Poor quality filling materials as a cause of discoloration
Everyone knows that white teeth look beautiful and healthy, and even a natural, slightly yellow color does not spoil the appearance.
But everything changes when the enamel darkens, and strongly and noticeably. Of course, you shouldn’t worry if your teeth darken after eating blueberries or bird cherries or eating other foods with food coloring. Sometimes the enamel can not only darken, but also become red, brown and even transparent. This happens when installing fillings containing tin, silver or resorcinol-formaldehyde. Such filling materials are considered obsolete; modern materials do not change color.
Also, the pigmentation of the crown can be affected by a filling, the materials for which were stored in violation of the conditions. Such substances quickly enter into chemical reactions with dentin, with saliva or food, which leads to a change in the color of the surface.
Blue tooth: normal or not?
If you once discovered a flaw in your snow-white smile in the mirror, then you should immediately think about the reasons for its appearance. A person can develop a blue tooth for many reasons. Some of them are pathological, while others are absolutely normal. Let's look at the main reasons why a blue tooth suddenly darkened your appearance.
The reason that you have a blue tooth may be due to regular food. Berries such as blackberries or blueberries give a similar color to the enamel. Also, some varieties of grapes and their juice can have a similar effect. It is worth noting that in these cases you will not have just one blue tooth, but the entire enamel will be stained. The supplied fillings will get a more intense color.
A blue tooth in a child or an adult can appear as a result of treatment. Some antibacterial drugs lead to such a reaction. Antimicrobial drugs of the tetracycline series are especially often the cause.
A blue tooth may appear if its roots die off. Often this problem is caused by gum diseases, such as periodontal disease. Root destruction occurs gradually and ends with tooth loss.
Problems in the body
Tooth enamel may turn blue due to certain problems in the digestive system. In this case, you will not be able to solve the problem on your own. Use the services of doctors.
Possible complications
If a child’s gums turn blue or black, this may be a consequence of anemia, gingivitis and stomatitis, and not the actual eruption of baby teeth.
If the black or blue areas of the gums are more than 2 cm, you need to see a doctor. A black hematoma indicates stagnant blood. A bruise this large can cause high fever and pain. Treatment in this case will be an incision in the blue gum, from which the blood is released. It is necessary to ensure that it does not become infected and suppuration begins.
Causes and symptoms of gum discoloration independent of tooth growth:
- A symptom of anemia is a change in the color of mucous membranes. This disease is caused by a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Other signs: decreased appetite and cold extremities. A bluish tint will appear near the lips, eyes and nose. This condition occurs in children due to a lack of iron in the body.
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of a child. Usually manifests itself with poor oral hygiene. The gums turn blue, bleed and itch. When teeth come in, the gums are injured, and the wound can fester.
- With stomatitis, not only the gums are blue, but also the entire oral cavity. Stomatitis is similar to gingivitis and develops against the background of a child’s weakened immune system. Ulcers may appear.
As already mentioned, with minor and not very long-lasting blueness, parents have no particular cause for concern. However, under no circumstances should we let things take their course. Firstly, damage to tissue and blood vessels in the gums can lead to various complications. And secondly, turning blue may not be so harmless.
The most serious and undesirable thing may be suppuration. It appears in the following cases:
- when the bruise does not go away for a long time;
- infection gets into the wound.
This development of events is possible against the background of reduced immunity in the child and insufficiently strict adherence to oral hygiene. As part of the prevention of suppuration, all toys, teethers and everything that may end up in the baby’s mouth must be clean.
If suppuration does begin, you should consult a doctor.
Conservative or surgical methods can be used to treat suppuration. The first is prescribed for a small hematoma, suppuration in the initial stage and the absence of complications. The second is if the hematoma is very large and interferes with normal teething.
- suppuration;
- compression of adjacent tissues;
- the formation of a benign neoplasm;
- cyst formation.
The inflammatory process develops in children with poor immunity and malnutrition. In this case, the process often spreads to adjacent areas of the face, causing widespread inflammation.
Most often, the bruise resolves after 2-3 weeks. If the hematoma does not disappear for a long time and tends to increase, and there are accompanying symptoms, then it is better to go to the clinic.
We suggest you read: Can a maxillary sinus cyst resolve on its own?
The following symptoms are reasons to visit a dentist:
- the size of the hematoma is more than 2 centimeters;
- prolonged increase in temperature above 38 degrees;
- the baby's moodiness and anxiety;
- signs of suppuration;
- bowel dysfunction;
- white or yellow plaque in the mouth;
- poor appetite;
- vomit;
- rash or erosion on the mucous membrane.
The nature of these symptoms indicates the addition of an inflammatory process or infection. A change in the color of the hematoma to a darker color indicates blood stagnation.
If the examination reveals an abscess, a minor operation will be performed to remove it under local anesthesia. The contents are washed out through the dissected surface and treated with antiseptic drugs. After the procedure, antibiotics and wound treatment are prescribed.
Important! You should not open ulcers yourself at home. The danger comes from injury to the mucous membrane and infection in the baby’s oral cavity.
The formation of pus and inflammation is likely due to non-compliance with hygiene standards. Thorough washing of fruits, vegetables, hands and toys will help avoid a painful procedure.
At the time of teething in an infant, careful observation and care is necessary. This will help the baby get through difficult times easier.
Blue gums during teething sometimes indicate the presence of pathology. It could be:
- hematoma requiring medical intervention;
- anemia;
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis.
If the bruise is more than 2 cm in diameter, then you should consult a doctor. This hematoma is often dark, almost black, due to accumulated blood. It is accompanied by fever and local pain. The doctor makes an incision and releases blood to avoid the development of pathology. Otherwise, it can lead to suppuration, inflammation or cyst formation.
Anemia is caused by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, which causes changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes. Blue discoloration will be noticeable not only on the gums, but also in the area of the lips, nails, and eyes. Anemia is also indicated by: weakness, loss of appetite, susceptibility to infections, cold extremities. This condition is usually caused by a lack of iron and occurs regardless of whether the tooth is erupting at the time or not.
Gingivitis is an inflammatory process in the gums. It usually occurs due to insufficient oral hygiene and is accompanied by itching, bleeding, and swelling. If the child already has teeth, then gingivitis can be caused by carious teeth, mechanical injuries, malocclusion, or a weakened immune system.
Stomatitis is another type of inflammation of the oral mucosa. Sometimes there is a blue tint against the background of redness, which affects not only the gums, but also the oral cavity. It, like gingivitis, is usually caused by the penetration of pathogens into weakened or damaged mucosa and is accompanied by ulcers and pain.
The fact that the gums turn blue during teething may indicate various diseases, while often remaining within the normal range. It is necessary to monitor changes in the child’s behavior and well-being, then it will be easier to determine the root cause of the deviations and take action if necessary. Children do not yet have a strong enough immune system, so it is important that from the first days of life they receive everything they need to develop it. Pediatric dentistry will help clarify any questions and doubts that arise when teeth begin to cut.
What are baby teeth used for?
How does a child cut teeth?
Important: The formation of a cyst or other formations occurs when the blood is not absorbed, and a membrane is formed around the hematoma and its contents are replaced by connective tissue.
Causes of darkening of tooth enamel in adults
To begin with, it is worth remembering that the color of a tooth is given not only by the enamel itself, but also by the dentin that lies underneath it. Therefore, the reasons for the change in surface color may lie deep inside. These include:
- untreated or recurrent caries, as well as other dental diseases,
- penetration of filling materials into the pulp,
- the presence of pins inside the crown, which can be visible through filling materials (for example, after restoration),
- pulp necrosis or absence,
- hemorrhage as a result of injury, impact, when blood penetrates the porous structure of the bone,
- smoking: tobacco tars settle on the surface layer by layer, which over time leads to severe darkening of the enamel,
- prolonged or uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs (especially tetracycline),
- metabolic disorders in the body and, as a consequence, acid-base imbalance in the oral cavity,
- some gastrointestinal diseases,
- overdose of chemicals (for example, zinc or fluoride),
- frequent consumption of black tea or coffee with insufficient or improper oral hygiene.
All of the above reasons can cause discoloration of the enamel, some of them are quite rare. This article discusses the most common cases.
Some lesions of hard tissues in the oral cavity are asymptomatic in the first stages, so the patient often does not know that he has a problem. Often, it is the darkening of the unit that indicates the presence of a problem. Let's take a closer look at them.
The most common of these problems is tooth decay. Under the influence of bacteria, the protective layer of the crown is destroyed, and the infection penetrates inside. There, the destruction continues, although the outside of the crown may look quite healthy. But when the affected area turns black, this blackness will begin to show through the enamel, and the tooth will appear to have darkened.
Treatment of caries consists of cleaning the hard tissues of the crown from the affected ones, after which the cavity is filled. Sometimes enamel bleaching is required to restore the crown to its original color.
Pulpitis
An acute disease is very easy to detect - by acute pain. In this case, as a rule, the tooth does not have time to change the shade. But if the inflammation has reached a chronic stage, then the pulp (nerve) gradually dies, which can affect the shade of the crown enamel - it becomes purple or gray. The tooth from which the nerve was extracted can also change color - we will discuss such situations in more detail below.
Periapical (that is, located at the apex of the tooth root) granuloma is a consequence of inflammation of periodontal tissue. Inflammation can occur against the background of pulpitis (when the infection penetrates into the soft tissues surrounding the tooth, from above, through the pulp) or against the background of periodontitis (arising from other infectious diseases or as a result of injury). The granuloma begins to grow and compress the surrounding tissue, which is why the unit stops receiving nutrients, darkens and begins to hurt.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with When a child’s teeth come out table
Modern medicine makes it possible to save a tooth using conservative antibacterial treatment or surgery, during which the granuloma is removed along with the root or part of it.
A radicular cyst is a “sac” of serous fluid that is localized at the apex of the roots. The cause of its appearance is chronic periodontitis or granuloma. The causes of periodontitis, in turn, can be any inflammatory processes in soft tissues, caused, for example, by sore throat or sinusitis, tissue trauma, a general decrease in immunity, as well as painful eruption of “eights”.
Radicular cysts are usually treated with surgical methods: cystotomy (opening the cavity and removing its contents) or cystectomy (removing the entire cyst).
The so-called everyday causes of long-term changes in enamel color include the formation of “smoker’s plaque” or “coffee-lover’s plaque.” The fact is that after each meal, bacteria remain on the surface of the crowns, which multiply in the acidic environment of saliva. Over time, this plaque covers the enamel with a dense layer, into which food dyes (when drinking coffee, strong tea, red wine) or tar (when smoking) are absorbed. And even if you brush your teeth after every cigarette you smoke or cup of coffee you drink, it is still impossible to stop the formation of plaque.
Here is a list of products containing natural or artificial dyes that, when consumed daily, can affect the color of the enamel:
- juices (unclarified grape, tomato, pomegranate, cherry),
- sparkling water,
- caramel, lollipops, other sweets,
- soy sauce, ketchup,
- beet,
- berries (blueberries, blackberries, cherries, bird cherry, honeysuckle).
Treatment in this case is carried out using professional hygiene: plaque is removed, and the teeth are whitened, ground and polished.
Of course, the front and back teeth sometimes become darker due to smoking, or when coloring pigments penetrate the enamel. For example, there is no point in worrying if your tooth turns dark after eating blueberries. But if the color of a tooth is radically different from the rest, this is most often a signal of problems inside the tooth. A tooth may darken after an impact, or after removal of a nerve. It is worth remembering that not only the enamel, but also dentin, the next layer underneath, is responsible for the color of a tooth. If the color of dentin has changed, then
the blackness or blueness of the tooth will still show through the enamel. The teeth themselves turn black for the following reasons:
- advanced caries (including secondary);
- staining the pulp with materials used for filling;
- transillumination of pins under the filling;
- pulp necrosis;
- wrong treatment.
It is important to know whether the darkening of the tooth was caused by any intervention or whether it happened on its own. For example, if this was preceded by injury, nerve removal or filling, this could be the reason. If a tooth without a nerve darkens after the canals have been filled, this may indicate that the nerve removal was not carried out correctly.
When a tooth no longer has a nerve, it is considered dead. Its pulp is deprived of nutrition, and therefore self-healing does not occur. Such teeth most often crumble and become brittle. A tooth may darken after improper root canal cleaning if the doctor missed any remaining organic matter there. Organic matter begins to decompose, dentin begins to darken and, accordingly, stains the dead tooth.
In no case. Not a single attempt to cure bad teeth on your own using “grandmother’s methods” has led to success. Rather, in this way you can only bring the problem to an extreme case, when an innocently darkened tooth can cause infection of the entire body and even hospitalization.
Rinsing with herbs, applying propolis to the affected tooth, various homemade ointments - all this can be considered as part of prevention, but not as the main method of treatment. It is strictly forbidden to warm up a diseased tooth with a compress, as sympathetic neighbors advise. If the cause of darkening is an infection, then in the warmth it will bloom wildly.
One way or another, if the tooth is darkened and hurts, you cannot do without a visit to the dentist.
The dental specialist, in turn, must find out the cause of the darkening based on the patient’s history and clinical picture,
After which he will establish the correct treatment tactics.
If the cause of darkening is just caries, then treatment will be easiest. The dentist will remove the affected tissue, select the correct shade of restoration material and treat the tooth. In the best case scenario, the tooth will remain alive and will no longer cause aesthetic or physical problems.
We suggest you read: The child’s gums have turned blue and swollen
If the tooth is considered dead (for example, the nerve died on its own or had to be removed), treatment will require an individual approach. It is no longer as strong as natural teeth, which means that other treatment methods must be selected.
And although modern dentistry already knows a lot of techniques that can restore your smile to its original appearance, the best way to avoid dental problems is their prevention, that is, maintaining oral hygiene, proper diet and avoiding traumatic situations.
If a tooth darkens, the following treatment options are possible:
- intracanal bleaching;
- restoration;
- veneers;
- crown.
Why can gums be blue?
The process of teeth emergence itself is associated with damage to the gum tissue and mucous membrane.
The oral cavity is one of the most blood-supplied areas, therefore it contains many small vessels. When damaged, they rupture, blood flows into the gums and accumulates in it.
Blue gums in a baby during teething
As a result, multiple hematomas are formed under the mucous membrane, due to which it acquires a bluish tint.
In addition, during the process of eruption, the blood vessels dilate and blood flow to them increases. Translucent through the mucous membrane, they give the gums a blue color.
In most cases, this process does not require intervention and the pathological changes go away on their own over time.
During this period, the child can be given carrots in small pieces or other dense foods, which will promote rupture of the mucous membrane and help teething. Small accumulations of blood resolve on their own.
You should definitely see a doctor when:
- the hematoma does not go away within 3 days or more;
- high and prolonged temperature;
- severe pain;
- The general condition worsens, that is, weakness and loss of appetite occur.
In other cases, you can get by with a preventive examination. Treatment depends on the complication - the contents of large hematomas are released through a small incision in the gum. Abscesses are also removed surgically.
There are several reasons that can provide a rational explanation for this phenomenon.
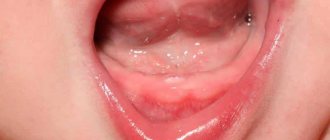
Blue gum during eruption. Photo.
A child’s gums may turn blue for the following reasons:
- when teething;
- if you are injured while playing or falling;
- inaccurate dental treatment.
The bruise is accompanied by slight swelling, soreness and blue discoloration of the affected area of the gum. Usually hematomas go away on their own and do not require serious intervention or assistance. To relieve severe pain, you can give your child painkillers and apply cooling compresses. On average, healing time depends on the severity of the damage and can range from three days to a couple of weeks.
Cyst (blue lump)
Most often, a cyst develops in babies during the teething period, but it can also be caused by inaccurate dental intervention. When a cyst forms, the gums detach from the bone and form a kind of pocket, which gradually fills with blood and pus. In appearance, the cyst may resemble a blue bulge or bump. If you find such a growth in your child’s mouth, you should immediately show it to the dentist.
Gingivitis
Another cause of blue gums is gingivitis. This is an inflammatory disease that is very often found in young children who are unable to provide normal hygienic oral care. In this case, in addition to blue gums, additional symptoms may be observed, such as:
- sore gums;
- bad breath;
- bleeding;
- increased reaction to hot or very cold foods.
Blue lump near an extracted tooth.
Teething in a child is an important stage in the development of the body and at the same time a very difficult period.
Swollen gums during teething in a child
The first symptoms of teething appear at about four months. The lower incisors usually appear at 7–12 months. At 16 months, the child's lateral incisors should emerge. The canines and first molars will grow when the baby is 1.5–2 years old. By the age of two, all baby teeth will appear. Parents should consult a doctor if at the age of 6 months the child does not have a single tooth.
Teething in a child is a rather difficult period not only for babies, but also for their parents. Not only does the baby become restless and capricious several weeks before the tooth appears, but the process itself can be accompanied by various alarming symptoms. One of these symptoms is often blue gums during teething.
As a rule, in 90% of cases, a bruise on the gum goes away on its own, without any treatment - after the long-awaited tooth appears, it gradually resolves.
To reduce pain and reduce the risk of additional injuries during teething in a baby, during this period you can use various ointments and gels and massage the gums.
Special gels, due to the lidocaine included in their composition, have a good analgesic effect. Sometimes, for additional cooling of children's gums, mint is also added to the preparations, which, in addition to the anesthetic effect, gives them a pleasant taste.
In addition, pharmaceutical products have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects, preventing various pathogens from penetrating dental wounds.
The modern range of such products is quite wide, among them “Kalgel”, “Dentinox”, “Kamistad”, “Cholisal” and others.
As for massage, the gums can be periodically massaged with your finger. In this case, it is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of your hands - before starting the procedure, you should carefully cut and clean your nails, wash your hands and treat them with an antiseptic.
The massage consists of light stroking movements. They should start a little further from the eruption area, then slowly move towards the place where the tooth should appear. At the same time, experts do not recommend touching the cutting surface itself.
The massage procedure can last up to 15 minutes (there may be breaks during the process so that the child gets used to it).
Gel teethers can also be used as massagers. But doctors strictly prohibit giving solid food to a child so that he can “scratch his teeth.” It can not only injure the gums, but also increase the risk of hard pieces getting into the respiratory tract.
Unfortunately, bluish gums can appear not only when a baby is teething. Gums may change color due to anemia, stomatitis or gingivitis.
- Anemia – with this pathology, the blue color of the gums is associated with a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Lethargy and apathy of the child will allow you to distinguish anemia from other causes. The baby may also develop cracks in the corners of the mouth and peeling skin. Often, not only the gums, but also the whites of the eyes, earlobes, and even the baby’s delicate skin can acquire a bluish tint.
- Gingivitis is characterized by changes in the color of the gums in limited areas directly next to the teeth.
- Stomatitis - with this disease, the gums do not have a pronounced blue color. There is only a bluish tint against the background of quite strong redness. A distinctive feature of stomatitis is a change in color of the entire mucous membrane of the oral cavity, and not just on the gums.
In addition, gums can change color as a result of not very careful treatment, injury (the baby fell unsuccessfully or chewed on an object that was too hard), as well as due to various characteristics of the child’s body.
Teething is an important event in a child’s life, as during this process baby teeth appear or are replaced by permanent molars.
During this period, various changes may appear, hematomas changing the color of the gums, often frightening parents.
Therefore, blue gums during teething may have a character corresponding to the condition.
All children go through an unpleasant period when they are teething. Special teething gels do an excellent job of relieving discomfort.
Another remedy that helps a child survive the difficult period of the appearance of his first teeth is candles. You can read how to use them and which products are recommended more than others here.
The acquisition of a blue tint by the gums at the site of the eruption of a new tooth is called cyanotic. Its appearance is associated with squeezing or rupture of small blood vessels when the tooth moves to the surface of the gum. If the area of blueness is small, this situation usually does not require any intervention.
If the blue area of the gum is large, the child should be shown to the dentist, as this may be a sign of hematoma formation. You should go to the clinic with your baby so that the doctor will make a small incision and release the blood that has collected under the surface of the gum.
We suggest you read: How to treat an ulcer on a child’s gums
To alleviate the baby’s condition, it is recommended:
- Local anesthesia using drugs specially designed for this purpose in the form of gels. They relieve inflammation and have an anesthetic effect.
- Using teethers. Thanks to the ability to chew on such toys filled with water or gel, the child relieves itching in the gums, and a decrease in pain and swelling is achieved by cooling the teethers in the refrigerator. A gentle massage performed by the mother with clean fingers wrapped in a sterile bandage also relieves pain and itching in the gums.
- Taking antipyretic drugs. Such medications, often represented by ibuprofen or paracetamol, eliminate pain, reduce gum soreness and lower body temperature if it has risen during teething.
- Use of traditional medicine. Children with teething are recommended to wipe their gums with decoctions with an anti-inflammatory effect. Chamomile is often used to prepare them, but mint, lavender, sage, and lemon balm can also be added. Another popular way to help a child teething is to treat the gums with a soda solution. Pour a teaspoon of soda into a glass of boiled, non-hot water and stir. Next, you need to soak gauze wrapped around your finger in the prepared product, and then wipe your gums.
Removing a darkened tooth
The pulp is a connective tissue with a large number of nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels. With its help, the tooth receives nutrition, has the ability to self-heal and fight infection. However, if it is deprived of its pulp, it will stop receiving nutrition, become weak, darken (because there is no nutrition) and eventually crumble. Dentists call such units dead.
Depulping (pulp removal) is a necessary procedure for cleaning root canals in case of pulpitis. However, it happens that the pulp dies without external influence - due to various bacterial lesions that were not treated in time. Thus, it not only stops nourishing the tooth, but also becomes a source of infection, which can affect not only the crown tissue, but also the gums and even the jawbone.
In addition, the color may change due to incorrectly selected root sealing paste. Very often, after filling, such a tooth becomes gray or slightly yellowish, sometimes purple, depending on the color of the paste.
Since dead teeth cannot receive nutrition through the roots, doctors resort to intracanal whitening (endo-whitening). To do this, the dentist opens the canal, cleans it well, and then fills it with whitening gel and closes it with a temporary filling. If the degree of blackening of the unit is large, then the procedure can be repeated after two weeks (but no more than four times in a row).
Another way to solve the problem is to install veneers (lumineers). These are plates that the doctor glues to the visible side of the crown with special glue. Modern dentistry offers a large selection of veneers made of ceramics, zirconium, and composite materials. However, this method of treatment has its contraindications (gum disease, mobility or destruction of the unit, etc.), which should be taken into account when discussing tactics for treating darkened enamel.
Making a crown is another common method of treating darkened, pulpless teeth. It allows not only to restore the unit’s aesthetic appearance, but also to protect it from further destruction. The tooth is ground, polished, and then, using a plaster cast, the dentist makes a crown, which is then placed on the prepared unit.
Restoration is a labor-intensive and short-lived way to solve the problem. This method is based on the fact that the darkened part of the crown is covered with filling material, restoring the aesthetics of the smile. However, the service life of such fillings is short, and the procedure must be repeated again and again.
This is the most radical method of solving the problem, but sometimes it is the only possible one. Removing a unit cannot be avoided in the following cases:
- the crown split, and the split went deep under the gum. If the roots are strong enough, then doctors remove only the supragingival part, and install a pin in the root canal and prosthetize with a crown made of filling materials,
- the tooth is loose, and the gums are injured or bleeding,
- more than 2/3 of the crown is destroyed,
- inflammation of soft tissue or bone (as a rule, in such a situation the tooth is a source of infection).
If the enamel has darkened due to exposure to food dyes, then the use of whitening pastes can get rid of the unpleasant color, but if the consumption of coloring products (black tea, coffee, red wine, soy sauce, etc.) occurs constantly, plaque will form again and again, and the paste will stop helping. The only way out is to do professional hygiene in a dental clinic.
In all other cases, it is impossible to restore the healthy color of the enamel using home remedies. It is important not to delay your visit to the dentist in order to start treatment on time.
Useful video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_KMQo_N3_eU
Thus, blue gums during teething in most cases is a manifestation of a physiological process that needs to be monitored so as not to miss possible complications.
Some babies cut their teeth with great discomfort for the baby, while others “peck” painlessly and almost unnoticed by their parents. Moreover, in all children, the main signs of the appearance of a new tooth are increased salivation and local changes in the oral cavity. Let us dwell in more detail on the changes in the gums that occur during normal tooth eruption, as well as on possible problems with the gums during tooth growth.
The appearance of the first tooth is a significant event in your baby’s infant life! How does a tooth erupt?
A child's gums begin to change long before the tooth emerges. Their tissues become looser and change color. The gums in the place where the tooth will soon appear swell and increase slightly in size. As for the color change, in most cases there is redness, but in some babies the color may be bluish, burgundy or dark purple.
When the erupting tooth comes close to the surface of the gum, parents see a white dot. It is a tooth visible through thinning gums. This is followed by the final stage of eruption, during which the crown of the tooth passes through the gum and the tooth is freed from its tissues. This is helped by the enzymes present in the child’s saliva, which literally “melt” the gum and give the tooth the opportunity to appear on its surface.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with what does plaque on an adult’s tongue indicate?
Saliva promotes the rapid emergence of the tooth crown from the gums of the baby. When changes in the gums appear during teething
The process of tooth eruption through the gum takes from one to three days, however, moderate swelling of the gums and increased salivation can be observed 2-4 weeks before the tooth erupts on the surface of the gums. The baby feels itching and, in order to relieve it, begins to pull various objects into his mouth. During this period, the risk of gum injury and infection increases.
Teething is a very painful process that causes a lot of tears in the baby. Why can gums be blue?
Why might gums turn black?
The acquisition of a dark color by the gum through which the tooth is cut, which can be blue, purple, crimson or even black, is associated with the formation of a hematoma or eruption cyst in its tissues. Such manifestations look quite frightening, but often do not cause much discomfort to the child and do not require medical intervention.
The appearance of a cyst or hematoma is most often observed when chewing teeth erupt, and a little less often when fangs or incisors are cut. In the baby’s mouth, parents notice a large formation in the form of a dark ball on the gum. It occurs when a tooth moves up through the gum and injures its tissue, rupturing blood vessels.
To ease your baby’s suffering, be sure to buy a high-quality teething toy.
Depending on the results of the examination, the doctor may recommend allowing the child to chew hard objects that can speed up the tooth’s breakthrough of the mucous membrane and get rid of the hematoma, for example, a teething toy, carrots or crackers. During chewing and physical impact on the gum, the mucous membrane breaks through faster and the tooth comes to its surface.
What to do if you have gum inflammation?
When to see a doctor
Parents should constantly examine the baby’s oral cavity during teething and monitor the general condition of the baby. Indications for seeking medical help are:
- The appearance of a hematoma on the gum.
- Temperature rise above 38°C.
- The appearance of severe diarrhea or repeated vomiting.
- Formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa.
- The appearance of white spots or a cheesy white coating on the mucous membrane.
- The appearance of a blistering rash in the child’s mouth.
- The appearance of a pronounced cough.
- Constant crying of the child.
- The appearance of a runny nose with yellow or greenish discharge.
In difficult cases, do not delay seeing a dentist! This will help avoid a lot of problems in the future.
About the first teeth, see the program of Dr. Komarovsky.
Teething symptoms
Atypical manifestation of tooth growth
Possible pathologies
The appearance of a hematoma
Subscribe Stay up to date with new products on our site
The discovery of a blue spot on a child’s gum raises many questions and even concerns among parents. In some cases, this condition is accompanied by pain, and sometimes it is completely asymptomatic. What can cause such a problem and what help should be provided to the baby?
Contact your dentist
If after all hygiene procedures the blue color of the tooth has not disappeared, then you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. Contact your dentist. The doctor will examine the stained tooth and take an x-ray if necessary. After this we can already talk about treatment. If the root is damaged, the pathological shoot will have to be removed. If everything is not so serious, then the dentist will offer you a suitable correction plan.
We suggest you read: Jaw crunches and hurts what to do
If a specialist (dentist or dentist) does not find a pathology in his area, you need to contact a therapist. If you have recently taken certain medications, be sure to tell your doctor. The doctor may ask you to undergo basic tests. They will help you understand the situation and prescribe the appropriate correction. In most cases, the pathological symptom disappears after a few days of treatment.
Treatment options
The choice of one or another treatment method is made by the attending dentist based on the diagnosis and visual examination of the small patient.
If you are sure that the bruise on the child’s gum is the result of an injury, you can try to provide the child with first aid, which consists of using the following methods:
- applying cold compresses to the injured half of the jaw;
- rinsing the mouth with decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the bruise does not resolve for a long time (more than 5 days), and the main symptom is accompanied by severe pain and a rise in temperature, then most likely an inflammatory process has begun deep in the gums. In this case, medical assistance is necessary, which may include both the use of medications and surgical intervention.
Treatment of the cyst is prescribed by the dentist after examining the child. There are two ways to do this:
- if the cyst formed during teething. In this case, experts recommend using special teething toys that help break the tissue and speed up the process of tooth extraction. If this technique does not help, and temperature is added to the main symptoms, it is possible to use the technique of dissecting the upper layer of the mucosa;
- if the cyst is large and accompanied by pain. In this case, the surface of the “blue bump” is usually dissected and the bloody or purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and washed. In some cases, complete healing may require several visits to the dentist.
Medicines are usually not prescribed for blue gums. The only exceptions are those cases when the hematoma is accompanied by the formation of an abscess and an increase in body temperature.
Teether toy
Treatment of gingivitis
In this case, experts recommend resorting to plaque removal and prescribing anti-inflammatory rinses. In some cases, antibiotics are used as a rinse solution.
Painkillers
If the blueness is accompanied by severe pain, the child can be given painkillers. The most popular are “Ibuklin”, “Ibufen”, “Nurofen” and many others. In addition, you can use analgesics in the form of suppositories, for example “Viferon” - suppositories that, in addition to pain relief, have an antiviral effect. In addition, you can use special dental gels:
- "Holisal";
- "Kamistad";
- "Baby Doctor"
It is worth understanding that any home therapy must be fully agreed with the attending dentist. In addition, sometimes experts themselves recommend supplementing the basic treatment with some folk recipes.
If the child is already quite independent and knows how to rinse his mouth, then this method will help to significantly speed up the process of relieving swelling and pain. The best options for preparing infusions are chamomile and calendula, which have an antibacterial effect.
To prepare the mixture you need:
- take 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile or calendula flowers;
- pour a glass of boiling water and leave for about an hour;
- Cool the infusion and strain.
You can rinse your mouth 4-5 times a day or after each meal.
Infusion of chamomile.
Such toys are sold in all pharmacies and children's stores. The teether contains distilled water inside, which allows you to significantly cool the toy by putting it in the refrigerator for a few minutes. This teether not only speeds up the process of teeth appearing, but also relieves swelling due to the cooling effect.
Applying compresses
Cold compresses help relieve swelling and inflammation. They have a special effect in the case of hematoma formation during dental surgery. To do this, you can take several lud cubes wrapped in a clean cloth and apply them for a while to the cheek or lip located above the injury.
Taking medications
Darkening of the enamel is a side effect of some medications. Most often these are drugs that are prescribed for iron deficiency anemia (Fenuls, Totema, etc.). They contain gluconates of manganese, copper and iron dihydrate, which cause tissue pigmentation, and since the drugs are used in liquid form, the teeth are the first to take the blow.
Another group of drugs that can deprive crowns of their natural color are tetracycline antibiotics. Most often, this pathology manifests itself in children whose mothers took oxytetracycline, metacycline, minocycline, etc. during pregnancy.
Fluorosis (excess fluoride)
Despite the fact that fluoride is an element that ensures the health of tooth enamel, its excess in the body can cause changes in the color and structure of the tooth surface. Fluorosis is a chronic disease in which too much fluoride enters the body. As a rule, this occurs when drinking water or foods oversaturated with this element, as well as when taking multivitamins or fluoride-containing pastes in an uncontrolled manner.
The disease most often affects children with primary incisors, but can also occur in adults, especially if they work in hazardous industries. The disease appears as white stripes on the surface or dark brown spots at the base (chalk-mottled form).
Treatment of fluorosis begins with reducing or stopping the entry of the element into the body; in some cases, getting rid of stains can only be done by installing crowns.
Why do my baby's gums turn blue when teething?
The rudiments of teeth are formed in a child during the prenatal period. By the fourth month of life, most children's incisors begin to emerge. In addition to itching, swelling and pain, blue areas may form on the gums.
Passing through dense bone tissue and mucous membrane, the tooth compresses them and injures the capillaries. Swelling and hematoma form, which gives the skin a bluish tint.
Probable causes of hematoma formation:
- rapid tooth eruption;
- fragility of blood vessels;
- lack of vitamins in the body.
Damage to larger capillaries creates more bruising. This usually happens when molars or fangs erupt, since their structure makes it more difficult for them to break through to the surface. Blue gums are not always a sign of abnormality, but require observation.
Dark enamel in children
In children, plaque is especially noticeable because the enamel of baby teeth is lighter than that of permanent teeth. Sometimes babies' teeth turn black on the inside, facing the tongue, sometimes dark spots appear on the outside. However, this does not always indicate a carious lesion.
Reasons that can cause enamel discoloration in children:
- long-term use of antibiotics,
- dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract,
- fungal infection of the soft tissues of the oral cavity (plaque looks like mold),
- use of fluoride-containing pastes for hygiene,
- weak immunity.
Treatment for this condition is carried out after diagnosis. Sometimes dental intervention is not even required.
How to distinguish cyanosis during teething from diseases?
Gums can change color due to various pathologies.
With stomatitis, the gums do not have a pronounced blue color, but only a tint against the background of redness. This disease can be distinguished by accompanying symptoms:
- pain;
- the mucous membrane changes throughout the entire oral cavity, and not just on the gums;
- there may be yellow fibrin deposits.
Gingivitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the gums. Blue gums in a child during teething differ in size from signs of gingivitis. This gum disease is characterized by local changes, that is, the gums change color in limited areas near the teeth.
As in the previous case, the mucous membrane has a reddish-blue color. It should be noted that both pathologies usually occur in weakened children with low reactivity of the immune system.
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells, and due to this, a change in the color of the blood. Therefore, the skin and mucous membranes acquire a pale blue color. This is especially visible on the gums, skin, white of the eye and earlobes.
Anemia can be distinguished by additional symptoms:
- lethargy, apathy;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- hair fragility;
- peeling of the skin.
- gingivitis;
- stomatitis;
- anemia.
Gingivitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the gums. Blue gums in a child during teething differ in size from signs of gingivitis. This gum disease is characterized by local changes, that is, the gums change color in limited areas near the teeth.
At the same time, the child becomes anxious, as pain appears
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells, and due to this, a change in the color of the blood. Therefore, the skin and mucous membranes acquire a pale blue color. This is especially visible on the gums, skin, white of the eye and earlobes.
Important: In addition, in children this pathology is often combined with stomatitis and damage to the upper respiratory tract.
Prevention of enamel pigmentation
Particular attention should be paid to the care of depulped units, because their service life directly depends on this. Don't overload them. If the pulp has been removed in the front tooth, then it is strictly forbidden to chew seeds, bite off hard food, or use toothpicks and other hard objects to remove food particles. If the molar is depulped, then it is also not recommended to chew hard food on this side - nuts, crackers, chips.
Otherwise, prevention comes down to proper and constant hygiene, visiting the dentist twice a year and following nutritional recommendations.
Video on the topic