1603
The possibilities of modern dentistry are rapidly expanding, and with them, irreparable problems associated with various pathologies of the oral cavity are becoming less and less.
But some of them, for example, fragmented alveolar atrophy, stand apart from other diagnoses. This is explained by the natural mechanism of the formation of the disease.
Definition
The alveolar process is a bony cavity characterized by a porous structure. The bed is formed by branches of the lower and upper jaw rows. They are penetrated by tiny blood capillaries and nerve processes.
With partial loss of teeth after a certain period of time, the normal bite is disrupted, and the main reason for this phenomenon is atrophy of the alveolar process.
Its height may vary depending on whether a person belongs to an older age group.
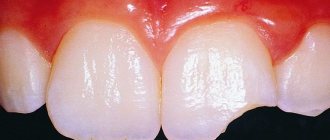
Having lost the root part of the organ, the socket is significantly deformed, its soft tissues gradually change their size downwards. The diameter of the stock also narrows. As the bone wound heals, the first signs of depletion of the marginal part of the socket appear, and the alveolar begins to quickly rebuild.
The pressing force of neighboring organs on this fragment is too great. Its functionality decreases sharply and then stops altogether.
Dysfunction is an irreversible phenomenon. Bone tissue will constantly decrease, making subsequent prosthetics impossible, due to excessive narrowing of the dental bed.
Structure
The alveolar process includes the following elements:
- The outer wall that includes the cheeks and lips.
- Internal, including tongue, jaw, teeth.
- The space between both walls is filled with dental sockets from which teeth grow. Interestingly, alveoli appear along with tooth growth and completely disappear after it falls out. They are part of the jaw, and are covered with a cortical layer on top. On an x-ray, it appears as a dense line, which is different from spongy tissue.
Reasons for the development of pathology
For all dental tissue anomalies of a dysplastic nature, all the factors that provoke their appearance can be classified in two directions:
- inflammatory – periodontitis, gingivitis. Caries in the neck of the tooth also plays an important role. These negative manifestations are the main reason for the development of tissue thinning against the background of the constant influence of these inflammatory processes on them;
- non-inflammatory – This is mainly inflammation of the periodontium in the chronic stage of the disease, as well as organ extraction.
Moreover, the nature of its damage can be either mechanical in nature, due to the injury received, or natural.Often this phenomenon occurs due to excessive pressure from neighboring organs, when there is no resistance to them at the site of fragment removal.
Indications and contraindications for plastic surgery of the anastomosis with the maxillary sinus, features of the recovery period.
Read here all the most important things about tooth replantation.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/operatsii-na-zubah/chto-takoe-udlinenie.html we will talk about the indications for surgical lengthening of the coronal part of the tooth.
Alveoloplasty methods
The human jaw is a part of the body that is quite difficult to operate on. After all, for a favorable result it is necessary to expand the patient’s mouth as much as possible, so some difficulties may arise during the work. Alveoloplasty occurs under anesthesia, since this process is quite painful. There are four ways to carry out the procedure:
- Performing correction within the bone. However, the doctor cannot immediately begin plastic surgery, since he must first make a vertical osteotomy, as well as transposition of the bone walls.
- Carrying out reconstruction by cutting the crest of the process.
- Plastic surgery can also occur on the surface of the bone slope. It is done overlay.
- Osteotomy. It is performed by a surgeon by breaking the wall. The resulting space as a result of the operation is filled with a special biomaterial.
Thus, all four methods are implemented differently. However, their common goal is to increase bone tissue in the part of the jaw where surgical treatment will take place in the future.
Degrees of expression
The manifesting ability of pathology is expressed in three degrees, having different clinical pictures:
- light - the ridge still retains its original size; on top it is surrounded by a mucous membrane of a rather dense consistency.
The relief of the upper jaw is pronounced, all the tuberous elements are clearly visible. At this stage, the prosthesis retains its fixation and does not exclude the procedure for artificial restoration of the organ; - medium-heavy - the soft tissues of the mucous membrane are already too thin, the bone socket has decreased significantly, the tubercles of the upper jaw are not so visible.
At this stage of pathology progression, standard prosthetics are difficult. To carry out the manipulation, preparatory procedures will be required; - sharp - this atrophy of the alveolar is its almost complete absence. The tubercles are almost absent, the jaw bed is narrowed to a minimum size.
The video shows a diagram of the formation of alveolar ridge atrophy.
Types of alveolar bone fractures
Types of traumatic injuries:
- With a partial fracture, the configuration of the jaw does not change, only the integrity of the outer layer of the bone is damaged.
- With an incomplete fracture, all layers of bone substance are damaged, but the alveolar process does not change shape and does not change its anatomical position.
- With a complete fracture, the gap between the fragments of the jaw is clearly visible.
- The formation of a bone defect is characterized by the complete separation of a certain section of the alveolar process.
- A comminuted fracture is a serious injury, since several fragments are formed that can mix in different directions.
The most favorable fractures are non-displaced. With them, in most cases, it is possible to restore the jaw completely. The displacement is formed due to mechanical action, as well as muscle contraction, which stretches the bone fragments in different directions.
Classification
After amputation of a tooth, the hole formed in its place reduces its original height by 30%. After this, the process stops, and the pathology enters the latency stage.
At the same time, the atypical process itself continues to progress latently. The destructive effect is never identical - this is determined by the order of amputation, provoking factors and the specifics of the surgery.
Against the background of this diagnosis, the jaw row begins to shift, and the uneven supply of force to the organs further atrophies the alveolar process.
Depending on the changes occurring to it, the anomaly is classified as follows.
According to Schroeder–Kurlyandsky
This version of the disease description looks like this:
- mild atrophy is the initial stage, allowing prosthetics to be carried out using standard methods. All anatomical fragments retain their structural content and original integrity;
- medium – thin mucosa, moderately acceptable diameter. Implantation is possible only with preliminary preparation;
- neglected or complete - the alveolar is almost absent. The jaw area is almost flat.
According to Kepler
This method divides the disease according to the following characteristics:
- unexpressed dystrophy - manifested by damaging processes in the mucous membrane of various degrees of change, but the alveolar itself against this background is completely preserved. The stage belongs to the class of favorable clinical situations;
- progressive dystrophy;
- hypoplasia with uneven distribution - the most severe pathology can be observed in the area of localization of the incisive organs, the least damaged are the growth areas of the molar fragments.
According to Oksman
The Oksman division of the diagnosis is more specific:
- hypoplasia of the lower jaw against the background of almost unexpressed atrophy of the upper alveolar;
- similar to the top point , the situation is exactly the opposite;
- equivalent dystrophic lesions of all alveolar fragments;
- disproportionate destructive pathologies.
How is the correction performed?
Correction is carried out in cases where the alveolar process has been deformed. It occurs on both the lower and upper jaw. It is done using alveoplasty or other methods.
In some cases, the process is lumpy, narrow and uneven. In this case, the biomaterial used is placed simultaneously on the bone surface and above it. Due to this, the doctor can give the bone the desired shape. During correction, it may also be necessary to dissect the periosteum and incise the mucous membrane of the appendix. After this, the doctor prepares the bone (gives it the desired shape), and then places the material used for implantation. The edges of the periosteum are sutured to create a more regular shape. The entire procedure is carried out under local anesthesia. In addition, the doctor can remove excess, cords, and overhanging edges. Reconstruction will occur without complications if the patient follows all the recommendations of his attending physician before and after the operation.
Treatment methods
The principle of therapeutic restoration of the appendix is to increase its height through the use of medical techniques and technological manipulations of varying degrees of complexity.
The choice of a specific option for eliminating the anomaly is determined by the degree of progression of the disease and its clinical manifestations.
Correction of the alveolar process
Correction of an organ fragment is carried out through plastic surgery. Alveoplasty aims to increase not only the parameters of bone tissue, but also their compaction in the area where implantation will subsequently be performed.
It is performed in the following ways:
- overlay - done either in the inner part of the socket or on the outer bone surface. Before this, the area is pre-treated, after which the soft fragments are excised.
It is necessary to check whether they will be sufficient to ensure normal blood flow and complete closure of the graft.The object is placed along the arch, and to make the bed of the lower jaw, it is placed at the base. If a bony aerial crest is used, the construct may fracture;
- inside – after dissecting the mucosal tissue and reinstalling the bone walls, a break is made, with the help of which the resulting space is filled with special biomaterials.
The method of implantation of the graft is carried out by cutting and bifurcating the bone jaw body. A transplant object is implanted into the inner part.The bone chips formed after the manipulation are moved to the localization area of the transplanted areas and the jaw area.
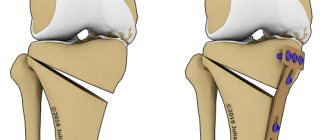
Relocation of the infrasocket nerve
In a number of cases, destructive pathological phenomena begin to form in the lower jaw row, against the background of which the size of the bone edge is localized lower than 1 cm from the infrasocket nerve branch.
With such a clinical picture, its movement is indicated. In medical terminology, such manipulation is called “transposition” of the nerve.
The procedure is classified as a surgical operation of medium complexity and is performed under local anesthesia. The risk of complications is present and depends on the qualifications and practical experience of the surgeon.
In what cases is hemisection of the tooth root prescribed, and how is the operation performed?
In this article we will talk about factors that indicate the need to remove a dental implant.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/kak-byit-esli-posle-ostalsya-oskolok.html we will find out what to do if a fragment remains after tooth extraction.
Planting the graft
If the process of atrophy of the appendix is too advanced and other treatment methods do not give positive dynamics, a graft planting technology is used, which can be:
- explantic - a metal intact structure is introduced into the periosteal zone, from which rods are then brought out into the existing void, intended for the installation of a removable artificial prosthesis;
- autoplastic - all excess bone fragments are removed, and deficiencies are increased due to them;
- alloplastic - polymer types of resin mixtures are used as extension materials.
Gingivosteoplasty
The main indication for its implementation is advanced stages of inflammation of periodontal tissues. Refers to patchwork operations on gums.
For transplantation, bone grafts are used - shavings, cartilage, flour. The operation has a number of modifications, the main of which is dissection of the gums in the premolar region and the area of the root organs.
Longitudinal cuts are placed vertically, according to the size of the pockets. The papillary segment is also excised and a flap fragment is formed. The technology shows a lasting, pronounced result, and the rehabilitation process is faster and less painful.
The video presents methods for treating alveolar process atrophy.
In what cases is alveolotomy justified and the essence of the operation?
911
At the stage of preparation for the installation of dentures, the patient may encounter various obstacles.
One of these may be a defect in the jaw or tooth root, which changes the structure of the dentition and can cause pain.
These defects can be corrected by an alveolotomy operation, which will be discussed later in the article.
General overview
Alveolotomy is the opening of the alveolus - the dental cell.
Indications for the operation may vary, but most often it is prescribed either to patients who have suffered a traumatic tooth extraction, as a result of which root fragments remained in the alveolar cavity, or to prepare for jaw prosthetics in patients with pathological changes.
Pathological changes in the jaw most often refer to exostoses - these are bony protrusions covered with a thin layer of mucous membrane.
Usually, upon palpation, they cause painful sensations in the patient, therefore, the installation of a prosthesis if they are present will be accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
The essence of the operation is that the alveolus is opened by making an incision over it and pulling back a flap of separated tissue for the duration of the operation. The offending bone or tooth is then chipped away, removed, and the tissue is sewn into place.
In some cases, the surgical site requires the addition of bone material to correct a chip or allow the bone to heal faster.
Indications
The main indicators for alveolotomy are:
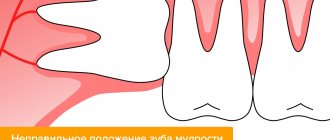
- deep-seated unerupted tooth;
- inflammation caused by the tooth root being too deep, when it is impossible to use other methods of removing it;
- chronic granulating inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth root;
- stuck fragments of tooth root;
- exostoses, painful on palpation;
- strands of the mucous membrane;
- modeling the edge of the alveolar process when removing several adjacent teeth.
The listed problems (in particular, exostoses) arise in patients for a variety of reasons.
One of them is heredity - if one of the parents had a similar problem, then there is a high probability that it will manifest itself in children.
In addition, various disorders of the jaw structure can arise due to dysontogenesis (developmental disorders in the prenatal period), jaw injuries, as well as complications of various dental procedures.
In other words, the alveolotomy operation mainly serves to eliminate pathological formations in the alveolar socket, as well as to form an alveolar ridge favorable for the installation of a denture.
Contraindications
Before resection of the hole, the doctor should make sure that the operation is appropriate.
For example, in patients with systemic diseases, alveolotomy is of very questionable expediency, since the process itself, both surgery and healing of postoperative wounds, can threaten the patient’s condition with deterioration, even death.
A relative contraindication is the patient’s advanced age, but the question of whether to perform surgery should be based more on objective health indicators.
An absolute contraindication is uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, blood diseases (coagulation disorders, acute leukemia, etc.) and cardiovascular diseases, the presence of immunodeficiency or infectious diseases (hepatitis, syphilis, etc.).
In addition, absolute contraindications include the detection of oncological tumors (regardless of malignancy or benignity, chronic osteoporosis, active phase of tuberculosis).
The operation may also be delayed due to some factors that can be eliminated using dental methods.
Such factors include malocclusion, advanced stage of dental mobility, the presence of hard or soft deposits on the teeth, as well as other cases of oral pathology.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the operation include:
- relative cheapness when it comes to correction of a single tooth root;
- short time required for manipulations;
- relatively low complexity of the operation;
- no need to use anesthesia;
- simple care during the recovery period after surgery;
- short recovery period.
The disadvantages of alveolotomy include the following features of the operation:
- the presence of a fairly deep wound, i.e. a relatively high risk of infection if the rules of the postoperative period are not followed;
- the presence of contraindications to the operation for a number of patients;
- the likelihood of an increase in the cost of surgery due to individual differences in clinical cases;
- relatively high traumatic rate - bone growths need to be chipped with a chisel or other tool;
- some risks of deformation of the dentofacial apparatus after surgery.
Thus, alveolotomy is a relatively simple and safe surgical procedure.
If the patient does not have systemic diseases and has a number of indications for the operation, then the benefits from it significantly outweigh the possible risks, especially since the postoperative period for the patient does not require any serious manipulations to care for the oral cavity.
Preparatory activities and course of action
Most often, exostoses are diagnosed by visual examination of the jaw. As they progress, they take on significant sizes, which allows them to be seen as elevations above the gums. On palpation the patient feels pain.
If the need for alveolotomy is associated with another problem, to specify it, an orthopantomogram is required - a panoramic X-ray of the jaws, which allows the doctor to clearly distinguish the location and structure of bone formations.
In addition, you need to take a general blood test and bring an extract from your medical card confirming the absence of systemic diseases.
Immediately before the operation, the patient’s facial skin is treated with an alcohol solution, and the oral cavity is treated with a furatsilin solution. The patient's face is isolated with a sterile sheet, and then an anesthetic injection is given depending on the location of the surgical site.
Further actions occur in the following sequence:
- The patient's lip and cheek are fixed with a Faraber hook to provide the doctor with an unobstructed view and access to the surgical area.
- The doctor makes an incision with a scalpel , after which the mucous layer of the gum is peeled off and fixed so as to open the alveolar cavity.
- Using a drill or chisel, the doctor chips away the bone defect , while the assistant cools the operating area to avoid burns.
- The bone fragment is removed from the socket , its cavity is thoroughly washed and processed, and the chip is either smoothed with a drill or corrected with bone material.
Today, bone material is almost always used , with preference given to allografts - i.e. synthetic materials.
Their advantage is that they do not require additional trauma to the patient and at the same time have a minimal risk of an immune response.
After the operation, the incision is sutured with silk surgical threads, which are removed 3-4 days later. It is advisable that a forming plate or periodontal bandage .
Possible complications
Natural complications after surgery are slight swelling and swelling at the incision site, sore gums and a slight increase in temperature. These consequences usually do not require any special treatment other than following medical recommendations.
If the patient has a weakened immune system , or if he does not follow medical instructions, neglects the treatment of the prosthesis and oral cavity, or does not take a course of antibiotics, then the alveolar wall may become infected.
Then a serious course of antibiotic therapy and other comprehensive measures will be required. Without treatment, the infection can affect the bone tissue and lead to bone perforation.
Price
The cost of treatment directly depends on the chosen method, the clinical picture of the progression of the pathology, the region of residence and the status of the medical institution where it is carried out and looks like this:
| Type of manipulation | Cost in rubles |
| Gingivitis - osteoplasty | From 800 to 10,000 |
| Correction of the alveolar process | From 8 400 |
| Relocation of the infrasocket nerve | From 6 200 |
| Planting the graft | From 4000 |
Problems: diagnostics
Teeth undergo changes throughout a person’s life. Not only are there fewer of them, but their mobility also increases. The bone tissue around them slowly degrades (resorption). The part that takes the load is more susceptible to this. In case of fractures, to determine the degree of damage, it is often not possible to palpate the alveolar processes of the jaws without pain relief. These areas are densely permeated with a network of nerve endings and are therefore painful.
Such areas, as well as foci of age-related destruction (destruction), sclerotic changes (replacement of bone connective tissue) and manifestations of osteomyelitis are diagnosed by radiographs in various projections. In some cases (tumors), MRI and examination of the maxillary sinuses using a contrast agent are prescribed. Obvious problems in the growth and development of the jaws, as well as their processes, are comprehensively diagnosed.
Reviews
The oral cavity is an important part of functioning. Not only the comfort of a person while chewing food, but also the activity of the most important organs of the gastrointestinal tract depends on its condition, on the integrity and health of the teeth.
Alveolar process atrophy is a disease that can significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life and lead to serious health problems.
If you are familiar with the situation discussed in this article, you can leave your comment in the appropriate section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: atrophy of the alveolar process, operations in dentistry
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
The main advantages and features of making porcelain crowns
Next article
The use of suture artificial crowns in orthopedic dentistry
What is augmentation and why is it necessary?
Augmentation is a method of building up the jaw bone. First of all, the height of the deformed lower part increases. This occurs through bone blocks, as well as artificial bone implantation. This method is applicable in cases where the patient has lost teeth, which has led to bone resorption.
The process is carried out in several stages. The surgeon must first provide access to the bone socket of the tooth that has been lost. It is filled with a special artificial bone preparation. After this, the doctor stitches the wound. Integration of bone tissue can occur from one to several months. All this time the patient must be under strict medical supervision. If any complications arise, another operation may be required. If the bone tissue is less than 10 mm in height, then during implantation the nerve, which is located in the lower socket, may atrophy slightly. To prevent this from happening, the doctor must perform its transposition.