 12:04 pm) Reply to comment
Hello, I wanted to ask you why I got a tooth abscess? How can I cure it painlessly? I'll be looking forward to your response. Thank you very much in advance. With respect, Nicholai.
Nikolay (12/11/2019 at 01:17 pm) Reply to comment
Please tell me, how is an abscess different from a gumboil? I just had flux several times, or so I thought. The tooth was opened, as a rule, this did not give any results, after which the gums were cut and a drainage gum was placed for 3 days. Then they pulled it out, processed it and that’s it. Can a doctor confuse an abscess and a flux?
Olga (01/13/2020 at 12:42 pm) Reply to comment
Thank you for the detailed steps to treat an abscess! I recently visited a new dentist, he said some nonsense, prescribed some strange procedures, not at all related to yours.
Anatoly (02/06/2020 at 16:12) Reply to comment
Not long ago there was an abscess that was surgically opened. The healing is not going very well, it hurts to eat and even when water gets in there is a slight discomfort. Tell me, will I have to remove the tooth now?
Julia (02/08/2020 at 11:25) Reply to comment
Please tell me if I had dental work done because I had an abscess, but I was not prescribed an antibiotic. Rinse only. This is right? Or is it still better to ask for a course of antibiotics to be on the safe side?
Anna (03/16/2020 at 15:47) Reply to comment
Tell me, can gum abscess occur from smoking? If the gums were not targeted, i.e. no scratches, etc. I take care of my teeth, but when smoking, brushing alone is not enough to properly protect them.
Alina (03/16/2020 at 04:11 pm) Reply to comment
Good afternoon. Does the harmful habit of throwing nasvay affect the appearance of this kind of gum disease? And at what ages are people more susceptible to this disease? Also, does rinsing your mouth with salt water help prevent gum abscesses?
Mikhail (04/23/2020 at 08:23) Reply to comment
If a patient has already undergone treatment for a tooth abscess once in his life, how susceptible is his body to the occurrence of new cases? Is there some kind of predisposition or pattern? If so, what is the best oral prophylaxis?
Oleg (04/23/2020 at 08:30) Reply to comment
Hello, can you tell me whether surgery is performed under local or general anesthesia? And if local, what drugs are used, and how high is the chance of feeling the intervention directly?
Vasily (04/23/2020 at 08:59) Reply to comment
There was such a situation that this problem (abscess) appeared, the tooth was intact. One doctor even said to remove the tooth, another carefully examined what was wrong, cleaned the canals, did a lot of things, and in several stages. I took antibiotics. She didn’t say the exact reason, but she says there is a possibility that it is due to hypothermia and decreased immunity. Please tell me, can an abscess really appear from hypothermia?
Karina (04/23/2020 at 10:40 am) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Preventive measures to prevent the problem
Treatment of a tooth abscess is a complex and painful process. Therefore, the best way to avoid such unpleasant procedures is to prevent the disease. First of all, it consists of maintaining oral hygiene.
To do this you need:
- visit a dentist regularly, at least once every six months;
- timely sanitization of the oral cavity and treatment of any gum diseases;
- use toothpaste that contains fluoride to brush your teeth, it is better to do this every time you eat, if this is not possible, then at least twice a day, morning and evening;
- regularly use special dental floss, which removes food debris between the teeth; the procedure must be carried out every day;
- remove tartar from the surface of teeth;
- In cases of damage to tooth enamel, loose teeth or chips, you must contact your dentist to prevent infection.