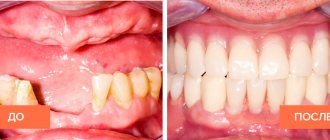
Classification of dentures
There are two main directions - prosthetics with removable and non-removable structures. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Removable prosthetics, for example, are the most inexpensive. But fixed prosthetics are more preferable from an aesthetic point of view.
Removable dentures
- Full. These dentures are used when there are no teeth at all on the jaw. The supporting surface of complete dentures is the gums and the upper palate, which results in a not entirely reliable fastening. Traditional materials are plastic or nylon.
- Partial. Partial dentures are possible when the patient still has at least one tooth in his jaw. Partial dentures distribute the load not only on the gums and palate, but also on the remaining teeth. Traditional materials are plastic or nylon, possibly reinforced with a metal frame.
Fixed dental prostheses
Fixed dentures are installed by a specialist for a long period of use. The main disadvantage of such prosthetics is the high cost of services and materials.
Fixed dentures include:
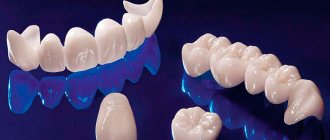
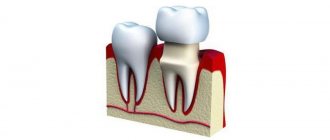
- Crowns. They are installed on the patient’s teeth or on implants. This is the simplest and most reliable type of prosthetics. Crowns are made from metal (such as gold or platinum), metal-ceramic, or ceramic.
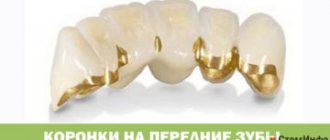
- Orthopedic “bridges”. The advantage of this prosthetics is the reliability of fixation. After the installation of the bridge, the patient does not require much adaptation, and the taste sensations when chewing food practically do not change. Orthopedic bridges are cheaper than implants. Bridges can be installed in the absence of supporting teeth, but in this case, the installation of implants is used, which will be a reliable support with a guarantee of more than 10 years.
- Veneers. The main purpose of veneers is aesthetic; in addition, dental chips, cracks and other defects are treated and protected from further destruction. The material for veneers is the same as for crowns: metal, metal-ceramics, ceramics.
- Implants. This type of prosthetics is the most reliable. The only drawback is the high cost. But the correct selection of materials and high-quality installation guarantees operation for decades, fully replacing natural teeth.
Types of Dentures
Removable dentures are also divided into several types, depending on the design and materials.
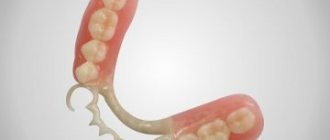
Clasp dentures
Manufacturers apply imitation gums to the metal frame and attach dental crowns that perform the functions of artificial teeth.
For clasp prosthetics, you need your own teeth, which are able to reliably hold the structure. A clasp denture is attached to the patient’s surviving teeth and secured with hooks. If there are no teeth capable of holding the structure, or their reliability as a support is in doubt, then preliminary installation of implants is recommended.
The main disadvantage is the aesthetic discrepancy between the fastening hooks of the prosthesis, which is especially noticeable when fixing the structure to the front teeth. For some patients, a metallic taste causes discomfort at first.
The price of the prosthesis itself and its manufacture depends on the availability of materials and the complexity of the design.
Nylon dentures
Made from very elastic material. Metal parts are not involved in the manufacture of the prosthesis. Fixation occurs due to the effect of suction to the patient’s gums. Experts especially recommend such models of dentures to those patients who suffer from various forms of allergies to metals or cannot tolerate the presence of a metallic taste in the mouth.
For more reliable fixation, plastic hooks, special creams, and gels can be used. They are used both for absolute and partial absence of teeth. Recommended for sore or sensitive gums.
The service life with careful use and proper care is at least 5 years. The prosthesis material practically does not irritate the gum tissue and does not cause inflammation.
When chewing, some displacement occurs and the pressure on the gums is uneven. Over time, the prosthesis may “sag,” which requires modification and adjustment by specialists. Special products are required for care. The prosthesis material is susceptible to temperature, the effects of active substances and plant pigments, so it is also recommended to refrain from strong tea, coffee, tobacco, hot dishes, and strong alcoholic drinks.
In terms of price level, nylon dentures cost approximately one and a half times more than clasp dentures.
Acrylic dentures
The material for dentures is acrylic plastic. Acrylic dentures are easy to make, use and care for. A plate prosthesis (as dentists call this design) can be used in the absence of teeth.
The principle of fixation is based on the suction effect, if there is a complete absence of teeth, or using a wire retainer in case of partial absence.
If a patient is missing 2 teeth in a row, then dentists recommend a “butterfly” plate prosthesis. “Butterfly” is popular for prosthetics of distant molars. Such dentures can be worn without removing them, and their service life reaches more than 4 years. An important “plus” is the low price.
The hard material of the denture can rub your gums. The prosthetic design blocks most of the receptors in the upper palate, which significantly dampens the taste sensations when chewing food.
Getting used to the model is difficult because diction may deteriorate, and the harsh impact on the palate and gums sometimes causes nausea.
When chewing hard food, the structure may crack or break.
Artificial teeth
Artificial teeth have been manufactured since ancient times. During excavations of the graves of ancient Etruscans, who lived more than 2000 years ago, artificial teeth made from animal bones were found. During the Roman Empire, such dentures were attached to healthy teeth using horsehair or gold wire. Fashar (18th century) made artificial teeth from ivory, cutting them together with a prosthetic base. This method was used until the middle of the 19th century. Linderer (1851) describes dentures with metal bases in which teeth made from animal bones, as well as human teeth, were strengthened. Fantzi (1808) was the first to make porcelain teeth into which he fused platinum pins. Mass production of artificial teeth began in 1825 in Stocktown, and in 1848 White founded an artificial teeth factory.
By the beginning of the 20th century. Hundreds of millions of artificial porcelain teeth were already being produced. In the Soviet Union, industrial production of artificial teeth began in 1929 at the Leningrad Porcelain Factory named after. M.V. Lomonosov, and in 1930 a specialized plant for the production of artificial teeth was created in Kharkov. The widespread use of plastic acrylic teeth began in the 30s abroad and since 1947 in the USSR. In the Soviet Union, I. I. Revzin, B. N. Bynin and others developed plastic teeth, which in 1947 began to be produced under the name “artificial teeth from AKR-7.”
Artificial teeth are a structural element of a denture. When making a prosthesis, they are considered as reinforcement of the product. The importance of artificial teeth lies mainly in ensuring the function of the masticatory apparatus, chewing food and improving speech. In addition, artificial teeth are of great aesthetic importance. The main criterion for the quality of artificial teeth is the degree of their similarity to natural ones, both in appearance and in chewing efficiency. Teeth are made from porcelain, plastic and alloys.
Medical and technical requirements for artificial teeth:
- 1) strength and sufficient wear resistance (abrasion);
- 2) lack of abrasive properties;
- 3) resistance to oral fluid;
- 4) biological indifference;
- 5) strong connection with the base material of removable dentures or supporting parts of fixed dentures;
- 6) the linear coefficient of thermal expansion of the tooth material should differ in value as little as possible from the coefficient of thermal expansion of the base material;
- 7) resemble natural teeth in shape, color and chewing efficiency;
 easy mechanical processing and lack of porosity;
easy mechanical processing and lack of porosity;- 9) vapor resistance in the oral cavity.
Types of fixed prosthetics
Fixed prosthetics are used in cases of minor tooth loss. Fixed structures do a good job of solving aesthetic problems: covering dental defects on the front side, changing the color scheme and correcting the shape of teeth.
Crowns
A popular method of prosthetics for damaged teeth.
- Metal crowns. Metal crowns are reliable, inexpensive, and do not require extensive grinding of the tooth during prosthetics. The deficiency is expressed in unnatural colors and shades, so most often they are used on those teeth that are not visible.
- Metal-ceramic crowns. They are very durable, have low (unlike metal) thermal conductivity and good wear resistance under chewing loads. The service period is at least 10 years. The disadvantage is the need for significant grinding of the tooth before installing a crown.
- Ceramic crowns. The main advantage of such crowns is color. It is almost impossible to visually distinguish an artificial ceramic tooth from a natural one. Disadvantages: fragility, high price. During use, crowns require some additional precautions and care.
Orthopedic “bridges”
Recommended if more than one tooth is missing. Prosthetic bridge models can be installed even if there are no supporting teeth on the jaw; for this purpose, several implants are implanted into the jawbone, which take on the main load when fixing the bridge and when chewing food.
The material for artificial teeth is selected in such a way as to visually match the color of the patients’ natural teeth.
The disadvantages of bridges that are installed on implants include a fairly long period of preliminary preparation before actual installation. Adhesive bridges, on the other hand, have a limited safety margin, are fragile, and additional precautions must be taken during their operation.
Microprosthetics
Microprosthetic designs include veneers, inlays, and lumineers. The main purpose of microprostheses is aesthetics, protection of chips, cracks and other minor damage to dental tissue.
Veneers and lumineers. These microprostheses are sometimes compared to false nails, because these are the same plates, but they are applied to the outside of the teeth to solve an aesthetic problem. The back side of the teeth remains, as before, without covering.
Porcelain or other ceramics is often chosen as the material for veneers and lumineers; sometimes a composite material is used, but less often, since it is significantly inferior to ceramics in reliability.
Ceramic inlays. Such microprostheses are protective for teeth that have undergone treatment. They close the dental cavity after eliminating caries or filling canals, as well as to compensate for defects in enamel tissue due to increased abrasion. The inlay protects longer than a conventional filling.
The weak point of veneers is that they cannot be used for large fillings or for extensive caries lesions. Ceramic veneers are quite fragile and require additional precautions during operation.
What is CAD/CAM in prosthetic dentistry
Technological progress affects absolutely all spheres of life of a modern person. It is not surprising that medicine and dentistry are also involved in the process of general computerization. CAD/CAM is an abbreviation for the most innovative technological process that, using software, allows us to solve unique problems during orthopedic treatment. The CAD/CAM system is a complex for digital design, modeling and subsequent automated production of products according to specified parameters.
The first stage is that after scanning the oral cavity and using the appropriate software, a virtual model of the future orthopedic design is built. In this case, the obtained data is agreed upon with the patient, and adjustments are made if necessary. As a result, the final option is determined. This completes the CAD phase.
The CAM system is the basis for bringing virtual ideas to life. At this stage, the creation of real products from standard blanks, ceramics or zirconium is already taking place. A milling machine is a device that takes on the function of carrying out the entire production process, completely replacing a dental technician.
How are dentures made?
The technology for making dentures is a clear sequence of steps. The specialist follows every point of the technology algorithm, which guarantees the quality and reliability of the design.
- During the first visits, the dentist “cleanses” the mouth of those dental debris and residues that cannot be restored; treatment is carried out for caries, tartar, and inflammatory processes in the gums.
- The next stage is making an impression of the patient’s jaws.
- Then the color of the material from which crowns, artificial teeth or veneers will be made is selected.
- If necessary, either the supporting teeth are ground or implants are implanted.
- In the laboratory, prostheses are created according to the order of the specialist and the wishes of the patient.
- Fitting day. During this appointment, prostheses are tried on, and those points that require correction or alteration are agreed upon with the patients.
- Installation. Installation of fixed prosthetic structures is carried out only after all previous manufacturing steps. The patient needs to use the prosthesis for two to three weeks to allow the adjustment period to pass. After this period, you need to visit the dentist to make sure that the denture does not rub the gums, does not scratch the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips or palate, fully performs the function of chewing food, does not fly off, and does not cause unpleasant or painful sensations.
 easy mechanical processing and lack of porosity;
easy mechanical processing and lack of porosity;