What are the advantages and disadvantages of the material
In the case of porcelain dentures, the dominance of advantages over disadvantages is noticeable. Thanks to continuous improvement, negative aspects are minimized. Pros:
- Aesthetic, organic.
- Lack of staining over time.
- Durability.
- Low sensitivity to temperature changes.
- Hypoallergenic due to the absence of metals in the prosthetic material.
Minuses:
- Expensive.
- Fragility.
- Lack of complete and tight adherence to the dental unit and gum.
- The material can wear away the surfaces of nearby teeth, causing their destruction.
Porcelain crowns do not cause allergies
Indications and contraindications for installation
When choosing a prosthetic method in favor of porcelain, you should focus on the indications for installation. These include:
- Restoration of the anterior region, molars.
- Allergies and sensitivity to polymers, metals.
- Complete destruction of several dental units located in the neighborhood.
- In case of anomalies in the development and location of teeth that are not amenable to orthodontic treatment.
- The presence of unaesthetic prostheses that need to be replaced.
- Wedge-shaped defect.
Contraindications are divided into absolute (installation cannot be performed under any circumstances) and relative (if certain conditions are met, the method is applicable).
Bruxism is a contraindication to the installation of porcelain crowns
. Absolute contraindications include:
- Severe periodontitis of adjacent or opposing teeth.
- Living pulp in children and adolescents.
Relative contraindications:
- Reduced resistance to abrasion of enamel and hard fabrics.
- Bruxism is tooth cutting.
- Some gross malocclusions.
- Living pulp of the mandibular incisors.
A feature of relative contraindications is their removability; after appropriate manipulations, prosthetics can be performed.
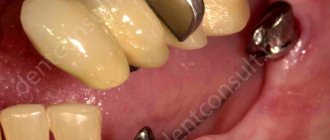
Before and after prosthetics
Installation conditions
All orthopedic products have certain indications for use. Taking the latter into account, the dentist selects the most suitable designs for a particular patient. Installation of porcelain crowns is indicated in the following cases:
- Allergic reactions to products made of metals or alloys. In such a situation, porcelain crowns are the optimal prosthetic option. This is due to its hypoallergenicity.
- For restoration of molars. Today, such use of crowns has become possible. This is due to changes in the technological process of manufacturing porcelain mass. Due to this, the material has an increased strength coefficient.
- For covering front teeth. The manufactured structures are characterized by being close to the natural color of the enamel. Even at close range, it is difficult to see the difference between real teeth and artificial teeth.
- High sensitivity to polymers. Due to the bioinertness of the material, it interacts well with the tissues of the oral cavity, which makes it suitable for those who have similar problems.
- In case of complete destruction of crowns or complex restoration of several adjacent teeth.
On the front teeth
In addition, installation of products is recommended for some diagnoses. Among them:
- non-carious enamel disorders.
- enamel hypoplasia;
- destruction of the cutting edge;
- wedge-shaped defects;
- light and shaped anomalies of teeth.
What types of porcelain crowns are there?
Porcelain dentures differ in the method of fixation:
- Crampons.
Contain a part consisting of wire. For these purposes, silver or palladium is used. The use of these metals is due to thermal expansion characteristics similar to porcelain.
- Diatonic.
They have a hollow inner part, fastening is carried out using cement used in dentistry.
Porcelain crowns on the front teeth are installed based on the crown type of attachment. For other cases, it is preferable to use diatonic fixation.
The color of the material is selected to match the natural shade of the teeth.
Pressed ceramics
An advantageous feature of this type is the increased strength imparted during manufacturing. Ceramic dental bridges are produced under high pressure under vacuum conditions. Such products have a number of advantages:
- Does not require a metal frame.
- Minimal traumatic treatment of the prosthetic area before installation.
- Lightness of design.
- Increased wear resistance.
- Does not require mandatory “killing” of the pulp.
Flaws:
- Cannot be used to create long bridges.
- Not installed on side surfaces.
- Production requires highly qualified manufacturers and specific technical equipment.
This is how the shade of the material is selected to match the color of the patient’s teeth.
Is placement on the front teeth the best option from an aesthetic point of view?
Defects in the frontal dental region are always striking, causing discomfort to a person. The difference in the color scheme of the prosthesis in relation to your own enamel looks unaesthetic. By using ceramic products, maximum similarity of the shade of the structure with the natural color of the enamel is achieved.
Thanks to these qualities, the smile looks natural; it is almost impossible to distinguish the prosthetic area from the untouched one. Therefore, porcelain products today are one of the most popular ways to restore the frontal region.
Possibility of prosthetics for chewing teeth
Previously, dentists did not recommend the use of ceramic dentures on molars. This was due to lower strength under load compared to other materials. A solution has been found - a frame made of zirconium dioxide.
Thanks to this improvement, modified porcelain dentures are as strong as metal ones, so there are no restrictions when installing on chewing surfaces.
Plastic crowns can only be used as temporary
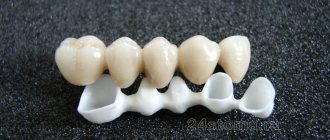
Types of dental bridges
Based on the type of materials from which dental bridges are made, we can currently distinguish:
Metal-ceramic
Metal-ceramic bridges
When making prosthetics with this type of bridge, a frame is modeled on plaster models from special dental wax according to certain rules, which is subsequently cast from various metal alloys, such as cobalt-chromium alloy, nickel-chromium, silver-palladium, gold, etc. After trying on the frame in the mouth, the color of the future ceramic coating is selected and the frame is handed over to the technician for further coating and glazing to give the bridges the appearance of natural teeth. During the work, several fittings are possible in the patient’s oral cavity.
Zirconium
Since the mid-1990s, zirconium dioxide has been used in dentistry, which, unlike metal, has proven itself to be a more biocompatible, more aesthetic, more durable and lightweight material for the manufacture of dental bridges. Currently, bridges are made entirely from zirconium dioxide or zirconium bridges coated with ceramics for a more natural aesthetics.
It is worth noting that for the manufacture of these types of bridges, very precise milling of this material from special blocks on special machines is used. This determines a better and tighter fit of the bridges to the supporting teeth, and it also allows you to save a lot of time by entrusting this type of work to special devices. The disadvantages of zirconium construction include, perhaps, the relatively high cost.
Porcelain
Porcelain bridges
Progress in dentistry has quickly reached a high level, thanks to which today patients can be offered bridges made entirely of porcelain, the so-called Imax and Empress dentures. An undeniable advantage of these materials is the ability to create bridges and crowns that sometimes exceed the natural appearance of teeth. Working with this type of material requires high modern standards of skill for both the doctor and the dental technician.
Metal-plastic
These types of bridges essentially repeat metal-ceramic bridges, but with some changes. The most important thing is the use of a plastic coating instead of a ceramic one, which significantly reduces the cost of prosthetics. Another difference is the bridge frame modeling technique. However, one must understand that the use of plastic almost always leads to negative results, such as frequent chipping, changes in color, rapid wear of the coating, and toxicity to the body. In view of this, these types of bridges are very rarely used in modern dentistry, and this is primarily explained by the medical postulate “do no harm,” rather than, as it sometimes seems to patients, by a “scam” for more expensive work.
Metal
Bridges, made entirely of metal, also belong to the old types of prosthetic structures; their main advantage is strength and low cost, and the main disadvantage is not aesthetics. There are many different metal alloys for the manufacture of these types of bridges, the most popular are cobalt-chromium alloy , nickel-chromium alloy, silver-palladium, and gold. Precious metal alloys are more biocompatible but less durable than steel alloys.
In addition to solid-cast bridges, stamped-brazed bridge structures used to be very popular. Crowns for these bridges are made from thin steel sleeves by pressing to the desired diameter and further stamping on a dental anvil. The intermediate part is cast from a metal alloy, after which it is soldered to the crowns with solder. For a more uniform appearance, the entire structure is subsequently covered with a metal protective coating that imitates gold. These types of bridges have only one advantage - low cost. At the same time, there are a lot of disadvantages, such as a loose fit to the tooth, and as a result, irritation of the gingival margin with chronic inflammation. The solder used to connect the parts of the bridge consists of a mixture of metals that are quite harmful to the body. The oxidation products of this solder often lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Compared to other materials, the strength of stamped-brazed bridges is inferior to others; often such bridges are very quickly worn down to holes, as a result of which caries occurs under the crown. The intermediate part of these bridges does not fit tightly to the edge of the gum, which is why food gets clogged under them. Another important disadvantage of these bridges is the lack of the correct anatomical shape of the crowns; most often, instead of tubercles and depressions, as on natural teeth, these crowns have only platforms that do not fully perform the function of chewing food. Today, these types of dental bridges are the most unaesthetic and unfavorable for the patient, so they are being replaced by more modern designs.
Plastic
In dentistry, there are many types of plastics from different manufacturers and with different characteristics. The main thing that unites them is their fragility, as a result of which plastic today is used only as a material for temporary orthopedic structures, for example, to cover prepared teeth until a permanent bridge is made. In order to avoid complications, such bridges should never be used for more than six months.
There are two main methods for making plastic bridges - clinical and laboratory . With a clinical bridge, it is made directly by the doctor in front of the patient using the so-called “silicone key”, while a laboratory bridge is made by a dental technician, takes longer and is made of more durable plastic. The choice of manufacturing method depends on the indications and clinical situation.
This or that type of material is selected depending on the clinical situation, the wishes of the patient and financial capabilities. Almost all modern clinics are increasingly switching to zirconium bridges and crowns, since zirconium oxide and dioxide today are the most versatile material for fixed prosthetics. However, its disadvantage is its high cost, so other materials for the manufacture of bridges do not lose their popularity.
Plastic and porcelain crowns – which are better?
The high cost of ceramics forces us to look for cheaper methods, for example, plastic analogues. This option loses significantly. Dentures made of plastic can withstand only a small load, their service life is limited by rapid abrasion, the paintability of the coating, due to porosity, bacteria can multiply on the surface, and the composition is allergenic.
From an aesthetic point of view, plastic crowns are much inferior to ceramic ones. The only advantage is their cheapness. Plastic dentures are used as a temporary measure; their function is aimed at protecting the dental unit from external influences.
Stages of manufacturing and installation of porcelain crowns
First of all, at the appointment, the dentist examines the patient’s oral cavity, identifies possible contraindications, and, if necessary, carries out a complete sanitation. Only after this can you proceed to the next stage - preparing the tooth for a porcelain crown and selecting the optimal shade for the future design using a special template.
Next, the doctor takes a combined impression of the tooth and the entire dentition. And if the quality of the casts is satisfactory, it is sent to a dental laboratory, where a plaster model is made based on them.
Direct production of a porcelain crown can be carried out in two ways. The first involves layer-by-layer application of porcelain substance, and the second uses injection molding technology. It is the second option that is more modern and gives the structure high strength,
Therefore, it is used in most dental laboratories.
After the impression falls into the hands of a specialist, he uses thin platinum foil to create a mold for the future dental crown and fills it with a porcelain composition, and then exposes it to high temperatures several times.
The final stage of making a porcelain crown is the correction of the structure, its staining and glazing.
After the crown is ready, it is first tried on. If the result suits both the doctor and the patient, it is finally fixed on the previously prepared tooth.
Comparative analysis of porcelain with other materials for prosthetics
| Quality | Porcelain | Plastic | Gold alloys | Zirconium compounds |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Strength | High when using metal elements | Low | High | High |
| Lifetime | Up to 10-15 years | Stopgap measure | About 15 years | More than 15 years |
| Aesthetics | Absolute similarity to enamel color | Stands out sharply | Stands out sharply | Limited color palette |
| Biological compatibility with oral tissues | High | Low | High | High |
The table shows that porcelain crowns occupy an advantageous position because they have the characteristics of durable materials, but benefit in terms of beauty and organicity. Plastic products have the worst performance. However, their use as a temporary tooth replacement is justified.
With proper care, a porcelain crown will last 10-15 years.
Porcelain crowns: features, pros and cons
Installation of dental crowns is an integral part of the dental prosthetics procedure. One of the most popular are porcelain crowns, which have excellent aesthetics and good functional properties.
Installation of crowns is an integral part of most modern dental prosthetic technologies. In this case, metal and composite, combined and porcelain crowns, and prostheses made of other materials are used. Let's look at the pros and cons of dental crowns made of porcelain - one of the most popular materials used in dental prosthetics.
What are porcelain crowns?
Porcelain (all-ceramic) crowns are made from pressed ceramics without the addition of metal impurities. The production technology uses porcelain produced by press casting with further firing. Dental crowns made using this technology have a good level of strength, although according to this criterion they are inferior to their metal and metal-ceramic counterparts. But crowns made of metal-free ceramics are significantly superior to their analogues in aesthetics and similarity to natural teeth. Therefore, porcelain teeth are especially popular in such a medical field as aesthetic dentistry.
Currently, porcelain dentures are installed not only on the front, but also on the lateral dentition. At the same time, artificial teeth made of ceramics may differ in structure and type of fastening to the base. The most popular are crampon teeth, equipped with metal elements for fastening the prosthesis. As a rule, such crowns are used mainly on the anterior dentition. Also worth noting are porcelain crowns, called “Da Vinci”. Thanks to the use of special technology, porcelain can transmit light, which is why dentures become absolutely indistinguishable from natural teeth.
Advantages and disadvantages of porcelain crowns
The key advantage of porcelain crowns is their maximum resemblance to natural teeth. Moreover, the aesthetic properties of porcelain teeth remain unchanged throughout their entire service life. Another very useful feature of porcelain is its complete biological inertness. This allows the use of all-ceramic teeth in situations where crowns made from other materials are not suitable.
Porcelain crowns also have certain disadvantages. First of all, this is the increased fragility characteristic of ceramic materials. Another significant disadvantage is the relatively high abrasiveness, which affects adjacent teeth in contact. In addition, among the disadvantages of porcelain teeth, doctors note the lack of complete fit in the places where the crown is fixed, and the gums are not always tightly attached to the prosthesis.
In general, porcelain dentures have sufficient strength and good functionality, therefore they are in steady demand among dental patients. Due to the relatively high cost of porcelain crowns, in comparison with analogues from other materials, this type of prosthetics is often offered by VIP dentistry.
How are porcelain crowns made?
The first step in the porcelain teeth manufacturing process is to take individual measurements from a specific client's teeth. To do this, the dentist usually removes a small layer of dental tissue (about 1 mm), which should provide a more durable fixation of the crown. Then, using a special color scale, the color shade of the future crown is selected, which will match the color of the patient’s natural teeth. After collecting the necessary data, the process of creating a porcelain tooth begins.
The mold for making porcelain blanks is usually platinum foil. This choice is due to the similar thermal properties of platinum and porcelain. Next, the prepared matrix is mounted on a jaw model, filled with ceramic mass and sent for annealing. After vacuum annealing, the porcelain blank undergoes additional processing, during which the crown is given the required dimensions. The final stages are staining and glazing of the finished tooth, as a result of which it acquires its final appearance.
Speaking about porcelain crowns, it is worth mentioning separately about veneers, which patients sometimes confuse with porcelain teeth. In fact, ceramic veneers are not crowns or dentures in the classical sense, but thin plates-onlays fixed to the teeth. In most cases, veneers are used to improve the aesthetics of the dentition.
Indications for installation of porcelain crowns
Porcelain dentures, with their excellent esthetics, are a good choice in many situations. If we talk directly about the indications, then porcelain crowns, due to their bioinertness, are well suited for patients with high sensitivity to polymer materials. At the same time, prosthetics using porcelain teeth can be performed not only on the front, but also on the lateral dentition.
Indications for the use of porcelain dentures also include cases where there is complete tooth destruction. Another option when all-ceramic crowns are optimally suited is the need for prosthetics of several adjacent teeth.
There are also some contraindications for the use of porcelain crowns. These include an advanced form of periodontal disease, as well as insufficient density of dental tissues. If the patient has dental anomalies, preliminary bite correction may be required.
Proper care and service life
Practice shows that with proper and timely care, porcelain teeth can last up to 10-15 years. It is important to remember here that porcelain is a relatively fragile material, and even a minor crack can cause the crown to fail over time. Therefore, excessive or “impact” loading on crowns should be avoided. For example, it is known that porcelain crowns fail faster in patients who have a habit of clenching their teeth. Eating hot and cold food at the same time can also reduce the lifespan of dentures.
You should take care of your porcelain teeth just as carefully as you would your natural teeth. Plaque cannot harm the dentures themselves, but the entry of bacteria under the crowns can lead to the development of caries and accelerated destruction of supporting teeth. Using a good fluoride toothpaste will help take care of another vulnerable spot - the area of the gums next to the crown.
Service life and care rules
The service life is limited to 10-15 years. This figure depends on the correct use and care of the product.
It is not recommended to subject dentures to heavy loads, since ceramics are quite fragile and may break if exposed to excessive force. Changes in food temperature should be avoided; due to a sudden change, the integrity of the coating may be damaged. Strong clenching of the teeth leads to a reduction in service life, often this happens involuntarily during sleep, so that the patient is not aware of it.
Hygienic care requires special care. Flosses, dental floss, and irrigators that clean with a jet of water under pressure will come in handy. When brushing, use a paste with an antibacterial effect; it will help prevent microorganisms from getting on the surface of the prosthetic element and prevent inflammatory processes.
Porcelain crowns create a perfect, natural smile. The expensive price is fully justified by many years of trouble-free use of prostheses. What could be more important than convenience and self-confidence when choosing a new look?
Porcelain veneers, care
To preserve and long-term use of porcelain veneers, the following conditions must be met:
- Clean structures twice daily using paste and a toothbrush. It is advisable to use an oral irrigator and dental floss every day, in the evening before bed.
- Do not overload porcelain teeth, in particular, bite through nut shells and bones, and also consume viscous toffees and chewing gum.
- Once every six months, it is necessary to check your bite at the dental clinic to prevent chipping of porcelain veneers.