Stomatitis in children
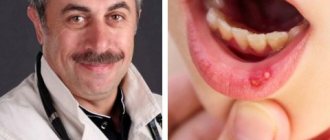
The most common dental diseases in children are stomatitis, which can occur even in newborns. There are catarrhal stomatitis, in which only redness and inflammation of the mucous membrane are observed, and aphthous stomatitis, which occurs with the formation of painful ulcers on the mucous membrane.
Aphthous stomatitis is more painful for a child, since ulcers not only lead to malnutrition, but also provoke a deterioration in the general health of the little patient, leading to an increase in temperature.
Stomatitis occurs in the presence of a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection. And the disease can also occur due to injury to mucosal tissue, in which microorganisms living in the oral cavity receive optimal conditions for the development of inflammation.
Dental diseases in children: 5 most common and dangerous diseases
Diseases of children's teeth are no less dangerous than their adult counterparts. It is a mistake to think that a new, healthy one will grow in place of a destroyed baby tooth, and the child will not be in the dental chair for a long time. In this article, we have collected the most common diseases of teeth and gums, their causes and characteristics in children.
You may be interested in: Pain can cause developmental delays in children Teeth whitening - the price of your smile
Caries of baby teeth
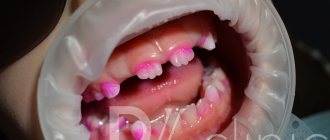
Caries in children can develop very rapidly, affecting several teeth in a short time. In most cases, the cause of the disease is a sweet tooth and poor oral hygiene. Heredity and improper use of pacifiers also play an important role.
It is not difficult to notice caries in a child: first, white spots appear on the teeth, which darken over time. Then the fragile tooth enamel begins to deteriorate, affecting the pulp, dentin and tooth root. With a high probability, a healthy permanent tooth will not be able to appear in place of a diseased milk tooth, so caries needs to be treated: strengthening the enamel, eliminating bacterial plaque, cleaning the carious cavity and applying a sealed filling.
Bite correction is possible AT ANY age!
Palchikov Anatoly Vladimirovich
dentist Ask your question
Pulpitis in children
The reason for the development of pulpitis in children is the looser connective tissue of baby teeth than in adults, weak dentin and low resistance to infections. When caries destroys the enamel and penetrates the pulp, it becomes inflamed, causing severe toothache and fever. It is noteworthy that children often develop a chronic form of pulpitis, complicating treatment and creating a risk of inflammation of the tissues of the permanent tooth.
Most often, the pediatric dentist tries to preserve the pulp so as not to provoke the development of malocclusion due to the early removal of a baby tooth, but this can only be done if the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner.
You may be interested in: Baby teeth: can’t be removed by treatment?
Malocclusion
Malocclusion in children can be congenital (due to heredity) or acquired. Common causes of malocclusion include thumb sucking, prolonged use of a pacifier, and early removal of baby teeth (adjacent teeth move toward the resulting gap).
In the early years, when the dental system is forming, it is necessary to regularly see an orthodontist. This does not mean that the child will have to wear complex leveling devices: the doctor will simply be able to notice and prevent malocclusion in time. You should also carefully treat diseases of baby teeth and prevent their early loss.
Periodontitis in children
Caries, pulpitis, dental trauma and the habit of gnawing hard objects are the main causes of periodontitis in primary teeth. Inflammation of the connective tissue between the tooth and gum threatens the spread of infection to neighboring areas, the development of purulent complications and disruption of the formation of permanent teeth.
In children, periodontitis is often asymptomatic, and only in the later stages do clinical signs appear: toothache, fever, loss of appetite. For treatment, the doctor cleans the root canal, relieves inflammation with injections and antibiotics, but often resorts to removing the affected tooth.
Periostitis in children
Popularly, periostitis is better known as gumboil. Inflammation of the periosteum leads to swelling of the gums and threatens severe suppuration. The cause of its development can be trauma, inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis and other diseases of the teeth and gums.
Periostitis is extremely dangerous for children, because due to fragile immunity it quickly turns into a purulent form, which involves severe pain, intoxication of the body, high temperature and a number of serious complications, including osteomyelitis.
Periodontitis will not go away on its own; moreover, there is a risk of developing a cyst. Treatment = canals need to be refilled, teeth after canal treatment must also be adequately restored
Palchikov Anatoly Vladimirovich
dentist Ask your question
If you find flux, go to the hospital immediately. Acute periostitis is an indication for hospitalization in children under five years of age. For treatment, surgical opening of the abscess, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory dressings, UHF and other physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Maria Nitkina
Caries in children
Caries is widespread among young patients. It can occur at any age from the time teeth appear. The main specificity of childhood caries is the rapid rate of its development. Enamel and dentin in children have a special structure and small volumes, so caries develops rapidly and can affect several areas of one tooth and different groups of teeth.
The main manifestations of childhood caries are changes in the color of the enamel, the formation of darkening, carious cavities, and pain when exposed to temperature stimuli. Possible refusal to eat or brush teeth.
Caries in a child - does caries occur in baby teeth?
One of the most common oral diseases for both adults and children is the well-known dental caries. Caries is the destruction of tooth walls under the influence of microbes, creating a cavity and leading to softening of hard tissues.
Dentists all over the world are still looking for the exact cause of this pathology, but they all agree that the most common reason is the presence of plaque caused by the consumption of carbohydrates and the lack of sufficient hygiene after them. Of course, in addition to this, it is worth noting the poor ecology, the composition of food and water, as well as the structure of the enamel, which is transmitted genetically from parents.
But, if you focus on plaque, then the right brush can become the savior of your child’s teeth. And, if for high-quality cleaning with a manual brush a child must be able to make “sweeping movements”, and parents must ensure that the cleaning time is at least two minutes, then electric brushes do everything themselves.
The Oral-B Stages Power electric toothbrush for children can perform “sweeping movements”: its round head makes reciprocating rotational movements, covering each tooth, the timer counts two minutes for you, and the Magic Timer app will engage your child in the brushing process - because he can choose a Disney character, with whom he will take care of his teeth and demonstrate his success to the dentist!
However, regardless of the cause, caries in temporary teeth, unlike permanent teeth, develops quite quickly. Of course, the situation worsens due to frequent snacking and lack of control of oral hygiene on the part of parents. That is, if a child brushes his teeth under your supervision or at least demonstrates the results of brushing to his elders every day, then the risk of missing incipient caries is much lower than in the absence of such control.
As for treatment, today there are several options for treating caries in children:
- If caries is just beginning , and the doctor notes only an area of demineralization (weakened enamel), then all kinds of fluoride gels, as well as careful oral hygiene at home, will help.
- However, if a cavity has already appeared , then remineralizing therapy is powerless. Then you shouldn’t expect that caries will “go away on its own” or “the tooth will fall out anyway”: the tooth, even though it is a baby tooth, requires treatment. Today, it is carried out with high-quality anesthesia (if required), as well as with the use of modern materials that help the pediatric dentist provide not only fast, but also the most effective treatment for even the smallest patients.
By the way , the materials used for filling cavities are in no way inferior to those used in adult dentistry. That is, parents can be calm about the risk of the filling falling out or any allergic reactions.
Malocclusion in children
Bite defects not only reduce the aesthetics of the smile of young patients, but also significantly complicate their lives in the future. They can lead to the formation of diseases of the intestines, stomach, respiratory tract, and improper formation of the maxillofacial bones. Defects in the development of bite should be determined at an appointment with an orthodontist. If the baby has teeth moving back and forward, there is a non-standard positioning of the jaws when closing, there are teeth rotated around their axis, interdental spaces, uneven rows, all this indicates the need for treatment.
Treatment of malocclusions should begin as early as possible, preferably in the temporary dentition.
Problems with teeth, teething? – not a problem at all, but a joy!
Also, many mothers are concerned that their peers have acquired teeth, but her child does not have them yet. The main thing is not to become hysterical, your baby is fine. The timing of the appearance of the first teeth is individual for each child. If there are no teeth yet, they will definitely be in the near future, and this slight delay does not mean that your child is behind in development. But the earlier appearance of teeth is not a reason for joy.
There is an opinion that if a child gets teeth after one year, they will be stronger, and the teething process itself will be painless. Don’t immediately panic if your baby’s teeth are positioned asymmetrically; this is normal for the first sixteen teeth to appear.
First teeth or Dental problems in babies
After a certain time, they will fall into place, the main thing is to take care of them on time and visit the dentist. After all, even children can have problems - caries, plaque, and sometimes even bad breath
.
So, your child is constantly chewing something, drooling from his mouth, trying to bite his finger, chest, and so on, his mood is terrible. Mommies, rejoice, very soon your beautiful creature will get her first teeth. One disadvantage of this condition is that during this period the child’s immunity is very weakened, and against this background, fever, runny nose, and sometimes cough appear.
At the time of the first teething, the child consumes a lot of liquid, and this leads to diluted stool. Often, the baby puts everything in his mouth, even dirty things, and this can lead not only to loose stools, but also to vomiting.
First teeth or Dental problems in babies
Gingivitis in children
Also common in children is a disease called gingivitis, which is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process in the gum tissue. The main symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding of the gum tissue, pain when brushing, swelling, redness of the dental papillae, gums, cyanosis of the gums, which occurs when the disease becomes chronic, and accumulation of plaque.
The main factor in the development of gingivitis is poor hygiene, which leads to the formation of a significant amount of deposits on the enamel near the gums.
Main dental diseases in children
The first year of a child’s life can also present surprises to parents in the form of oral diseases. Most often, these are injuries to the oral mucosa, which still has a very delicate structure that can be easily damaged even by a soft pacifier. There is also a danger of developing fungal diseases or the appearance of herpetic stomatitis, sometimes even recurrent.
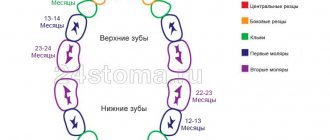
Teething symptoms
What are the symptoms of teething in a one-year-old child? What are the symptoms of teething in children? Typically, symptoms of teething in children under one year old include:
- Profuse salivation. It may cause coughing and hoarseness, as well as a rash in the mouth and chin.
- Swelling, redness and soreness of the gums
- Itchy gums. Babies often try to relieve it by chewing almost anything they can get their hands on.
- Decreased appetite or complete absence of it, as well as refusal to eat
- Temperature increase
- Sleep disturbance
- Increased excitability
- Changing the stool
- Runny nose
It is important to understand that when teething in children, the symptoms can be different and it is not at all necessary that the child has everything on the list. Symptoms of teething in children after one year are very often similar to those present before one year. Even when molars erupt in children, the symptoms may be similar, but everything, of course, is purely individual.
Complications during teething
It is important to monitor the symptoms of a child’s first teeth erupting in order to predict complications. Complications may include:
- Early teething. The norm is 6 months, but it may be that the child’s teeth begin to erupt at 2 months
- Too late teething. It is possible that even at 8 months the child has not yet erupted teeth. The consequence of this situation can be edentia - this is the complete or partial absence of teeth in the oral cavity.
- Incorrect teething sequence
- Abnormal tooth formation or dental anomalies
- Tooth growth abnormalities
- Enamel hypoplasia. It is a lesion of tooth enamel that occurs in children under 10 months of age.
- Aphthous ulcers or aphthous stomatitis. It is the process of small purulent ulcers appearing in the mouth
- Gum hematoma. May occur when a blood vessel is damaged
At the INTAN implantation and dentistry centers you can provide a wide range of pediatric dentistry services. All services are provided only by highly qualified dentists who have a special approach to children and knowledge of how to carry out treatment so that the little patient likes it.