Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity is often called a mirror of the state of the body. A qualified dentist, after performing a visual examination of the oral mucosa and teeth, can determine what chronic diseases the patient has and advise him to see a specific doctor. Thus, diseases of the endocrine or nervous system, gastrointestinal tract or blood diseases can be diagnosed using the oral cavity.
At the same time, if there are chronic diseases in the oral cavity, then they, in turn, can become a provoking factor for the development of rheumatism, pyelonephritis and some other diseases. Remember how, for example, pregnant women before giving birth and patients before a planned operation need to obtain a certificate of oral sanitation. Therefore, prevention is very important for everyone. Moreover, we are talking not only about a beautiful and healthy smile, but also about health in general, and also, of course, about those funds from the family budget that will have to be spent on treatment at the dentist.
Prevention of oral diseases
When they talk about the prevention of oral diseases, they primarily mean:
- Self-regular oral care.
- Periodic visits to the dental clinic.
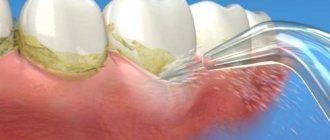
Why do you need to take care of your mouth? The fact is that after each meal, food particles remain on the teeth and mucous membranes of the mouth, as a result, upon contact with saliva, bacteria and microbes begin to multiply in the mouth, which ultimately leads to the appearance of caries, bad breath, plaque and dental plaque. stone
Some people, unfortunately, do not understand the importance of this procedure, erroneously claiming that animals don’t brush their teeth or anything. But we must not forget that animals live much shorter lives, and, most importantly, they monitor their diet, consuming sufficient quantities of food of plant origin.
Dental diseases
Dentistry
– a medical discipline that studies the organs of the oral cavity, their physiological and pathological conditions, and also deals with the prevention and treatment of diseases of these organs. The field of dentistry covers not only diseases of the teeth, but also the entire dental system, as well as the oral mucosa. Along with treatment, modern dentistry pays great attention to the aesthetic side of the issue, striving to create the “ideal smile” for each patient. Dentists attach particular importance to proper oral care as the most effective method of preventing dental diseases.
Based on treatment methods, specialized areas are distinguished in dentistry:
- therapeutic dentistry (treatment of diseases of enamel and tooth canals)
- surgical dentistry (surgical treatment of diseases of the oral cavity)
- orthopedic dentistry (dental prosthetics)
- orthodontics (bite correction)
- periodontology (treatment of gum and periodontal diseases - tissues surrounding the tooth)
- pediatric dentistry (development of methods for treating dental diseases, taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of children at different periods of development).
In recent years, new areas of dentistry have received widespread development: implantology and aesthetic dentistry.
Dentistry covers a wide range of diseases. She treats:
- inflammatory processes of the oral mucosa (stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, cheilitis)
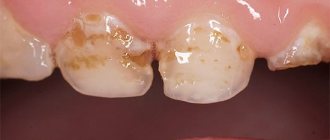
- dental diseases (caries, periodontitis, periodontal disease, pericoronitis, pulpitis, enamel hypoplasia, tartar)
- pathological processes of the maxillofacial area (jaw cysts, perimaxillary phlegmons and abscesses, dentition defects)
- congenital malformations of the facial area (cleft palate and lip)
- traumatic injuries to teeth (dislocation or fracture of a tooth), jaws, tongue, lips
- diseases of the salivary glands, etc.
Oral infections serve as a breeding ground for pathogens to spread throughout the body. The state of the oral cavity can be used to judge the overall health of a person. According to the Russian Dental Association, 87% of Russians need oral sanitation, which, depending on the indications, includes treatment of caries and filling of defects, removal of plaque, stone, roots and teeth, orthodontic and orthopedic treatment.
The most important indicator of the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole is the condition of the teeth. Their formation occurs during the period of intrauterine development, the eruption of milk teeth occurs at approximately six months, and permanent teeth erupt at 6-8 years. Permanent teeth that erupt in childhood are given to a person for the rest of his life, so they require special care and attention at all stages of life.
Today dentistry offers painless, safe and highly effective treatment for various oral diseases. Modern filling materials, as well as tooth-preserving techniques, are used in dental treatment.
They try to resort to tooth extraction as a last resort, when it is necessary to eliminate the source of infection in the oral cavity or when it is impossible to save and restore the tooth.
If, however, the tooth could not be saved, then highly durable and aesthetic denture materials will allow you to accurately recreate the architecture of the tooth and the color of the tooth enamel.
Nowadays, healthy teeth and a beautiful smile are an integral attribute of a person’s well-being and success in society. Aesthetic dentistry works to create the perfect “Hollywood” smile. The scope of activity of this area of dentistry includes aesthetic restoration of teeth, teeth whitening, improvement of shape, size - everything that makes a smile irresistible and flawless.
Today dentistry is one of the most dynamically developing medical sciences: new high-tech techniques and materials appear every year.
However, maintaining oral health depends not only on the dentist and modern technology. It is largely determined by the patient’s lifestyle. Limiting sweets, eliminating bad habits, good hygiene of teeth and gums, and preventive dental examinations will help keep your teeth beautiful and healthy for many years. The medical directory of diseases on the “Beauty and Medicine” website will give you the opportunity to learn as much as possible about how you can counter the threat of tooth loss and what to do if this trouble has already happened. Further…
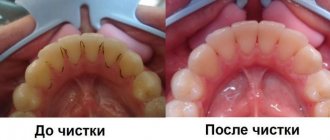
Brushing your teeth with a toothbrush
The most important thing in preventing oral diseases is brushing your teeth. Every person, regardless of age, including children, should brush their teeth morning and evening. Moreover, observing certain rules.
- You need to brush your teeth for at least five minutes.
- Brush your teeth with rotational movements, otherwise, if you brush straight, the plaque will simply be driven into the gum pockets and between the teeth.
- Do not press the brush too hard to avoid damaging the enamel.
- When brushing your teeth, mentally divide all your teeth into four sections and brush each one separately so as not to spread germs throughout the jaw.
- You need to brush not only the teeth from above, but also near the gums, at the base, and also the gums themselves.
- Dentists recommend placing the brush at an angle of 45 degrees when brushing your teeth.
- First you need to brush the far teeth of the upper jaw, then the front teeth, turning the brush vertically, and then start cleaning the teeth of the lower jaw. Finish brushing your teeth by massaging your gums and brushing your tongue.
- In this case, you should take no more than a pea-sized amount of toothpaste.
Healthy eating
The presence of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet helps to cope with plaque on the enamel and germs on the gums. In addition, vitamins strengthen the immune system and resist the development of diseases, including dental ones. Gums will be strong and healthy if you eat carrots, sorrel, green salad, lingonberries, apples, black currants.
To avoid problems with teeth, you need to introduce lemon, herbs, dandelion and nettle leaves as salads and soups, radish, kohlrabi into your diet; lingonberry, rowan, birch juices.
You should not often consume sweet, overly sour, salty foods, tea, coffee. You need to give up fast food products as quickly as possible, as they contain chemicals and dyes that have a detrimental effect on the enamel.
By following these rules, you can significantly reduce the risk of serious oral diseases.
How to choose the right toothbrush
Just as important as brushing your teeth is choosing a good toothbrush. Experts advise purchasing a brush with artificial bristles, which is considered more hygienic, practical and durable. As for the optimal degree of hardness, if the patient does not have any special indications, a regular brush of medium hardness will suit him.
It is also worth paying attention to the size of the toothbrush - optimally it should cover three teeth.
We must not forget that the brush needs to be changed periodically. It’s difficult to say how often to do this, because for some the brush can wear out in a month, while for others it can last two to three months. This depends on many factors, in particular, how often you brush your teeth, with what force you do it, how long the procedure lasts, and what toothpaste you use.
Therefore, some dentists advise purchasing toothbrushes with colored tufts of bristles, which are indicators. On a new brush they are always bright, and when the bristles wear out, they take on a pale blue tint. Noticed this on your toothbrush? It's time to go to the pharmacy for a new one.
If your brush does not have such indicators, simply change it at least once a quarter.
Recently, electric toothbrushes have become popular, although the attitude towards them from professional dentists is rather ambiguous. Therefore, before purchasing such a modern brush, it is better to consult your doctor.
Battery-powered teeth polishing devices are also available on the market. According to dentists, they can be used, but not often, as they can damage the enamel.
Toothbrush care
There are also rules on how to care for your toothbrush so that it helps maintain oral health and does not harm your teeth and gums. What is needed for this?
- Never give your own toothbrush or borrow someone else’s toothbrush, even from your own family members.
- After each brushing procedure, the brush should be washed with soap. You can use it next time only when it is completely dry.
- It is advisable for each person to have two brushes: one for use at home, the second “travel brush” to take with you on trips.
- To clean the brush from germs, you can use various antiseptics or rinses.
- Each brush should be dried in a cup separately from the others, without touching them. Ideally, you can use a “cap” or case for each brush.
How to choose toothpaste
When choosing a toothpaste, it is a good idea to consult your doctor. Do not get carried away with abrasive toothpastes: it is better to alternate them with regular ones. For children, you should buy special children's pastes, according to their age. For people with sensitive gums and teeth - professional pastes.
In general, all toothpastes that are available in pharmacies today can be divided into:
- hygienic, which are suitable for everyone, as they do not contain special medicinal components;
- therapeutic and prophylactic: they can also be used daily as a prophylactic against various diseases;
- medicinal: they should be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
If for some reason a person does not like toothpastes, then he can use special dental gels to clean his teeth. However, we must not forget that in terms of their abrasive properties they are significantly inferior to pastes.
And during the day, when it is not possible to use toothpaste, or after morning or evening brushing, you can use dental elixirs.
We recommend Asepta toothpastes. They are designed to meet all oral hygiene requirements. The components they contain effectively clean teeth, strengthen enamel, prevent the occurrence of caries, and gently freshen breath.
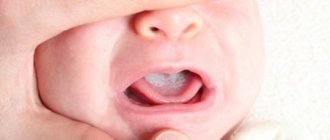
Oral care for newborns and young children (up to 3 years)
Dental care for children should begin with the eruption of the first tooth. Before teeth appear, oral hygiene can be performed with special wipes or a clean cloth moistened with water. Once all the teeth have erupted, soft toothbrushes (Curaprox or Nenedent) and age-appropriate toothpaste can be gradually introduced. If the child is breastfed, then he receives a sufficient amount of fluoride from the mother's milk (if she eats a balanced diet and takes vitamin complexes). When breastfeeding is completed, fluoride comes from food and water.
Attention
, poor oral hygiene, frequent night feedings and constant drinking of sugary drinks between main feedings provokes the appearance of early caries!
At an early age, it is advisable to see the dentist once a year, starting from the appearance of the first teeth, unless the doctor prescribes a different schedule of visits.
Clinical researches
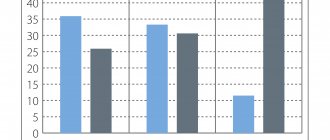
ASEPTA toothpastes are clinically proven effective. For example, repeated clinical studies have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA SENSITIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 62%, reduce the sensitivity of teeth and gums by 48% and reduce inflammation by 66%.
In addition, it was proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA COFFEE AND TOBACCO for a month improved the hydration of the mucous membrane by 3.3 times, the remineralizing efficiency increased by 3.9 times, at the same time, the cleansing effect has increasing dynamics and reaches 60.5% at 4 weeks of use.
Sources:
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” COFFEE and TOBACCO Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky. First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa
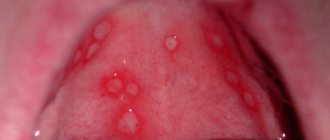
The oral mucosa is the site of exposure to external and internal factors and the manifestation of various diseases. Diseases of the oral mucosa are determined by: - external factors (various microorganisms, mechanical, physical, chemical influences); — systemic internal factors (body reactivity, depending on age, genetic characteristics, immune system, concomitant diseases). Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa is aimed at eliminating or reducing the influence of these factors. Individual prevention should be carried out at an outpatient dental appointment. Unfortunately, measures for the mass prevention of this pathology have not yet been developed. The epidemiology of diseases of the oral mucosa has been practically not studied. There are only works on examining certain groups of the population and studying the structure of diseases according to appealability. Knowledge of the etiology and pathogenetic mechanisms of the occurrence of diseases of the oral mucosa allows, to one degree or another, to carry out preventive measures, which are mainly aimed at eliminating risk factors and causes of the development of pathology. Since the etiopathogenesis of a large group of diseases has not been sufficiently studied, it is not possible to propose effective methods of prevention. Prevention of mechanical damage to the oral mucosa is the removal of decayed teeth, timely filling of carious cavities, grinding of sharp edges of teeth, fillings, elimination of bad habits (biting the mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips, tongue), making new and correcting old dentures. If radiation therapy is indicated for dental patients, this can cause a reaction on the part of the mucous membrane, expressed in hyperemia, swelling, even radiation ulcers, and a reaction on the part of the salivary glands. In preventing a decrease in the radiation reaction of the mucous membrane, careful therapeutic and surgical sanitation of the oral cavity before carrying out this treatment becomes important, and it is necessary to fill carious teeth with cement or plastic. In the oral cavity, electric currents can occur between dissimilar metals, which are accompanied by various symptoms from the oral mucosa. Prevention of this complication is the manufacture of dentures and fillings from homogeneous metal. Particular attention should be paid to persons who, during work, come into contact with substances harmful to the body, which causes corresponding changes in the oral mucosa. Prevention of these diseases is improved working conditions, individual prevention (constant and thorough oral care, thorough hand washing before eating) and regular preventive dental examinations. To prevent infectious diseases that appear on the oral mucosa (childhood infections, tuberculosis, syphilis, viral, fungal, etc.), it is necessary to take measures to prevent infection from entering the body. In children's institutions, the dentist is required to train staff to conduct daily examinations of children. To prevent acute herpetic stomatitis, all children who have been in contact with the patient are lubricated with antiviral ointments twice a day for three days. Prophylactic administration of gamma globulin is possible. Prevention of recurrent herpes due to insufficiently studied pathogenesis is not always effective. It is mainly aimed at increasing the nonspecific reactivity of the body (with the help of immunomodulators, restoratives, hyposensitizing drugs). It is important to eliminate foci of chronic infection in the patient’s body and to improve the overall health of the patient. Candidomycosis (thrush) is one of the most common diseases of the oral mucosa. The disease can affect both infants and adults. Prevention of thrush in newborns and infants is timely treatment of the pregnant woman and sanitization of the birth canal. It is necessary to carry out sanitary and hygienic measures, consisting of thorough disinfection (boiling dishes, linen, patient care items). Among the local factors contributing to the development of candidomycosis, poor oral hygiene, the presence of carious teeth, periodontal diseases, and prolonged wearing of plastic dentures without proper care are important. Therefore, to prevent the disease, it is necessary to carry out rational oral hygiene and treat teeth and gums. The materials used in dentistry can cause the development of allergic contact stomatitis. Allergens are organic and inorganic components of acrylic prostheses. Intolerance increases in individuals with a history of allergies and as the time elapses since the manufacture of the prostheses increases.
Prevention of contact allergic stomatitis is the manufacture of dentures from indifferent and other materials that do not cause allergies. To prevent injuries caused by taking medications, most often antibiotics, it is recommended to take medications strictly according to indications, simultaneously with desensitizing therapy. A carefully collected medical history often prevents the occurrence of drug allergies. Prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa with an autoimmune component is difficult, since their etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully identified. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and various intoxications play a role in the occurrence of chronic aphthous stomatitis and exudative erythema multiforme. In these patients, examination may reveal the presence of bacterial sensitization, as well as disturbances in the blood T-lymphocyte system. Some authors note the hereditary nature of the disease. Based on the above, the identification and treatment of concomitant pathologies is important for the prevention of diseases. Careful sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary to eliminate foci of chronic infection. During the inter-relapse period, agents are used that increase the specific and nonspecific reactivity of the body. Preventive measures to prevent changes in the oral mucosa due to pathology of internal organs include early detection and treatment of the underlying disease, rational hygiene and thorough sanitation of the oral cavity. Particular attention in the prevention of diseases of the oral mucosa, red border of the lips and tongue should be paid to precancerous diseases, which more often occur in older men. Primary prevention of cancer and precancer is based on the prevention and elimination of risk factors: chronic mechanical, physical and chemical injuries to the oral mucosa, occupational hazards, excess solar radiation, galvanism, hypovitaminosis, hormonal disorders, etc. Leukoplakia is the most common in clinical practice. , warty form of precancer, abrasive precancerous cheilitis of Manganotti. Of the risk factors for leukoplakia, exposure to tobacco smoke comes first. When burning tobacco, in addition to the thermal effect, various chemicals are formed, which, when they enter the oral cavity with smoke, irritate the mucous membrane. In the development of local lesions caused by smoking, pipe smoking is the most harmful. The risk of the disease increases if patients who smoke or abuse alcohol have dentures and do not regularly visit the dentist.
Chronic injury, as one of the risk factors, can be caused by sharp edges of teeth, roots, poorly made dentures, and tartar. Excessively hot and spicy foods, strong alcoholic drinks and drugs can also lead to leukoplakia. Lack of vitamin A in the body, hormonal disorders, anemia, etc. are factors contributing to the occurrence of leukoplakia. Ways to prevent cancer and precancer of the oral mucosa and red border are based on knowledge of etiological factors. In this regard, it is necessary to promote cessation of tobacco use and, first of all, smoking of pipes, cigarettes and unfiltered cigarettes, frequent consumption of alcohol, hot and irritating foods, as well as the inclusion in the diet of foods rich in vitamins A, C, B. In industries where workers are exposed to carcinogenic agents, it is necessary to achieve improvements in technological processes, compliance with safety regulations and the use of personal protective equipment. Means of combating excess solar radiation are protective clothing, ointments, hygienic lipstick, and compliance with solar procedures. Regular visits to the dentist for the purpose of timely treatment of carious teeth, removal of dental plaque, rational prosthetics and compliance with the rules of hygienic oral care will significantly reduce the risk of diseases of the mucous membrane. A dentist is obliged to observe the principle of oncological vigilance and, during preventive examinations and medical examinations, conduct an examination of the oral mucosa and red border, carry out individual and mass sanitary educational work. In the process of clinical examination, it is necessary to form risk groups for this pathology, followed by regular treatment and preventive measures. Changes in the oral mucosa during AIDS are diverse: fungal and viral lesions, gingivostomatitis, chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, xerostomia, hairy leukoplakia. Specific prevention of HIV infection has not been developed. Since the greatest risk occurs when the patient's blood and saliva penetrate damaged skin, it is necessary to carefully avoid damaging it with sharp instruments. In order to prevent the spread of HIV infection, when visiting a dentist, you should strictly follow the rules for sterilizing dental instruments. Dentists wearing gloves and a mask prevent the possibility of contracting an infection from a sick patient.
Consumer Reviews
Kate about ASEPTA ACTIVE toothpaste
“I have chronic gingivitis, in order to prevent receding gums, loss of teeth and other unpleasant consequences of this disease, I use the Asepta Paradontal series. I have a special paste from this manufacturer, a rinse aid and an adhesive balm as a last resort. During an exacerbation, with the help of this balm, it was possible to bring the gums back to normal within a week. It was terrible - my gums were swollen and everything hurt. Since then, on schedule - paste + rinse aid. And now the disease has not made itself felt for six months.”
astra 4 about ASEPTA Sensitive toothpaste (otzovik.com):
“I recently purchased Asepat Sensitive toothpaste. During this period, I just needed a product that reduced the sensitivity of the enamel. Having bought it, I immediately decided to try the paste in action.
Asepta Sensitive toothpaste has a slightly salty taste, like all toothpastes in this category. However, it does not spoil its taste at all. The mint aroma, however, dominates. After cleaning, your mouth remains pleasant and fresh.
Asepta Sensitive paste is presented in a soft tube that stands quite well on the stem.
Its color is pale green and does not create a lot of foam when cleaning, which I really like. Asepta Sensitive toothpaste polishes the tooth surface well, but at the same time does not injure it.
When purchasing, I was attracted by the composition: it contains extracts of medicinal herbs and thermal mud, designed to soothe teeth and gums. This preventive toothpaste really helps with the problem of sensitive teeth, as I have repeatedly seen. After just 2 weeks of regular use, I felt the result: the enamel did not react so strongly to extraneous irritants.
For this reason, I want to recommend it to anyone who has encountered this problem. A good, effective remedy."
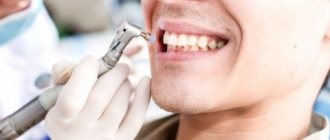
Treatment and prevention of dental diseases using laser
For a huge number of patients, visiting the dentist is associated with unpleasant sensations from the ringing sound when the turbine handpiece is working, from vibration and painful sensations during the preparation of a carious cavity.
Nowadays, a patient with a negative experience of treatment at the dentist has a choice. Laser treatment is painless and free of sound stimuli. Laser technologies are widely used in dentistry:
for the prevention and treatment of caries, in aesthetic dentistry, in the treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa, periodontal disease, in maxillofacial and plastic surgery, orthodontics, orthopedics, in cosmetology, in the manufacture and repair of dentures and appliances.
Recently, laser technologies have been used in the diagnosis of dental diseases in the early stages of development. The laser fluorescence spectroscopy method allows you to determine the degree of risk of developing dental caries.
Helium-neon laser, erbium, diode, carbon dioxide, frequency doubling lasers are used in dental treatment. There are two types of dental lasers currently in use. Soft radiation lasers have a biostimulating effect and are used to treat soft tissues of the oral cavity. Hard radiation lasers are used in surgical dentistry, endodontics and for the treatment of periodontal tissue.
Laser light has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the permeability of vascular walls, has a fibrino-thrombolytic effect, increases the oxygen content in tissues, which enhances metabolism, accelerates wound healing, has an analgesic, desensitizing, muscle relaxant, bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect, increases the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics and stimulates the immune defense system.
During surgical interventions in the oral cavity
bacteremia can be short-term or transient. The risk of its development depends on many factors: the level of general and local immunity, the condition of the soft tissues at the surgical site, the type and virulence of microorganisms.
In order to prevent microbial contamination, oral cavity sanitation is usually carried out, ensuring optimal preoperative preparation of patients using antibiotics. However, antibiotic prophylaxis, instead of the desired result, can lead to the development of resistant strains of microorganisms, allergies, gastrointestinal disorders, and increase the drug load on the patient’s body.
Non-drug methods of preparing the oral cavity for surgery in surgical dental practice include low-intensity laser energy. Laser exposure promotes the disappearance of signs of soft tissue inflammation after a course of treatment (three to five sessions), and a bactericidal effect is observed after one or two sessions.
They use a laser single-channel dental device ALTP-2-1 with a semi-arc emitter, which is placed on the vestibular (outer) surface of the gum of the dentition for 4-6 minutes for each jaw. The wavelength used is 0.63 µm and the output power is 6 mW/cm2.
A study of the effect of low-intensity laser energy on different types of microorganisms showed that hemolytic and hemolyzing streptococci, as well as Peptococcus, Str. epidermidis and Staph. aureus. The use of irradiation for 2-4 minutes caused almost complete cleansing of the lesion from these microorganisms.
To a much lesser extent, low-intensity laser energy affects Yersinia and Str, which are resistant to low-intensity laser energy. lactis. In cases of contamination of oral tissues with Yersinia, an exposure of at least 6 minutes was required.
This non-drug method of preventing bacteremia is the future, since an important advantage of laser therapy is the absence of side effects during its use. With bacteriological control, it is possible to achieve not only bacteriostatic, but also bactericidal effects.
Using the laser-optical method, it is possible to identify pathological processes in periodontal tissues based on the level of reduction in blood flow determined using this method. This is important for the early diagnosis of diseases of the tissues surrounding the teeth.
The use of lasers in surgical dentistry is especially promising.
The use of the KaVo GENTLEray 980 diode laser with a wavelength of 980 nm creates such advantages as reduced bleeding during surgery, swelling and pain after surgery, a good bactericidal effect, which allows you to reduce the dose of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs in the postoperative period.
For caries at the spot stage, low-intensity laser radiation is used to remineralize the enamel. However, this method cannot become widespread, since not every children's dental clinic is equipped with a laser unit.
The success of treatment of complicated caries depends on the quality of treatment, including disinfection of the root canals of the tooth before filling. The laser was used to evaporate residual pulp from the root canals. In this case, the bacteria are completely destroyed and the canal walls are “glazed.” The dentist uses a KaVo GENTLEray 980 diode laser with a wavelength of 980 nm.
After mechanical treatment of the root canal, widening the apical foramen, irrigating the canal with a 3% sodium hypochlorite solution, washing it and drying it, an endodontic emitter is inserted into it. It is flexible and easily passes through convoluted channels (requires insertion to a depth of 2-4 mm to the apex). The laser is activated for only 20 seconds, during the session they make spiral movements with the emitter, lowering it to the top and returning it to its original position.
The positive aspects of the method include:
eliminating the risk of thermal burn of periodontal tissues; The laser promotes rapid regeneration of bone structures in the periapical region, and this is the most reliable way to disinfect root canals.
Laser therapy method
is a modern painless method of treating dental caries. Er, Cr: YSGG and Er: YAG dental lasers are used to prepare carious cavities. The principle of laser operation is the process of removing calcium-containing biological tissue by absorbing laser energy by tiny particles of water.
During the absorption of laser energy, instantaneous evaporation of water occurs, accompanied by an increase in volume (micro-explosion). In the process of microexplosions, there is literally evaporation (ablation) of the hard tissues of the tooth, but not all of them, but those areas of the tooth where the water content is higher. There is less water in tooth enamel than in dentin, and carious dentin contains even more moisture. The latter has a large ablation, and the weakest ablation is in the enamel.
The pulse duration is very short and the tissue is not heated, unlike preparation with a turbine tip.
The advantages of using a laser are undeniable:
painless treatment, microcracks do not form in the hard tissues of the teeth, the conditions for fixing the filling material are improved, since the edges of the cavity are not “melted”, the carious cavity is sterile after laser preparation. There are no complications after laser preparation. Typically, complications are associated with overheating of tooth tissues, burns of the dental pulp (pulp) of the tooth when working with a regular bur.
In orthopedic dentistry, lasers are used to fix braces, inlays, and veneers. This requires the use of a very high intensity light flux, since it is necessary to polymerize the light-curing material through the tooth tissue or through the veneer mass. This is the so-called “afterburner” mode.
Light curing devices are available in four types:
1) halogen, used for more than 20 years. These are models Estus prophy, Estus trio, Estus solo, Spectrum 800, Demetron, VIP, Optilux 380, 401, 501, Polofit Lux, etc.; 2) plasma-arc photopolymerizers. The effect of plasma torches on body tissues has not yet been sufficiently studied. The power of the light flux is high and in practice shrinkage of the filling material is observed. These are models Virtuoso, Den mat, Power Pac, ADT, etc.; 3) laser photopolymerizers. The light source in them is an argon laser. The disadvantage is the high cost of the device; 4) photopolymerizers of cold radiation. Their efficiency is very high - 10 times higher than halogen ones, and they do not create a thermal effect. These are Elipar free light lamps and a whole series of Estus lamps.
In the Republic of Belarus, the Optima laser dental unit was created and its clinical trials were completed at the departments of therapeutic and orthopedic dentistry of the Belarusian State Medical University and the Belarusian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education. In terms of medical use and technical characteristics, Optima is not inferior to foreign analogues, and in terms of performance and cost it is even more profitable.