1581
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is often subject to various damages, both due to mechanical trauma and as a result of the development of certain diseases.
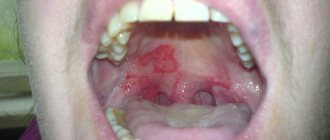
Most often, this leads to the formation of ulcerative lesions of various shapes and sizes on the gums, tongue and palate.
In addition to widespread stomatitis, other diseases, such as mucositis, can cause such rashes.
Causes
The occurrence of a disease indicates a disruption in the functioning of human systems and organs.
This disease occurs for the following reasons :
- disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- allergic reactions;
- metabolic problems;
- development of complications after implantation;
- chronic aphthous stomatitis;
- diseases of the immune system;
- consequences of radiation and chemotherapy.
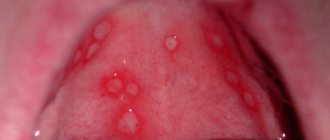
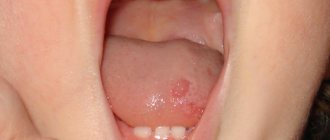
Photo: formation of ulcers with oral mucositis
Why do complications occur after implantation?
Implant rejection occurs, as a rule, for two reasons: violations are made by the doctor or the patient. Failure to comply with oral hygiene rules is the easiest way to develop peri-implantitis or mucositis. It is important not only to properly care for your teeth, but also to visit the dentist at least once every six months. Immediately after implantation, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and do not overload the implant.
The success of implantation depends 90% on the actions of the doctor. An implantologist is like a sapper: make one mistake and everything is lost, the implant will not take root. Contraindications to implantation are not taken into account, the location for the implant is chosen incorrectly, the load on the jaw is incorrectly calculated - mucositis or peri-implantitis develops.
Clinical signs
Oral mucositis manifests itself through symptoms characteristic of this disease :
- erythema - dilation of capillaries, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;
- swelling of the affected area;
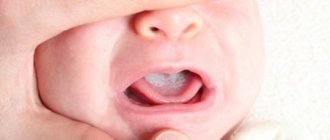
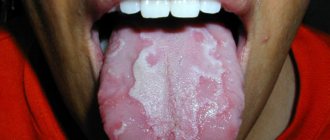
- necrosis of the mucous membrane, which is expressed by white spots;
- thinning of the oral mucosa;
- the formation of ulcers in several places at the same time . They can be localized on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, and the palate;
- infection of aphthae (ulcers) with subsequent discharge of pus.
Read about methods of treating mouth ulcers and the causes of their occurrence in a separate article.
In the next post, we will discuss whether stomatitis in children is contagious.
At the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/krasota-i-uxod/opolaskivateli/opisanie-dlya-polosti-rta-listerin.html you can leave your review about Listerine mouth rinse.
Tension rises: after the murder of a teacher in France, mosques are closed
A national farewell ceremony was held in Paris for teacher Samuel Paty, who was barbarously killed by an Islamist last week. During class, the teacher showed caricatures of the Prophet Muhammad, for which a fanatic beheaded him right outside the school building.
400 people came to say goodbye to Pati; sanitary standards no longer allow. The ceremony will last no more than an hour, because after that a curfew will begin and you will not be allowed to be on the streets. Usually national funeral services are held at the Invalides' Home, but in this case, with the consent of the relatives, it was decided to hold it at the Sorbonne University, which is a symbol of enlightenment, literary and cultural influence of France. This is where Samuel Paty will be buried.
President Emmanuel Macron and the entire cabinet are present at the ceremony. Afterwards, a posthumous ceremony will take place to present Paty with the Legion of Honor, and then Samuel Paty will be made commander of the Order of Academic Palms - this is the highest academic award in France. Next will be a farewell ceremony, ending with a minute of silence.
The investigation piece by piece reconstructs the entire chain of events that led to the tragedy. About six months ago, the teacher’s killer suddenly changed his behavior: he abandoned his friends, began disappearing from the mosque, and started talking about jihad and the Islamic state. The re-publication of cartoons of the Prophet Muhammad in Charlie Hebdo in September this year pushed him into crime. The killer carefully prepared for the attack - he bought a knife in advance and wrote down all the information about the victim in a notebook.
“It was established that the attacker, knowing only the name of the teacher and the name of the college. This became possible only with the assistance of the students,” said the head of the French National Anti-Terrorism Prosecutor’s Office, Jean-François Ricard.
Seven of them face charges of complicity in a crime. Among them were two students, 14 and 15 years old, who sold their teacher for 300 euros - they showed the terrorist what Samuel Paty looked like.
“My son was standing at the bus stop. His friend came up to him and said: “Look, that guy over there gave me money so that I can tell him who Mr. Pati is,” said the mother of one of the students.
The same charge could be brought against the father of one of the students. It was his video on social networks that caused great resonance in radical circles. It later emerged that his daughter had not attended a lesson on freedom of speech in which Pati showed a caricature of the Prophet Muhammad. But a few days later, the father recorded a video where he indicated the name of the college, the name of the teacher and even called for action. As the investigation showed, the terrorist contacted him three times, twice by phone, and once on social networks. True, the man claims that there were so many calls these days that he no longer remembers who he talked to.
The radical preacher Abdelhakim Sefrioui, who is on the list of people posing a threat to France, helped push this story. He went with his father to the director and helped him record videos for social networks. His association, called Sheikh Yassin, has now been declared extremist and ordered to be dissolved.
“You have seen in recent days dozens of specific actions that have been taken against associations, as well as against individuals, who promote radical Islamism. This is the ideology of state destruction. We will not allow them to continue doing this,” said French President Emmanuel Macron.
In the Paris suburb of Bobigny, Macron set up a center to combat radicalization. Since 2020, the prefect’s forces have closed many underground Islamic schools and organizations there.
Another tough decision: for helping to disseminate a video recorded by the father of one of the students, the authorities decided to close this mosque in the suburb of Pantan. It was built in 2013 and united six Islamic associations. The imam communicated with believers in two languages - French and Arabic. They all claim that he preached peace, so the decision of the authorities here was met with hostility.
“We are sad, we cannot sleep. We have a very good imam, on Fridays he talks to us about religion, says that you need to be polite, even if someone insults you,” said one of the parishioners, Faraji Zakh.
“I know that most of the people who go to this mosque, as well as to other mosques in the suburbs, are adequate people and know the basic principles of Islam. This is a religion of peace and love,” noted another local resident.
In the meantime, French publications continue to play with fire. The Nouvelle Republic newspaper reprinted Charlie Hebdo cartoons in memory of the murdered teacher, for which it received threats. Tension in society itself is also growing. On Sunday evening, in a park near the Eiffel Tower, two girls with a knife attacked two Muslim women with children because they asked to take their dogs on a leash.
The women suffered numerous cuts and are in the hospital. The attackers were detained and charged with attempted murder.
Stages and criteria of toxicity
There is an international scale that determines the degree of oral toxicity of the disease. Data determined by the World Health Organization.
The main stages are described below:
- «0» – there are no clinical signs, there is no toxic effect on the body.
- «1» – redness of a certain area on the oral mucosa, itching, but ulcers have not yet appeared. At this stage, the mucous membrane may undergo damage (atrophy).
- «2» – this stage is characterized by the appearance of small ulcers. The person's chewing and speech functions are not impaired; he can chew solid food. Ulcers can be with or without redness of the mucous membrane.
- «3» – at this stage, the ulcers increase in number and size, erythema is present, but not in all cases. It is difficult for a person to eat solid foods and requires a liquid diet.
- «4» – the most difficult stage for the patient. At this stage of the disease, the patient has many ulcers, they vary in size. Due to pain, the patient cannot eat solid and liquid foods.
There is an urgent need for the use of parenteral nutrition (taking formula for feeding through a tube or tube). Natural nutrition is impossible due to the serious condition of the patient.Whether a person is able to take nutrition at this stage is determined by the doctor based on his condition. If this ability is lost, a special mixture and liquids for treatment are prescribed.
WHO staff also defined toxicity criteria for oral mucositis as a consequence of chemotherapy .
| Stage | Research | Clinical manifestations |
| 1 | Redness of the mucous membrane | The main symptoms are mild, medical attention is not required |
| 2 | Skin lesions, plaque formation | The patient feels moderate pain, there are no difficulties with eating |
| 3 | Ulcers can merge into one, become large in size, skin lesions are observed, bleeding and minor damage to the mucous membrane may occur | The patient feels severe pain, has difficulty chewing food, swallowing |
| 4 | The death of mucosal tissue, spontaneous and intense bleeding raises the question of a threat to the patient’s life | Emergency medical intervention is required, consequences arise that threaten not only the patient’s health, but also his life |
| 5 | Death | |
To maintain the health of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular the oral cavity, before a course of chemotherapy you need to visit a dentist for professional oral hygiene, which will help preserve your teeth.
Mucositis: a modern view of the problem
Oral Hygiene Clinical studies have clearly shown that biofilm accumulation is associated with the development of peri-implantation mucositis around integrated implants. Ferreira et al. reported on 212 patients with three different oral implant systems who were diagnosed with mucositis. All implants functioned for a period ranging from 6 months to 5 years. A modified plaque index was recorded, and overall oral hygiene was defined as good (mean score ≤1), low (mean score >1 and <2), and very low (mean score ≥2). The authors reported a significant association between plaque scores and mucositis. The prevalence of mucositis was reported to be 64.6%. Results from another study involving 218 patients with 999 implants in place over a period of 9 to 14 years showed that plaque levels were significantly associated with the presence of mucositis in patients. Regular biofilm monitoring should be considered the standard of care and treatment in the presence of preimplantation mucositis, either by the patient alone or by a medical specialist. Presence or absence of maintenance implant therapy (SIT) Among patients not adherent to regular maintenance therapy (SIT), mucositis was reported to be a common problem in 48% of cases during a follow-up period of 9 to 14 years. Conversely, results from another cohort study with 5-year follow-up showed that implants placed in patients with controlled periodontal conditions and compliance with the SIT program had a 20% prevalence of mucositis. In this study, upon diagnosis of periplantation mucositis, all but one of the implants were successfully treated according to an anti-infection protocol. Results from a 3-month randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial showed that mechanical debridement with or without topical chlorhexidine gel combined with optimal biofilm self-control completely eliminated bleeding in 38% of implants diagnosed with mucositis in a study. In partially edentulous patients with mucositis, combined with lack of adherence to SIT, a higher percentage of cases result in peri-implantitis during 5-year follow-up. The results of this study showed an incidence of peri-implantitis of 18.0% in the SIT group and 43.9% in the non-SIT group, respectively, during a 5-year follow-up. Regression analysis showed that the absence of SIT in the overall patient population was significantly associated with the onset of peri-implantitis with an odds ratio of 5.92. Therefore, therapy for peri-implantation mucositis should be considered prevention of peri-implantitis. Materials and surface characteristics of implant components There is little evidence of the influence of implant surface roughness on the incidence of mucositis in the implant site. A 12-month comparative analysis of patients with treated titanium abutments (Ra = 0.2 µm) and polished ceramic abutments (Ra = 0.06 µm) showed that further reduction in surface roughness had no effect on probing bleeding rates ( BOP). A study in humans has established a relationship between changing abutment and abutment surface roughness and the early inflammatory response of the peri-implant mucosa. Although a statistically significant difference was observed between patients in terms of biofilm accumulation on the abutment surface and inflammatory cell accumulation, no association was observed between the inflammatory response and abutment surface roughness at the 4-week follow-up. Comparing titanium implants and abutments, it was found that zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) implants and abutments have more beneficial properties in terms of biocompatibility. It should be noted, however, that there are no clinically significant differences in BOP values between these materials, and in some cases higher BOP have been reported for ZrO2 constructs compared to titanium abutments. Implant-supported prosthesis design The ability to remove biofilm around implant-supported prostheses plays an important role in the prevention of peri-implantitis. Implants with a supramucosal portion provide a significant reduction in probing depth after treatment of mucositis compared to those with only a submucosal portion. This finding supports previous observations of the relationship between subgingival restoration on natural teeth and periodontal inflammation and attachment loss. The results of a clinical retrospective study showed a large number of implants diagnosed with peri-implantitis due to insufficient biofilm control or lack of oral hygiene access, while peri-implantitis was rarely found in sites where biofilm control and hygiene were not compromised. Therefore, oral hygiene instructions and recommendations should be individually tailored to patients receiving dental implant treatment because mucositis can be considered a precursor to peri-implantitis. In addition, whenever possible, the marginal edge of an implant-supported prosthesis should be placed at or above the mucosal level to facilitate access and control biofilm. Implant structures that impede access for biofilm removal should be corrected or replaced with other prostheses. Dimensions of keratinized mucosa at the implant site The influence of the size of keratinized mucosa at the implant site as an indicator of risk for the development of mucositis has been studied in several human studies. Although some studies have reported higher rates of mucositis in implant sites that have insufficient or inadequate width (less than 2 mm) of keratinized gingiva, others have found no such association. Overall, the evidence for the presence or minimum width of keratinized mucosa around implants to maintain soft tissue health and stability is somewhat controversial. In clinical situations with adequate oral hygiene, plastic surgery with soft tissues in case of their deficiency is not mandatory.
Excessive cement Excessive cement is associated with clinical signs of peri-implantation mucositis. Patients who have a single crown with excess cement show more signs of mucositis compared to those who have the same crowns without excess cement. In addition, mucositis was more prevalent in patients with cement-retained prostheses compared with those with cement-screw fixation. Therefore, to avoid excess cement, the edges of the restoration should be positioned at or above the mucosa or the restorations should be cemented to custom abutments to ensure proper removal of cement.
Drugs that cause
It has been proven that some drugs (cytostatics) have a negative effect on the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium. Medicines destroy them, leaving behind ulcers on the mucous membranes.
Drugs that have a toxic effect include:
- doxorubicin, epirubicin;
- cyclophosphamide, procarbazine, embiquin and other alkylating agents;
- taxane group;
- antibiotics used in oncology;
- vinca alkaloids;
- antimetabolites: fluorouracil, thioguanine and others.
All these drugs and medications belonging to the above groups cause collagen destruction and epithelial dysplasia in the oral cavity.
Under their influence, cells of the immune system are suppressed, saliva loses its protective properties, and the mucous membrane suffers.
What factors increase the likelihood of development?
Mucositis does not appear in people who have persistent protective properties of the body . Health care professionals have identified risk factors for oral mucositis.
The development of this disease depends on the type of antitumor treatment used, its intensity, and the order of its implementation. If a person is undergoing combination therapy, the likelihood of developing mouth ulcers increases.
Recently, genetic predisposition has been identified as a risk factor for mucositis..
This component has not been fully studied, but experts do not deny that heredity plays an important role in the frequency of stomatitis and its intensity.
Complications
With insufficient oral hygiene in patients with mucositis, a secondary bacterial infection is observed, which is clinically manifested by suppuration of ulcers and an increase in intoxication syndrome. In persons with severe immunodeficiency, generalization of the infectious process with the development of sepsis is noted. Restriction of oral nutrition during mucositis leads to a progressive decrease in body weight up to cachexia, which is accompanied by the formation of irreversible dystrophic changes in the internal organs.
We invite you to read Temporomandibular joint pain: symptoms and treatment of inflammation and dysfunction of the jaw joint
Differential diagnosis of oral diseases
The formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa is not always associated with undergoing chemotherapy or other types of cancer treatment.
There are other reasons and diagnoses for which aphthae appear on the oral mucosa .
Let's look at them in the table.
| Disease, medical definition | Causes | Symptoms and test results | Course of the disease | Principles of disease treatment |
| Oral mucositis | Antitumor radical treatment | Erythema, ulcers on the mucous membrane, pain when chewing | Many patients have grade 3 and 4 toxicity | Pain relievers, medicated mouth rinses |
| Aphthous stomatitis | The main cause of the disease has not been identified | A small number of aphthae on the mucosa (2-3) | The ulcers are not widespread throughout the mucous membrane, there is pain, severity level – 2 | Local agents, cauterizing solutions |
| Herpes mucositis | Herpes virus | A small number of white spots in the mouth | Stage 1-2 toxicity | The use of drugs against the herpes virus |
| Oral candidiasis | Candida fungus | With a low intensity of pain, there are quite a lot of white plaques in the mouth | Toxicity is not great - stages 1-2 | Antifungal drugs are used; nystatin drugs are effective |
| Mechanical damage in the oral cavity | The main reason is installation, adaptation to dentures | Redness, swelling of the affected area | The degree is not determined, the patient has difficulty eating | Replacing dentures, getting used to them |
| Gangrenous stomatitis | Infection caused by bacteria | Pseudomembrane with tissue death | The grade is not defined, but in rare cases it is classified as 3-4 | Antibiotics, local antibacterial agents |
| Necrotizing stomatitis in acute manifestations | Occurs due to the proliferation of bacteria, the body is not able to fight them due to low immunity | High body temperature, acute pain, bleeding ulcers | Hard to tolerate, toxicity grade 3-4 | Inpatient monitoring, use of antibiotics and immune-stimulating drugs |
Mucositis – the best of the worst
Mucositis after implantation is also a common problem, although not as serious as peri-implantitis. This is the initial stage of implant rejection, when only soft tissues become inflamed and the bone is not affected.
How does mucositis manifest:
- erythema - redness;
- thinning of the mucosa at the site of inflammation;
- hyperplasia - swelling of the gums;
- ulcers on the inside of the cheeks and gums;
- white spots on the mucous membrane are a symptom of the death of soft tissue.
Painful sensations while eating, increased body temperature, malaise, dry mouth, and weight loss also accompany dental mucositis. The disease rarely leads to the loss of an implant, but the danger is different: with advanced mucositis, the mucous membrane in the mouth is so inflamed that the patient cannot even swallow, nutrition is only possible through a tube.
Recommendations for the treatment and prevention of OM
To treat patients with oral mucositis, a complex of measures and drugs is used to promote wound healing, restoration of mucosal tissue and increased immunity.
As OM progresses, medications are used that reduce the intensity of the main symptoms, reduce the inflammatory process, and swelling.
Antibacterial agents are prescribed to prevent complications.
Oral care rules
To increase the effectiveness of mucositis treatment, you need to follow a few simple rules for oral care :
- It is important to drink 2-3 liters of fluid per day to remove toxins from the body.
- Before going to bed, after eating any food, it is necessary to brush your teeth and gums to prevent the spread of bacteria in the oral cavity.
- Constantly rinse your mouth with medications.
- If there is pain, the dentures must be removed and cleaned at rest.
- Monitor the condition of the mucous membrane, look at the effectiveness of treatment.
- Lubricate lips.
How oral sanitation is carried out and what it is, we will talk in the next publication.
In this article we will talk about the causes of increased salivation during pregnancy.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/krasota-i-uxod/opolaskivateli/obzor-dlya-polosti-rta-lesnoy-balzam.html we have collected reviews on the effectiveness of the Forest Balsam mouth rinse.
What foods to eat?
In order not to harm the treatment, you need to avoid damage to the mucous membrane and the effects of various products on the ulcers .
It is important to remember such moments:
- Alcohol can increase damage to the mucous membranes; it should not be consumed, like all alcohol-containing substances.
- Do not eat foods that are too hot, spicy or hard.
- It is unacceptable to drink hot or cold; all food and drink must be warm.
- Acidic drinks can worsen the condition of the mucous membrane.
- Food should contain a lot of protein, high calorie content is undesirable.
Medications
- Special gels or sprays are prescribed to relieve pain ; antiviral oxolinic ointment can be used.
- Interferon-based drugs are used to enhance immunity .
- Enzymes are also actively used ; they help cope with necrotic plaque on ulcers.
- is effective in the fight against ulcers and pain - due to the absence of its interaction with food, it is active for up to 8 hours.
For recommendations on the use of another drug used to treat mucositis, see the video:
To achieve the effect, along with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, antibacterial and painkillers, patients also use medicinal recipes of traditional medicine.
Cotton swabs with various tinctures and ointments are applied to the affected areas of the oral mucosa.
Painful mouth ulcers after anticancer treatment are not uncommon. Against the background of weakened immunity, ulcers can quickly increase in number and size. There is a high probability that they will become infected.
In this case, the course of the disease and the toxic effect from it can cause irreparable harm to human health and life. Therefore, when they appear, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor to diagnose the disease and treat it.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags inflammation infection care ulcers
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
How the T4A trainer works, design features, indications for use
Next article
What is the Bruckle apparatus and what is it intended for?
Prognosis and prevention
The outcome depends on the severity of local manifestations and the general condition of the patient. Since mucositis develops against the background of severe oncological pathology, the prognosis is determined by the severity of the underlying disease. Most patients experience improvement during treatment, with preservation of pathological lesions in the oral cavity.
To prevent mucositis, it is necessary to rationally choose regimens and dosages of antitumor drugs, conduct an examination of the oral cavity and treat carious teeth before each course of chemotherapy, and monitor the correct selection of dentures. During the course of treatment, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with antiseptics, cryotherapy before taking chemotherapy, and the prophylactic use of derinat-lidocaine gels.