← Return to store
The oral mucosa is a bacterial environment.
As a result of the vital activity of microbes, formations appear on the tongue, palate and cheeks. In general, this is the norm and by regularly carrying out hygiene procedures, as well as using a mouthwash, a person can easily get rid of plaque. But what to do if this problem begins to bother you and leads to consequences such as bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the mouth? In this article we will tell you about the reasons for changes in the color of the tongue, the types of plaque and ways to get rid of it at home.
Experienced therapists can make a primary history just by looking at the patient's tongue. The way the oral cavity looks is one of the most accurate indicators of the health of the body as a whole.
Normally, a person's tongue has a light pink tint, but a small amount of plaque is acceptable. It should be light, loose, and the receptors should be visible through it. Why is this not a deviation?
A completely clean surface is rare and indicates proper self-care. Experts consider it normal to have a thin layer of plaque on the tongue, gums and teeth.
These deposits may consist of:
- saliva;
- epithelial particles;
- leftover food;
- bacteria.
All of these components are considered natural waste products of our body. This can be eliminated with the help of daily hygiene procedures: mechanical cleaning of teeth and tongue with a brush.
You should consult a doctor if plaque:
- changed color from light gray or white to yellow, greenish, brown or even black;
- became denser and led to the appearance of the “coated tongue” symptom.
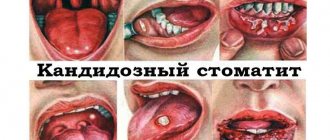
The reason for the visit may also be other changes, such as the appearance of white particles in the saliva. If this secretion has become cloudy, then there is a high probability of a fungal disease - candidiasis. Thus, deposits on the walls of the oral cavity consist of pathogens and leukocytes on which they feed. In this case, it is necessary to consult with a medical specialist as quickly as possible so that he can prescribe treatment.
Other common causes of plaque on the tongue, gums, teeth and inner cheeks include:
- Taking antibiotics and other medications. This occurs due to the fact that the aggressive chemical composition of medications disrupts the acid balance of the gastric microflora. As a result, the environment inside the mouth becomes more alkaline, leading to the formation of a white film.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the disproportion of beneficial and harmful bacteria, a white or yellowish sediment is observed on the tongue. As a rule, disturbances in the digestive system are accompanied by bad breath.
- Decreased immune function of the body. Most of the immune cells that actively fight infections and other pathogens are concentrated in our stomach. Therefore, the appearance of the tongue serves as an accurate indicator of the weakening of the protective function. If you feel unwell and notice thickening of plaque in your mouth, then most likely you have reduced resistance to disease. If these symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor.
- Bad habits. Regular drinking of alcohol or smoking cigarettes leads to a more active spread of bacteria in the walls of the mucous membrane. Dentists note that smokers have denser plaque, which is difficult to clean at home and requires the intervention of a specialist. Often the deposits have a dark tint, and patients themselves note a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Infectious and/or viral diseases. Regardless of the type of infection or strain of the virus, the human immune system suffers and the number of pathogens increases, which leads to their “settlement” in the mouth.
- Poisoning. During intoxication, the body tries to establish self-regulation and get rid of the substance recognized as poison. Therefore, profuse nausea, diarrhea and sweating occur. When the cause itself is eliminated and after the normal state is restored, the plaque will disappear on its own.
- Food. The appearance of plaque after eating food is not a deviation, since it consists of food particles that are easy to get rid of by rinsing. But dentists recommend doing a short flossing session after you've eaten. In the Stommarket online store you will find a special medical thread, Curaprox, which has the optimal thickness for removing food debris from hard-to-reach places.
- Disturbances of the endocrine system. A coated tongue is a sign of problems with hormone production. Therefore, if you suspect abnormalities in the functioning of the internal secretion organs, consult a doctor immediately.
REMEMBER! The distribution of plaque depends on the anatomical features of the tongue. It is a muscular organ covered with a mucous membrane. There is always a greater accumulation of “sediment” at the root, since this part is less mobile and comes into contact only with the soft palate. The tip of the tongue and the rest of the surface should normally have more transparent layers, because they are more capable of self-cleaning when a person speaks or eats.
To avoid problems with your oral health, the optimal frequency of medical examinations should be once every six months.
It is better to entrust the difference between natural formations and pathological ones to a medical specialist. But still, a person himself is able to conduct a primary diagnosis.
What you need to pay attention to first:
- color;
- density;
- location;
- character (consistency: uniform, lumpy, rough or smooth; presence or absence of spots);
- localization;
- ease of cleansing;
- frequency of reappearance.
If you do not complain about the state of your health, but there is still plaque, then these are usually formations that appear in the morning after a night's sleep or in the evening. They are light in color - white or transparent. Through them it is easy to see the surface of the tongue and the papillae on it. It is a thin, non-viscous film. It is evenly distributed over the walls of the oral cavity and can be easily cleaned with a toothbrush or floss.
White
This color is characteristic of “healthy” plaque. At night, saliva production slows down, so self-cleaning of the oral cavity occurs to a lesser extent and bacteria quickly accumulate on the cheeks and gums.
But white color can also be a signal of pathologies such as the presence of fungal diseases (candidiasis or, in common parlance, thrush), infection, inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (for example, glossitis). If tongue swelling persists throughout the day, despite the use of care products, it is necessary to undergo an examination and identify pathogenic factors.
A white, dense coating on the root of the tongue is a harbinger of problems with the gastrointestinal tract: ulcers, gastritis, dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis. Taking synbiotics, drugs combining probiotics and prebiotics that restore intestinal microflora, will help solve this problem. Enzymes and sorbents (Mezim, Laktofiltrum, Festal and others) will also help improve the body’s condition after illnesses and a course of taking pills.
Remember! Medications must be prescribed by a doctor.
Yellow
If the film has become denser along the entire length of the tongue and the color has changed to yellowish or greenish, then the first reason may be the presence of pus. This symptom accompanies the appearance of sore throat and colds, which cause complications in the throat. Powerful antiseptics eliminate this disease.
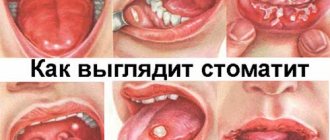
Why is the tongue covered with a white coating, what is the reason for this?
White coating on the tongue is not always associated with diseases.
Sometimes this can be a temporary phenomenon that goes away in a few hours or days. However, in some situations, various diseases may be detected during diagnosis. Many doctors begin examining the body when white plaque appears on the gastrointestinal tract. In most cases, detected diseases are accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture.
- Acute gastritis is a very common type of gastrointestinal disease and is diagnosed in people of all ages. The pathology is sometimes accompanied by heartburn, acute pain in the stomach, and nausea. Patients are concerned about dry mouth and tongue. A coating with a grayish tint forms, although the tongue usually remains clean on the sides and at the very end. A common symptom of gastritis is bad breath.
- Chronic gastritis occurs in a more smoothed form, pain may be less pronounced. Many patients note heaviness in the abdomen after eating and frequent belching. The tongue is coated with a white-yellow or grayish coating, and the taste buds may be enlarged. Also, sometimes red spots on the mucous membrane stand out clearly.
- Stomach and intestinal ulcers are serious diseases that can lead to various complications. Patients note acute pain that may go away after eating, and sometimes bleeding occurs. The coating on the tongue is located at the root, has a whitish-gray color and a dense consistency. It is quite difficult to remove it, since it is tightly attached to the taste buds.
- Acute pancreatitis occurs when the pancreas becomes inflamed. Taste sensitivity is impaired, and a white-yellow coating is found on the tongue. Patients suffer from dry mouth and severe pain in the left hypochondrium.
- Chronic pancreatitis has less pronounced symptoms, and a white coating forms on the tongue due to candidiasis, which develops against the background of metabolic disorders and lack of vitamins.
- Malignant formations in the stomach are accompanied by general weakness, weight loss, lack of appetite and severe pain in the abdominal area. A dense white coating appears on the tongue due to the large number of leukocytes.
- Dysbacteriosis can also cause plaque to appear. It is usually pure white, but in severe forms a yellow tint may appear. This coating is easily removed, but soon it appears again, sometimes even with greater force. Most often found on the left side of the tongue. Sometimes the plaque forms such a thick layer that it is impossible to see the color of the taste buds underneath.
- Poisoning is accompanied by vomiting, nausea and severe digestive upset. Also, sometimes the temperature rises and severe sharp pains in the abdominal area are tormented. A white coating with an unpleasant odor may appear. If poisoning occurs due to various toxic substances, then the surface of the tongue becomes covered with ulcers and erosions with a large number of dead cells.
In addition to gastrointestinal diseases, the cause of white plaque can be other pathologies that appear due to various pathogens.
- Various colds that occur with complications can cause the tongue to turn yellow. Moreover, the higher the patient’s temperature and the more severe his condition, the greater the thickness of the plaque. A severely weakened body cannot fully cope with pathogenic microorganisms that begin to rapidly divide in the oral cavity. Due to various pathologies that lead to difficulty breathing through the nose, a white-yellow coating may occur. It often disappears when the consumption of clean drinking water increases.
- Syphilis is a serious sexually transmitted disease. Its consequences can be very serious. The plaque forms on the back wall of the throat and on the root of the tongue, has a dense structure and is white in color.
- HIV infection leads to a significant decrease in immunity and weakening of the entire body. Against this background, pathogenic microorganisms, including fungi of the genus Candida, often begin to multiply. Painful ulcers may also form on the tongue.
- Tonsillitis can contribute to the occurrence of various concomitant diseases. Very often, inflammation of the tongue occurs, which becomes covered with a dense white coating. Sometimes its base may hurt.
- Scarlet fever is a very serious disease that can lead to various complications.
Patients complain of very high fever, headaches and skin rashes. The plaque spreads not only to the tongue, but also to the throat. When suffering from scarlet fever, the tongue becomes covered with a white coating on the first day. - Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease. The causative agent is gonococcus, which can also infect the oral cavity. A whitish-yellow coating appears in it and on the tongue, as well as purulent ulcers. Patients experience itching, burning and dry mouth, pain when swallowing, and the voice becomes hoarse. There is also increased salivation, an unpleasant odor, and the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful to the touch.
- Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Accompanied by severe pain in the throat, difficulty swallowing, swelling of the walls of the larynx. A white coating appears on the back of the throat and can also spread to the surface of the tongue.
- Sore throat is accompanied by high fever, severe sore throat and general weakness. The tonsils, palate and tongue may be coated with a thick white coating. Sometimes the color may take on a yellowish tint.
- Candidiasis can affect many internal organs and is a very common disease. It can appear after long-term use of antibiotics, during which the content of microorganisms is disrupted and pathogenic flora begins to multiply intensively. Reduced immunity, oral contraceptives, drugs, and alcohol may also be the cause. The tongue with thrush sometimes burns, turns red and swells. The plaque is very dense, thick, white, difficult to remove, and in its place an ulcerated surface is found. Sometimes it is unevenly located on the surface of the tongue.
- Galvanic stomatitis occurs in people who wear various dental devices made of metal. A white coating appears on the tongue, which may have a heterogeneous structure and sometimes forms pimples. In some cases, there may be erosion and a burning sensation.
- Desquamative glossitis or geographic tongue is often detected against the background of dysbacteriosis. In this case, a white coating and red spots appear.
- Dental diseases can also cause plaque to appear. Due to pathological processes occurring in the oral cavity, bacteria begin to multiply rapidly and form a white film on the surface of the tongue. The cause of the white coating is not always the disease. Sometimes it can occur after taking various medications and even foods.
There are other reasons for the appearance of plaque:
- A white coating on the tongue may appear after eating various fermented milk products, such as cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, and cheese.
- Sweet foods are a favorable environment for the growth of various bacteria, which leads to the appearance of white plaque. This phenomenon is temporary and can be easily eliminated after rinsing the mouth or brushing the tongue.
- Individual intolerance to toothpaste or mouth rinse. This happens quite rarely, but for some people, frequent contact with these products causes unpleasant chemical and allergic reactions, which can subsequently cause a white coating on the tongue.
- Violation of hygiene rules, in which teeth and tongue are rarely brushed, and food debris and various bacteria accumulate on them every day.
- Bad habits are a common cause of the problem. Abuse of alcohol and cigarettes negatively affects the condition of the entire body. When smoking, the tongue is exposed to high temperatures and harmful chemicals, and its mucous membrane is damaged. After alcohol abuse, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and dehydration occurs. Very often, after drinking drinks, the next morning people suffer from dry mouth, unpleasant odor and a coating on the tongue.
- Taking antibiotics seriously affects the balance of microflora in the human body. There is also an increased load on the liver, which sometimes cannot cope with the amount of harmful substances received. In these situations, either white or white-yellow coating may appear on the tongue.
Eating fermented milk products may cause white plaque to appear, but this is not a sign of disease.
In some cases, the cause of the appearance of white plaque may be a violation of the division of tongue cells. Various hereditary and systemic diseases can lead to this.
- Leukoplakia is common in people who smoke. Plaque is formed as a result of the death of cells that die due to tobacco smoke. The disease can affect the mucous membrane of the mouth, respiratory tract and other organs. It is most often found in people aged 30–40 years.
- Lichen pilaris is a skin disease that can also affect the mucous membranes. With the erosive form, an inflammatory process begins in the oral cavity, grayish plaques and ulcers appear. The top of the tongue is covered with a white coating, and if you try to remove it, bleeding may begin due to open wounds.
- Brunauer syndrome is a serious disease that is inherited. With it, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating) and keratoderma (impaired keratinization processes) are observed. A very common sign of this disease is a white coating on the tongue.
- Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome is an extremely rare genetic pathology in which atrophy or congenital cutaneous hypoplasia is detected; the skin of patients is very smooth, fragile, and practically hairless. One of the symptoms of this syndrome is also a white coating on the tongue.
Plaque on the tongue: normal or not?
The human language is a kind of litmus test for the health of the entire organism. Normally, a healthy person should have a tongue without plaque, but this is ideal, which is rare today. If the tongue is coated, there are only two cases where you should not worry about it.
- After meal.
Eating foods such as strong tea, black coffee, red wine, blueberries, and beets causes temporary staining of the tongue and an unnatural coating on it, but both phenomena go away on their own and do not cause damage to health. - After the night.
A constant coating on the tongue in the morning is normal. At night, bacteria living in the mouth actively multiply, leaving traces of their vital activity. A thorough morning toilet will put everything in its place.
Tongue care kit from miradent.
Reasons for appearance
Open your mouth and show your tongue - it is with this action that the diagnosis of many diseases begins when a person consults a doctor.
If there is a coating on the tongue—white or yellow—and the patient’s breath is not fresh, the patient is diagnosed with halitosis. Most often, the disease is associated with insufficient oral hygiene or problems with teeth and gums. But often a complex of such symptoms indicates diseases of the internal organs and requires a full diagnosis.
Main reasons
A coated tongue and a pronounced unpleasant odor may indicate the following problems:
- poor oral hygiene, insufficient care of artificial structures in the oral cavity;
- caries - depending on the intensity of the odor and the density of plaque, either single or extensive;
- gastrointestinal diseases, or temporary disruptions in intestinal function associated with overeating or drinking alcohol;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- disorders of the liver and kidneys;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs, abuse of paste with an antibiotic effect.
Some problems can be solved on your own by improving hygiene and taking a course of drugs that restore microflora. Most diseases require a visit to a doctor - a dentist, therapist or specialist.
White
First of all, you should pay attention to the nature of the plaque. If it is white and dense enough, covers the entire tongue, and not just the root, the smell from the mouth is sour, and a slight bitterness is felt in the mouth when eating - the patient has problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Most often this is gastritis or a stomach ulcer in the initial stage. A specific cheesy coating indicates the development of candidal stomatitis, which is also accompanied by burning of the mucous membrane, redness and inflammation of the gums. The cause of candidiasis is a fungus, which can be treated with topical medications and rinses with soda.
Glossitis is also a common problem with similar symptoms. With this disease, an inflammatory process appears in the tissues of the tongue (the organ turns red, slightly swells), a dense light plaque appears and a putrid odor from the mouth.
Yellow
If gastrointestinal diseases - gastritis and ulcers - become chronic, the plaque acquires a pronounced yellowish tint. The density and extent of plaque indicates the stage of the disease - the brighter and thicker the plaque, the greater the problem.
Chronic gastritis or ulcers are also accompanied by a specific odor - slightly glandular, bitter and unpleasant. There is a constant taste of bile in the patient's mouth. This also indicates additional problems with the gallbladder.
Long-term use of antibiotics puts increased stress on the liver and kidneys - while toxins released by the body turn the tongue yellowish. As a rule, symptoms disappear as soon as the local microflora normalizes. A white coating mixed with yellowness appears on the root of the tongue in inflammatory diseases:
- purulent sore throat;
- pharyngitis;
- flu;
- ORZ.
The most harmless is the yellow coating that appears when taking vitamins - the coloring substances remain on the mucous membrane for some time, but do not pose a danger. With proper hygiene, both plaque and odor disappear without a trace in a couple of days.
You should consult a doctor if, in addition to a slight odor and plaque, symptoms such as:
- constant heartburn;
- stomach pain, digestive problems;
- bowel disorder - constipation and diarrhea.
With a complex of symptoms, we can talk about an infectious disease, dysentery, and in rare cases, gonorrhea. It is also urgent to visit a doctor if:
- bad breath cannot be removed using standard methods (brushing teeth, chewing gum, rinsing);
- the coating on the tongue is dense, white or yellow, when cleaning it is removed for a very short time and appears again;
- There is a constant bitterness, unpleasant dryness, and coppery tastes in the mouth.
If there are signs of a concomitant disease, you should first contact a therapist at your place of residence. He will conduct an initial diagnosis, prescribe tests and, if necessary, refer you for examination and treatment to a specialist.
If there are no signs of the disease, but bad breath and a faint white plaque are present almost constantly, you need to visit the dentist, since the disease most likely affects only the oral cavity. The doctor will examine the teeth and gums, prescribe treatment, and recommend medications for oral hygiene - including dental floss, irrigator and rinses with medicinal herbs.
Very often, the cause of plaque and bad breath is bacteria that settle in the loose tissue of tartar. After cleaning the stones and professional hygiene, the problem goes away in a couple of days.
Diagnostics
If you suspect gastrointestinal diseases, you should visit a gastroenterologist. He will examine the patient and prescribe the following studies:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- general and clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine.
If the cause of the disease is discovered, he will either prescribe treatment or refer you to an endocrinologist and infectious disease specialist. In women, halitosis can be caused by hormonal imbalances. If you suspect these problems, you need to consult a gynecologist or get tested, and if necessary, undergo treatment with hormonal drugs and herbal medicine.
- First of all, you need to give up bad habits - smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Be sure to visit a dentist, treat caries, and have your teeth professionally cleaned by a specialist, including removal of stones.
- When treated with antibiotics, take a course of drugs that restore microflora.
- Treat stomatitis with rinses with baking soda and salt, and local medications (Tantum Verde).
- For chronic throat diseases, consult an otolaryngologist.
If no diseases are detected, but bad breath and plaque are bothering you, improve your oral hygiene.
Improving oral hygiene can completely relieve unpleasant symptoms. To get rid of halitosis you need to:
- brush your teeth twice a day, clean the root of your tongue;
- use dental floss;
- use an irrigator;
- rinse your mouth with decoctions of chamomile and sage;
- if you are prone to stomatitis, rinse the cavity several times a week after brushing your teeth with warm water with the addition of natural soda;
- for inflammation, drop propolis tincture with alcohol into water (5 drops per glass of water), keep the mixture in your mouth for 2 minutes twice a day;
- rinse your mouth with warm water after each meal, if possible - with the addition of a small amount of chamomile decoction.
Introducing solid plant foods into your diet will also help. Carrots, cabbage, apples will saturate the body with vitamins and get rid of unpleasant plaque, while strengthening the gums.
To enhance the effect of any treatment, it is worth changing your lifestyle - be sure to give up bad habits, especially smoking, add seasonal fruits and vegetables to your daily menu, walk in the fresh air, take vitamins - especially vitamin C during the spread of viral infections. A strong immune system is the best assistant in the fight against the symptoms of halitosis and plaque on the tongue.
Bad breath and a white coating on the tongue are usually caused by the accumulation of bacteria, dead cells and food debris. During normal functioning of the body, this mass should be cleaned from the internal surfaces of the oral cavity. If the process is disrupted, it is necessary to urgently look for the cause of the pathology.
Poor diet, smoking, alcohol consumption and various diseases can contribute to the proliferation of bacteria that form deposits in the oral cavity. We will try to figure out why there is a white coating on the tongue and bad breath, how to identify the pathology, and what the treatment should be.
A white coating on the tongue accompanied by an unpleasant odor can have different causes and symptoms. Based on the symptoms, you can roughly determine a possible disease or disorder in the body:
- If the white film is thin and there is little odor, it may be a viral disease, while a thicker crust and a persistent bad odor indicate serious infections.
- Deposits can cover the entire tongue or be localized only in the root part.
- Depending on the consistency and density, deposits can be wet, soft or dry. The smell from the mouth is disgusting in all cases.
- The resulting white layer can easily separate from the surface or adhere tightly to the tongue.
Based on these signs and what exactly your breath smells like, an experienced therapist should roughly determine the source of the appearance of white plaque on the tongue.
Reasons for violation
Strong bad breath and white plaque can indicate all sorts of diseases: each requires a specific approach to treatment. Let's look at a few of the main and most common causes of the unpleasant "white tongue" problem.
Insufficient hygiene
Irregular or careless brushing of teeth and tongue with a brush and paste promotes the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that form a persistent white crust.
Constant hygiene allows you to remove the white film without medical assistance.
Under normal conditions, morning and evening cleansing should be sufficient, but if the procedure does not help, there may be disruptions in the functioning of certain components in the body.
Digestive system diseases
White coating on the tongue and bad breath can signal the following diseases:
- Gastritis. Accompanied by an inflammatory process and the appearance of white deposits on the surface of the tongue. If the acidity of gastric juice is increased, the tongue will become moist and rough, and if it is decreased, the tongue will be dry and smooth.
- Ulcer. The disease causes the formation of a persistent white coating on the root of the tongue and a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Pancreatitis. Promotes disruption of material metabolism and the appearance of white-yellow deposits on the tongue.
Infections
When your breath smells and there are white deposits, the causes may be infectious diseases of a different nature:
- angina;
- scarlet fever;
- dysentery;
- cholera;
- whooping cough.
Other violations
White deposits and bad breath can be caused by stomatitis. The disease usually affects children with weak immunity, as the mucous membrane becomes vulnerable to microbes, inflammation, and infections.
Candidiasis, kidney disease, and disturbances in the functioning of the liver and pancreas can provoke a white coating and an unpleasant odor. All of these diseases are accompanied by bitterness in the mouth and dry mucous membranes.
What if it's a disease?
A strong coating on the tongue and bad breath are already a reason to be wary. An experienced doctor will determine which disease the plaque on the tongue is a sign of, comparing the degree of density of the deposit, color and location.
Glossitis
One of the typical diseases characterized by plaque on the tongue is glossitis - inflammation of the tongue caused by injury or of an infectious nature. With glossitis, red spots appear on the tongue, which is why the disease is sometimes called “geographic tongue.” Read more in the article.
Gastritis
If your mouth is sour and there is a coating on your tongue, this is a sign of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Usually the plaque disappears if you follow a diet.
Thrush
With thrush, the plaque is located under the tongue. It is distributed unevenly and has the character of spots.
Chlamydia
With chlamydia, a sexually transmitted disease, a thick, sticky coating appears on the roof of the mouth and tongue as a result of a malfunction in the immune system after an attack by chlamydia.
Bronchitis and pneumonia
Plaque on the sides of the tongue will indicate an upper respiratory tract disease. In most cases, it is whitish and is easily removed by brushing your teeth and tongue, but also quickly returns to its original place.
Alcoholism
A coating on the tongue after alcohol abuse is common. People talk about this figuratively: “It’s like cats have shit in your mouth.” However, in chronic alcoholics, the dark brown coating never goes away and is localized at the root of the tongue.
If the tongue is coated, one cannot say with certainty that a specific type of cancer is present. But it is precisely this symptom, coupled with a number of other characteristics, that indicates a complication of an oncological disease (for example, a malignant tumor in the lungs).
Plaque on the tongue of a pregnant woman, with rare exceptions, is not a sign of illness - it is the result of changes in hormonal levels.
Types of white coating on the tongue
There are many varieties of white plaque based on its color shade, location on the tongue and accompanying symptoms. Each of these signs is very important in diagnosing diseases and allows us to reduce the list of possible pathologies in a patient.
Features that white plaque may have:
- does not go away within 24 hours;
- occurs in the morning after sleep;
- has a bad smell.
Associated symptoms:
- an unpleasant bitter or sour taste appears in the mouth;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- the tongue changes its size, swells and swells, teeth marks are imprinted on it;
- viscous saliva is secreted;
- the surface of the tongue becomes rough, loose, or cracks form on it;
- the tongue becomes painful, stings, burns, and sometimes even goes numb;
- taste sensitivity is impaired;
- dryness appears in the mouth and on the surface of the tongue.
Bad breath is a common symptom of gastrointestinal diseases
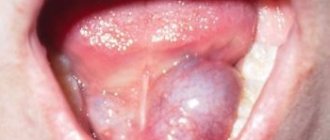
Also, sometimes various formations may appear on the tongue:
- pimples;
- sores;
- blisters;
- red spots;
- red dots, pimples.
Sometimes spots, pimples and ulcers may appear on the tongue
The location of plaque on the tongue is also an important diagnostic sign, as it may indicate pathology of a specific internal organ.
- if plaque appears in the central part of the tongue, then this may indicate stomach diseases;
- at the very base of the tongue - intestinal diseases;
- plaque on the tip of the tongue is associated with heart disease;
- the edges of the tongue indicate diseases of the liver and spleen;
- plaque on the back of the tongue may be a symptom of problems with the pancreas;
- a white coating on the palate may appear due to candidiasis;
- on the tongue and tonsils, near the throat - with sore throat.
By the area of the tongue covered with plaque, one can judge about diseases of a particular organ.
The coating on the tongue is not always pure white; sometimes it takes on a slightly different color:
- white-yellow;
- white-brown;
- white-gray;
- white-green.
Sometimes the tongue can take on various shades, including white and yellow.
Based on saturation, the following types of plaque can be distinguished:
- light, small, easily removable;
- dense and thick;
- unevenly distributed;
- curdled.
Main causes of plaque
- Infection.
The main cause of plaque on the tongue in adults is infectious diseases, characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. - Impaired immune function.
When the body's protective barrier cracks, this serves as a catalyst for the activation of pathogenic bacteria, which usually occurs against the background of an increase in body temperature. - Gastrointestinal pathologies.
Various chronic ailments of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Helicobacter. Plaque on the tongue due to gastritis, if the disease is not treated, becomes denser over time and provokes bad breath. A clear sign of enterocolitis in adults is considered to be plaque on the root of the tongue. - Side effect of drugs.
Plaque on the tongue after antibiotic treatment is a common phenomenon. Medicines that include substances that inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic bacteria negatively affect the acid-base balance in the mouth, which entails an increase in the number of microorganisms “responsible” for the appearance of plaque. - The consequences of nicotine.
If you are an “experienced” smoker, then you shouldn’t be surprised by a gray or yellow coating on your tongue. Nicotine abuse has a detrimental effect on the microflora of the body in general and the oral cavity in particular.
A provoking factor for the appearance of plaque on the tongue is also helminthic infestations, such as giardiasis. For differential diagnosis in this situation, it is necessary to take a stool test for helminth eggs.
How much does your tongue need to be cleaned?
Every person from an early age knows that teeth must be brushed 2 times a day: morning and evening. Thanks to this, not only plaque is removed, but also tooth enamel is enriched with calcium and fluoride. It also freshens your breath. Therefore, not only your teeth need to be cleaned, but also your tongue.
The surface of the muscular organ of the oral cavity consists of many long papillae. When eating, some particles get stuck in these papillae. Toxins and various bacteria also get there, for which this is an ideal place for reproduction due to the lack of oxygen. This is why a coating with an unpleasant odor appears on the tongue.
It has been scientifically proven that we no longer owe fresh breath to brushing our teeth, but to cleaning the surface of our tongue.
If your mouth smells bad, then it means that it is time to pay proper attention to your tongue and clean it from the accumulation of bacteria. Thanks to cleaning, taste buds are more activated, which improves the taste of food.
How to clean your tongue
Modern toothbrushes are designed in such a way that the back side can be used to clean the surface of the tongue. You can also find special scrapers in stores. To avoid injury to the epithelium, it is necessary to act with optimal pressure. At the end of the procedure, be sure to rinse your mouth.
Traditional medicine helps us fight
For any illness, you should begin to treat the cause of its occurrence, and not the symptoms that appear against its background. They can be reduced using proven traditional medicine. This is how you can reduce bad breath. The most effective means of control are:
- herbal infusions used for rinsing the mouth (chamomile, calendula, mint, oak bark and sage); decoctions not only disinfect, but also prevent the development of certain diseases;
- flax seeds - taking a decoction in the morning on an empty stomach can get rid of many problems associated with the state of the digestive system.
Rinsing with herbal infusions removes plaque and odor.
What does plaque color tell you?
White
As we have already said, a thin white mucous coating on the tongue after sleep is not a deviation from the norm. A white coating of increased density indicates constipation, and a cheesy coating on the tongue indicates the unhealthy activity of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Yellow
A bright yellow coating on the tip of the tongue indicates hepatitis A (Botkin's disease). If there are problems in the functioning of the gallbladder, a yellowish coating and cracks appear on the tongue.
Dark
A dark coating on the tongue is a sign that something is wrong with the lungs. You don’t often see a completely black plaque: for example, in advanced stages of cholera due to dehydration of the body or in Crohn’s disease.
Tightly coated tongue
If a person regularly notices that his tongue is tightly covered with a thick coating, giving an unpleasant taste and aroma, you need to pay attention to the color of the coating.
Indeed, in addition to white and yellow shades, plaque can acquire the most unexpected colors:
- Brown – long-term alcohol consumption, gastrointestinal and gallbladder diseases.
- White-gray – long-term use of medications (antibiotics).
- Orange – worsening stomach ailment.
- Bluish – anemia from a lack of vitamins.
- Black - Crohn's disease, poisoning, liver problems.
- Green – poor nutrition and impaired liver function.
The thicker the plaque, and the more difficult it is to get rid of it using normal hygiene procedures, the more serious the disease develops in the body.
What to do?
How to remove plaque from the tongue? To begin with, determine exactly the reason why the plaque occurs and treat the underlying disease by following the doctor’s instructions. For preventive purposes, in order to minimize the amount and density of plaque, you must follow simple rules of personal hygiene:
- brush your teeth in the morning and before bed with toothpaste and a brush that has a tongue cleansing pad;
- use antibacterial mouthwash;
- use a special spoon to clean the tongue, moving from its periphery to the front surface.
Forget or treat?
As you can see, the causes of plaque on the tongue and the consequences of its occurrence can be different. Yes, it is not fatal, but it is very unpleasant and indicates problems with the health of the body as a whole. Therefore, it is extremely important to pay sufficient attention to the tongue during daily hygiene, and if the first signs of plaque appear on it, promptly consult a doctor.
If you follow all the care instructions, and a thick coating on your tongue persists for more than 3 days, consult a doctor for help!
Infectious diseases
A list of the most common infectious diseases will help you understand what plaque on the tongue means.
- Pityriasis rosea. The spots appear all over the tongue and may peel a little, but there is no inflammation. During the course of the disease, several spots may merge into one large spot.
- Whooping cough and foot and mouth disease. The tongue is white-yellow, there is an unpleasant odor , and small ulcers appear.
- Dysentery. A thick white coating, under which there may be erosion.
- Scarlet fever. At the beginning of the disease, the tongue is whitish-gray and slightly swollen. After several days, the plaque disappears, leaving behind a bright red mucosal surface, characterized by dryness and inflammation of individual papillae.
- Cholera. Due to the large loss of water, the body is greatly weakened, which causes a black plaque.
- Diphtheria. A greasy gray-white coating on the tongue and oral cavity. When getting rid of it, the mucous membrane looks inflamed and there is pain.
- Stomatitis. A large number of ulcers of various shapes, a thick, gray-green coating on the tongue and pronounced bad breath When cleaned, the sores bleed.
- Candidiasis. The appearance of swelling of the oral cavity, its redness, the appearance of white dots, under which small ulcers are hidden. Increasing in number, the dots form a plaque with a hue ranging from white-gray to yellowish.
- Leptotrichosis. A thick layer of white-gray plaque that is quite difficult to remove. Underneath it are hidden small, dense inflammations in the form of thorns.
- Erythema. The color of the tongue is gray-yellow, there are small erosions that cause pain.
Content
A white coating on the tongue can indicate various diseases, the severity of which varies from simple problems with oral hygiene to precancerous conditions. Overgrowth of bacteria is the main cause of white coating on the tongue. If you suffer from this problem, consult your doctor to determine the causes of the disease and prescribe a course of treatment.
In addition, the thickness of the layers indicates the stage of the disease, that is, a very thin layer, when the color of the tongue and its papillae are visible - the disease is in the initial stage, constant thick layers - a chronic disease.
Toddler problems
It happens that parents notice that the child’s tongue looks unhealthy. It may be covered with a white or yellow layer, and sometimes becomes crimson in color. This cannot be ignored.
Plaque on the root of a child’s tongue may indicate a malfunction of the intestines. But if its entire surface is covered with a white or grayish layer, then it is worth checking whether the baby has dysbiosis. But a yellowish tint may indicate overheating.
A dense white coating on the tongue occurs with most infectious diseases. This may indicate acute respiratory infections, flu, sore throat, scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other diseases. As a rule, its appearance coincides with an increase in temperature.
But in children, plaque can also occur due to thrush. This is one of the main reasons why a baby's tongue becomes white. But with this fungal disease, not only the root is affected. Almost the entire tongue becomes white; lesions can be on the cheeks, the inside of the lips and the palate.
Many people advise using soda to remove white plaque on the root of a child’s tongue. But this will not solve the main problem. If plaque covers only the base of the tongue, then you should consult a pediatrician. He may refer you to a gastroenterologist. Only after a complete examination can we say exactly what led to the appearance of plaque.
If the underlying disease is eliminated, the plaque on the root of the tongue will disappear. The reasons for its formation must be correctly determined. Also, by the intensity of plaque, you can determine how effective the prescribed therapy is.
You, of course, can remove the layer from the tongue, but it will appear again, because the reason for its appearance will not be eliminated. This can be done using a cotton or gauze swab soaked in a soda solution.
If you notice plaque only in the morning, then you can safely remove it. It usually does not indicate any problems. You can get rid of the white layer using a special tongue cleaning brush. Many toothbrush manufacturers make it on the reverse side. You can also get rid of the white layer using a regular teaspoon or a special scraper.
It's important to do it right. You need to clean your tongue using movements from its base to the end. You can use toothpaste or powder for these purposes. This way you can not only remove visible cover, but also remove a huge number of microbes. Many people advise brushing your tongue regularly, as this helps maintain proper microflora in the oral cavity.
By the way, oral care is also necessary in order to maintain teeth and gums in normal condition. This will keep problems with them to a minimum.
Plaque coloring
So, what does tongue coating mean? The color of the plaque itself will help us answer this question. It can be white, yellow, gray, green, brown, orange, black, blue.
White
White coating on the tongue is a very common thing. Surely in the morning you noticed that your tongue is covered with a white coating. This is not scary if the layer is thin (the pale pink color of the tongue is visible). Treatment for such plaque is not required; it simply needs to be carefully cleaned off using a spoon or the specially adapted back of a toothbrush.
The causes of white plaque on the tongue can be divided into physiological and pathological.
Normally, a small (the pink color of the mucous membrane of the tongue can be seen through it) white coating (predominantly in the area of its root), odorless, is allowed. It can often be observed in the morning after sleep or during hot periods of the year. Frequent consumption of carbohydrates, dehydration, and rare meals contribute especially strongly to the formation of plaque outside of pathology.
With a diet rich in carbohydrates, halitosis (bad breath) is observed simultaneously with plaque deposition. In addition to plaque, dehydration is manifested by deep cracks in the tongue, dry mucous membranes, and wounds in the corners of the mouth. Plaque during rare meals is caused by a reduced self-cleaning function and is characterized by an unpleasant odor.
How to treat white coating on the tongue? If you find it in yourself, treatment can only be prescribed after a thorough examination by a doctor. In some cases, drug treatment may not be needed at all. If incipient gastritis is detected in a timely manner, you can get rid of it with the help of a special diet.
Very often, patients are interested in which doctor to go to if a white plaque is detected. It is best to start with a general practitioner; he will examine the surface of the tongue, determine the color and density, and at the same time ask you about your general well-being, on the basis of which he can draw certain conclusions about the state of your health. Next, the therapist can give a referral for a more thorough examination by a gastroenterologist if there are suspicions of disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
After eliminating the underlying disease, plaque on the tongue disappears on its own some time after completion of treatment and correction of the nutritional system.
But with diseases the picture is completely different. The plaque becomes thicker and darker, the color of the surface of the tongue is practically no longer visible through it, and the film of bacteria is located in a completely different way. It accumulates where the zones of one or another internal organ or system are located, and this is what it looks like.
Black plaque may be a result of Crohn's disease or cholera.
Other shades of coating on the tongue
Stomach cancer - the entire surface of the tongue is covered with a dense white coating consisting of epithelial cells, mucus, microflora, and a large number of leukocytes.
In diseases of the liver and gallbladder, the fibrinous coating on the tongue becomes intensely yellow. With hepatitis , yellowness appears in the front of the tongue. The intensity of yellow plaque increases with seasonal exacerbation of liver and gall bladder diseases.
In Crohn's disease , when the amount of adrenal hormones decreases. An increased amount of melanin (skin pigment) is produced in the skin and mucous membranes. As a result, the tongue becomes covered with dark spots.
Other diseases:
In pustular psoriatic erythroderma, the tongue is covered with round-shaped lesions with a grayish-white coating, the size of a pea, slightly rising above the level of the mucous membrane, and resembles a geographic map (“geographical” tongue).
Tongue psoriasis
“Geographic tongue” is observed with glossitis. In this case, the tongue is covered with red spots that resemble a geographical map. At times a slight burning sensation is felt. The reasons for this are not yet fully understood. Such language does not pose any danger, although it looks ugly. Often the spots go away on their own.
Thrush or candidal stomatitis of the mouth. Plaque covers the tongue, the area under the tongue, and the inner surface of the cheeks. Often such plaque is distributed unevenly, with spots. Fungal or candidal stomatitis is mainly observed in infants. With normal plaque, the spots do not cause any discomfort, as this is considered normal.
Is it possible to remove plaque on the tongue?
How to remove plaque on the tongue?
To get rid of plaque on the tongue, you need to find out and eliminate the cause of its occurrence. It should be borne in mind that a change in the color of plaque on the tongue can occur after eating. Pieces of food get stuck between the papillae that cover the tongue. And then a plaque appears. For example, a dark coating on the tongue may occur after a cup of strong tea. This type of plaque is absolutely harmless and disappears on its own. In other cases, you need to consult a doctor who will help identify and eliminate the root cause. So, for example, if there is a dense yellow coating on the tongue, your treatment will need to be handled by a gastroenterologist.
Types of plaque
What to do if plaque does appear? The first step is to visually determine its characteristics (color tone, consistency, appearance, etc.), which directly depend on:
- occurrence of illness;
- the severity of the resulting illness;
- appearance date.
The color scheme depends on the form of the disease. Lighter forms are characterized by yellow, white and gray shades, while more complex ones are characterized by green, crimson and even black. When assessing this factor, one should take into account the presence of bad habits (including smoking) and food consumed, which may contain dyes.
The thickness of the coating indicates the duration of the disease occurring in the body. A small thickness can serve as a warning for the onset of the disease. With a thin layer, you can easily distinguish the color of the muscular organ of the oral cavity itself.
The consistency also varies in nature: wet or dry, oily or curdled.
Plaque that can be easily removed, or rather the one that appears in the morning, should not cause concern. But if the film is present throughout the day and is not removed, then you should start to worry.
Thick plaque is an advanced disease
The film can be located evenly over the entire surface, or in small spots on different sides of the organ.
Types of infectious diseases
When an infection enters the body, the tongue also turns white. The most common infections include the following:
- Whooping cough - small ulcers form on the tongue, an unpleasant odor appears, and the surface becomes white-yellow.
- Pityriasis rosea - small spots appear on the surface, which can later merge into one whole and peel off.
- Scarlet fever - the tongue plate swells slightly and turns white-gray; after a few days, the coating disappears, and the surface becomes bright red.
- Dysentery - the plaque that appears forms a rather thick layer that hides the possible appearance of erosion.
- Diphtheria - the inflamed mucous membrane is covered with a gray-white fatty coating, pain appears.
- Cholera - dehydration of the body during the disease leads to the appearance of an almost black plaque.
- Stomatitis - ulcers of different sizes appear, which begin to bleed during cleaning, the surface of the mucous membrane is covered with a thick layer of plaque, which has an unpleasant odor.
- Leptotrichosis - small inflammations of the mucous membrane, having a spiky shape, covered with a thick layer of white matter.
- Candidiasis - redness and swelling of the oral cavity occurs, the white dots that appear constantly increase in number, forming a white-gray coating, and in some places yellowish.
- Erythema - small erosions form under the plaque layer, creating pain.
Stomatitis - spots and sores
Impact of the gastrointestinal tract
Stomach diseases are not uncommon today. Very often, the reasons for the formation of white plaque are hidden in it. When such cases are identified, specialist consultation, a thorough examination and an effective course of treatment for the disease are required.
- Gastritis. With chronic gastritis, a white-yellow coating forms on the root of the tongue in the oral cavity. In acute cases, swelling and a gray coating appear, creating an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Stomach cancer. The surface becomes completely white, mucus appears mixed with epithelial cells. Do not panic; only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis after examination.
- A peptic ulcer is accompanied by the appearance of hard-to-remove plaque on the back of the mouth.
- Enterocolitis. Typically, a thick layer of plaque forms in the acute form of this disease.
- Gallbladder and liver. The mucous membrane acquires a bright yellow tint.
- Dysbacteriosis. In the oral cavity, some of the papillae become inflamed, giving them a color ranging from brown to almost black.
- Crohn's disease. The body begins to produce melanin in large doses, which leads to the appearance of dark spots on the tongue plate.
- Pancreatitis. The white-yellow tone of the mucous membrane is accompanied by an increase in the papillae.
Dense plaque with enterocolitis