How to treat loose stools in children?
What can the color of stool tell you?
Our readers successfully use Monastic Tea to treat gastritis and ulcers.
Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here... Loose stools are just a symptom. There are many other characteristics of stool that will help at least suggest the cause of the disease:
- yellow stool mixed with mucus may indicate an intestinal infection;
- light, almost white stool may indicate problems with the liver and biliary tract or be a consequence of taking certain medications; in a one-year-old child who eats formula, such feces may be a variant of the norm; In addition, feces lighten when there is an excess of calcium and carbohydrates in the baby’s diet;
- feces with mucus in a two-month-old breastfed baby may indicate that the mother does not follow a diet and eats a lot of fatty foods that the child’s enzyme system cannot yet cope with;
- yellow stool and high temperature are almost always signs of an infectious process in the intestines;
- loose, foamy stools combined with a sour odor and bloating may be symptoms of lactase deficiency.
When to see a doctor
In newborns and children of the first year of life who are breastfed, such loose stools are normal. Parents needlessly panic if they discover loose stools in a one-month-old baby, who is outwardly absolutely healthy and calm.
In other cases, diarrhea is a sign of a serious pathology. If you don't notice it and don't seek help, the outcome can be disastrous. When diarrhea threatens the baby's life:
- the temperature rose to 38 or higher;
- if parents suspect that diarrhea is associated with the intake of spoiled food, medicines, and household chemicals;
- against the background of diarrhea, vomiting and severe abdominal pain began;
- diarrhea began abruptly, it is profuse, frequent and lasts more than a day;
- the stool is black or contains blood;
- signs of dehydration appeared: dry mucous membranes, tears disappeared, and in newborns the fontanel may become sunken.
Important! Dark green stool (meconium) is normally observed in babies in the first days of life. Then it becomes liquid with an admixture of mucus and lumps. This is how the process of populating the digestive tract with beneficial microflora takes place.
If you cannot deal with liquid feces on your own, it is better to contact a specialist to find out whether it is normal or whether the baby is sick.
What should you do first if your child has diarrhea?
If a baby at 3 months or a child at 5 years old begins to experience repeated vomiting and diarrhea, parents should adhere to the following recommendations before a specialist arrives:
- the key danger of diarrhea in babies is dehydration, which can cause problems with brain function and internal organs in a child; therefore, the most important thing is to ensure a sufficient supply of water and electrolytes (salts) to the body of a small patient;
- it must be soldered in the first minutes/hours after the onset of diarrhea, so that it is not too late;
- If the baby is breastfed, then you should constantly put him to the breast.
How can you replenish the loss of fluid in your baby’s body:
- special saline solutions that are sold in pharmacies; their dosage depends on the child’s body weight; for infants they are poured into a bottle or given from a spoon;
- a solution prepared at home (take a teaspoon of salt and 7 tablespoons of sugar per liter of boiled water);
- In parallel with saline solutions, decoctions, fruit drinks and dried fruit compotes are given.
Important! Plain water, rice water, carbonated drinks, teas will not help cope with dehydration. In addition to water, it is necessary to restore the balance of salts in the body, which are released during diarrhea and vomiting.
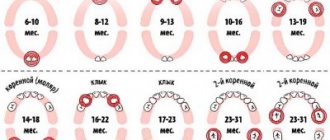
Read also: Sequence of teeth in children
How to treat diarrhea in children?
Treatment for diarrhea depends on the cause that caused it. Let's look at what is done with diarrhea for various diseases.
- A combination of loose stools with fever and abdominal pain. In children, such signs are most often characterized by poisoning or intestinal infection. In addition, this may be a symptom of acute surgical pathology (appendicitis, etc.). In such cases, you should not wonder how to treat diarrhea, but immediately consult a doctor.
- Loose stools, flatulence and abdominal discomfort after taking certain foods. If parents notice a connection between their baby’s loose stools and the intake of some food, then perhaps he is simply intolerant to this product. You need to remove this product from your diet and if your stool returns to normal, then everything is fine.
- Diarrhea due to lactase deficiency. Some children (3 years and older), after introducing cow's milk into the diet, experience a deficiency of the enzymes that break it down. For treatment, it is necessary to rebuild the diet and not include whole milk in it.
- Diarrhea due to medication. If your child is already being treated for an illness, he or she may experience diarrhea due to taking antibiotics and other medications. To treat diarrhea, drugs are used that restore normal intestinal microflora (Enterozermina, Linex, etc.).
- Loose stools during teething. During this period, the baby begins to put foreign objects into his mouth and may contract an infection. If after eruption the diarrhea disappears, then there is no need to worry. If not, then you may suspect an intestinal infection, which requires consulting a doctor.
- Blood in the stool may indicate intussusception or internal bleeding. In such cases, you need to be examined by a doctor to determine the source of the problem.
What else you need to remember when you have diarrhea in a child
If you suspect an intestinal infection or poisoning, after the parents have replenished the salt and water balance, you can give the child enterosorbents (Enterosgel, charcoal, Polyphepam). They partially absorb poisons and toxins that have accumulated in the intestines. These drugs do not act on the bacteria themselves, but help cleanse the stomach.
Only a doctor who knows the cause of the child’s condition and its concomitant diseases can prescribe antibiotics for diarrhea or, conversely, cancel them. The use of antidiarrheals should also be under the supervision of a physician. For example, the drug Imodium copes well with diarrhea, but is used only in children after 6 years of age and has a number of contraindications.
Often parents do not know how to properly feed their child with diarrhea or whether to feed them at all. Food is necessary, but in small portions and in a reduced volume so that the inflamed intestines can digest it. Breastfed babies continue to be fed as usual. For a bottle-fed baby, a fermented milk formula is selected. At older ages, children are fed steamed or boiled dishes. The choice of diet and diet is largely determined by the cause of diarrhea.
Loose stools in a baby are not always a sign of pathology. In some cases, this is a variant of the norm, in others it is a signal that the food is not suitable for the child. The combination of diarrhea with other symptoms may indicate an infection, allergy, or acute surgical pathology. If you have questions, it is better to seek help and find out a reliable diagnosis.
Diet for diarrhea on teeth in a child
After the examination, the pediatrician will prescribe plenty of fluids. Some medications, like Regidron, taste bad. In order for the baby to drink the product, you will need to dilute it with compote. Before giving the medicine to the child, the mother needs to taste the medicine herself. If the temperature is elevated, then drink liquid in larger quantities than with diarrhea.
Prevention
During teething diarrhea after 6 months of life, you need to follow the following tips:
- painkillers are used carefully after a doctor’s prescription and after reading the instructions;
- Antibiotics can only be prescribed by a doctor and it is strictly forbidden to give them to a child on your own;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- Depending on your age, proper dental care is required;
- You cannot walk with a child who has a high temperature;
- When teeth are cutting through, you should not take your child to crowded places and invite friends to visit.
If you follow the pediatrician's recommendations correctly, the process of changing teeth will become less stressful for the baby. The appearance of an intestinal disorder requires special monitoring of the baby's health. If your stool changes, you should seek help from your pediatrician.
The process of teething is difficult for a baby. At this moment, all the functions of his organs also undergo changes, and viruses lie in wait for the baby everywhere. Parents should know that diarrhea during primary teething does not last more than a day. Otherwise, there may be loose stools for several days, which is not normal. Therefore, if a change in consistency and color is observed, urgent assistance from a specialist is required. If a child has previously erupted teeth, but not all of them have appeared, then the parents must provide special food.
The information" on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Author: Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
>
Frequent associated symptoms
The main symptoms that occur during teething:
The reasons for the development of diarrhea in teething babies are said to be excessive secretion of saliva and accelerated peristalsis of the digestive tract. In addition, the immune system weakens during this period, and the child intensively chews and bites various things that he comes across. This causes an increased risk of developing infections.
Signs of diarrhea accompanying teething are usually an increase in stool frequency and a looser consistency. The smell and color of stool often do not change. In addition, with such diarrhea, the child is not lethargic and eats normally (appetite may decrease slightly due to discomfort and pain). These are signs of diarrhea caused by minor irritation of the digestive tract. This irritation goes away as soon as the gum inflammation subsides.
E. Komarovsky: does diarrhea come from teeth?
Diarrhea occurs quite often in teething babies. However, a well-known doctor reminds that the period of teething is a time of increased risk for the development of various intestinal infections, since the immune function of the baby’s body decreases, and due to the baby’s desire to constantly rub his teeth with any foreign objects, more microorganisms and viruses enter his gastrointestinal tract. And if, simultaneously with diarrhea, the baby’s body temperature rises, and the stool itself changes in consistency, smell and color, then most likely it is an infection, so the baby should be shown to a specialist as soon as possible.
Nutrition rules during this period
Dental diarrhea in a child requires dietary adjustments. An exception is the situation if the baby eats only mother's milk or artificial formula. First of all, you should remove certain foods from your diet, these include:
- meat;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- pears;
- peaches and apricots;
- plums
In addition, it is necessary to exclude vegetable oils and reduce the consumption of dairy products as much as possible.
When a child has diarrhea on his teeth, you should include in the menu such side dishes as mashed potatoes and boiled rice. You can bake apples as a dessert. A banana has fastening properties, which is easy to simply mash with a fork and replace an entire meal with it. It is useful to offer lean soups and rice porridges.
Special attention should be paid to drinking. It can be varied with drinks that also have an effect on the stool. In this case, strong tea and jelly will do. With them you can offer your baby dry bread or regular crackers. They not only stop diarrhea, but also massage the gums well. However, you need to carefully monitor your child so that he does not choke.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Tsiprolet: instructions for use, analogues, composition, indications
How to treat?
To help a child during the teething period, parents should focus their efforts on eliminating pain and discomfort. You can give your baby solid vegetables and special toys, massage the gums, and use dental gels and painkillers. It is important to maintain hygiene, wash toys, dishes and hands more often.
Since diarrhea during the period of teething is a short-term phenomenon, there is no need to treat it in any special way. Parents' actions should include replenishing the fluid lost by the baby and reducing the load on the baby's digestive system. If a child is breastfed and receives complementary foods, it is recommended to reduce the volume of complementary foods and increase the number of breastfeedings.
Treatment methods for the condition
It is necessary to influence the cessation of the entry of infectious agents into the child’s body (especially if it is an infant), so as not to aggravate the condition. To do this you need to adhere to the following rules:
- After defecation, wash the child with running water and discard wet wipes. Their composition may irritate the skin and mucous membranes and may not completely cleanse.
- During the period of diarrhea, avoid using new hygiene and cosmetic products, as they can provoke allergic reactions due to reduced local immunity.
- Try to thoroughly clean and wash all objects that a child can put in his mouth - toys, teethers, crib items.
- Carry out wet cleaning in the children's room more often.
- When walking, try to have less contact with others - with children with signs of ARVI. Immune defense is weakened and there is a high risk of getting sick.
We suggest you read How to get rid of garlic smell from your mouth quickly: 5 ways
General recommendations for diarrhea during the dental period:
- Meals should be small, with a predominance of liquid (water, breast milk); if the baby refuses to eat, you should not insist and feed him. For older children, offer bananas, carrots, rice water, and potato dishes.
- Do not take medications, antibiotics or nitrofuran agents on your own. You should consult a specialist.
- Lightly stroking the tummy helps relieve spasms, rumbling, and pain from diarrhea.
- If there is a significant increase in temperature and to relieve pain, antipyretic drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol) can be used. If you have a low-grade fever, these medications should not be given. They cause suppression of interferon production, which can provoke infectious processes.
- The water-drinking regime to eliminate and prevent dehydration should be organized as follows, depending on the age of the child: increase the number of breastfeeding, often offer to drink liquid in small sips (water, compote, tea, fruit juice). In case of significant dehydration, special solutions are used - Regidron, Gastrolit, Humana-electrolyte.
- Assistance in restoring intestinal microflora with the prescription of drugs that contain useful drugs from lactobacilli, bifidobacteria - Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Enterozermina, Lactobacterin, Bifiform.
- Home cooking folk remedies are used only after consultation with the pediatrician (use for newborns is prohibited), include decoctions, herbal teas: mint decoction, chamomile teas, hawthorn infusion, blueberry infusion, bird cherry infusion, decoction of barley grains, sage, infusion of St. John's wort, nettle leaves, blackberries.
When should you go to the pediatrician?
Medical care is needed for children who have started to develop an intestinal infection while teething.
You can judge this process by the following symptoms:
- the baby has a high body temperature;
- stool may turn green, streaked with blood and a lot of mucus;
- the stool has a putrid or sharp sour smell;
- the child's condition worsened, the baby became lethargic and refused to eat.
If your baby exhibits such signs, it is important to immediately consult a doctor to prevent dehydration and worsening of the condition. You should not treat the baby yourself, since dehydration in infants develops quite quickly.
mother of two children with medical education
Drug therapy: is there a need?
Now, how to treat teething diarrhea in babies. This is where you should be extremely careful. Diarrhea during teething in a baby, in the absence of symptoms of other diseases, does not require drug treatment. Drinking plenty of fluids, eating the right foods, or frequent breastfeeding and maternal care is all the baby needs to recover.
We recommend: Child 2 years old - diarrhea without fever, causes and treatment methods
If your temperature rises, consult your pediatrician. Having confirmed that all this is due to teething, and there are no other reasons for concern, you can bring down high values with the help of Panadol or Ibuprofen in accordance with the age dosage. If you need to take multiple doses, do not forget about the intervals between them. If the temperature continues to persist despite medications, call an ambulance.
Another unpleasant complication that can cause diarrhea and irritation of delicate skin that lasts for several days. Rash and redness can cause your baby as much anxiety day and night as the teething themselves. To eliminate itching, pain and burning sensation, it is recommended to use Panthenol or Bepanten. The duration of their use is not limited; be guided by the condition of the skin.
This is where home treatment for loose stools not complicated by infection ends. All other drugs can be prescribed only after consultation with a doctor if there are real indications.
Can a baby have diarrhea when teething?
Quite often, children have digestive problems, which manifest themselves as diarrhea. As a rule, this is due to bacteria entering the gastrointestinal tract. This is not surprising, given that at the beginning of life a child experiences the world in all possible ways, including taste. However, it also happens that diarrhea occurs when a child is teething, why? — the reasons may vary: from changes in diet and increased salivation to a bacterial infection.
Can a baby have diarrhea when teething?
Often, after a child starts teething, diarrhea appears. This leads parents to the conclusion that the child has “diarrhea on the teeth.”
Read also: Age of teething in children
However, pediatricians are of the opinion that these phenomena are not interrelated. Even the idea that increased salivation during teething can in some way irritate the digestive tract and affect the digestive processes is highly questionable. There is too little evidence to establish a direct link between these phenomena.
Thus, the most plausible explanation in this case is that when a child grows teeth, he experiences discomfort and often pulls various objects into his mouth. With the latter, foreign microorganisms enter his body. This is the only possible way for bacteria to enter the child’s digestive tract.
There is an additional factor, which is that during the first two years of life, the child has to deal with a number of infectious diseases that occur during this period of life. Treating diarrhea as a side symptom of tooth growth allows parents to relax and not perceive diarrhea as something dangerous to the health and life of the child. Instead of seeking medical help, parents decide to wait out the acute period. Thus, there is a high risk of missing a problem, which can later result in serious complications.
To avoid such undesirable situations, it is very important to monitor the child and seek medical advice if you notice deviations from the norm.
Teething: main symptoms
Examination of the baby's oral cavity will help to partially eliminate the possibility of bowel disorders. Komarovsky and other pediatricians include the following changes as symptoms of teething:
- increased saliva production as a protective reaction against pathogenic microflora entering the body;
- swelling and increase in the size of the soft tissues of the gum shell;
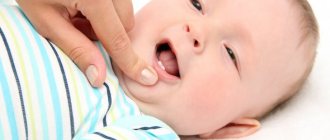
- itching in the area of teething and pain in the gums, trying to eliminate which the child gnaws on various objects, since the pressure they exert on the tissue helps the pain disappear;
- the appearance of discernible contours of the future tooth under the soft tissue shell;
- at the same time, the primary stage of tooth growth in a child may be accompanied by weakness, increased body temperature and general malaise.
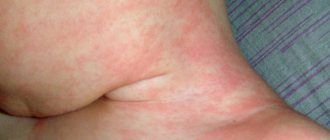
Swelling gums
Despite the increase in the size of the soft tissues, their redness and the presence of some loosening of the structure at the site of the tooth exit, one should be very careful about the nature of the swelling. A stressful situation can cause a decrease in immunity, which greatly increases the risk of not only diarrhea, but also infection with pathogenic forms. Alarming symptoms are the presence of inflammatory processes in the child’s oral cavity, if detected, parents should immediately consult a doctor.
Read also: Is it necessary to lower the temperature when teething?
Child's anxiety
Changes in the child's behavior, crying and whims are also associated with the pain that the baby experiences when teething. The described symptoms can manifest themselves at night in the form of sleep disturbances, when the intervals between the baby's sleep and wakefulness are reduced. The nervous system of children reacts to stress with increased excitability; during this period, it is important for parents to be sympathetic to the child’s whims and understand their nature.
Fever
Individual symptoms of teething in a baby may include a fever of up to 38°C, a rash and nasal congestion.
An increase in temperature is a reaction of the immune system to a violation of the integrity of the gum structure when a tooth appears. If an elevated temperature in children during the period when teeth are being cut persists for 3 days or more, it is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disease. Diarrhea with the appearance of teeth has its own characteristics, which include an increase in the number of bowel movements, the absence of visual and structural changes in the stool. Alarming symptoms include the watery consistency of the child’s discharge, the presence of blood or foreign inclusions in the stool. If the color of the stool changes to black or if it has some kind of green tint, you should consult a pediatrician.