Why perforation occurs and how to avoid it
Such consequences can be avoided by properly planning removal using a CT scanner and following gentle removal protocols.
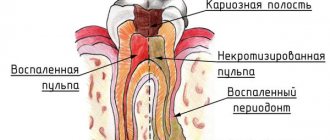
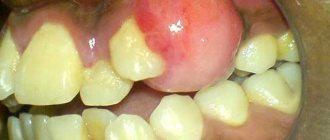
There is a group of patients with the anatomy of roots whose apices penetrate into the sinus, and if such patients are treated as a standard removal protocol, perforation and all associated complications will certainly occur. Only this is visible in the image created by a computer tomograph in a special ENT mode, and this is not possible in any clinic. In our Center this can be done with the latest SIRONA-SIEMENS equipment and the GALILEOS diagnostic software package.
Having studied the CT image, the surgeon must be prepared for an emergency situation. If perforation does occur, it is important to perform immediate microsurgical closure in a sterile operating room to avoid the development of an inflammatory process.
Even an experienced doctor without a good image on a modern expensive tomograph may not notice the details and skip the patient to a regular dental surgeon, not pay attention to the anatomical features and not carry out the necessary actions. The patient will find out about this later by the characteristic symptoms:
- passage of air, whistling and squelching in the socket of the extracted tooth;
- foamy, bloody or yellowish nasal discharge;
- strange, unreasonable organic odors in the nose and mouth,
- change in voice timbre (nasality).
If you do not carry out timely emergency closure of the anastomosis after tooth extraction, the hole itself may never heal. The gum tissues heal, epithelialize, and shrink, but the bones in the area of such a fistula between the nose and mouth never grow together due to the difference in the growth periods of the bone and gum, the gum will instantly take up all the free space, the slowly growing bone simply will not have time to fill the defect.
Within 2-3 weeks, a thin fistulous tract forms from the oral cavity to the sinus. In this case, the diameter of the hole is reduced naturally due to the formation of scar tissue; the symptoms of perforation may temporarily disappear or not appear. But this does not prevent infection from entering the sinus due to food entering the sinus.
As a result, the sinus becomes inflamed, signs of unilateral sinusitis appear, which should confuse a thinking patient (sometimes there are coincidences, but sinusitis-sinusitis, which comes as an accompaniment of the flu or a cold, is always bilateral).
Treatment of sinus perforation during tooth extraction
The tactics for managing a patient with perforation depends primarily on the condition of the sinus itself and the time of detection of this defect. This defect should only be treated by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of perforation of the main sinus of the upper jaw has the following objectives:
- Closing the defect.
- Prevent the process of inflammation in the sinus.
- Prescribe treatment if there is inflammation.
- If there are foreign particles, they must be removed.
If the perforation was immediately noticed and there are no signs of infection, then the treatment measures are as follows:
- Preservation of a blood clot in a tooth socket.
- Take measures to prevent its infection (application of a tampon with iodine solution).
- Apply stitches to the gums, if necessary.
- Treatment is carried out until the granulations grow and the defect is closed.
- The tampon is not removed from the hole.
- If the defect does not close on its own, it is covered with a plastic plate. It is fixed to the teeth.
- Prescribing a course of drug therapy aimed at counteracting inflammation.
If the perforation is complicated by gum rupture and penetration of foreign particles into the soft tissues surrounding the tooth socket, plastic closure of the defect is performed on the same day. Or after some time, when you are confident that the fabric will hold the seams. Before this, all foreign bodies are removed and areas that have undergone necrosis are excised.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removal of a tooth from the maxillary sinus (its fragments) and other foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas.
- Closing the defect.
Other causes of perforation
The remaining 5% of clinical cases of sinus perforation injuries occur for the following reasons::
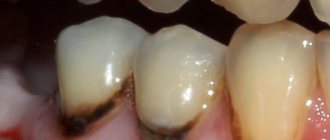
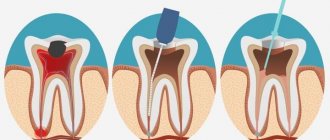
- Not ideal endodontic treatment of tooth canals - the therapist treated the canals, was in a hurry, used excessive force when filling the canal, and under the influence of a rotating canal filler with pressure, the filling material fell beyond the tooth root. We often encounter cases where even fragments of endodontic instruments are sometimes found in the thickness of the filling material, which jam in the canal and tear into pieces, leaving metal fragments in different places of the tooth root;
- Punitive sinus lifting - an inexperienced or rude doctor does not feel the density of the tissues, breaks through the Schneiderian membrane, the bone material is forced into the gap and enters the sinus;
- Author's implantation - it happens that due to the lack of skills in performing a sinus lift and the desire to restore the missing bone, a decision is made - the implant is placed in the residual bone that exists, without bone grafting. Result: the implant completely fails or partially comes out into the sinus.
A fragment of an endodontic instrument in a tooth canal
Methods for diagnosing perforation of the maxillary sinus floor
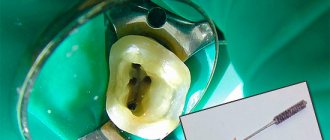
During diagnosis, a comprehensive study and analysis of the typical clinical picture observed with perforation of the maxillary sinus is used. The condition of the tooth socket, the presence of air bubbles, nosebleeds, and pain are taken into account. X-ray diagnostics are also performed, which show the area of perforation with high accuracy.
The dentist can perform a probing procedure for a perforated canal or an extracted tooth using a thin medical probe. This helps to reliably understand that there is no bone bottom in the wound. The instrument itself must pass freely through soft tissue without encountering obstacles along the way.
X-rays of the sinuses can detect characteristic darkening in the images, which are formed as a result of the accumulation of blood clots. Among other things, X-rays can show filling material, implants, and fragments of dental roots. X-rays with a contrast agent are often taken to help clearly visualize the condition of the bone tissue and surrounding tissues.
In such situations, a contrast agent is introduced into the cavity through a perforation fistula. An additional method of instrumental diagnostics is computed tomography, which determines the degree of perforation and the presence of foreign bodies, such as tooth fragments or residual filling material. If perforation is suspected, general clinical tests are required, which can show the presence of a focal infection in the patient’s body.
Why you should entrust your treatment to the ENT Department of Dentistry
ENT dentistry combines two areas of medical services and treatment options - otolaryngology and dentistry . This is a modern format for the clinic’s work on comprehensive rehabilitation in the treatment of traumatic and inflammatory processes in the upper jaw, penetrating into the maxillary sinus or passing along its borders.
The Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin” has been specializing in providing care to patients with combined ENT and dental pathology for many years. Medical and surgical treatment programs are carried out by candidates of medical sciences, maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training.
Statistics for the 20 years of work of the Center and for the last 10 years of work of the Department, unfortunately, are inexorable. The main providers of patients with complications are our colleagues who are caught in the dead end of an unsuccessful treatment plan. We are grateful to our colleagues who do not hesitate to send us patients with ENT complications, despite the reputational damage. It is always possible to avoid a dramatic outcome if you stop treatment in time.
Features of the work of the ENT department "Doctor Levin"
ENT unit Chammed XU-7 visual
Modern equipment of the ENT surgeon’s workplace
- We perform complex ENT surgeries
- Advanced technologies and methods
Ultrasound surgery without blood
The PiezoSurgery device affects only hard tissues and does not damage the gums, nerves, blood vessels and membranes. We do not use chisels, cutters and drills in the work of the Department!
Sirona Galileos 3D tomograph
Accurate diagnosis of odontogenic diseases and neoplasms of the maxillary sinuses
- ENT mode for sinus diagnostics
- High quality images
- X-ray control after surgery
Treatment while sleeping under sedation
We perform operations only in medicated sleep, under sedation, without pain or nervous overload.
- Forget about the risks of general anesthesia!
- Rehabilitation after sedation - 40 minutes
- No need for hospitalization!
Dental microscope SEILER Evolution XR6
Each ENT operation is performed with full optical control of the surgical field by a maxillofacial surgeon
Rehabilitation without a hospital in just 1-2 days
Effective methods for relieving swelling, hematoma and pain after surgery
- Microcurrent therapy
- PRP plasma lifting
- Day hospital
Hospitalization
The day hospital at our Center is a post-operative support service for patients. Necessary if the patient has concomitant cardiac issues, such as hypertension, arrhythmia, AOS, etc.
Gentle ultrasound surgical protocols for low-impact PiezoSurgery operations in combination with microscopic surgery performed by operating teams consisting of pairs of the most experienced surgeons at our Center allow you to carry out treatment so delicately that you will not need mandatory hospitalization, which is so popular in Moscow hospitals.
All operations are performed only in medicated sleep, without pain or nervous overload.
The treatment will be carried out with respect for your personal time, in a short time and at a comfortable time, the operating teams and anesthesiology department work seven days a week and holidays.
Stages of treatment
Diagnostics
X-ray 3D examination on a computed tomograph in a special ENT mode to determine the extent of inflammation, localization of foreign bodies, and the nature of neoplasms.
Planning
The maxillofacial surgeon together with the ENT doctor assess the situation and make a diagnosis. Determine the scale, choose treatment tactics and method of operation
Analyzes
They are prescribed individually depending on the clinical situation - to determine the stage of the inflammatory process and the nature of the tumor. For older patients and patients with chronic diseases, an examination is required before sedation (in other cases not required)
Operation
Performed under sedation in medicated sleep without the use of general anesthesia according to the selected sinus access protocol
Postoperative control
After surgery, is required to assess the quality of the operation.
Rehabilitation
Lasts 1-2 days. To accelerate the resolution of edema and hematomas, microcurrent and plasma therapy are used. Medications are prescribed, incl. antibiotics. To avoid the patient purchasing counterfeit products “on the side,” the patient receives the entire package of medications at the clinic free of charge.
Completion of ENT treatment
After 10-14 days, the sutures are removed, a control CT image is taken, and a date for a medical examination is set.
Treatment of chronic disease
Chronic odontogenic sinusitis is treated with standard methods; surgery is advisable in rare cases.
When the tooth that caused the inflammation has been removed, a puncture of the maxillary sinus is performed. There is a drainage tube in the sinus for up to 2 weeks. Through it, the doctor introduces a solution of antibiotics and antiseptics, and enzymes.
If traditional treatment is ineffective, surgery is resorted to. Its essence lies in excision of the affected tissue from the maxillary cavity, expansion of the anastomosis.
After some time (from 5 to 6 days), it is necessary to begin rinsing with saline solution.