Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Identification of any signs indicating an inflammatory process or discomfort from fixed dentures is a reason to contact your doctor.
Types of complications with fixed dental prosthetics
The most common types of complications encountered with fixed prosthetics are:
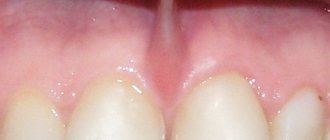
Stomatitis and gingivitis (inflammatory processes of the gums)
Stomatitis and gingivitis
This type of complication mainly arises from improper grinding of teeth; this concerns preparation without the so-called ledge on which the lower part of the crown sits and in no case should it hang over the tooth or be pressed into the gum. The second reason may be a very massive intermediate part of the bridge, which puts pressure on the gum. Accompanied by cutting pain, redness and swelling in the pressure area. It would also be incorrect to consider too large or too small a space between the intermediate part and the gum - the rinsing space; this will lead to the accumulation of food debris and bacteria, which will ultimately cause an unpleasant odor and an inflammatory reaction. The presence of sharp edges of bridges and individual crowns can provoke chronic injury - rubbing of the tongue and cheeks . In case of any inflammatory phenomena of the oral mucosa after prosthetics, you should consult a doctor. As anti-inflammatory therapy, you can use various gels, for example Metrogyl Denta, as well as various herbal decoctions and extracts, for example Rotokan.
Dental diseases under dentures (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis)
It is important to understand that all orthopedic structures are fixed either to completely healthy teeth or to teeth prepared in advance for prosthetics. In case of insufficient diagnosis or improper preparation of the oral cavity for prosthetics, complications such as caries under the crowns, pulpitis or even periodontitis may occur. A pathological process that goes undetected in time will ultimately lead to tooth extraction. Periodontitis can also be caused by non-compliance with certain rules when planning the structure, for example, if a bridge is too long in length or a crown that is too high, which will lead to overload of the tissues that hold the tooth in the bone.
Periodontitis (inflammatory processes of all tissues surrounding the tooth)
Periodontitis
The most important cause of periodontitis in fixed prosthetics is the preparation of teeth without a ledge. As a result, the dental technician will not be able to make the correct crown on the model. It will definitely hang over the tooth and cement will remain under the overhanging edge during fixation, which will provoke a pathological reaction and it is not possible to remove this cement from there without damaging the structure. This is manifested by cyanosis of the gums, swelling and bleeding , followed by recession, darkening and exposure of the gray edge of the crown. Naturally, aesthetics are also compromised.
The choice of design depends on many factors, such as the general condition of the body, gum biotype, length of the defect, etc. If all conditions are not taken into account sufficiently, an inflammatory reaction of all tissues surrounding the tooth may occur, which will lead to rapid atrophy of the bone around the affected tooth and, accordingly, its loss. To prevent this complication, an odonto-periodontogram is often performed before prosthetics, which is a graphical recording of the condition of the periodontium and the degree of atrophy of its tissues. Odontoparodontogram during prosthetics helps to choose the correct design of the prosthesis and determine the number of supporting teeth.
Allergic reactions to materials used in prosthetics
Allergic reactions to materials used in prosthetics.
Mainly allergies after orthopedic treatment when an artificial prosthesis comes into contact with the gums and can manifest itself locally in the form of gingivitis with symptoms such as redness and rashes on the oral mucosa, burning and dryness in the mouth, or more general ones. reactions of the body, such as a rash on the skin of the face , swelling, an attack of bronchial asthma. Such reactions can appear either immediately or several hours or even days after installation of the prosthesis. Any allergic reaction during prosthetics requires analysis of the cause and subsequent treatment.
Galvanic syndrome
Such a reaction as galvanism requires special consideration. It manifests itself in the presence of various metals in the oral cavity, and this only happens on exposed metal and does not apply to dentures lined with ceramics. When saliva enters, which acts as an electrolyte, the metals acquire different potentials, resulting in the formation of galvanic currents. Symptoms of this complication are a metallic taste in the mouth, dryness, burning, headaches, sleep disturbances, and local darkening of metal dentures is possible. When galvanism is detected, it is necessary to replace all metal structures with prostheses made of more bioinert materials .
Cementation and loosening of a fixed structure
Dental cements on which permanent structures are fixed must meet certain requirements. However, sometimes de-cementation (“unsticking”) of the permanent structure occurs. This can occur from excessive load, an incorrectly ground tooth, a bridge that is too long, expired or insufficient cement for fixation, as well as one large or several small fillings on a tooth that fly off while remaining in the crown.
Chips of the lining of artificial teeth and crowns
Chips in the lining of artificial teeth and crowns
The lining of crowns and artificial teeth consists of porcelain, this material is beautiful and strong, but if overloaded, it cannot withstand deformation and chips. The cause may be an error in the planning of the orthopedic design, a technical error in manufacturing, as well as the patient's frequent consumption of too hard foods, such as nuts and bones. Sometimes chips can be restored without removing the orthopedic structure, right in the oral cavity, but only the attending physician can resolve this issue.
Malocclusion due to crowns and teeth that are too low or too high
In the case of too low clinical crowns, the efficiency of the chewing function will be quite low, and in the case of too high crowns, the entire masticatory apparatus . Malocclusion sooner or later causes even more serious disorders of the temporomandibular joint, as well as neurological disorders, which can often be expressed in the form of headaches. If the patient feels that he is not grinding food tightly and too large pieces of food remain, or feels pain in the joints after prosthetics, he should immediately consult a doctor to correct the bite.
Violation of the plane during prosthetics
For any prosthetics, the so-called occlusal plane is very important. By it we mean a plane passing through the cutting edges of the central incisors and the distal cusps of the seventh teeth separately for the upper and lower jaws. Incorrect prosthetics can lead to disruption of this plane and disruption of the movements of the temporomandibular joint. This often manifests itself with serious adverse consequences in the form of facial and headaches, pain in the joint area, and clicking when opening the mouth. Such errors require long and careful treatment. In this case, in-depth gnathological studies will be needed, which are carried out in our clinic. Gnathology examines the interaction of all organs of the dental system and affects many factors. Today, much attention is paid to the development of gnathology and neuromuscular dentistry.
Fractures of bridges and crowns
Fractures of bridges and crowns
Fractures, as a rule, can occur in those fixed prostheses that cannot withstand excessive load, as well as due to technical errors: too thin a frame or a very narrowed part. This complication mainly applies to stamped-soldered and temporary plastic structures. Stamped-brazed structures today are practically replaced by prostheses made of stronger materials. And replacing temporary plastic ones, if necessary, is practically easy and does not take much time.
Causes of complications after fixed prosthetics
Errors in diagnosis and planning of orthopedic treatment
Errors in diagnosing and planning orthopedic treatment
Perhaps the most important and most difficult stage of orthopedic treatment is planning and choice of design. An incompletely studied medical history, insufficient X-ray examinations and incorrect interpretation of images, an inattentive approach to the patient’s complaints. All this today is a gross mistake by the doctor.
Mistakes when preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics
Before orthopedic treatment, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity: professional oral hygiene, removal of severely damaged teeth that cannot be properly restored with fillings or inlays, therapeutic treatment of teeth necessary according to indications, and soft tissue and bone grafting is also possible. Errors in preparation can be detected after prosthetics, so a very careful approach of all doctors is necessary.
Errors in the clinical stages of prosthetics
Orthopedic treatment usually consists of several stages. Making a mistake at any of the medical stages can lead to adverse consequences. The most common medical errors in permanent prosthetics include incorrect preparation of teeth , inaccurately taken impressions, incorrect bite determination, incorrect fitting of frames, non-compliance with the rules when installing a prosthesis, as well as non-compliance with the stages of prosthetics.
Errors in technical stages of prosthetics
Half the success of proper orthopedic treatment depends on the dental technician. Failure to comply with certain rules for the manufacture of dentures leads to further complications. Most often, these are errors in the inaccurate production of plaster models, poor casting of frames, and incorrect modeling of the cutting or chewing surface of the teeth by a dental technician.
Remedies
If you experience any discomfort after installing a prosthesis, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Only a specialist can accurately diagnose. Examination and collection of detailed information about symptoms will help identify the type of complication.
Therapy consists not only of relieving unpleasant symptoms, but also of eliminating the main cause of the development of the pathological process in the oral cavity. Individual treatment is selected in each specific case.
Treatment methods may include:
- Local treatment (antiseptic treatment, anti-inflammatory and regenerating ointments);
- Taking medications (antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics);
- Correction of the prosthetic structure;
- Product replacement.
For minor complications, local therapy and careful oral hygiene can help. The most effective solution is to replace the prosthesis, taking into account all the characteristics of the body.